A Primer on the Clinical Aspects of Sarcoidosis for the Basic and Translational Scientist
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. How Understanding the Clinical Aspects of Sarcoidosis Can Assist the Scientist
3. Common Sarcoidosis Phenotypes
3.1. Implications for the Scientist
3.2. Implications for the Scientist
3.3. Implications for the Scientist
3.4. Implications for the Scientist
4. Sarcoidosis Risk Factors
4.1. Implications for the Scientist
4.2. Environmental Risk Factors
4.3. Implications for the Scientist
5. Drug Treatment of Sarcoidosis and Drug Inducers of Sarcoidosis: Sarcoidosis Pharmacotherapy
Implications for the Scientist
6. Drug-Induced Sarcoidosis-Like Reactions (DISRs)
Implications for the Scientist
7. Summary
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Judson, M.A. A sarcoidosis clinician’s perspective of MHC functional elements outside the antigen binding site. Hum. Immunol. 2019, 80, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judson, M.A.; Marchell, R.M.; Mascelli, M.; Piantone, A.; Barnathan, E.S.; Petty, K.J.; Chen, D.; Fan, H.; Grund, H.; Ma, K.; et al. Molecular profiling and gene expression analysis in cutaneous sarcoidosis: The role of interleukin-12, interleukin-23, and the T-helper 17 pathway. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 66, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judson, M.A.; Baughman, R.P.; Costabel, U.; Drent, M.; Gibson, K.F.; Raghu, G.; Shigemitsu, H.; Barney, J.B.; Culver, D.A.; Hamzeh, N.Y.; et al. Safety and efficacy of ustekinumab or golimumab in patients with chronic sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Judson, M.A.; Boan, A.D.; Lackland, D.T. The clinical course of sarcoidosis: Presentation, diagnosis, and treatment in a large white and black cohort in the United States. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2012, 29, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Baughman, R.P.; Teirstein, A.S.; Judson, M.A.; Rossman, M.D.; Yeager, H., Jr.; Bresnitz, E.A.; DePalo, L.; Hunninghake, G.; Iannuzzi, M.C.; Johns, C.J.; et al. Clinical characteristics of patients in a case control study of sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1885–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chamuleau, R.A.; Sprangers, R.L.; Alberts, C.; Schipper, M.E. Sarcoidosis and chronic intrahepatic cholestasis. Neth. J. Med. 1985, 28, 470–476. [Google Scholar]
- Devaney, K.; Goodman, Z.D.; Epstein, M.S.; Zimmerman, H.J.; Ishak, K.G. Hepatic sarcoidosis. Clinicopathologic features in 100 patients. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1993, 17, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatti, R.; Sharma, O.P. Course of asymptomatic liver involvement in sarcoidosis: Role of therapy in selected cases. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 1997, 14, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hercules, H.D.; Bethlem, N.M. Value of liver biopsy in sarcoidosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1984, 108, 831–834. [Google Scholar]
- Sartwell, P.E.; Edwards, L.B. Epidemiology of sarcoidosis in the U.S. Navy. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1974, 99, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westney, G.E.; Judson, M.A. Racial and ethnic disparities in sarcoidosis: From genetics to socioeconomics. Clin. Chest Med. 2006, 27, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouser, E.D.; Maier, L.A.; Wilson, K.C.; Bonham, C.A.; Morgenthau, A.S.; Patterson, K.C.; Abston, E.; Bernstein, R.C.; Blankstein, R.; Chen, E.S.; et al. Diagnosis and Detection of Sarcoidosis. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, e26–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judson, M.A. The Diagnosis of Sarcoidosis: Attempting to Apply Rigor to Arbitrary and Circular Reasoning. Chest 2018, 154, 1006–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Judson, M.A.; Baughman, R.P. How many organs need to be involved to diagnose sarcoidosis?: An unanswered question that, hopefully, will become irrelevant. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2014, 31, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake, G.W.; Costabel, U.; Ando, M.; Baughman, R.; Cordier, J.F.; du Bois, R.; Eklund, A.; Kitaichi, M.; Lynch, J.; Rizzato, G.; et al. ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society/World Association of Sarcoidosis and other Granulomatous Disorders. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 1999, 16, 149–173. [Google Scholar]
- Judson, M.A. The diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2019, 25, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Bauer, K.L.; Fischoeder, A.; Bhardwaj, N.; Oliver, S.J. The anergic state in sarcoidosis is associated with diminished dendritic cell function. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Judson, M.A. Lung transplantation for pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 11, 738–744. [Google Scholar]
- James, W.E.; Koutroumpakis, E.; Saha, B.; Nathani, A.; Saavedra, L.; Yucel, R.M.; Judson, M.A. Clinical Features of Extrapulmonary Sarcoidosis Without Lung Involvement. Chest 2018, 154, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, A.; Terado, Y.; Izumi, M.; Fujioka, Y.; Franke, F.E. Where does the antigen of cutaneous sarcoidosis come from? J. Cutan. Pathol. 2010, 37, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordignon, M.; Rottoli, P.; Agostini, C.; Alaibac, M. Adaptive immune responses in primary cutaneous sarcoidosis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2011, 2011, 235142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Judson, M.A. Environmental Risk Factors for Sarcoidosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.P.; Culver, D.A.; Judson, M.A. A concise review of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moller, D.R.; Chen, E.S. Genetic basis of remitting sarcoidosis: Triumph of the trimolecular complex? Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2002, 27, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broos, C.E.; Koth, L.L.; van Nimwegen, M.; In ‘t Veen, J.; Paulissen, S.M.J.; van Hamburg, J.P.; Annema, J.T.; Heller-Baan, R.; Kleinjan, A.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; et al. Increased T-helper 17.1 cells in sarcoidosis mediastinal lymph nodes. