Diagnosis of Subclinical Keratoconus with a Combined Model of Biomechanical and Topographic Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Study Design
- Group 1: 61 with healthy corneas. They had the following characteristics: (1) normal topography; (2) negative topographic keratoconus classification; (3) normal biomicroscopy; and (4) no eye disease history. Only one eye per patient was included.
- Group 2: 20 patients with subclinical keratoconus (SCKC). This early stage included patients with (1) minor topographic keratoconus signs and suspicious topographic findings (mild asymmetric bow-tie with or without skewed axis); (2) mean K (mean curvature of keratometry) < 46.5 D; (3) minimum corneal thickness (MCT) > 490 μm; (4) no slit-lamp findings (no central thinning with Fleischer’s ring nor Vogt’s striae); and (5) clinical keratoconus in the fellow eye.
2.2. Patient Exam
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zadnik, K.; Fink, B.; Nichols, J.J.; Yu, J.; Schetchman, K. Between-Eye Asymmetry in Keratoconus. Cornea 2002, 21, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, H.; Watters, G. An evaluation of the keratoconic cornea using computerised corneal mapping and ultrasonic measurements of corneal thickness. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 1996, 16, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirbas, N.; Pflugfelder, S. Topographic pattern and apex location of keratoconus on elevation topography maps. Cornea 1998, 17, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doh, H.J.; Kim, K.B.; Joo, C.K. The Clinical Feature of Keratoconus. J. Kor. Ophthal. Soc. 2000, 41, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar]
- Jinabhai, A.; O’Donnell, C.; Tromans, C.; Radhakrishnan, H. Optical quality and visual performance with customised soft contact lenses for keratoconus. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2014, 34, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinabhai, A.; Radhakrishnan, H.; Tromans, C.; O’Donnell, C. Visual performance and optical quality with soft lenses in keratoconus patients. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2012, 32, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak-Nielsen, S.; Ramlau-Hansen, C.H.; Ivarsen, A.; Plana-Ripoll, O.; Hjortdal, J. Incidence and prevalence of Keratoconus in Denmark—An update. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019, 97, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godefrooij, D.A.; de Wit, G.A.; Uiterwaal, C.S.; Imhof, S.M.; Wisse, R.P. Age-specific Incidence and Prevalence of Keratoconus: A Nationwide Registration Study. Am. Ophthalmol. 2017, 175, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristianslund, O.; Hagem, A.M.; Thorsrud, A.; Drolsum, L. Prevalence and incidence of keratoconus in Norway: A nationwide register study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, S.; Grabner, G.; Ruckhofer, J.; Dietrich, M.; Reitsamer, H. Genetics in Keratoconus—What is New? Open Ophthalmol. J. 2017, 11, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naderan, M.; Shoar, S.; Rezagholizadeh, F.; Zolfaghari, M.; Naderan, M. Characteristics and associations of keratoconus patients. