Abstract
The aim of this study was to estimate the immunogenic effect of mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. This study included 510 participants who received mRNA vaccine. The measurement of anti-COVID-19 antibodies was performed using the Abbott SARS-CoV-2 IgG quantitative assay (Abbott). Overall, mean titer of anti-Spike antibodies was 19,319.2 ± 1787.5 AU/mL. Vaccination induced a robust immunogenic response in those previously infected with SARS-CoV-2 compared with non-infected subjects. Additionally, individuals that were asymptomatic after vaccination produced lower levels of antibodies compared to feverish individuals. In conclusion, remarkably high levels of anti-Spike COVID-19 antibodies were observed after vaccination.
1. Introduction
The novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) that is a result of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS CoV-2) is an emerging global health problem that was firstly reported in Wuhan, China, in December 2019 [1]. Due to person-to-person transmission, the infection was rapidly spread worldwide.
Vaccination is a safe and effective method for protection against infectious diseases. Vaccines train the immune response to recognize and neutralize an infectious agent. On account of the long-standing vaccination programs during childhood and adulthood, large epidemics of infectious diseases have reduced worldwide [2].
For the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic control, it is fundamental to develop vaccines and to rapidly organize their implementation. There are multitudes of anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates, based on several different mechanisms of action that are currently in development or finished phase III trials [3,4]. Since December 2020, several vaccines have been authorized worldwide. In Greece, vaccination was started from Healthcare professionals and on 13 March 2021, 1,283,472 doses of vaccines were used [5].
The aim of this study was to estimate the seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies among persons who took two doses of mRNA vaccine in the Thrace region and to explore risk factors for any adverse events.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Study Design
This study was performed at the University General Hospital of Alexandroupolis and Democritus University of Thrace in Alexandroupolis, Greece. The study protocol was approved by the local committee of ethics and deontology in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (Number 1070/11-01-2021).
2.2. Study Population
This study included 510 persons, which includes both uninfected (n = 487) and previously infected persons (n = 23) with confirmed COVID-19 by RT-PCR occurring 2 to 3.5 months prior to vaccination. All persons were vaccinated with mRNA (BNT162b2 Pfizer/BioNTech) vaccine. Serum samples were collected before vaccination and 1 month after the second dose. The period of sampling was from 10 February 2021 to 16 March 2021.
2.3. IgG Testing
The measurement of anti-COVID-19 antibodies was performed using the Abbott Architect i1000SR instrument (Abbott Diagnostics, Abbott Park Road, IL, USA) and the Abbott SARS-CoV-2 IgG quantitative kit by following the manufacturer’s instructions. The assay is a chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay for the qualitative detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Abs type IgG against the CoV-2 Spike protein (Sp) in human serum. Quantitative results > 50 AU/mL are reported as positive in accordance with the Abbott-determined positivity cutoff of 50 AU/mL.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) for normally distributed data. The counting data were expressed by rate (%). The Mann–Whitney U test was used for independent samples and the Wilcoxon test was used for paired sample analysis. The p value < 0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference.
3. Results
3.1. Safety Assesment
Overall, 510 persons were enrolled in the study. The demographic data is presented in Table 1. Summary data (numbers and percentages) for participants with any adverse events reflected that the most common were local adverse events. The injection-site event was pain after injection and this was noted in 114 participants (22.5%) after the first dose and/or the second dose and the pain resolved over 1 to 5 days. The most common system adverse events were fever—95 (18.6%); headache—78 (15.3%); myalgias—68 (13.3%); arthralgia—12 (2%); fatigue—57 (11.2%); and lymphadenopathy—22 (4.3%) (Table 1). The severe adverse events resulting in the discontinuation of the second dose injections were recorded in 3/510 (0.59%) participants who presented with severe allergic reactions. Only one woman developed delayed hypersensitivity reaction and the reaction initially started as macular on the fourth day after vaccination, but subsequently developed maculopapular lesions with symmetrical distribution on the extremities.

Table 1.
Demographical, clinical, and adverse events data of study population.
3.2. The Immunogenic Effect
Overall, the immunization with administration of two doses were completed in 507 participants (99.4%). Anti-Spike SARS-CoV-2-IgG antibodies were detected in 508 out of 510 (99.6%), with the mean value 19,319.2 ± 1787.5 AU/mL. Participants who suffered from COVID-19 had higher levels of anti-Spike antibodies in comparison to non-infected 25,599.5 ± 10,646.8 vs. 19,221.3 ± 1803.66, p = 0.049, respectively (Figure 1A). Moreover, COVID-19 patients had developed higher levels of anti-Spike antibodies after vaccination 593.7 ± 379.2 vs. 25,599.5 ± 10,646.8 AU/mL, p < 0.00001 (Figure 1B). Patients with fever developed higher titer of anti-Spike Abs in comparison to asymptomatic participants (28,899.6 ± 4831.01 vs. 14,685.9 ± 214.1 p < 0.00001) Figure 1C. Moreover, patients with autoimmune disorders had lower titer of anti-Spike Abs than the general population in a statistically significant manner 6311.18 ± 557.1 vs. 19,319.2 ± 1787.5 AU/mL.