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojas, M.; Restrepo-Jimenez, P.; Monsalve, D.M.; Pacheco, Y.; Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Ramirez-Santana, C.; Leung, P.S.C.; Ansari, A.A.; Gershwin, M.E.; Anaya, J.M. Molecular mimicry and autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 95, 100–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggmark, A.; Hamsten, C.; Wiklundh, E.; Lindskog, C.; Mattsson, C.; Andersson, E.; Lundberg, I.E.; Gronlund, H.; Schwenk, J.M.; Eklund, A.; et al. Proteomic profiling reveals autoimmune targets in sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlstrom, J.; Dengjel, J.; Winqvist, O.; Targoff, I.; Persson, B.; Duyar, H.; Rammensee, H.G.; Eklund, A.; Weissert, R.; Grunewald, J. Autoimmune T cell responses to antigenic peptides presented by bronchoalveolar lavage cell HLA-DR molecules in sarcoidosis. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 133, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, A.J.; Kaiser, Y.; Wolfgeher, D.; Ai, J.; Eklund, A.; Clark, M.R.; Grunewald, J. In Situ Humoral Immunity to Vimentin in HLA-DRB1*03(+) Patients With Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Quernheim, J.; Gaede, K.I.; Fireman, E.; Zissel, G. Diagnoses of chronic beryllium disease within cohorts of sarcoidosis patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyara, M.; Amoura, Z.; Parizot, C.; Badoual, C.; Dorgham, K.; Trad, S.; Kambouchner, M.; Valeyre, D.; Chapelon-Abric, C.; Debré, P.; et al. The immune paradox of sarcoidosis and regulatory T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunninghake, G.W.; Fulmer, J.D.; Young, R.C., Jr.; Gadek, J.E.; Crystal, R.G. Localization of the immune response in sarcoidosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1979, 120, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planck, A.; Katchar, K.; Eklund, A.; Gripenbäck, S.; Grunewald, J. T-lymphocyte activity in HLA-DR17 positive patients with active and clinically recovered sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2003, 20, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, C.; Shaginurova, G.; Shelton, D.A.; Herazo-Maya, J.D.; Oswald-Richter, K.A.; Rotsinger, J.E.; Young, A.; Celada, L.J.; Kaminski, N.; Sevin, C.; et al. Local and Systemic CD4(+) T Cell Exhaustion Reverses with Clinical Resolution of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 3642832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polverino, F.; Curtis, J.L. The ABCs of Granulomatous Lung Diseases: Age-associated B Cells. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 922–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.P., 3rd; Kazerooni, E.A.; Gay, S.E. Pulmonary sarcoidosis. Clin. Chest Med. 1997, 18, 755–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, M.; Lee, K.S.; Itoh, H.; Hatabu, H. The spectrum of pulmonary sarcoidosis: Variations of high-resolution CT findings and clues for specific diagnosis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 73, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberstein, A.; von Zitzewitz, H.; Schweden, F.; Muller-Quernheim, J. Non invasive evaluation of the inflammatory activity in sarcoidosis with high-resolution computed tomography. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 1997, 14, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muller, N.L.; Kullnig, P.; Miller, R.R. The CT findings of pulmonary sarcoidosis: Analysis of 25 patients. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1989, 152, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Watanabe, O.; Sato, K.; Endo, K.; Heianna, J.; Itoh, I.; Watarai, J. The CT findings of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1996, 179, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalkanis, A.; Kalkanis, D.; Drougas, D.; Vavougios, G.D.; Datseris, I.; Judson, M.A.; Georgiou, E. Correlation of spleen metabolism assessed by 18F-FDG PET with serum interleukin-2 receptor levels and other biomarkers in patients with untreated sarcoidosis. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teirstein, A.S.; Machac, J.; Almeida, O.; Lu, P.; Padilla, M.L.; Iannuzzi, M.C. Results of 188 whole-body fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography scans in 137 patients with sarcoidosis. Chest 2007, 132, 1949–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsu, M.; Hatabu, H.; Morikawa, K.; Uematsu, H.; Ohno, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Nagai, S.; Izumi, T.; Konishi, J.; Itoh, H. Large coalescent parenchymal nodules in pulmonary sarcoidosis: “sarcoid galaxy” sign. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2002, 178, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sider, L.; Horton, E.S., Jr. Hilar and mediastinal adenopathy in sarcoidosis as detected by computed tomography. J. Thorac. Imaging 1990, 5, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.N.; Levin, D.L. Distribution of thoracic lymphadenopathy in sarcoidosis using computed tomography. J. Thorac. Imaging 1999, 14, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sève, P.; Jamilloux, Y.; Tilikete, C.; Gerfaud-Valentin, M.; Kodjikian, L.; El Jammal, T. Ocular Sarcoidosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 41, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodaghi, B.; Touitou, V.; Fardeau, C.; Chapelon, C.; LeHoang, P. Ocular sarcoidosis. Presse Med. 2012, 41, e349–e354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezrek, O.; El Kaddoumi, M.; Cherkaoui, O. ‘‘Candle Wax Dripping’’ Lesions in Sarcoidosis. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, e171845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tana, C.; Wegener, S.; Borys, E.; Pambuccian, S.; Tchernev, G.; Tana, M.; Giamberardino, M.A.; Silingardi, M. Challenges in the diagnosis and treatment of neurosarcoidosis. Ann. Med. 2015, 47, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gullapalli, D.; Phillips, L.H., 2nd. Neurosarcoidosis. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2004, 4, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, A.; Muller, N.L. Imaging of pneumoconiosis. Imaging 2003, 15, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasse, A.; Katic, C.; Germann, M.; Buchwald, A.; Zissel, G.; Muller-Quernheim, J. Phenotyping sarcoidosis from a pulmonary perspective. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mana, J.; Gomez-Vaquero, C.; Montero, A.; Salazar, A.; Marcoval, J.; Valverde, J.; Manresa, F.; Pujol, R. Lofgren’s syndrome revisited: A study of 186 patients. Am. J. Med. 1999, 107, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunewald, J.; Eklund, A. Lofgren’s syndrome: Human leukocyte antigen strongly influences the disease course. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gran, J.T.; Bohmer, E. Acute sarcoid arthritis: A favourable outcome? A retrospective survey of 49 patients with review of the literature. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 25, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillerdal, G.; Nou, E.; Osterman, K.; Schmekel, B. Sarcoidosis: Epidemiology and prognosis. A 15-year European study. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1984, 130, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Baughman, R.P.; Nagai, S.; Balter, M.; Costabel, U.; Drent, M.; du Bois, R.; Grutters, J.C.; Judson, M.A.; Lambiri, I.; Lower, E.E.; et al. Defining the clinical outcome status (COS) in sarcoidosis: Results of WASOG Task Force. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2011, 28, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, C.A.; Dornfeld, M.C.; Baughman, R.; Judson, M.A. Clinical phenotypes in sarcoidosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2014, 20, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietinalho, A.; Ohmichi, M.; Lofroos, A.B.; Hiraga, Y.; Selroos, O. The prognosis of pulmonary sarcoidosis in Finland and Hokkaido, Japan. A comparative five-year study of biopsy-proven cases. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2000, 17, 158–166. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, E.S.; Song, Z.; Willett, M.H.; Heine, S.; Yung, R.C.; Liu, M.C.; Groshong, S.D.; Zhang, Y.; Tuder, R.M.; Moller, D.R. Serum amyloid A regulates granulomatous inflammation in sarcoidosis through Toll-like receptor-2. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huho, A.; Foulke, L.; Jennings, T.; Koutroumpakis, E.; Dalvi, S.; Chaudhry, H.; Chopra, A.; Modi, A.; Rane, N.; Prezant, D.J.; et al. The role of serum amyloid A staining of granulomatous tissues for the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Respir. Med. 2017, 126, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patterson, K.C.; Chen, E.S. The Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis and Implications for Treatment. Chest 2018, 153, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasa, V.R.; Forsslund, H.; Enger, T.; Lorenz, D.; Kullberg, S.; Eklund, A.; Sköld, M.; Wahlström, J.; Grunewald, J.; Brighenti, S. Enhanced CD8(+) cytolytic T cell responses in the peripheral circulation of patients with sarcoidosis and non-Löfgren’s disease. Respir. Med. 2018, 138s, S38–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, D.R. Pulmonary fibrosis of sarcoidosis. New approaches, old ideas. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2003, 29, S37–S41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chappell, A.G.; Cheung, W.Y.; Hutchings, H.A. Sarcoidosis: A long-term follow up study. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2000, 17, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Shlobin, O.A.; Nathan, S.D. Management of end-stage sarcoidosis: Pulmonary hypertension and lung transplantation. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 39, 1520–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.T.; Heurich, A.E.; Sutton, A.L.; Lyons, H.A. Mortality in sarcoidosis. A changing pattern of the causes of death. Eur. J. Respir. Dis. 1981, 62, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Judson, M.A. Strategies for identifying pulmonary sarcoidosis patients at risk for severe or chronic disease. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2017, 11, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chan, K.M.; Schmidt, L.A.; Myers, J.L. Histopathology of Explanted Lungs from Patients with a Diagnosis of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Chest 2016, 149, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patterson, K.C.; Strek, M.E. Pulmonary fibrosis in sarcoidosis. Clinical features and outcomes. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2013, 10, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostard, R.L.; Prompers, L.; Weijers, R.E.; van Kroonenburgh, M.J.; Wijnen, P.A.; Geusens, P.P.; Drent, M. F-18 FDG PET/CT for detecting bone and bone marrow involvement in sarcoidosis patients. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 37, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varone, F.; Sgalla, G.; Iovene, B.; Richeldi, L. Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease. A Proposed Integrated Algorithm for Management. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heron, M.; van Moorsel, C.H.; Grutters, J.C.; Huizinga, T.W.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.; Nagtegaal, M.M.; Ruven, H.J.; van den Bosch, J.M. Genetic variation in GREM1 is a risk factor for fibrosis in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Tissue Antigens 2011, 77, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouvrier-Hanu, S.; Puech, B.; Piette, F.; Boute-Benejean, O.; Desbonnet, A.; Duquesnoy, B.; Farriaux, J.P. Blau syndrome of granulomatous arthritis, iritis, and skin rash: A new family and review of the literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1998, 76, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruit, A.; Grutters, J.C.; Ruven, H.J.; van Moorsel, C.H.; Weiskirchen, R.; Mengsteab, S.; van den Bosch, J.M. Transforming growth factor-beta gene polymorphisms in sarcoidosis patients with and without fibrosis. Chest 2006, 129, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibold, M.A.; Wise, A.L.; Speer, M.C.; Steele, M.P.; Brown, K.K.; Loyd, J.E.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Zhang, W.; Gudmundsson, G.; Groshong, S.D.; et al. A common MUC5B promoter polymorphism and pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Noth, I.; Garcia, J.G.; Kaminski, N. A variant in the promoter of MUC5B and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1576–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stock, C.J.; Sato, H.; Fonseca, C.; Banya, W.A.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Adamali, H.; Russell, A.M.; Denton, C.P.; Abraham, D.J.; Hansell, D.M.; et al. Mucin 5B promoter polymorphism is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis but not with development of lung fibrosis in systemic sclerosis or sarcoidosis. Thorax 2013, 68, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rybicki, B.A.; Maliarik, M.J.; Major, M.; Popovich, J., Jr.; Iannuzzi, M.C. Epidemiology, demographics, and genetics of sarcoidosis. Semin. Respir. Infect. 1998, 13, 166–173. [Google Scholar]