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2015, 38, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon-Shaag, A.; Millodot, M.; Shneor, E.; Liu, Y. The genetic and environmental factors for keratoconus. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 795738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vellara, H.R.; Patel, D.V. Biomechanical properties of the keratoconic cornea: A review. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2015, 98, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriquez, M.A.; Hadid, M.; Izquierdo, L., Jr. A Systematic Review of Subclinical Keratoconus and Forme Fruste Keratoconus. J. Refract. Surg. 2020, 36, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Luna, G.; Pérez-Rueda, A. A predictive model for early diagnosis of keratoconus. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020, 20, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Nogueira, L.P.; Caldas, D.L.; Fontes, B.M.; Luz, A.; Cazal, J.O.; Alves, M.R.; Belin, M.W. Evaluation of corneal shape and biomechanics before LASIK. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2011, 51, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, K.; Ishii, R.; Shimizu, K.; Igarashi, A. Evaluation of corneal elevation, pachymetry and keratometry in keratoconic eyes with respect to the stage of Amsler-Krumeich classification. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, S.; Ortak, H.; Yeter, V.; Alim, S.; Sayn, O.; Tas, U.; Sönmez, B. Mapping corneal thickness using dual scheimpflug imaging at different stages of keratoconus. Cornea 2013, 32, 1470–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miháltz, K.; Kovács, I.; Takács, Á.; Nagy, Z.Z. Evaluation of keratometric, pachymetric, and elevation parameters of keratoconus corneas with pentacam. Cornea 2009, 28, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis, U.; Loiacono, C.; Richiardi, L.; Turco, D.; Mutani, B.; Grignolo, F.M. Sensitivity and specificity of posterior corneal elevation measured Pentacam in discriminating keratoconus/subclinical keratoconus. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 1534–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.; Ambrósio, R.; Inoue, R.; Maeda, N.; Miki, A.; Nishida, K. Detection of Subclinical Corneal Ectasia Using Corneal Tomographic and Biomechanical Assessments in a Japanese Population. J. Refract. Surg. 2019, 35, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, B.V.; Machado, A.P.; Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Ribeiro, G.; Araújo, L.N.; Luz, A.; Lyra, J.M. Analysis of waveform-derived ORA parameters in early forms of keratoconus and normal corneas. J. Refract. Surg. 2013, 29, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elham, R.; Jafarzadehpur, E.; Hashemi, H.; Amanzadeh, K.; Shokrollahzadeh, F.; Yekta, A.A.; Khabazkhoob, M. Keratoconus diagnosis using Corvis ST measured biomechanical parameters. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2017, 29, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yan, Z.; Tian, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X. Relationship Among Corneal Stiffness, Thickness, and Biomechanical Parameters Measured by Corvis ST, Pentacam and ORA in Keratoconus. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-García, P.; Peris-Martínez, C.; Abbouda, A.; Ruiz-Moreno, J.M. Detection of subclinical keratoconus through non-contact tonometry use of discriminant biomechanical functions. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Huang, Y.-F.; Wang, L.-Q.; Bai, H.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, J.-J.; Wu, Y.; Gao, M. Corneal Biomechanical Assessment Using Corneal Visualization Scheimpflug Technology in Keratoconic and Normal Eyes. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 3, 147516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peris-Martínez, C.; Díez-Ajenjo, M.A.; García-Domene, M.C.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; Luque-Cobija, M.J.; Del Buey-Sayas, M.Á.; Ortí-Navarro, S. Evaluation of Intraocular Pressure and Other Biomechanical Parameters to Distinguish between Subclinical Keratoconus and Healthy Corneas. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Xu, L.; Fan, Q.; Gu, Y.; Yang, K. Accuracy of new Corvis ST parameters for detecting subclinical and clinical keratoconus eyes in a Chinese population. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinciguerra, R.; Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Elsheikh, A.; Roberts, C.J.; Lopes, B.; Morenghi, E.; Azzolini, C.; Vinciguerra, P. Detection of Keratoconus with a New Biomechanical Index. J. Refract. Surg. 2016, 32, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Lopes, B.T.; Faria-Correia, F.; Salomão, M.Q.; Bühren, J.; Roberts, C.J.; Elsheikh, A.; Vinciguerra, R.; Vinciguerra, P. Integration of Scheimpflug-Based Corneal Tomography and Biomechanical Assessments for Enhancing Ectasia Detection. J. Refract. Surg. 2017, 33, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atalay, E.; Özalp, O.; Erol, M.A.; Bilgin, M.; Yıldırım, N. A Combined Biomechanical and Tomographic Model for Identifying Cases of Subclinical Keratoconus. Cornea 2020, 39, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanza, M.; Cennamo, M.; Iaccarino, S.; Romano, V.; Bifani, M.; Irregolare, C.; Lanza, A. Evaluation of corneal deformation analyzed with a Scheimpflug based device. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2015, 38, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroni, D.; Gadhvi, K.A.; Hristova, R.; McLean, K.; Rocha de Lossada, C.; Romano, V.; Kaye, S. Influence of Corneal Visualization Scheimpflug Technology Tonometry on Intraocular Pressure. Ophthalmol Sci. 2021, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, M.; Czanner, G.; Vinciguerra, R.; Romano, V.; Ahmad, S.; Batterbury, M.; Britten, C.; Willoughby, C.E.; Kaye, S.B. Improving precision for detecting a change in the shape of the cornea in patients with keratoconus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montanino, A.; Angelillo, M.; Pandolfi, A. A 3D fluid-solid interaction model of the air puff test in the human cornea. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 94, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.; Marshall, J. A review of corneal biomechanics: Mechanisms for measurement and the implications for refractive surgery. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 68, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, X.L.; Yang, S.L.; Yan, X.M.; Li, H.L. Examination and discriminant analysis of corneal biomechanics with Corvis ST in keratoconus and subclinical keratoconus. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2019, 51, 881–886. [Google Scholar]
- Koc, M.; Aydemir, E.; Tekin, K.; Inanc, M.; Kosekahya, P.; Kiziltoprak, H. Biomechanical Analysis of Subclinical Keratoconus With Normal Topographic, Topometric, and Tomographic Findings. J. Refract. Surg. 2019, 35, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán-López, S.; Cadarso-Suárez, L.; López-Ratón, M.; Cadarso-Suárez, C. Corneal Biomechanics in Unilateral Keratoconus and Fellow Eyes with a Scheimpflug-based Tonometer. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2018, 95, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
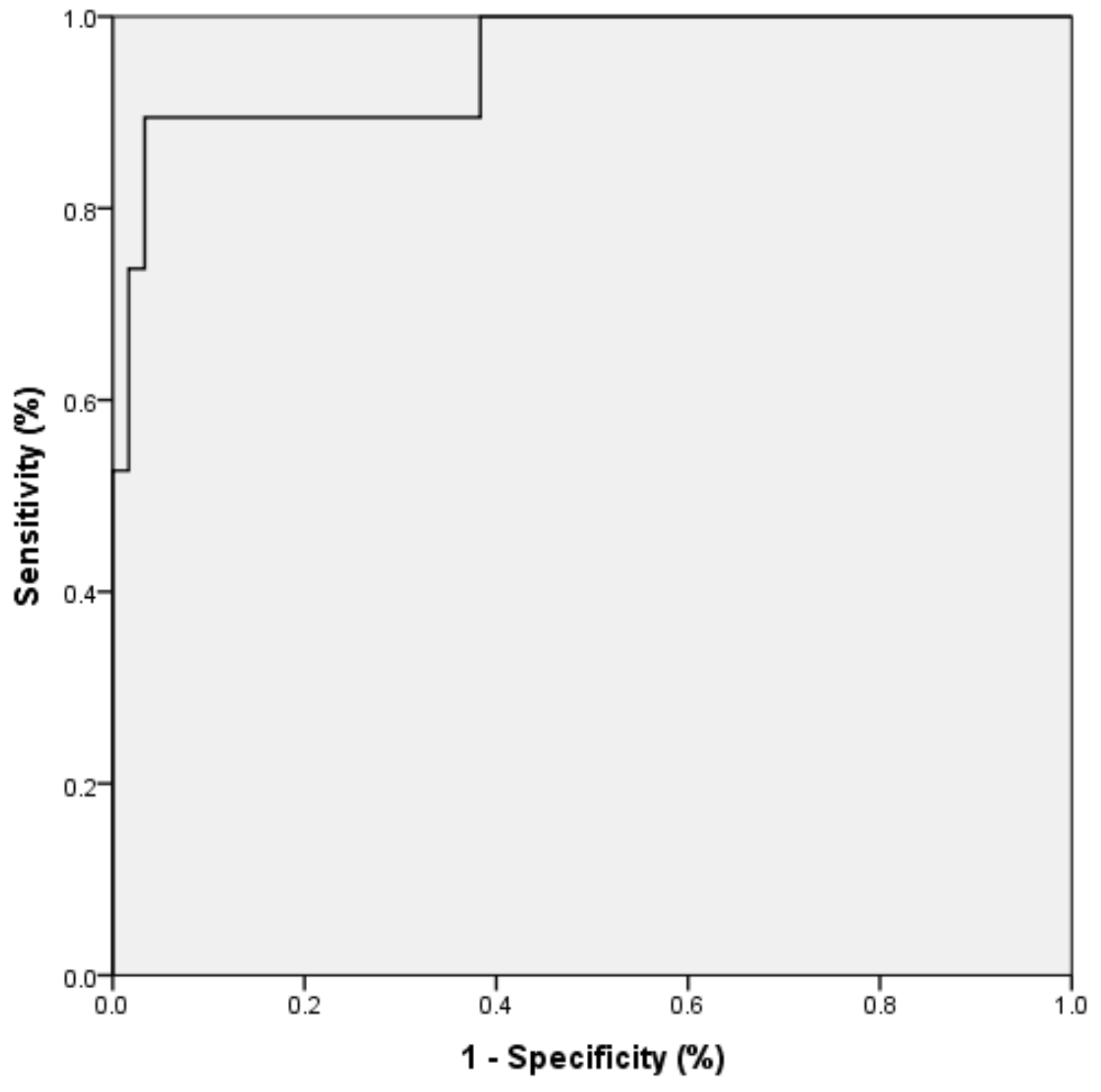
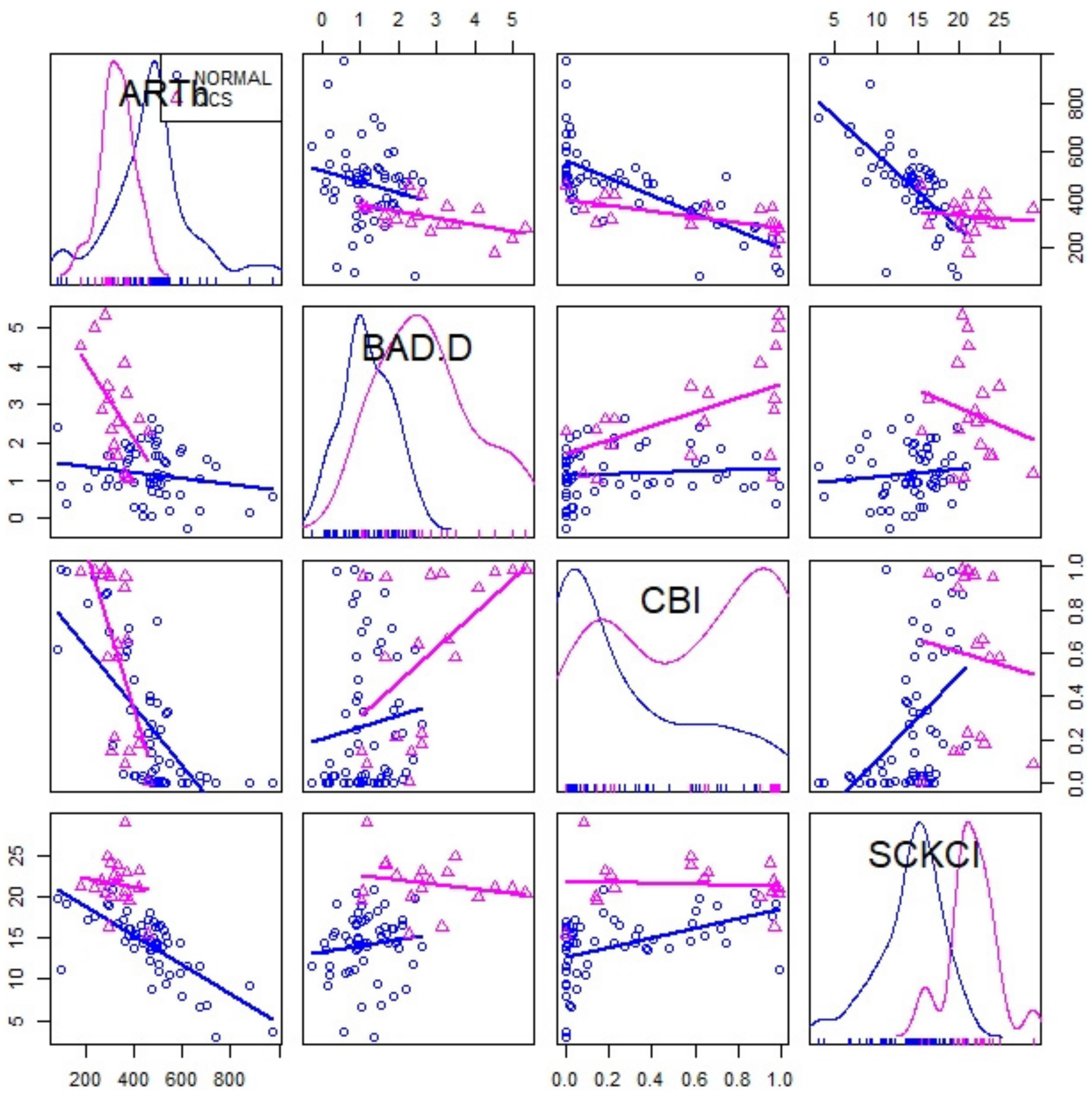
| Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error | 95% Confidence Interval | Sig. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||||
| Age (years) | Normal | 45.85 | 20.04 | 2.57 | 40.72 | 50.99 | 0.09 |
| SCKC | 37.2 | 13.19 | 2.95 | 31.03 | 43.37 | ||
| BSCVA (decimal scale) | Normal | 0.98 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.97 |
| SCKC | 0.99 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.95 | 1.02 | ||
| Sph Eq *(diopters) | Normal | −1.04 | 3.16 | 0.47 | −1.98 | −0.1 | 0.52 |
| SCKC | −1.85 | 1.6 | 0.44 | −2.81 | −0.88 | ||
| Q (µm) | Normal | −0.34 | 0.27 | 0.04 | −0.41 | −0.27 | 0.57 |
| SCKC | −0.41 | 0.19 | 0.04 | −0.5 | −0.32 | ||
| KMAX (diopters) | Normal | 45.54 | 2.07 | 0.27 | 45.01 | 46.07 | 0.61 |
| SCKC | 46.15 | 2.12 | 0.47 | 45.16 | 47.14 | ||
| CCT (µm) | Normal | 529.48 | 51.08 | 6.59 | 516.29 | 542.68 | 0.17 |
| SCKC | 511.4 | 30.04 | 6.72 | 497.34 | 525.46 | ||
| IOP (mmHg) | Normal | 16.19 | 3.55 | 0.45 | 15.28 | 17.1 | 0.00 * |
| SCKC | 13.6 | 2.06 | 0.46 | 12.64 | 14.56 | ||
| RMS HOA (µm) | Normal | 0.51 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.45 | 0.57 | 0.31 |
| SCKC | 0.63 | 0.3 | 0.07 | 0.49 | 0.77 | ||
| Coma 0° (µm) | Normal | 0 | 0.23 | 0.03 | −0.06 | 0.06 | 0.91 |
| SCKC | −0.05 | 0.28 | 0.06 | −0.18 | 0.09 | ||
| Anterior Coma 90° (µm) | Normal | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.03 | −0.04 | 0.06 | 0.00 * |
