Association between Odontogenic and Maxillary Sinus Conditions: A Retrospective Cone-Beam Computed Tomographic Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Assessment of Odontogenic Condition
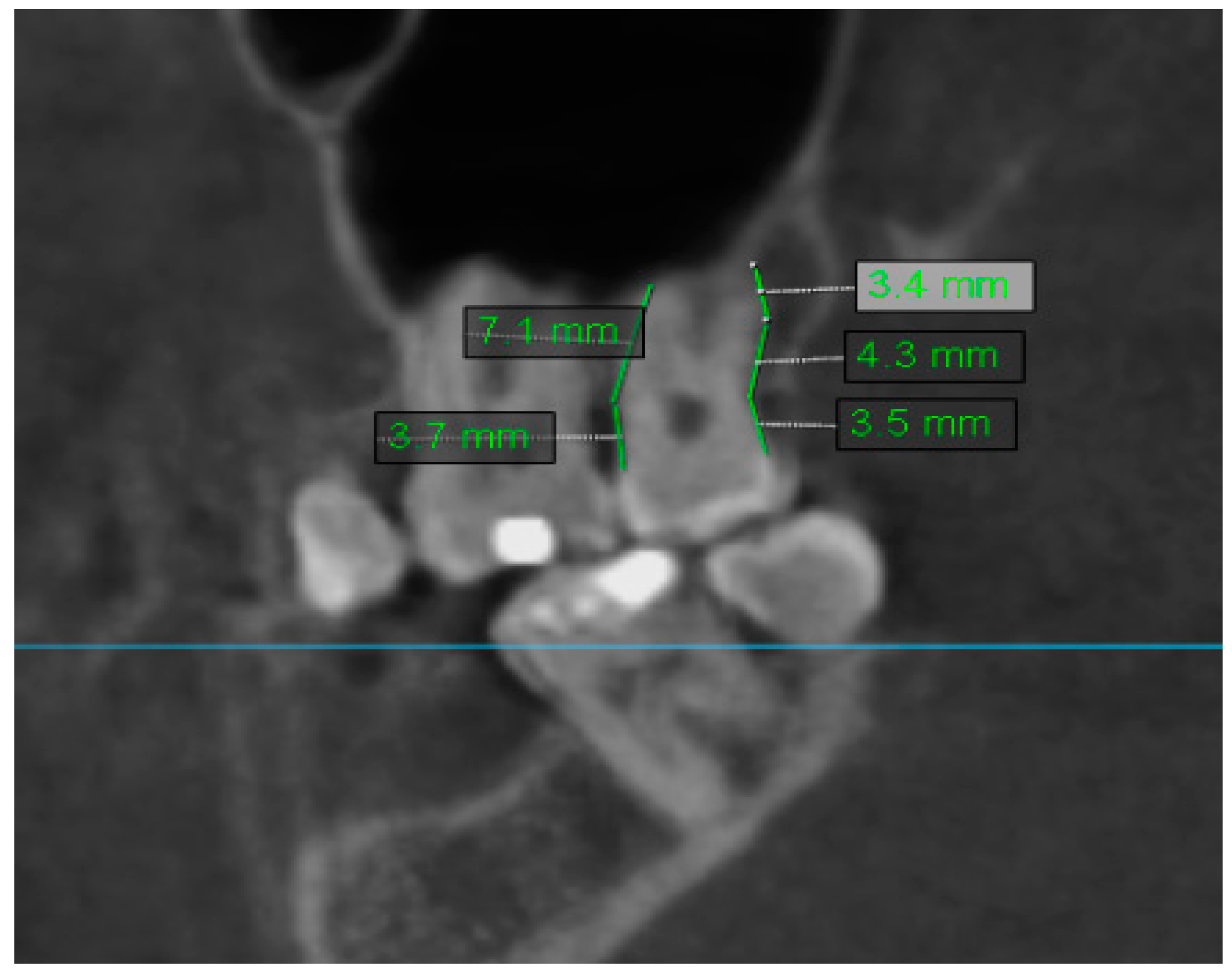
2.2. Assessment of Anatomic Relation between Teeth and Maxillary Sinus
2.3. Assessment of Periodontal Bone Loss
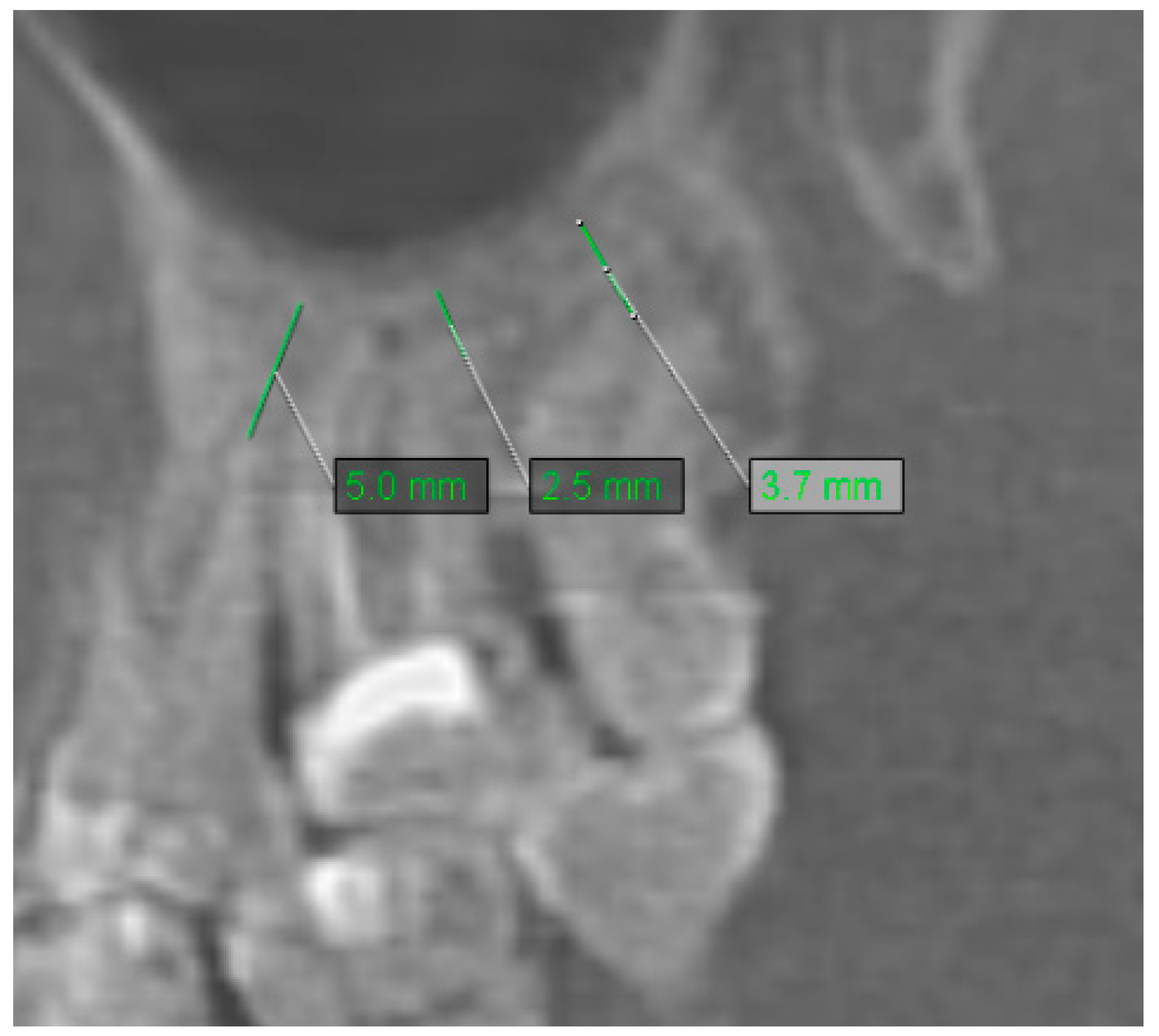
2.4. Assessment of Mucosal Thickening
2.5. Methodology of Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison Analysis of Mucosal Thickening According to Odontogenic Condition
3.2. Comparison Analysis of Mucosal Thickening According to Periodontal Bone Loss
3.3. Comparison Analysis of Mucosal Thickening According to Anatomic Relation between Teeth and Maxillary Sinus
3.4. Comparative Analysis of the Average Mucosal Thickening, Classified in a Three-Grade Scale and Odontogenic Condition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borgonovo, A.E.; Cicciù, M.; Re, D.; Rizza, F.; Frigo, A.C.; Maiorana, C. Maxillary sinus septa and anatomic correlation with the Schneiderian membrane. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2015, 26, 1394–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.; Qin, L.; Song, Y.L.; Xie, C.; Li, D.H. Longitudinal response of membrane thickness and ostium patency following sinus floor elevation: A prospective cohort study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennie, C.E.; Hood, C.M.; Blenke, E.J.; Schroter, R.S.; Doorly, D.J.; Jones, H.; Towey, D.; Tolley, N.S. Physical and computational modeling of ventilation of the maxillary sinus. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 145, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goller-Bulut, D.; Sekerci, A.E.; Köse, E.; Sisman, Y. Cone beam computed tomographic analysis of maxillary premolars and molars to detect the relationship between periapical and marginal bone loss and mucosal thickness of maxillary sinus. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2015, 20, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capelli, M.; Gatti, P. Radiological study of maxillary sinus using CBCT: A relationship between mucosal thickening and common anatomic variants in chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillet, M.; Bowles, W.R.; McClanahan, S.L.; John, M.T.; Ahmad, M. Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of maxillary sinusitis. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dis, M.L.; Miles, D.A. Disorders of the maxillary sinus. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 1994, 38, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, S.C.; Pharoah, M.J. Oral Radiology; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbazian, M.; Vandewoude, C.; Wyatt, J.; Jacobs, R. Comparative assessment of panoramic radiography and CBCT imaging for radiodiagnostics in the posterior maxilla. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 18, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharan, A.; Madjar, D. Correlation between maxillary sinus floor topography and related root position of posterior teeth using panoramic and cross-sectional computed tomography imaging. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 102, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phothikhun, S.; Suphanantachat, S.; Chuenchompoonut, V.; Nisapakultorn, K. Cone-beam computed tomographic evidence of the association between periodontal bone loss and mucosal thickening of the maxillary sinus. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janner, S.F.; Caversaccio, M.D.; Dubach, P.; Sendi, P.; Buser, D.; Bornstein, M.M. Characteristics and dimensions of the Schneiderian membrane: A radiographic analysis using cone beam computed tomography in patients referred for dental implant surgery in the posterior maxilla. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011, 22, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Pan, Y. Significance of maxillary sinus mucosal thickening in patients with periodontal disease. Int. Dent. J. 2015, 65, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shear, M.; Speight, P. Cysts associated with the maxillary antrum. In Cysts of the Oral and Maxillofacial Regions; Shear, M., Speight, P., Eds.; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 162–170. [Google Scholar]
- Timmenga, N.; Raghoebar, G.M.; Boering, G.; Van Weissenbruch, R. Maxillary sinus function after sinus lifts for the insertion of dental implants. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1997, 55, 936–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Choi, B.H.; Jeong, S.M.; Li, J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.J. A retrospective study of the effects on sinus complications of exposing dental implants to the maxillary sinus cavity. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2007, 103, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bergh, J.P.A.; ten Bruggenkate, C.M.; Disch, F.J.M.; Tuinzing, D.B. Anatomical aspects of sinus floor elevations. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2000, 11, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeli, G.; Artzi, Z.; Kozlovsky, A.; Segev, Y.; Landsberg, R. Antral computerized tomography pre-operative evaluation: Relationship between mucosal thickening and maxillary sinus function. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011, 22, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, H.; Ericson, S.; Hugoson, A. The effects of periodontal treatment on mucous membrane thickening in the maxillary sinus. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1986, 13, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, M. Rhinosinusitis in oral medicine and dentistry. Aust. Dent. J. 2014, 59, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, F.; Coutinho, T.M.; Carvalho Ferreira, D.; Souza, R.C.; Gonçalves, L.S. Odontogenic sinusitis: A comprehensive review. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2017, 75, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudack, C.; Sachse, F.; Alberty, J. Chronic rhinosinusitis- need for further classification? Inflamm. Res. 2004, 53, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallo, J.; Suominen-Taipale, L.; Huumonen, S.; Soikkonen, K.; Norblad, A. Prevalence of mucosal abnormalities of the maxillarysinus and their relationship to dental disease in panoramic radiography: Results from the Health 2000 Health Examination Survey. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010, 109, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selden, H.S. Endo-antral syndrome and various endodontic complications. J. Endod. 1999, 25, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osguthorpe, J.D.; Hadley, J.A. Rhinosinusitis. Current concepts in evaluation and management. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 83, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, S.; Privitera, S.; Maiolino, L.; Serra, A.; Garotta, M.; Blandino, G.; Speciale, A. Bacteriological findings and antimicrobial resistance in odontogenic and non-odontogenic chronic maxillary sinusitis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatin, A.S.; Sysolyatin, S.P.; Sysolyatin, P.G.; Melnikov, M.N. Chronic maxillary sinusitis of dental origin: Is external surgical approach mandatory? Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 1056–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, S.; Khan, F.R. Failure of endodontic treatment: The usual suspects. Eur. J. Dent. 2016, 10, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, U.; Orhan, K. Association between odontogenic conditions and maxillary sinus mucosal thickening: A retrospective CBCT study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.A.; Matsumoto, B.J. Odontogenic sinusitis: An ancient but under-appreciated cause of maxillary sinusitis. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 20, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhini, A.B.; Branstetter, B.F.; Ferguson, B.J. Unrecognized odontogenic maxillary sinusitis: A cause of endoscopic sinus surgery failure. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2010, 24, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Yokoi, H.; Kohno, N. Association between odontogenic infections and unilateral sinus opacification. Auris Nasus Larynx 2015, 42, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Som, P.M. CT of paranasal sinus. Neuro Radiol. 1985, 27, 189–201. [Google Scholar]
- Rak, K.M.; Newell, J.D.; Yakes, W.F.; Damiano, M.A.; Luethke, J.M. Paranasal sinuses on MR images of the brain: Significance of mucosal thickening. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1991, 156, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savolainen, S.; Eskelin, M.; Jousimies-Somer, H.; Ylikoski, J. Radiological findings in the maxillary sinuses of symptomless young men. Acta Otolaryngol. 1997, 529, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, S.; Karnik, P.; Shirke, P.; Shanbhag, V. Association betweenperiapical lesion sand maxillary sinus mucosal thickening: A retrospective cone-beam computed tomographic study. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauman, C.H.J.; Chandler, N.P.; Tong, D.C. Endodontic implications of the maxillary sinus: A review. Int. Endod. J. 2002, 35, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Q.; Duan, X.; Zheng, G.; Wang, H.; Huang, D. Associations between maxillary sinus mucosal thickening and apical periodontitis using cone-beam computed tomography scanning: A retrospective study. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhi, M.; Pozve, N.J.; Khorrami, L. Using cone beam computed tomography to detect the relationship between the periodontal bone loss and mucosal thickening of the maxillary sinus. Dent. Res. J. 2014, 11, 495–501. [Google Scholar]