- Baughman, R.P.; Field, S.; Costabel, U.; Crystal, R.G.; Culver, D.A.; Drent, M.; Judson, M.A.; Wolff, G. Sarcoidosis in America. Analysis Based on Health Care Use. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.R.; Stone, C.H.; Havstad, S.; Rybicki, B.A. Racial differences in sarcoidosis granuloma density. Lung 2009, 187, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arkema, E.V.; Grunewald, J.; Kullberg, S.; Eklund, A.; Askling, J. Sarcoidosis incidence and prevalence: A nationwide register-based assessment in Sweden. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1690–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosoda, Y.; Sasagawa, S.; Yamaguchi, T. Sarcoidosis and tuberculosis: Epidemiological similarities and dissimilarities. A review of a series of studies in a Japanese work population (1941–1996) and the general population (1959–1984). Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2004, 21, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hulten, E.; Aslam, S.; Osborne, M.; Abbasi, S.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Blankstein, R. Cardiac sarcoidosis-state of the art review. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 6, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, F.; Modi, P.; Tanner, L.S. Lofgren Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Duchemann, B.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Jacobe de Naurois, C.; Sanyal, S.; Brillet, P.Y.; Brauner, M.; Kambouchner, M.; Huynh, S.; Naccache, J.M.; Borie, R.; et al. Prevalence and incidence of interstitial lung diseases in a multi-ethnic county of Greater Paris. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.H.; Chung, P.I.; Wu, C.Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Chiu, Y.W.; Chang, Y.T.; Liu, H.N. Comorbid autoimmune diseases in patients with sarcoidosis: A nationwide case-control study in Taiwan. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquart, N.; Cadelis, G.; Tressières, B.; Cordel, N. Epidemiology of sarcoidosis in Afro-Caribbean people: A 7-year retrospective study in Guadeloupe. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 54, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghè, D.; Dall’Asta, L.; Garavelli, C.; Pastorelli, A.A.; Muscarella, M.; Saccani, G.; Aiello, M.; Crisafulli, E.; Corradi, M.; Stacchini, P.; et al. Sarcoidosis in an Italian province. Prevalence and environmental risk factors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, N.; Sileo, C.; Calender, A.; Pacheco, Y.; Rosental, P.A.; Cavalin, C.; Macchi, O.; Valeyre, D.; Clement, A. Paediatric sarcoidosis. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2019, 29, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybicki, B.A.; Iannuzzi, M.C.; Frederick, M.M.; Thompson, B.W.; Rossman, M.D.; Bresnitz, E.A.; Terrin, M.L.; Moller, D.R.; Barnard, J.; Baughman, R.P.; et al. Familial aggregation of sarcoidosis. A case-control etiologic study of sarcoidosis (ACCESS). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkema, E.V.; Cozier, Y.C. Epidemiology of sarcoidosis: Current findings and future directions. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2018, 9, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinetti, M.; Luisetti, M.; Cuccia, M. HLA and sarcoidosis: New pathogenetic insights. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2002, 19, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Rossman, M.D.; Thompson, B.; Frederick, M.; Maliarik, M.; Iannuzzi, M.C.; Rybicki, B.A.; Pandey, J.P.; Newman, L.S.; Magira, E.; Beznik-Cizman, B.; et al. HLA-DRB1*1101: A significant risk factor for sarcoidosis in blacks and whites. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 73, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adrianto, I.; Lin, C.P.; Hale, J.J.; Levin, A.M.; Datta, I.; Parker, R.; Adler, A.; Kelly, J.A.; Kaufman, K.M.; Lessard, C.J.; et al. Genome-wide association study of African and European Americans implicates multiple shared and ethnic specific loci in sarcoidosis susceptibility. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levin, A.M.; Iannuzzi, M.C.; Montgomery, C.G.; Trudeau, S.; Datta, I.; McKeigue, P.; Fischer, A.; Nebel, A.; Rybicki, B.A. Association of ANXA11 genetic variation with sarcoidosis in African Americans and European Americans. Genes Immun. 2013, 14, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morais, A.; Lima, B.; Peixoto, M.J.; Alves, H.; Marques, A.; Delgado, L. BTNL2 gene polymorphism associations with susceptibility and phenotype expression in sarcoidosis. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kreider, M.E.; Christie, J.D.; Thompson, B.; Newman, L.; Rose, C.; Barnard, J.; Bresnitz, E.; Judson, M.A.; Lackland, D.T.; Rossman, M.D. Relationship of environmental exposures to the clinical phenotype of sarcoidosis. Chest 2005, 128, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Patel, D.; Welch, A.M.; Wilson, C.; Mroz, M.M.; Li, L.; Rose, C.S.; Van Dyke, M.; Swigris, J.J.; Hamzeh, N.; et al. Association Between Occupational Exposures and Sarcoidosis: An Analysis From Death Certificates in the United States, 1988–1999. Chest 2016, 150, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henke, C.E.; Henke, G.; Elveback, L.R.; Beard, C.M.; Ballard, D.J.; Kurland, L.T. The epidemiology of sarcoidosis in Rochester, Minnesota: A population-based study of incidence and survival. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986, 123, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirkok, S.S.; Basaranoglu, M.; Coker, E.; Karayel, T. Seasonality of the onset of symptoms, tuberculin test anergy and Kveim positive reaction in a large cohort of patients with sarcoidosis. Respirology 2007, 12, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilsher, M.L. Seasonal clustering of sarcoidosis presenting with erythema nodosum. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 12, 1197–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fite, E.; Alsina, J.M.; Mana, J.; Pujol, R.; Ruiz, J.; Morera, J. Epidemiology of sarcoidosis in Catalonia: 1979–1989. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 1996, 13, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, D.; Agarwal, R.; Aggarwal, A.N. Seasonality of sarcoidosis: The ‘heat’ is on. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2013, 30, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ungprasert, P.; Crowson, C.S.; Matteson, E.L. Seasonal variation in incidence of sarcoidosis: A population-based study, 1976–2013. Thorax 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, T.T.; Plant, B.J.; Henry, M.T.; Bredin, C.P. Sarcoidosis in Ireland: Regional differences in prevalence and mortality from 1996–2005. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2010, 27, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McDonough, C.; Gray, G.C. Risk factors for sarcoidosis hospitalization among U.S. Navy and Marine Corps personnel, 1981 to 1995. Mil. Med. 2000, 165, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kajdasz, D.K.; Judson, M.A.; Mohr, L.C., Jr.; Lackland, D.T. Geographic variation in sarcoidosis in South Carolina: Its relation to socioeconomic status and health care indicators. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 150, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kowalska, M.; Niewiadomska, E.; Zejda, J.E. Epidemiology of sarcoidosis recorded in 2006-2010 in the Silesian voivodeship on the basis of routine medical reporting. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2014, 21, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Deubelbeiss, U.; Gemperli, A.; Schindler, C.; Baty, F.; Brutsche, M.H. Prevalence of sarcoidosis in Switzerland is associated with environmental factors. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prezant, D.J.; Dhala, A.; Goldstein, A.; Janus, D.; Ortiz, F.; Aldrich, T.K.; Kelly, K.J. The incidence, prevalence, and severity of sarcoidosis in New York City firefighters. Chest 1999, 116, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kern, D.G.; Neill, M.A.; Wrenn, D.S.; Varone, J.C. Investigation of a unique time-space cluster of sarcoidosis in firefighters. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 148, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorham, E.D.; Garland, C.F.; Garland, F.C.; Kaiser, K.; Travis, W.D.; Centeno, J.A. Trends and occupational associations in incidence of hospitalized pulmonary sarcoidosis and other lung diseases in Navy personnel: A 27-year historical prospective study, 1975–2001. Chest 2004, 126, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, L.S.; Rose, C.S.; Bresnitz, E.A.; Rossman, M.D.; Barnard, J.; Frederick, M.; Terrin, M.L.; Weinberger, S.E.; Moller, D.R.; McLennan, G.; et al. A case control etiologic study of sarcoidosis: Environmental and occupational risk factors. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, J.; Rose, C.; Newman, L.; Canner, M.; Martyny, J.; McCammon, C.; Bresnitz, E.; Rossman, M.; Thompson, B.; Rybicki, B.; et al. Job and industry classifications associated with sarcoidosis in A Case-Control Etiologic Study of Sarcoidosis (ACCESS). J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2005, 47, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, G.P.; Rybicki, B.A.; Kirkey, K.L.; Coon, S.W.; Major, M.L.; Maliarik, M.J.; Iannuzzi, M.C. Occupational risk factors for sarcoidosis in African-American siblings. Chest 2003, 123, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, E.; Jarvholm, B.; Andersson, M. Silica dust and sarcoidosis in Swedish construction workers. Occup. Med. 2019, 69, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronsmans, S.; Verbeken, E.K.; Adams, E.; Keirsbilck, S.; Yserbyt, J.; Wuyts, W.A.; Swennen, R.; Hoet, P.H.; Nemery, B. Granulomatous lung disease in two workers making light bulbs. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2019, 62, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicki, B.A.; Amend, K.L.; Maliarik, M.J.; Iannuzzi, M.C. Photocopier exposure and risk of sarcoidosis in African-American sibs. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2004, 21, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Izbicki, G.; Chavko, R.; Banauch, G.I.; Weiden, M.D.; Berger, K.I.; Aldrich, T.K.; Hall, C.; Kelly, K.J.; Prezant, D.J. World Trade Center “sarcoid-like” granulomatous pulmonary disease in New York City Fire Department rescue workers. Chest 2007, 131, 1414–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drent, M.; Bomans, P.H.; Van Suylen, R.J.; Lamers, R.J.; Bast, A.; Wouters, E.F. Association of man-made mineral fibre exposure and sarcoidlike granulomas. Respir. Med. 2000, 94, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kajdasz, D.K.; Lackland, D.T.; Mohr, L.C.; Judson, M.A. A current assessment of rurally linked exposures as potential risk factors for sarcoidosis. Ann. Epidemiol. 2001, 11, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, T.; Aparicio, G.; Garcia-Patos, V. Is there any association between Sarcoidosis and infectious agents?: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, C.; Huang, H.; Xu, Z. Immunological Evidence for the Role of Mycobacteria in Sarcoidosis: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Eom, M.; Kim, S.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Lee, H.; Choi, E.H. Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and non-tuberculous mycobacteria from cutaneous sarcoidosis lesions by reverse blot hybridization assay. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, B.; Sheikh, J.A.; Agarwal, R.; Verma, I. Levels of circulating immune complexes containing Mycobacterium Tuberculosis-specific antigens in pulmonary tuberculosis and sarcoidosis patients. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 35, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotsinger, J.E.; Celada, L.J.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Atkinson, J.B.; Drake, W.P. Molecular Analysis of Sarcoidosis Granulomas Reveals Antimicrobial Targets. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eishi, Y.; Suga, M.; Ishige, I.; Kobayashi, D.; Yamada, T.; Takemura, T.; Takizawa, T.; Koike, M.; Kudoh, S.; Costabel, U.; et al. Quantitative analysis of mycobacterial and propionibacterial DNA in lymph nodes of Japanese and European patients with sarcoidosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milman, N.; Lisby, G.; Friis, S.; Kemp, L. Prolonged culture for mycobacteria in mediastinal lymph nodes from patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. A negative study. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2004, 21, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drake, W.P.; Dhason, M.S.; Nadaf, M.; Shepherd, B.E.; Vadivelu, S.; Hajizadeh, R.; Newman, L.S.; Kalams, S.A. Cellular recognition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ESAT-6 and KatG peptides in systemic sarcoidosis. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, E.S.; Wahlstrom, J.; Song, Z.; Willett, M.H.; Wiken, M.; Yung, R.C.; West, E.E.; McDyer, J.F.; Zhang, Y.; Eklund, A.; et al. T cell responses to mycobacterial catalase-peroxidase profile a pathogenic antigen in systemic sarcoidosis. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8784–8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald-Richter, K.A.; Culver, D.A.; Hawkins, C.; Hajizadeh, R.; Abraham, S.; Shepherd, B.E.; Jenkins, C.A.; Judson, M.A.; Drake, W.P. Cellular responses to mycobacterial antigens are present in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid used in the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3740–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Homma, J.Y.; Abe, C.; Chosa, H.; Ueda, K.; Saegusa, J.; Nakayama, M.; Homma, H.; Washizaki, M.; Okano, H. Bacteriological investigation on biopsy specimens from patients with sarcoidosis. Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 1978, 48, 251–255. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, C.; Iwai, K.; Mikami, R.; Hosoda, Y. Frequent isolation of Propionibacterium acnes from sarcoidosis lymph nodes. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Hyg. A 1984, 256, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, J.G.; Middleton, W.G.; Gaddie, J.; Petrie, G.R.; Choo-Kang, Y.F.; Prescott, R.J.; Crompton, G.K. Sarcoidosis: A disorder commoner in non-smokers? Thorax 1986, 41, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlens, C.; Hergens, M.P.; Grunewald, J.; Ekbom, A.; Eklund, A.; Höglund, C.O.; Askling, J. Smoking, use of moist snuff, and risk of chronic inflammatory diseases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, L.S.; Rose, C.S.; Maier, L.A. Sarcoidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMurdo, M.G.; Mroz, P.M.; Culver, D.A.; Dweik, R.; Maier, L. Chronic beryllium disease: Update on a moving target. Chest 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, M.V.; Martyny, J.W.; Mroz, M.M.; Silveira, L.J.; Strand, M.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Sato, H.; Newman, L.S.; Maier, L.A. Risk of chronic beryllium disease by HLA-DPB1 E69 genotype and beryllium exposure in nuclear workers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dyke, M.V.; Martyny, J.W.; Mroz, M.M.; Silveira, L.J.; Strand, M.; Cragle, D.L.; Tankersley, W.G.; Wells, S.M.; Newman, L.S.; Maier, L.A. Exposure and genetics increase risk of beryllium sensitisation and chronic beryllium disease in the nuclear weapons industry. Occup. Environ. Med. 2011, 68, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fontenot, A.P.; Torres, M.; Marshall, W.H.; Newman, L.S.; Kotzin, B.L. Beryllium presentation to CD4+ T cells underlies disease-susceptibility HLA-DP alleles in chronic beryllium disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12717–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yanardag, H.; Pamuk, O.N.; Karayel, T. Cutaneous involvement in sarcoidosis: Analysis of the features in 170 patients. Respir. Med. 2003, 97, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baughman, R.P.; Judson, M.A.; Wells, A.U. The indications for the treatment of sarcoidosis: Well’s Law. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2017, 34, 280–282. [Google Scholar]
- Judson, M.A. Corticosteroids in Sarcoidosis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 42, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinzie, B.P.; Bullington, W.M.; Mazur, J.E.; Judson, M.A. Efficacy of short-course, low-dose corticosteroid therapy for acute pulmonary sarcoidosis exacerbations. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 339, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judson, M.A. An approach to the treatment of pulmonary sarcoidosis with corticosteroids: The six phases of treatment. Chest 1999, 115, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.P.; Nunes, H.; Sweiss, N.J.; Lower, E.E. Established and experimental medical therapy of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 1424–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beegle, S.H.; Barba, K.; Gobunsuy, R.; Judson, M.A. Current and emerging pharmacological treatments for sarcoidosis: A review. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baughman, R.P.; Winget, D.B.; Lower, E.E. Methotrexate is steroid sparing in acute sarcoidosis: Results of a double blind, randomized trial. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2000, 17, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muller-Quernheim, J.; Kienast, K.; Held, M.; Pfeifer, S.; Costabel, U. Treatment of chronic sarcoidosis with an azathioprine/prednisolone regimen. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 14, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahoo, D.H.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Xu, M.; Pearson, K.; Parambil, J.G.; Lazar, C.A.; Chapman, J.T.; Culver, D.A. Effectiveness and safety of leflunomide for pulmonary and extrapulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, O.P. Effectiveness of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in treating selected patients with sarcoidosis with neurological involvement. Arch. Neurol. 1998, 55, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.P.; Drent, M.; Kavuru, M.; Judson, M.A.; Costabel, U.; du Bois, R.; Albera, C.; Brutsche, M.; Davis, G.; Donohue, J.F.; et al. Infliximab therapy in patients with chronic sarcoidosis and pulmonary involvement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Judson, M.A.; Baughman, R.P.; Costabel, U.; Flavin, S.; Lo, K.H.; Kavuru, M.S.; Drent, M. Efficacy of infliximab in extrapulmonary sarcoidosis: Results from a randomised trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnes, P.J. How corticosteroids control inflammation: Quintiles Prize Lecture 2005. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 148, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zissel, G.; Muller-Quernheim, J. Sarcoidosis: Historical perspective and immunopathogenesis (Part I). Respir. Med. 1998, 92, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fehrenbach, H.; Zissel, G.; Goldmann, T.; Tschernig, T.; Vollmer, E.; Pabst, R.; Muller-Quernheim, J. Alveolar macrophages are the main source for tumour necrosis factor-alpha in patients with sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 21, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziegenhagen, M.W.; Rothe, M.E.; Zissel, G.; Muller-Quernheim, J. Exaggerated TNFalpha release of alveolar macrophages in corticosteroid resistant sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2002, 19, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Medica, I.; Kastrin, A.; Maver, A.; Peterlin, B. Role of genetic polymorphisms in ACE and TNF-alpha gene in sarcoidosis: A meta-analysis. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 52, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grutters, J.C.; Sato, H.; Pantelidis, P.; Lagan, A.L.; McGrath, D.S.; Lammers, J.W.; van den Bosch, J.M.; Wells, A.U.; du Bois, R.M.; Welsh, K.I. Increased frequency of the uncommon tumor necrosis factor—857T allele in British and Dutch patients with sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.; Nautiyal, A.; Kalkanis, A.; Judson, M.A. Drug-induced sarcoidosis-like reactions. Chest 2018, 154, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daien, C.I.; Monnier, A.; Claudepierre, P.; Constantin, A.; Eschard, J.P.; Houvenagel, E.; Samimi, M.; Pavy, S.; Pertuiset, E.; Toussirot, E.; et al. Sarcoid-like granulomatosis in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor blockers: 10 cases. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen Aubart, F.; Lhote, R.; Amoura, A.; Valeyre, D.; Haroche, J.; Amoura, Z.; Lebrun-Vignes, B. Drug-induced sarcoidosis: An overview of the WHO pharmacovigilance database. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoenfeld, Y.; Agmon-Levin, N. ‘ASIA’—Autoimmune/inflammatory syndrome induced by adjuvants. J. Autoimmun. 2011, 36, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alijotas-Reig, J.; Esteve-Valverde, E.; Gil-Aliberas, N.; Garcia-Gimenez, V. Autoimmune/inflammatory syndrome induced by adjuvants-ASIA-related to biomaterials: Analysis of 45 cases and comprehensive review of the literature. Immunol. Res. 2018, 66, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miro-Mur, F.; Hindie, M.; Kandhaya-Pillai, R.; Tobajas, V.; Schwartz, S., Jr.; Alijotas-Reig, J. Medical-grade silicone induces release of proinflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells without activating T cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 90, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Lastra, O.; Medina, G.; Cruz-Dominguez Mdel, P.; Ramirez, P.; Gayosso-Rivera, J.A.; Anduaga-Dominguez, H.; Lievana-Torres, C.; Jara, L.J. Human adjuvant disease induced by foreign substances: A new model of ASIA (Shoenfeld’s syndrome). Lupus 2012, 21, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alijotas-Reig, J.; Hindie, M.; Kandhaya-Pillai, R.; Miro-Mur, F. Bioengineered hyaluronic acid elicited a nonantigenic T cell activation: Implications from cosmetic medicine and surgery to nanomedicine. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 95, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Chan, K.T.; Chong, L.Y.; Lau, K.S.; Tam, C.M.; Lam, C.W. Cutaneous and pulmonary sarcoidosis in a Hong Kong Chinese woman with silicone breast prostheses. Respirology 2003, 8, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, P.; Del Olmo, J.; Alberola, I. In situ and distant foreign body granulomas caused by silicone. Treatment with allopurinol. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 1064–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuber, S.S.; Howell, L.P.; Yoshida, S.H.; Gershwin, M.E. Remission of sarcoidosis following removal of silicone gel breast implants. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1994, 105, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Johnson, D.B. Immune-related adverse events and anti-tumor efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.W.; Razak, A.R.; Bedard, P.L.; Siu, L.L.; Hansen, A.R. A systematic review of immune-related adverse event reporting in clinical trials of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1824–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Burel, S.; Champiat, S.; Mateus, C.; Marabelle, A.; Michot, J.M.; Robert, C.; Belkhir, R.; Soria, J.C.; Laghouati, S.; Voisin, A.L.; et al. Prevalence of immune-related systemic adverse events in patients treated with anti-Programmed cell Death 1/anti-Programmed cell Death-Ligand 1 agents: A single-centre pharmacovigilance database analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 82, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alroqi, F.J.; Charbonnier, L.M.; Baris, S.; Kiykim, A.; Chou, J.; Platt, C.D.; Algassim, A.; Keles, S.; Al Saud, B.K.; Alkuraya, F.S.; et al. Exaggerated follicular helper T-cell responses in patients with LRBA deficiency caused by failure of CTLA4-mediated regulation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1050–1059.e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, E.S.; Moller, D.R. Etiology of sarcoidosis. Clin. Chest Med. 2008, 29, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamias, G.; Delladetsima, I.; Perdiki, M.; Siakavellas, S.I.; Goukos, D.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Daikos, G.L.; Gogas, H. Immunological Characteristics of Colitis Associated with Anti-CTLA-4 Antibody Therapy. Cancer Investig. 2017, 35, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.S. Reassessing Th1 versus Th17.1 in sarcoidosis: New tricks for old dogma. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, N.A.; Celada, L.J.; Herazo-Maya, J.D.; Abraham, S.; Shaginurova, G.; Sevin, C.M.; Grutters, J.; Culver, D.A.; Dworski, R.; Sheller, J.; et al. Blockade of the programmed death-1 pathway restores sarcoidosis CD4(+) T-cell proliferative capacity. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lomax, A.J.; McGuire, H.M.; McNeil, C.; Choi, C.J.; Hersey, P.; Karikios, D.; Shannon, K.; van Hal, S.; Carr, U.; Crotty, A.; et al. Immunotherapy-induced sarcoidosis in patients with melanoma treated with PD-1 checkpoint inhibitors: Case series and immunophenotypic analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulos, J.; Carven, G.J.; van Boxtel, S.J.; Evers, S.; Driessen-Engels, L.J.; Hobo, W.; Gorecka, M.A.; de Haan, A.F.; Mulders, P.; Punt, C.J.; et al. PD-1 blockade augments Th1 and Th17 and suppresses Th2 responses in peripheral blood from patients with prostate and advanced melanoma cancer. J. Immunother. 2012, 35, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, L.W.P.; Chopra, A.; Judson, M.A. Paradoxical Reactions and the Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, D.R.; Forman, J.D.; Liu, M.C.; Noble, P.W.; Greenlee, B.M.; Vyas, P.; Holden, D.A.; Forrester, J.M.; Lazarus, A.; Wysocka, M.; et al. Enhanced expression of IL-12 associated with Th1 cytokine profiles in active pulmonary sarcoidosis. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 4952–4960. [Google Scholar]
