Exhaled Breath Condensate—A Non-Invasive Approach for Diagnostic Methods in Asthma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Exhaled Breath Condensate—Definition
3. Exhaled Breath Condensate—Collection Devices
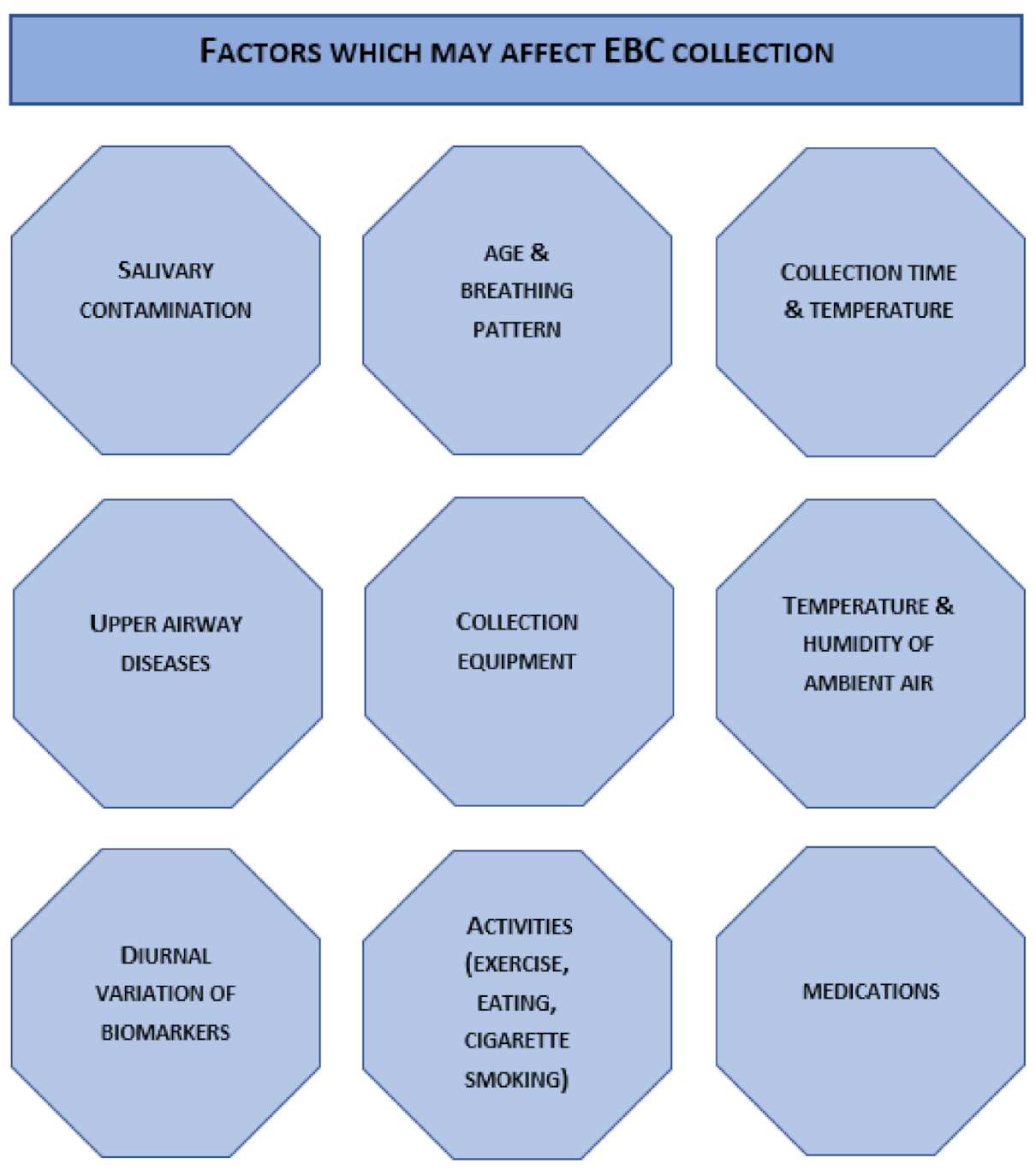
4. Exhaled Breath Condensate—Sampling Procedure
5. Analysis of Exhaled Breath Condensate
6. Biomarkers in Exhaled Breath Condensate of Asthmatic Patients
6.1. Acidity
6.2. Metals
6.3. Oxidative Stress
6.4. Cytokines
6.5. Leukotrienes
6.6. Enzymes
6.7. Nitric Oxide Products
6.8. Hormones
6.9. Proteins
6.10. Micro-RNAs
7. Microbiota in Exhaled Breath Condensate
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vos, T.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdulkader, R.S.; Abdulle, A.M.; Abebo, T.A.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 328 Diseases and Injuries for 195 Countries, 1990–2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Mutius, E.; Smits, H.H. Primary Prevention of Asthma: From Risk and Protective Factors to Targeted Strategies for Prevention. Lancet 2020, 396, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Pocket Guide for Health Professionals; Global Initiative for Asthma: Fontana-on-Geneva Lake, WI, USA, 2017; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ramratnam, S.K.; Bacharier, L.B.; Guilbert, T.W. Severe Asthma in Children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lødrup Carlsen, K.C.; Mowinckel, P.; Hovland, V.; Håland, G.; Riiser, A.; Carlsen, K.H. Lung Function Trajectories from Birth through Puberty Reflect Asthma Phenotypes with Allergic Comorbidity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 917–923.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lötvall, J.; Akdis, C.A.; Bacharier, L.B.; Bjermer, L.; Casale, T.B.; Custovic, A.; Lemanske, R.F.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Wenzel, S.E.; Greenberger, P.A. Asthma Endotypes: A New Approach to Classification of Disease Entities within the Asthma Syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, S.E. Asthma: Defining of the Persistent Adult Phenotypes. Lancet 2006, 368, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Kant, K.D.G.; van der Sande, L.J.T.M.; Jöbsis, Q.; van Schayck, O.C.P.; Dompeling, E. Clinical Use of Exhaled Volatile Organic Compounds in Pulmonary Diseases: A Systematic Review. Respir. Res. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, I.; Hunt, J.; Barnes, P.J. Exhaled Breath Condensate: Methodological Recommendations and Unresolved Questions. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 523–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papineni, R.S.; Rosenthal, F.S. The Size Distribution of Droplets in the Exhaled Breath of Healthy Human Subjects. J. Aerosol Med. Depos. Clear. Eff. Lung 1997, 10, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, N.; Lai, K. BAL Fluid 8-Isoprostane Concentrations in Eosinophilic Bronchitis and Asthma. J. Asthma 2009, 46, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, S.; Mehta, A.A. Role of Cytokines in Pathophysiology of Asthma. Iran. J. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Horváth, I.; Barnes, P.J.; Högman, M.; Olin, A.; Amann, A.; Antus, B.; Baraldi, E.; Bikov, A.; Boots, A.W.; Bos, L.D.; et al. A European Respiratory Society Technical Standard: Exhaled Biomarkers in Lung Disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradi, M.; Rubinstein, I.; Andreoli, R.; Manini, P.; Caglieri, A.; Poli, D.; Alinovi, R.; Mutti, A. Aldehydes in exhaled breath condensate of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczulla, R.; Dragonieri, S.; Schot, R.; Bals, R.; Gauw, S.A.; Vogelmeier, C.; Rabe, K.F.; Sterk, P.J.; Hiemstra, P.S. Comparison of exhaled breath condensate pH using two commercially available devices in healthy controls, asthma and COPD patients. Respir. Res. 2009, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamuruyev, K.O.; Borras, E.; Pettit, D.R.; Aksenov, A.A.; Simmons, J.D.; Weimer, B.C.; Schivo, M.; Kenyon, N.J.; Delplanque, J.; Davis, C.E. Analytica Chimica Acta Effect of Temperature Control on the Metabolite Content in Exhaled Breath Condensate. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosias, P.P.; Robroeks, C.M.; Kester, A.; Den Hartog, G.J.; Wodzig, W.K.; Rijkers, G.T.; Zimmermann, L.J.; Van Schayck, C.P.; Jöbsis, Q.; Dompeling, E. Biomarker Reproducibility in Exhaled Breath Condensate Collected with Different Condensers. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosias, P.P.; Robroeks, C.M.; Niemarkt, H.J.; Kester, A.D.; Vernooy, J.H.; Suykerbuyk, J.; Teunissen, J.; Heynens, J.; Hendriks, H.J.; Jöbsis, Q.; et al. Breath Condenser Coatings Affect Measurement of Biomarkers in Exhaled Breath Condensate. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vass, G.; Huszár, É.; Barát, E.; Valyon, M.; Kiss, D.; Pénzes, I.; Augusztinovicz, M.; Horváth, I. Comparison of Nasal and Oral Inhalation during Exhaled Breath Condensate Collection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, C.; Kuhn, H.; Seyfarth, H.J.; Pankau, H.; Winkler, J.; Schauer, J.; Wirtz, H. Factors Influencing Breath Condensate Volume. Pneumologie 2001, 55, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidi, E.M.; Lappas, A.S.; Tzortzi, A.S.; Behrakis, P.K. Exhaled Breath Condensate: Technical and Diagnostic Aspects. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Respiratory Research, Inc. Available online: https://respiratoryresearch.com/rtube/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- MEDIVAC Srl. Available online: www.medivac.it/en/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Romero, P.V.; Rodríguez, B.; Martínez, S.; Cañizares, R.; Sepúlveda, D.; Manresa, F. Analysis of Oxidative Stress in Exhaled Breath Condensate From Patients With Severe Pulmonary Infections. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2006, 42, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czebe, K.; Barta, I.; Antus, B.; Valyon, M.; Horváth, I.; Kullmann, T. Influence of Condensing Equipment and Temperature on Exhaled Breath Condensate PH, Total Protein and Leukotriene Concentrations. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosias, P.P.R.; Dompeling, E.; Hendriks, H.J.E.; Heijnens, J.W.C.M.; Donckerwolcke, R.A.M.G.; Jöbsis, Q. Exhaled Breath Condensate in Children: Pearls and Pitfalls. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 15, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraldi, E.; Ghiro, L.; Piovan, V.; Carraro, S.; Zacchello, F.; Zanconato, S. Safety and Success of Exhaled Breath Condensate Collection in Asthma. Arch. Dis. Child. 2003, 88, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.S.; Sandrini, A.; Campbell, C.; Chow, S.; Thomas, P.S.; Yates, D.H. Comparison of biomarkers in exhaled breath condensate and bronchoalveolar lavage. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, F.C.; Darlow, B.A.; Winterbourn, C.C. Problems Associated with Collecting Breath Condensate for the Measurement of Exhaled Hydrogen Peroxide from Neonates on Respiratory Support. Biol. Neonate 2003, 84, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhold, P.; Knobloch, H. Exhaled Breath Condensate: Lessons Learned from Veterinary Medicine. J. Breath Res. 2010, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beurden, W.J.C.; Dekhuijzen, P.N.R.; Harff, G.A.; Smeenk, F.W.J.M. Variability of Exhaled Hydrogen Peroxide in Stable COPD Patients and Matched Healthy Controls. Respiration 2002, 69, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajdocsi, R.; Bikov, A.; Antus, B.; Horvath, I.; Barnes, P.J.; Kharitonov, S.A. Assessment of Reproducibility of Exhaled Hydrogen Peroxide Concentration and the Effect of Breathing Pattern in Healthy Subjects. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2011, 24, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, J.; Ngamtrakulpanit, L.; Pajewski, T.N.; Turner, R.; Nguyen, T.A.; Smith, A.; Urban, P.; Hom, S.; Gaston, B.; Hunt, J. Exhaled breath condensate pH is a robust and reproducible assay of airway acidity. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheideler, L.; Manke, H.G.; Schwulera, U.; Inacker, O.; Hämmerle, H. Detection of nonvolatile macromolecules in breath. A possible diagnostic tool? Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 148, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosias, P. Methodological Aspects of Exhaled Breath Condensate Collection and Analysis. J. Breath Res. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikov, A.; Galffy, G.; Tamasi, L.; Bartusek, D.; Antus, B.; Losonczy, G.; Horvath, I. Exhaled Breath Condensate PH Decreases during Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction. Respirology 2014, 19, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almstrand, A.C.; Bake, B.; Ljungström, E.; Larsson, P.; Bredberg, A.; Mirgorodskaya, E.; Olin, A.C. Effect of Airway Opening on Production of Exhaled Particles. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhold, P.; Jaeger, J.; Schroeder, C. Evaluation of Methodological and Biological Influences on the Collection and Composition of Exhaled Breath Condensate. Biomarkers 2006, 11, 118–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Danao, M.G.C. Decomposition and Solubility of H2O2: Implications in Exhaled Breath Condensate. J. Breath Res. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grob, N.M.; Aytekin, M.; Dweik, R.A. Biomarkers in Exhaled Breath Condensate: A Review of Collection, Processing and Analysis. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazeminasab, S.; Emamalizadeh, B.; Jouyban-Gharamaleki, V.; Taghizadieh, A.; Khoubnasabjafari, M.; Jouyban, A. Tips for Improving the Quality and Quantity of the Extracted DNA from Exhaled Breath Condensate Samples. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, G.M.; Garey, K.W.; Robbins, R.A.; Danziger, L.H.; Rubinstein, I. Collection and Analysis of Exhaled Breath Condensate in Humans. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effros, R.M.; Casaburi, R.; Su, J.; Dunning, M.; Torday, J.; Biller, J.; Shaker, R. The Effects of Volatile Salivary Acids and Bases on Exhaled Breath Condensate PH. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huszár, É.; Vass, G.; Vizi, É.; Csoma, Z.; Barát, E.; Molnár-Világos, G.; Herjavecz, I.; Horváth, I. Adenosine in Exhaled Breath Condensate in Healthy Volunteers and in Patients with Asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 20, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carraro, S.; Giordano, G.; Piacentini, G.; Kantar, A.; Moser, S.; Cesca, L.; Berardi, M.; Di Gangi, I.M.; Baraldi, E. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Exhaled Breath Condensate and Serum of Children with Asthma. Chest 2013, 144, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohanian, A.S.; Zimmerman, J.; Debley, J.S. Effects of Sample Processing, Time and Storage Condition on Cysteinyl Leukotrienes in Exhaled Breath Condensate. J. Breath Res. 2010, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, A.J.; Madden, M.C.; Esther, C.R. Transition and post-transition metals in exhaled breath condensate. J Breath Res. 2018, 12, 027112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkan, F.G.; Yılmaz, E.; Hangül, M.; Öztürk, D.; Demirkan, H.; Soylak, M.; Köse, M. Exhaled Breath Condensate Magnesium Levels of Infants with Bronchiolitis. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2018, 60, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannier, M.; Rosias, P.; Jöbsis, Q.; Dompeling, E. Exhaled Breath Condensate in Childhood Asthma: A Review and Current Perspective. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, N.C.; Lowe, L.A.; Murray, C.S.; Woodcock, A.; Simpson, A.; Custovic, A. Exhaled Breath Condensate PH and Childhood Asthma: Unselected Birth Cohort Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.F.; Fang, K.; Malik, R.; Snyder, A.; Malhotra, N.; Platts-mills, T.A.E.; Gaston, B.; Jf, H.; Fang, K.; Malik, R.; et al. Implications for Asthma Pathophysiology. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostikas, K.; Papatheodorou, G.; Ganas, K.; Psathakis, K.; Panagou, P.; Loukides, S. PH in Expired Breath Condensate of Patients with Inflammatory Airway Diseases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Barnes, P.J.; Francis, J.; Wilson, N.; Bush, A.; Kharitonov, S.A. Breath Condensate PH in Children with Cystic Fibrosis and Asthma: A New Noninvasive Marker of Airway Inflammation? Chest 2004, 125, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.R.; Hill, V.L.; Burks, M.L.; Peters, J.I.; Singh, H.; Kannan, T.R.; Vale, S.; Cagle, M.P.; Principe, M.F.R.; Baseman, J.B.; et al. Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Children with Acute and Refractory Asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 110, 328–334.