- Boutsioukis, C.; van der Psimma, Z.; Sluis, L.W. Factors affecting irrigant extrusion during root canal irrigation: A systematic review. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 599–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bornstein, M.M.; Wasmer, J.; Sendi, P.; Janner, S.F.; Buser, D.; von Arx, T. Characteristics and dimensions of the Schneiderian membrane and apical bone in maxillary molars referred for apical surgery: A comparative radiographic analysis using limited cone beam computed tomography. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.S.; Dastoury, K. Prevalence of sinus membrane thickening and association with unhealthy teeth: A retrospective review of 831 consecutive patients with 1,662 cone-beam scans. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 2454–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, G.R.; Nicita, F.; Puleio, F.; Alibrandi, A.; Cervino, G.; Lizio, A.S.; Pantaleo, G. Accuracy of periapical radiography and CBCT in endodontic evaluation. Int. J. Dent. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lathiya, V.N.; Kolte, A.P.; Kolte, R.A.; Mody, D.R. Analysis of association between periodontal disease and thickness of maxillary sinus mucosa using cone beam computed tomography—A retrospective study. Saudi Dent. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roque-Torres, G.D.; Ramirez-Sotelo, L.R.; Vaz, S.L.; Bóscolo, S.M.; Bóscolo, F.N. Association between maxillary sinus pathologies and healthy teeth. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 82, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.T.; Hu, S.W.; Huang, J.Y.; Chang, Y.C. Assessment of relationship between maxillary sinus membrane thickening and the adjacent teeth health by cone-beam computed tomography. J. Dent. Sci. 2021, 16, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sex | N | % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Woman | 50 | 50% | |||||
| Man | 50 | 50% | |||||
| Wiek [lata] | |||||||
| N | Mean | SD | Median | Min | Max | Q1 | Q3 |
| 100 | 46,63 | 15,5 | 47 | 22 | 84 | 33 | 60 |
| Odontogenic Condition | Mucosa Thickening (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Mean + SD | Median | Quartiles | p < 0.001 NND P > NE,R,C,I,E,H NE > R,C,I,E,H R > C,I,E,H C > I,E,H |
| H (N = 468) | 2.87 ± 5.04 | 1.5 | 0.7–2.5 | |
| P (N = 104) | 12.35 ± 10.12 | 10.05 | 4.45–15.48 | |
| C (N = 133) | 6.38 ± 7.07 | 3.7 | 2.2–7.5 | |
| I (N = 41) | 3.8 ± 4.99 | 1.7 | 1.1–5.4 | |
| R (N = 366) | 6.46 ± 9.07 | 2.1 | 1.3–7.82 | |
| E (N = 49) | 3.25 ± 4.72 | 1.6 | 0.9–3.2 | |
| NE (N = 39) | 6.86 ± 8.9 | 3.5 | 2.05–8.4 | |
| Results of Analysis of Mucosal Thickening According to Periodontal Bone Loss | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tooth Number | Correlation Coefficient | p | Correlation Current | Strength of Correlation |
| 18 | 0.314 | p = 0.154 NND | --- | --- |