| SCKC | −0.5 | 0.47 | 0.11 | −0.72 | −0.28 | ||
| Posterior Coma 90° (µm) | Normal | −0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 * |
| SCKC | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.16 | ||
| Sph Ab ** (µm) | Normal | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.67 |
| SCKC | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.21 | ||
| BAD-D | Normal | 1.18 | 0.65 | 0.08 | 1.02 | 1.35 | 0.00 * |
| SCKC | 2.64 | 1.37 | 0.31 | 2 | 3.28 | ||
| Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error | 95% Confidence Interval for Mean | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||||
| Def. Amp. Max [mm] | Normal | 1.03 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 1.01 | 1.06 | 0.01 * |
| SCKC | 1.13 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 1.08 | 1.18 | ||
| A1 Time [ms] | Normal | 7.52 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 7.42 | 7.62 | 0.00 * |
| SCKC | 7.22 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 7.11 | 7.32 | ||
| A1 Deflection Length [mm] | Normal | 2.35 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 2.27 | 2.43 | 0.24 |
| SCKC | 2.24 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 2.12 | 2.35 | ||
| A1 Velocity [m/s] | Normal | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.00 * |
| SCKC | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.17 | ||
| A2 Time [ms] | Normal | 21.60 | 1.03 | 0.13 | 21.33 | 21.86 | 0.08 |
| SCKC | 22.01 | 0.58 | 0.13 | 21.74 | 22.28 | ||
| A2 Deflection Length [mm] | Normal | 3.21 | 0.80 | 0.11 | 3.00 | 3.42 | 0.68 |
| SCKC | 3.00 | 0.76 | 0.17 | 2.65 | 3.36 | ||
| A2 Velocity [m/s] | Normal | −0.23 | 0.04 | 0.01 | −0.24 | −0.22 | 0.00 * |
| SCKC | −0.27 | 0.04 | 0.01 | −0.29 | −0.25 | ||
| HC Time [ms] | Normal | 17.03 | 0.66 | 0.09 | 16.86 | 17.20 | 0.88 |
| SCKC | 17.12 | 0.40 | 0.09 | 16.93 | 17.31 | ||
| Peak Dist. [mm] | Normal | 4.80 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 4.70 | 4.90 | 0.00 * |
| SCKC | 5.10 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 4.98 | 5.22 | ||
| Radius [mm] | Normal | 7.11 | 1.18 | 0.15 | 6.80 | 7.41 | 0.34 |
| SCKC | 6.75 | 0.78 | 0.18 | 6.38 | 7.11 | ||
| DA Ratio Max (2mm) | Normal | 4.61 | 3.46 | 0.44 | 3.72 | 5.50 | 1.00 |
| SCKC | 4.60 | 0.50 | 0.11 | 4.36 | 4.83 | ||
| DA Ratio Max (1mm) | Normal | 1.68 | 0.65 | 0.08 | 1.51 | 1.84 | 0.80 |
| SCKC | 1.61 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 1.58 | 1.63 | ||
| Integrated Radius [mm−1] | Normal | 8.27 | 1.38 | 0.18 | 7.92 | 8.62 | 0.10 |
| SCKC | 9.04 | 1.34 | 0.30 | 8.41 | 9.67 | ||
| ARTh | Normal | 481.87 | 189.43 | 24.46 | 432.94 | 530.81 | 0.00 * |
| SCKC | 332.46 | 67.37 | 15.46 | 299.99 | 364.94 | ||
| SP A1 | Normal | 113.54 | 18.51 | 2.39 | 108.76 | 118.32 | 0.00 * |
| SCKC | 89.61 | 15.25 | 3.41 | 82.47 | 96.74 | ||
| CBI | Normal | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.35 | 0.01 * |
| SCKC | 0.59 | 0.38 | 0.09 | 0.41 | 0.77 | ||