- Callejas-Rubio, J.L.; Ortego-Centeno, N.; Lopez-Perez, L.; Benticuaga, M.N. Treatment of therapy-resistant sarcoidosis with adalimumab. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 25, 596–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussirot, É.; Aubin, F. Paradoxical reactions under TNF-α blocking agents and other biological agents given for chronic immune-mediated diseases: An analytical and comprehensive overview. RMD Open 2016, 2, e000239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

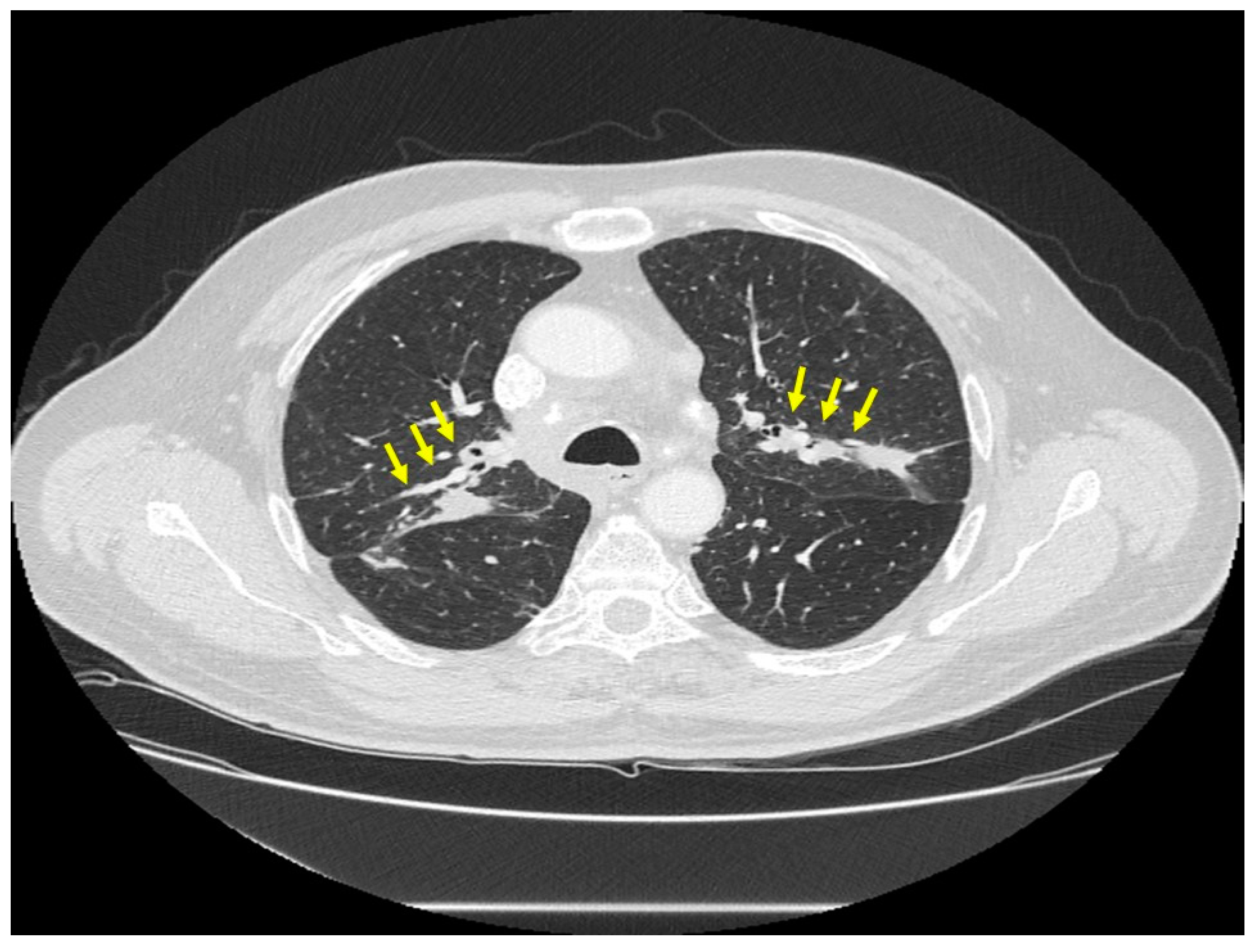
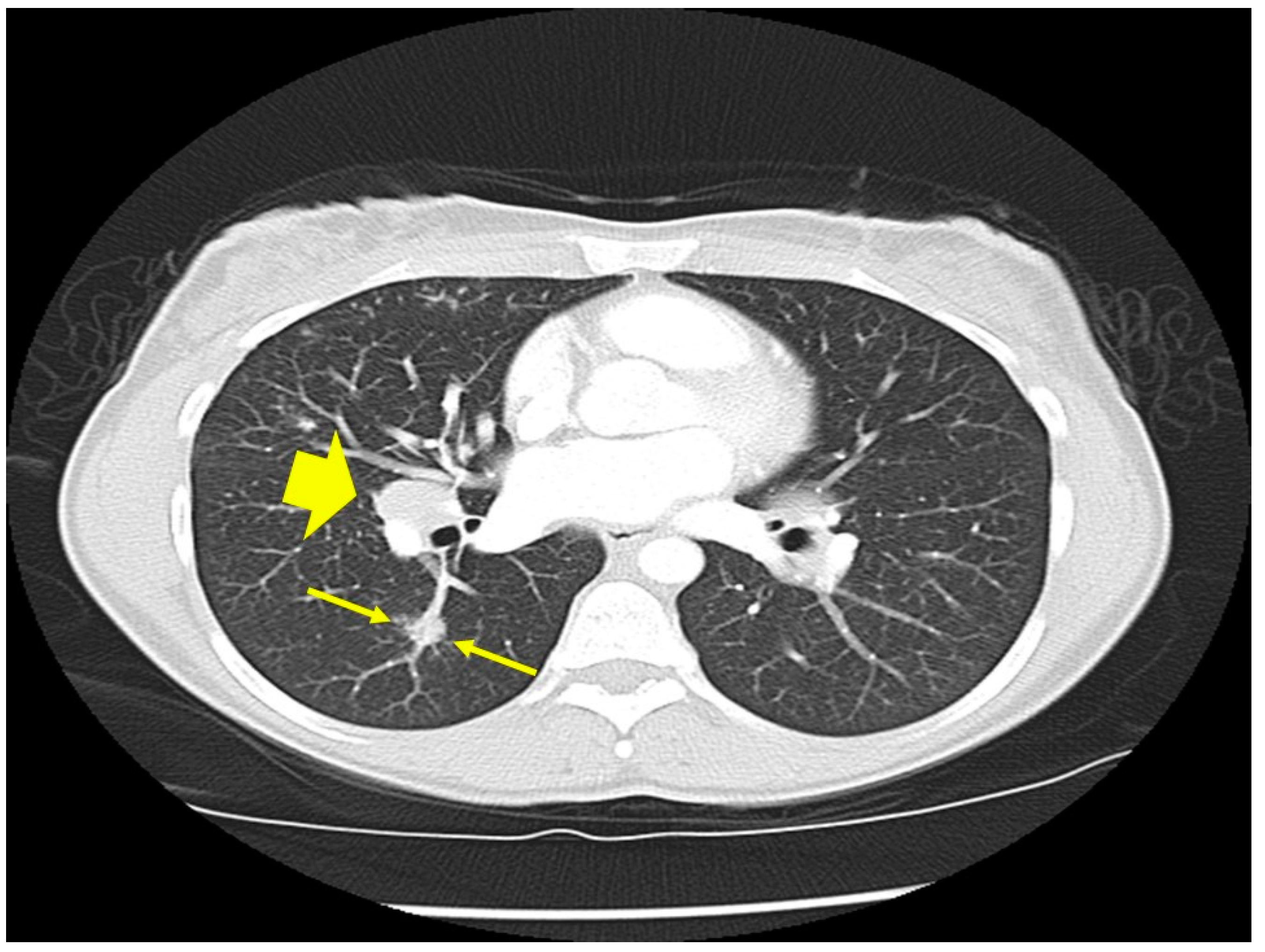
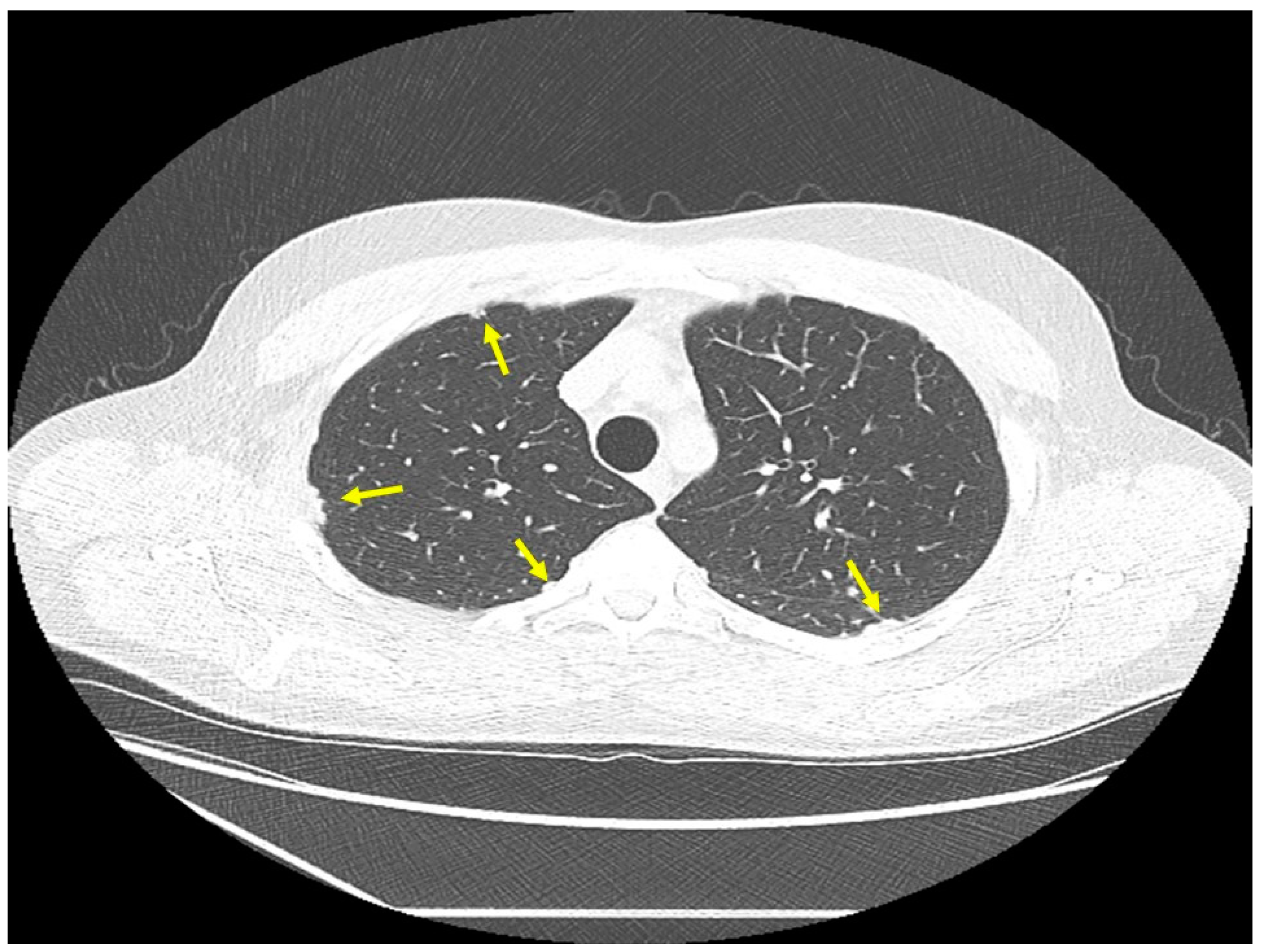
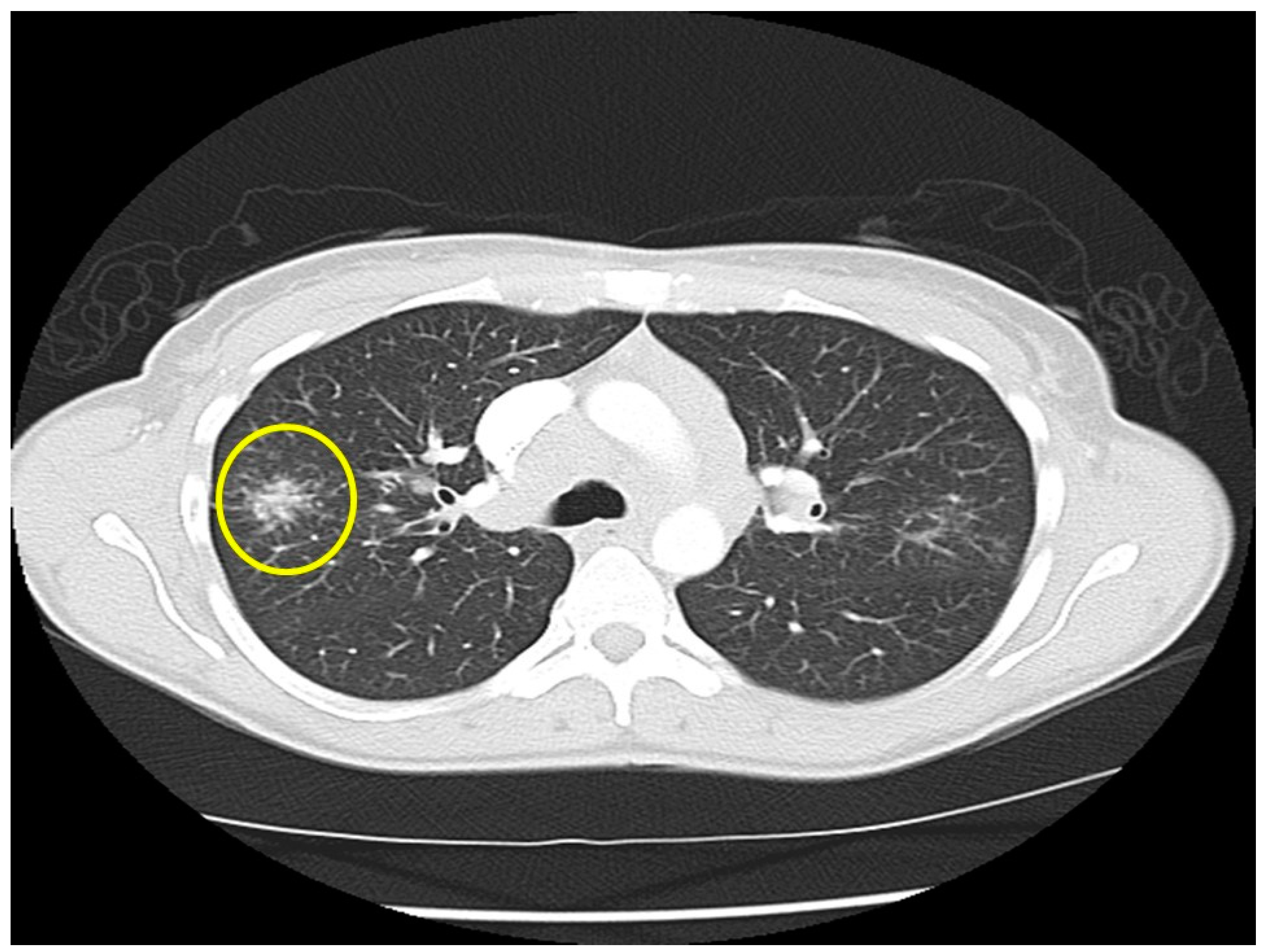


| Organ | White (n = 429) | Black (n = 819) | Total (n = 1248) |
|---|---|---|---|
| n, (%) | n, (%) | n, (%) | |
| Lung | 363 (84) | 749 (91) | 1112 (89) |
| Neurologic | 28 (7) | 85 (10) | 113 (9) |
| Peripheral lymph node | 52 (12) | 102 (13) | 154 (12) |
| Kidney | 3 (1) | 8 (1) | 11 (1) |
| Heart | 17 (4) | 39 (5) | 56 (4) |
| Skin | 97 (23) | 305 (37) | 402 (32) |
| Eye | 62 (15) | 225 (28) | 287 (23) |
| Liver | 68 (16) | 182 (22) | 250 (20) |
| Bone Marrow | 29 (7) | 66 (8) | 95 (8) |
| Spleen | 41 (10) | 52 (6) | 93 (7) |
| Bone/Joint | 30 (7) | 53 (7) | 83 (7) |
| Ear, Nose, Throat | 33 (8) | 87 (11) | 120 (10) |
| Parotid, Salivary gland | 13 (3) | 21 (3) | 34 (3) |
| Muscle | 5 (1) | 7 (1) | 12 (1) |
| Hypercalcemia | 42 (10) | 47 (6) | 89 (7) |
| General Categories | Specific Conditions |
|---|---|
| Infections | |
| Mycobacteria | Tuberculosis |
| Non-tuberculous mycobacteria | |
| Fungi | Cryptococcus |
| Histoplasmosis | |
| Blastomycosis | |
| Coccidioidomycosis | |
| Other infections | Mycoplasma |
| Pneumocystis jiroveci | |
| Brucellosis | |
| Toxoplasmosis | |
| Leishmaniasis | |
| Schistosomiasis | |
| Bartonella | |
| Mononucleosis (Epstein Barr virus) | |
| Cytomegalovirus | |
| Coxiella burnetii (Q fever) | |
| Treponema (syphilis, yaws) | |
| Environmental and occupational exposures | |
| Hypersensitivity pneumonitis | |
| Pneumoconioses | Beryllium (chronic beryllium disease) |
| Titanium | |
| Aluminum | |
| Malignancies | Lymphoma |
| Sarcoidosis-like reaction of malignancy | |
| Vasculitidies/Connective tissue diseases | Granulomatosis with polyangiitis |
| Rheumatoid nodules | |
| Localized granulomatous reactions to foreign substances | Lung aspiration |
| Foreign body reactions | |
| Drug-induced sarcoidosis-like reactions (DISRs) | Highly active retroviral therapy (HAART) |
| Immune checkpoint inhibitors | |
| Tumor necrosis alpha antagonists | |
| Interferon | |
| Diffuse granulomatous reactions from an autoimmune inflammatory syndrome induced by adjuvants | |
| Granulomatous lesions of unknown significance (GLUS syndrome) | |
| Granulomatous interstitial lung disease (GLILD) related to common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) | |
| Necrotizing sarcoid granulomatosis | |
| Blau syndrome | |
| Orofacial granulomatosis | |
| Crohn’s disease | |
| Primary biliary cirrhosis | |
| Risk Factor Exposure/Occupation | Location and/or Study Population | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Spring season (disease onset) | Rochester, MN; Turkey; New Zealand; Catalonia, Spain | [100,101,102,103] |
| Summer season (disease onset) | USA Veterans | [104] |
| Fall season (disease onset) | Rochester, MN | [105] |
| Specific regions of Ireland | Ireland | [106] |
| Northern latitudes | Ireland | [106] |
| Northern latitudes | Japan | [83] |
| Southeast United States | United States | [107] |
| Coastline of South Carolina | South Carolina | [108] |
| Living in forest or arable land | Poland | [109] |
| Living near areas with metal industries | Switzerland | [110] |
| Living in areas with potato production, artificial meadows, grain production | Switzerland | [110] |
| Firefighters | NYC | [111] |
| Firefighters | Providence, RI | [112] |
| Ship servicemen | US Navy | [113] |
| Aviation structural mechanics | US Navy, AA | [113] |
| Culinary specialists | US Navy, W | [113] |
| Using insecticides | USA | [114] |
| Musty odors at work | USA | [114] |
| Building materials | USA | [115] |
| Hardware | USA | [115] |
| Garden supplies | USA | [115] |
| Mobile homes | USA | [115] |
| Industrial organic dusts | USA | [115] |
| Education | Detroit, AA | [116] |
| Metal machining | Detroit, AA | [116] |
| Metalworking | Detroit, AA | [116] |
| Transportation services | Detroit, AA | [116] |
| Construction workers | Sweden | [117] |
| Silica (metal-halide lamp production) | N/A | [118] |
| Photocopier toner | USA, AA | [119] |
| World Trade Center dust | FDNY | [120] |
| Working in high humidity | Detroit MI, AA | [116] |
| Titanium | Detroit MI, AA | [116] |
| Vegetable dust | Detroit MI, AA | [116] |
| Man-made mineral fibers | N/A | [121] |
| Woodstove use | SC | [122] |
| Fireplace use | SC | [122] |
| Musty odor exposure | Detroit MI, AA | [116] |
| Non-public water use | SC | [122] |
| Living/working on a farm | SC | [122] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Judson, M.A. A Primer on the Clinical Aspects of Sarcoidosis for the Basic and Translational Scientist. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132857
Judson MA. A Primer on the Clinical Aspects of Sarcoidosis for the Basic and Translational Scientist. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(13):2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132857
Chicago/Turabian StyleJudson, Marc A. 2021. "A Primer on the Clinical Aspects of Sarcoidosis for the Basic and Translational Scientist" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 13: 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132857
APA StyleJudson, M. A. (2021). A Primer on the Clinical Aspects of Sarcoidosis for the Basic and Translational Scientist. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(13), 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132857