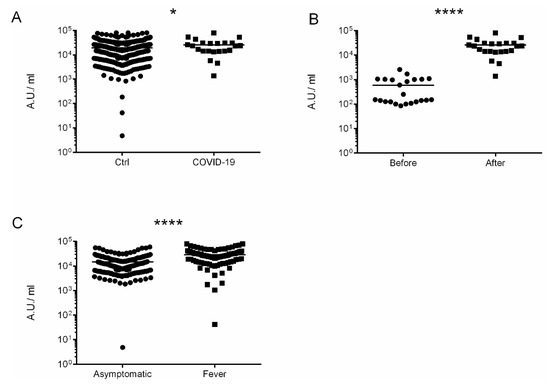
Figure 1.
The immunogenic effect of mRNA vaccine. (A) Levels of antibodies after vaccination. Comparison of controls vs. COVID-19 patients. (B) Levels of antibodies in COVID-19 patients before and after vaccination. (C) Levels of antibodies after vaccination in asymptomatic persons vs. systemic adverse events (fever) persons. The date is presented as log10. * p = 0.049 and **** p < 0.0001.
4. Discussion
This study provides data on the magnitude of IgG titers after mRNA vaccination in an adult population in the Thrace region, Greece. Overall, in this study, only three severe adverse events occurring after the receipt of the first vaccine that led to postponing the second dose has been reported. The adverse events after the receipt of Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in the United States were reported in 4393 (0.2%) cases. Among these, cases of severe allergic reaction, including anaphylaxis, were recorded [6]. In this study the association of systemic symptoms, such as fever with higher IgG responses to Spike, was observed. These results are in agreement with previously reported studies. The cases of the acute onset of a single lymphadenopathy (supraclavicular or Axillary) after intramuscular administration of an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine recorded in 20 participants in this study. These results are in line with what is previously reported by O R Mitchell et al. and Fernández-Prada et al. [7,8]. The mean value of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein in patients with autoimmune disorders in this study was lower than in the general population (6311.18 ± 557.1 vs 19,319.2 ± 1787.5 AU/mL). The data on specific COVID-19 vaccine responses in patients under immunosuppressive therapy have been poorly documented until now. Immunosuppressive therapy in patients with autoimmune disorders or transplantation may impair vaccine responses. These data were previously shown upon vaccination of immunosuppressive patients and predominantly focuses on influenza and pneumococcal vaccines [9]. A limitation of the study is the relatively small group of vaccinated patients after SARS CoV infection.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, and validation, T.G.K.; laboratory investigation, S.Z., E.K., E.G.K. and I.N.; clinical data curation, I.M., G.R., L.L. and D.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K., T.G.K. and I.M.; writing—review and editing, C.T., D.C, T.G.K. and I.M.; supervision, G.M. and M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of General University Hospital of Alexandroupolis (protocol code: 1070/11-01-2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset generated during the study contains sensitive personal information. Some of this data is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassimos, D.; Effraimidou, E.; Medic, S.; Konstantinidis, T.; Theodoridou, M.; Maltezou, H.C. Vaccination Programs for Adults in Europe, 2019. Vaccines 2020, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logunov, D.Y.; Dolzhikova, I.V.; Zubkova, O.V.; Tukhvatullin, A.I.; Shcheblyakov, D.V.; Dzharullaeva, A.S.; Grousova, D.M.; Erokhova, A.S.; Kovyrshina, A.V.; Botikov, A.G.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine in two formulations: Two open, non-randomised phase 1/2 studies from Russia. Lancet 2020, 396, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccination against SARS-Cov-19. Available online: https://emvolio.gov.gr/ (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- CDC COVID-19 Response Team; Food and Drug Administration. Allergic Reactions Including Anaphylaxis After Receipt of the First Dose of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine—United States, December 14–23, 2020. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, O.; Dave, R.; Bekker, J.; Brennan, P. Supraclavicular lymphadenopathy following COVID-19 vaccination: An increasing presentation to the two-week wait neck lump clinic? Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 59, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Prada, M.; Rivero-Calle, I.; Calvache-González, A.; Martinón-Torres, F. Acute onset supraclavicular lymphadenopathy coinciding with intramuscular mRNA vaccination against COVID-19 may be related to vaccine injection technique, Spain, January and February 2021. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2100193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.; Winthrop, K.; Emery, P. COVID-19 vaccination and antirheumatic therapy. Rheumatol. Oxf. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).