| B | S.E. | Wald | df | Sig. | Exp (B) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | −0.04 | 0.05 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 0.96 |
| IOP (mmHg) | 1.52 | 2.68 | 0.32 | 1.00 | 0.57 | 4.57 |
| Anterior Coma 90 (µm) | 0.02 | 1.93 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.02 |
| Posterior Coma 90° (µm) | 40.21 | 16.52 | 5.93 | 1.00 | 0.01 * | 2.899E+17 |
| A1 Velocity [m/s] | −34.52 | 62.95 | 0.30 | 1.00 | 0.58 | 0.00 |
| A2 Velocity [m/s] | −98.81 | 44.43 | 4.95 | 1.00 | 0.03 * | 0.00 |
| A1 Time [ms] | −25.29 | 28.01 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 0.37 | 0.00 |
| ARTh | −0.02 | 0.01 | 4.42 | 1.00 | 0.04 * | 0.98 |
| Def. Amp. Max [mm] | −27.39 | 18.15 | 2.28 | 1.00 | 0.13 | 0.00 |
| Peak Dist. [mm] | −1.32 | 3.89 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.74 | 0.27 |
| Constant | 187.97 | 181.22 | 1.08 | 1.00 | 0.30 | 4.293E+81 |
| Resid | Dif Resid | Dev | Dif Dev | Pr (>Chi) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | 68 | 22.35 | |||
| Model 2 | 75 | 32.62 | −7 | −10.27 | 0.1738 * |
| B | SE. | Wald | df | Sig | Exp(B) | 95% CI for EXP(B) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | VIF ** | |||||||
| ARTh | −0.02 | 0.01 | 9.48 | 1.00 | 0.00 * | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.33 |
| Posterior Coma 90° [µm] | 26.31 | 8.28 | 10.10 | 1.00 | 0.00 * | 2675E+11 | 24,049.33 | 2976E+18 | 1.34 |
| A2 Velocity [m/s] | −56.35 | 18.11 | 9.68 | 1.00 | 0.00 * | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.38 |
| Constant | −10.65 | 4.24 | 6.31 | 1.00 | 0.01 * | 0.00 | |||
| Observed | Predicted | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| NORMAL | SCKC | Percentage Correct | |
| NORMAL | 58 | 2 | 96.7 |
| SCKC | 2 | 17 | 89.5 |
| Overall Percentage | 94.9 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Rueda, A.; Jiménez-Rodríguez, D.; Castro-Luna, G. Diagnosis of Subclinical Keratoconus with a Combined Model of Biomechanical and Topographic Parameters. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132746
Pérez-Rueda A, Jiménez-Rodríguez D, Castro-Luna G. Diagnosis of Subclinical Keratoconus with a Combined Model of Biomechanical and Topographic Parameters. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(13):2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132746
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Rueda, Antonio, Diana Jiménez-Rodríguez, and Gracia Castro-Luna. 2021. "Diagnosis of Subclinical Keratoconus with a Combined Model of Biomechanical and Topographic Parameters" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 13: 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132746
APA StylePérez-Rueda, A., Jiménez-Rodríguez, D., & Castro-Luna, G. (2021). Diagnosis of Subclinical Keratoconus with a Combined Model of Biomechanical and Topographic Parameters. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(13), 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132746