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, P.R.; Kampschmidt, J.C.; Dube, P.H.; Cagle, M.P.; Chaparro, P.; Ketchum, N.S.; Kannan, T.R.; Singh, H.; Peters, J.I.; Baseman, J.B.; et al. Mycoplasma Pneumoniae and Health Outcomes in Children with Asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 119, 146–152.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eszes, N.; Bikov, A.; Lázár, Z.; Bohács, A.; Müller, V.; Stenczer, B.; Rigõ, J.; Losonczy, G.; Horváth, I.; Tamási, L. Changes in Exhaled Breath Condensate PH in Healthy and Asthmatic Pregnant Women. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2013, 92, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antus, B.; Barta, I.; Kullmann, T.; Lazar, Z.; Valyon, M.; Horvath, I.; Csiszer, E. Assessment of Exhaled Breath Condensate Ph in Exacerbations of Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Longitudinal Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterová, E.; Chládek, J.; Kohoutová, D.; Knoblochová, V.; Morávková, P.; Vávrová, J.; Řezáčová, M.; Bureš, J. Exhaled Breath Condensate: Pilot Study of the Method and Initial Experience in Healthy Subjects. Acta Medica 2018, 61, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A.M.; Holbrook, J.T.; Wei, C.Y.; Brown, M.S.; Wise, R.A.; Teague, W.G. Exhaled Breath Condensate PH Does Not Discriminate Asymptomatic Gastroesophageal Reflux or the Response to Lansoprazole Treatment in Children with Poorly Controlled Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2014, 2, 579–586.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Chatziparasidis, G.; Chatziefthimiou, A.; Molyvdas, P.A. Magnesium as a Relaxing Factor of Airway Smooth Muscles. J. Aerosol Med. Depos. Clear. Eff. Lung 2001, 14, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2021 Global Initiative for Asthma Main Report. Available online: https://ginaasthma.org/gina-reports/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Banović, S.; Navratil, M.; Vlašić, Ž.; Topić, R.Z.; Dodig, S. Calcium and Magnesium in Exhaled Breath Condensate of Children with Endogenous and Exogenous Airway Acidification. J. Asthma 2011, 48, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffarelli, C.; Calcinai, E.; Rinaldi, L.; Povesi Dascola, C.; Terracciano, L.; Corradi, M. Hydrogen Peroxide in Exhaled Breath Condensate in Asthmatic Children during Acute Exacerbation and after Treatment. Respiration 2012, 84, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, C.; Shashibhushan, B.L.; Sagar; Asif, M.; Manjunath, P.H. Hydrogen Peroxide in Exhaled Breath Condensate: A Clinical Study. Lung India 2012, 29, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganas, K.; Loukides, S.; Papatheodorou, G.; Panagou, P.; Kalogeropoulos, N. Total Nitrite/Nitrate in Expired Breath Condensate of Patients with Asthma. Respir. Med. 2001, 95, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antczak, A.; Kurmanowska, Z.; Kasielski, M.; Nowak, D. Inhaled Glucocorticosteroids Decrease Hydrogen Peroxide Level in Expired Air Condensate in Asthmatic Patients. Respir. Med. 2000, 94, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Quimbar, M.E.; Davis, S.Q.; Al-Farra, S.T.; Hayes, A.; Jovic, V.; Masuda, M.; Lippert, A.R. Chemiluminescent Measurement of Hydrogen Peroxide in the Exhaled Breath Condensate of Healthy and Asthmatic Adults. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 14594–14600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quimbar, M.E.; Krenek, K.M.; Lippert, A.R. A Chemiluminescent Platform for Smartphone Monitoring of H2O2 in Human Exhaled Breath Condensates. Methods 2016, 109, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, V.; Carraro, S.; Bozzetto, S.; Zanconato, S.; Baraldi, E. Exhaled Biomarkers in Childhood Asthma: Old and New Approaches. Asthma Res. Pract. 2018, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraldi, E.; Carraro, S.; Alinovi, R.; Pesci, A.; Ghiro, L.; Bodini, A.; Piacentini, G.; Zacchello, F.; Zanconato, S. Cysteinyl Leukotrienes and 8-Isoprostane in Exhaled Breath Condensate of Children with Asthma Exacerbations. Thorax 2003, 58, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraldi, E.; Ghiro, L.; Piovan, V.; Carraro, S.; Ciabattoni, G.; Barnes, P.J.; Montuschi, P. Increased Exhaled 8-Isoprostane in Childhood Asthma. Chest 2003, 124, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.K.