| 17 | 0.41 | p < 0.001 NND | Positive | Weak |
| 16 | 0.22 | p = 0.078 NND | --- | --- |
| 15 | 0.194 | p = 0.116 NND | --- | --- |
| 14 | 0.299 | p = 0.017 NND | Positive | Very weak |
| 13 | 0.248 | p = 0.02 NND | Positive | Very weak |
| 23 | 0.115 | p = 0.283 NND | --- | --- |
| 24 | 0.344 | p = 0.003 NND | Positive | Weak |
| 25 | 0.17 | p = 0.177 NND | --- | --- |
| 26 | 0.147 | p = 0.288 NND | --- | --- |
| 27 | 0.239 | p = 0.045 NND | Positive | Very weak |
| 28 | 0.322 | p = 0.083 NND | --- | --- |
| Results of Analysis of Mucosal Thickening According to Anatomic Relation between Teeth and Maxillary Sinus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tooth Number | Correlation Coefficient | p | Correlation Current | Strength of Correlation |
| 18 | −0.121 | p = 0.439 NP | --- | --- |
| 17 | 0.041 | p = 0.726 NP | --- | --- |
| 16 | −0.315 | p = 0.009 NP | Negative | Weak |
| 15 | −0.297 | p = 0.014 NP | Negative | Very weak |
| 14 | −0.168 | p = 0.163 NP | --- | --- |
| 13 | 0.027 | p = 0.801 NP | --- | --- |
| 23 | −0.015 | p = 0.886 NP | --- | --- |
| 24 | 0.026 | p = 0.823 NP | --- | --- |
| 25 | −0.051 | p = 0.674 NP | --- | --- |
| 26 | −0.179 | p = 0.176 NP | --- | --- |
| 27 | −0.329 | p = 0.004 NP | Negative | Weak |
| 28 | 0.136 | p = 0.345 NP | --- | --- |
| Teeth Group | Mucosal Thickening Grade 1 | Mucosal Thickening Grade 2 | Mucosal Thickening Grade 3 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | 305 (52.59%) | 134 (31.02%) | 29 (15.43%) | <0.001 |
| P | 6 (1.03%) | 46 (10.65%) | 52 (27.66%) | |
| C | 28 (4.83%) | 83 (19.21%) | 22 (11.70%) | |
| I | 23 (3.97%) | 15 (3.47%) | 3 (1.60%) | |
| R | 179 (30.86%) | 116 (26.85%) | 71 (37.77%) | |
| E | 29 (5.00%) | 16 (3.70%) | 4 (2.13%) | |
| NE | 10 (1.72%) | 22 (5.09%) | 7 (3.72%) | |
| All teeth | 580 (48%) | 432 (36%) | 188 (16%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuligowski, P.; Jaroń, A.; Preuss, O.; Gabrysz-Trybek, E.; Bladowska, J.; Trybek, G. Association between Odontogenic and Maxillary Sinus Conditions: A Retrospective Cone-Beam Computed Tomographic Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132849
Kuligowski P, Jaroń A, Preuss O, Gabrysz-Trybek E, Bladowska J, Trybek G. Association between Odontogenic and Maxillary Sinus Conditions: A Retrospective Cone-Beam Computed Tomographic Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(13):2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132849
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuligowski, Piotr, Aleksandra Jaroń, Olga Preuss, Ewa Gabrysz-Trybek, Joanna Bladowska, and Grzegorz Trybek. 2021. "Association between Odontogenic and Maxillary Sinus Conditions: A Retrospective Cone-Beam Computed Tomographic Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 13: 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132849
APA StyleKuligowski, P., Jaroń, A., Preuss, O., Gabrysz-Trybek, E., Bladowska, J., & Trybek, G. (2021). Association between Odontogenic and Maxillary Sinus Conditions: A Retrospective Cone-Beam Computed Tomographic Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(13), 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132849