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Wilson, N.M.; Bush, A.; Barnes, P.J. Exhaled 8-Isoprostane in Childhood Asthma. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.H.; Yan, D.C.; Tseng, H.Y.; Tung, T.H.; Lin, S.J.; Lin, Y.W. Cysteinyl Leukotriene Levels Correlate with 8-Isoprostane Levels in Exhaled Breath Condensates of Atopic and Healthy Children. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 74, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, A.M.; Crossman-Barnes, C.J.; Tang, J.; Fowler, S.J.; Davies, G.A.; Wilson, A.M.; Loke, Y.K. Biomarkers in Adult Asthma: A Systematic Review of 8-Isoprostane in Exhaled Breath Condensate. J. Breath Res. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lan, R.Y.; Selmi, C.; Gershwin, M.E. The Regulatory, Inflammatory, and T Cell Programming Roles of Interleukin-2 (IL-2). J. Autoimmun. 2008, 31, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonpiyathad, S.; Pornsuriyasak, P.; Buranapraditkun, S.; Klaewsongkram, J. Interleukin-2 Levels in Exhaled Breath Condensates, Asthma Severity, and Asthma Control in Nonallergic Asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2013, 35, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H.; Fahy, J.V. The Cytokines of Asthma. Immunity 2019, 50, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Th2 Cytokines and Asthma: An Introduction. Respir. Res. 2001, 2, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robroeks, C.M.H.H.T.; Van De Kant, K.D.G.; Jöbsis, Q.; Hendriks, H.J.E.; Van Gent, R.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Damoiseaux, J.G.M.C.; Bast, A.; Wodzig, W.K.W.H.; Dompeling, E. Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Biomarkers in Exhaled Breath Condensate Indicate the Presence, Severity and Control of Childhood Asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.K.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Wilson, N.M.; Bush, A.; Barnes, P.J. Increased Interleukin-4 and Decreased Interferon-γ in Exhaled Breath Condensate of Children with Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1290–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkeli, A.; Yilmaz, O.; Taneli, F.; Horasan, G.D.; Kanik, E.T.; Kizilkaya, M.; Gozukara, C.; Yuksel, H. IL-5, IL-8 and MMP -9 Levels in Exhaled Breath Condensate of Atopic and Nonatopic Asthmatic Children. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, D.; Alonso, A.; Rijkers, G.; Heynens, J.; Rosias, P.; Muris, J.; Joäbsis, Q.; Dompeling, E. Prediction of Asthma Exacerbations in Children by Innovative Exhaled Inflammatory Markers: Results of a Longitudinal Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmach, I.; Sztafińska, A.; Jerzyńska, J.; Podlecka, D.; Majak, P.; Stelmach, W. New Insights into Treatment of Children with Exerciseinduced Asthma Symptoms. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2016, 37, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon, M.; Irvin, C.G. Role of IL-6 in Asthma and Other Inflammatory Pulmonary Diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares Segovia, B.; Cortés Sandoval, G.; del Rosario Estrada Pacheco, F. Increased Interleukin-6 (IL-6) in Exhaled Breath Condensate of Asthmatic Children. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2017, 53, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorska, K.; Nejman-Gryz, P.; Paplinska-Goryca, M.; Korczynski, P.; Prochorec-Sobieszek, M.; Krenke, R. Comparative Study of IL-33 and IL-6 Levels in Different Respiratory Samples in Mild-to-Moderate Asthma and COPD. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2018, 15, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrad, R.; Kaabachi, W.; Rafrafi, A.; Berraies, A.; Hamzaoui, K.; Hamzaoui, A. IL-8 Gene Variants and Expression in Childhood Asthma. Lung 2017, 195, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Lu, M.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Wu, T.C.; Hsu, J.Y.; Jan, M.S.; Chen, C.M. Differences in IL-8 in Serum and Exhaled Breath Condensate from Patients with Exacerbated COPD or Asthma Attacks. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Gupta, S.; Dastidar, S.; Ray, A. Cysteinyl Leukotrienes and Their Receptors: Molecular and Functional Characteristics. Pharmacology 2010, 85, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares Segovia, B.; Cortés Sandoval, G.; Amador Licona, N.; Guízar Mendoza, J.M.; Núñez Lemus, E.; Rocha Amador, D.O.; Ramírez Gómez, X.S.; Monroy Torres, R. Parameters of Lung Inflammation in Asthmatic as Compared to Healthy Children in a Contaminated City. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Keskin, O.; Balaban, S.; Keskin, M.; Kucukosmanoglu, E.; Gogebakan, B.; Ozkars, M.Y.; Kul, S.; Bayram, H.; Coskun, Y. Relationship between Exhaled Leukotriene and 8-Isoprostane Levels and Asthma Severity, Asthma Control Level, and Asthma Control Test Score. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2014, 42, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, O.; Uluca, U.; Keskin, M.; Gogebakan, B.; Kucukosmanoglu, E.; Ozkars, M.Y.; Kul, S.; Bayram, H.; Coskun, Y. The Efficacy of Single-High Dose Inhaled Corticosteroid versus Oral Prednisone Treatment on Exhaled Leukotriene and 8-Isoprostane Levels in Mild to Moderate Asthmatic Children with Asthma Exacerbation. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2016, 44, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, E.W. Importance of the Leukotriene B4-BLT1 and LTB4-BLT2 Pathways in Asthma. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 33, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trischler, J.; Müller, C.M.; Könitzer, S.; Prell, E.; Korten, I.; Unverzagt, S.; Lex, C. Elevated Exhaled Leukotriene B4 in the Small Airway Compartment in Children with Asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015, 114, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadler-Olsen, E.; Fadnes, B.; Sylte, I.; Uhlin-Hansen, L.; Winberg, J.O. Regulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity in Health and Disease. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosby, L.M.; Waters, C.M. Epithelial Repair Mechanisms in the Lung. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S.D. Matrix degrading proteinases in COPD and asthma. In Asthma and COPD. Basic Mechanism and Clinical Management, 2nd ed.; Barnes, P.J., Drazen, J., Rennard, S.I., Thomson, N.C., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 343–352. [Google Scholar]
- Grzela, K.; Zagorska, W.; Krejner, A.; Litwiniuk, M.; Zawadzka-Krajewska, A.; Banaszkiewicz, A.; Kulus, M.; Grzela, T. Prolonged Treatment with Inhaled Corticosteroids Does Not Normalize High Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in Exhaled Breath Condensates of Children with Asthma. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2015, 63, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzela, K.; Zagórska, W.; Krejner, A.; Banaszkiewicz, A.; Litwiniuk, M.; Kulus, M.; Grzela, T. Inhaled Corticosteroids Do Not Reduce Initial High Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 in Exhaled Breath Condensates of Children with Asthma Exacerbation: A Proof of Concept Study. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 41, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Thomas, P.S. Exhaled Breath Condensate as a Method of Sampling Airway Nitric Oxide and Other Markers of Inflammation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2005, 11, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Aldakheel, F.M.; Bourke, J.E.; Thomas, P.S.; Matheson, M.C.; Abramson, M.J.; Hamilton, G.S.; Lodge, C.J.; Thompson, B.R.; Walters, E.H.; Allen, K.J.; et al. NOx in Exhaled Breath Condensate Is Related to Allergic Sensitization in Young and Middle-Aged Adults. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, N.; Kirerleri, E.; Ones, U.; Tamay, Z.; Salmayenli, N.; Darendeliler, F. Leptin: Does It Have Any Role in Childhood Asthma? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodini, A.; Tenero, L.; Sandri, M.; Maffeis, C.; Piazza, M.; Zanoni, L.; Peroni, D.; Boner, A.; Piacentini, G. Serum and Exhaled Breath Condensate Leptin Levels in Asthmatic and Obesity Children: A Pilot Study. J. Breath Res. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inci, D.; Basek, P.; Wildhaber, J.H.; Moeller, A. Leptin Levels in Exhaled Breath Condensate from Asthmatic Children: A Pilot Study. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2012, 50, 593–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ishida, A.; Ohta, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Kakehata, S.; Okubo, K.; Ikeda, H.; Shiraishi, H.; Izuhara, K. Expression of pendrin and periostin in allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol. Int. 2012, 61, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Akashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Ashizuka, S.; Motoki, T.; Suzuki, R.; Sagara, N.; Yanagida, N.; Sato, S.; et al. Periostin as a Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Pediatric Asthma. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 27, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Basha, N.R.; Osman, H.M.; Abdelaal, A.A.; Saed, S.M.; Shaaban, H.H. Increased Expression of Serum Periostin and YKL40 in Children with Severe Asthma and Asthma Exacerbation. J. Investig. Med. 2018, 66, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Ohbayashi, H.; Ariga, M.; Furuta, O.; Kudo, S.; Ono, J.; Izuhara, K. Serum Periostin Reflects Dynamic Hyperinflation in Patients with Asthma. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00347–02019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novosad, J.; Krčmová, I.; Bartoš, V.; Drahošová, M.; Vaník, P.; Růžičková-Kirchnerová, O.; Teřl, M.; Krejsek, J. Serum Periostin Levels in Asthma Patients in Relation to Omalizumab Therapy and Presence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Postep. Dermatologii i Alergol. 2020, 37, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardzynska, A.; Makowska, J.S.; Pawelczyk, M.; Piechota-Polanczyk, A.; Kurowski, M.; Kowalski, M.L. Periostin in Exhaled Breath Condensate and in Serum of Asthmatic Patients: Relationship to Upper and Lower Airway Disease. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2017, 9, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejman-Gryz, P.; Górska, K.; Krenke, K.; Peradzyńska, J.; Paplińska-Goryca, M.; Kulus, M.; Krenke, R. Periostin Concentration in Exhaled Breath Condensate in Children with Mild Asthma. J. Asthma 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narożna, B.; Langwiński, W.; Szczepankiewicz, A. Non-Coding RNAs in Pediatric Airway Diseases. Genes 2017, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkerton, M.; Chinchilli, V.; Banta, E.; Craig, T.; August, A.; Bascom, R.; Cantorna, M.; Harvill, E.; Ishmael, F.T. Differential Expression of MicroRNAs in Exhaled Breath Condensates of Patients with Asthma, Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, and Healthy Adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 217–219.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, F.C.; Paciência, I.; Ferreira, A.C.; Martins, C.; Rufo, J.C.; Silva, D.; Cunha, P.; Farraia, M.; Moreira, P.; Delgado, L.; et al. Development and Validation of Exhaled Breath Condensate MicroRNAs to Identify and Endotype Asthma in Children. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, M.N.; Crother, T.R.; Arditi, M. The Microbiome in Asthma. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2016, 28, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendinning, L.; Wright, S.; Tennant, P.; Gill, A.C.; Collie, D.; McLachlan, G. Microbiota in Exhaled Breath Condensate and the Lung. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A.K.; Brady, J.S.; Romano-Keeler, J.; Drake, W.P.; Norris, P.R.; Jenkins, J.M.; Isaacs, R.J.; Boczko, E.M. A Pilot Study of the Noninvasive Assessment of the Lung Microbiota as a Potential Tool for the Early Diagnosis of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Chest 2015, 147, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zakharkina, T.; Koczulla, A.R.; Mardanova, O.; Hattesohl, A.; Bals, R. Detection of Microorganisms in Exhaled Breath Condensate during Acute Exacerbations of COPD. Respirology 2011, 16, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Lacedonia, D.; Palladino, G.P.; Logrieco, G.; Crisetti, E.; Susca, A.; Logrieco, A.; Foschino-Barbaro, M.P. Aspergillus Spp. Colonization in Exhaled Breath Condensate of Lung Cancer Patients from Puglia Region of Italy. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Malerba, M.; Lacedonia, D.; Susca, A.; Logrieco, A.; Carone, M.; Cotugno, G.; Palmiotti, G.A.; Foschino-Barbaro, M.P. Analysis of the Fungal Microbiome in Exhaled Breath Condensate of Patients with Asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2016, 37, e41–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Susca, A.; Scioscia, G.; Lacedonia, D.; Cotugno, G.; Soccio, P.; Santamaria, S.; Resta, O.; Logrieco, G.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P. A Survey of Fungal Microbiota in Airways of Healthy Volunteer Subjects from Puglia (Apulia), Italy. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, K.S.; Fuschino, M.E.; Mokhiber, K.; Triner, W.; Spivack, S.D. Exhaled Breath Condensate Appears to Be an Unsuitable Specimen Type for the Detection of Influenza Viruses with Nucleic Acid-Based Methods. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 163, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Houspie, L.; De Coster, S.; Keyaerts, E.; Narongsack, P.; De Roy, R.; Talboom, I.; Sisk, M.; Maes, P.; Verbeeck, J.; Van Ranst, M. Exhaled Breath Condensate Sampling Is Not a New Method for Detection of Respiratory Viruses. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, D.J.; Toomey, S.; Madden, S.F.; Casey, M.; Breathnach, O.S.; Morris, P.G.; Grogan, L.; Branagan, P.; Costello, R.W.; De Barra, E.; et al. Use of Exhaled Breath Condensate (EBC) in the Diagnosis of SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19). Thorax 2021, 76, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniscalco, M.; Motta, A. Metabolomics of Exhaled Breath Condensate: A Means for Phenotyping Respiratory Diseases? Biomark. Med. 2017, 11, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniscalco, M.; Fuschillo, S.; Paris, D.; Cutignano, A.; Sanduzzi, A.; Motta, A. Clinical Metabolomics of Exhaled Breath Condensate in Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2019, 88, 121–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exhaled Biomarkers; Monographs; Horvath, I., de Jongste, J.C., Eds.; European Respiratory Society: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name of Device | Producer | Cooling System | Specific Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| EcoScreen1 | Cardinal Health, Hoechber, Germany | Electrical cooling System | Not currently manufactured |
| EcoScreen2 | FILT Lungen-& Thorax Diagnostik GmbH, Germany | Electrical cooling System | Fractionated collection possible |
| RTube | Respiratory Research, USA | Pre-cooled sleeve sensitive to higher ambient temperature | May be used at home by unsupervised subjects |
| TurboDECCS | Medivac, Italy | Electrical cooling System | Fractionated collection possible |
| ANACON | Biostec, Valencia, Spain | Electrical cooling System | May be used in mechanically ventilated patients |
| Fields of Interests | Biomarkers |
|---|---|
| Acidity | pH |
| Metals | Magnesium |
| Oxidative stress | H2O2, 8-isoprostane |
| Cytokines | IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-9, IL-13 |
| Leukotrienes | LTB4, LTC4, LTD4, LTE4 |
| Enzymes | MMP-9 |
| Nitric oxide products | ADMA, NOx |
| Hormones | Leptin |
| Proteins | Periostin |
| Genetics | miRNAs |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Połomska, J.; Bar, K.; Sozańska, B. Exhaled Breath Condensate—A Non-Invasive Approach for Diagnostic Methods in Asthma. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122697
Połomska J, Bar K, Sozańska B. Exhaled Breath Condensate—A Non-Invasive Approach for Diagnostic Methods in Asthma. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(12):2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122697
Chicago/Turabian StylePołomska, Joanna, Kamil Bar, and Barbara Sozańska. 2021. "Exhaled Breath Condensate—A Non-Invasive Approach for Diagnostic Methods in Asthma" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 12: 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122697
APA StylePołomska, J., Bar, K., & Sozańska, B. (2021). Exhaled Breath Condensate—A Non-Invasive Approach for Diagnostic Methods in Asthma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(12), 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122697






