The Spatial Selective Auditory Attention of Cochlear Implant Users in Different Conversational Sound Levels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Participants
2.2. Behavioral Experiment
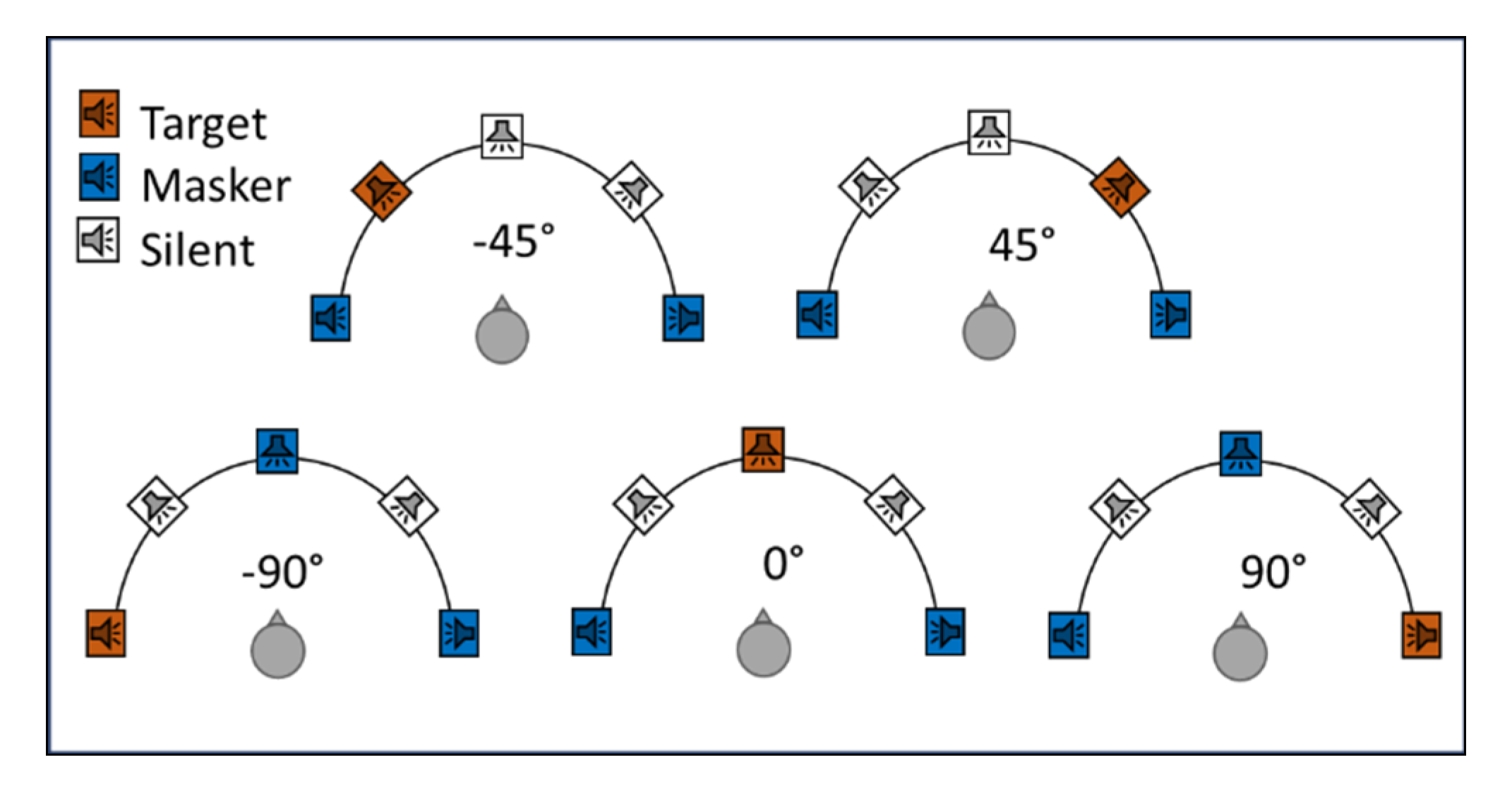
2.2.1. Stimuli
2.2.2. Procedure
2.3. Electrophysiological Experiment
2.3.1. EEG Recording Setup
2.3.2. Recording the Data for Training the Decoder
2.3.3. Recording the Data for Testing in the Three-Speaker Cocktail Party Scenario
2.3.4. EEG Based Speech Detection Accuracy
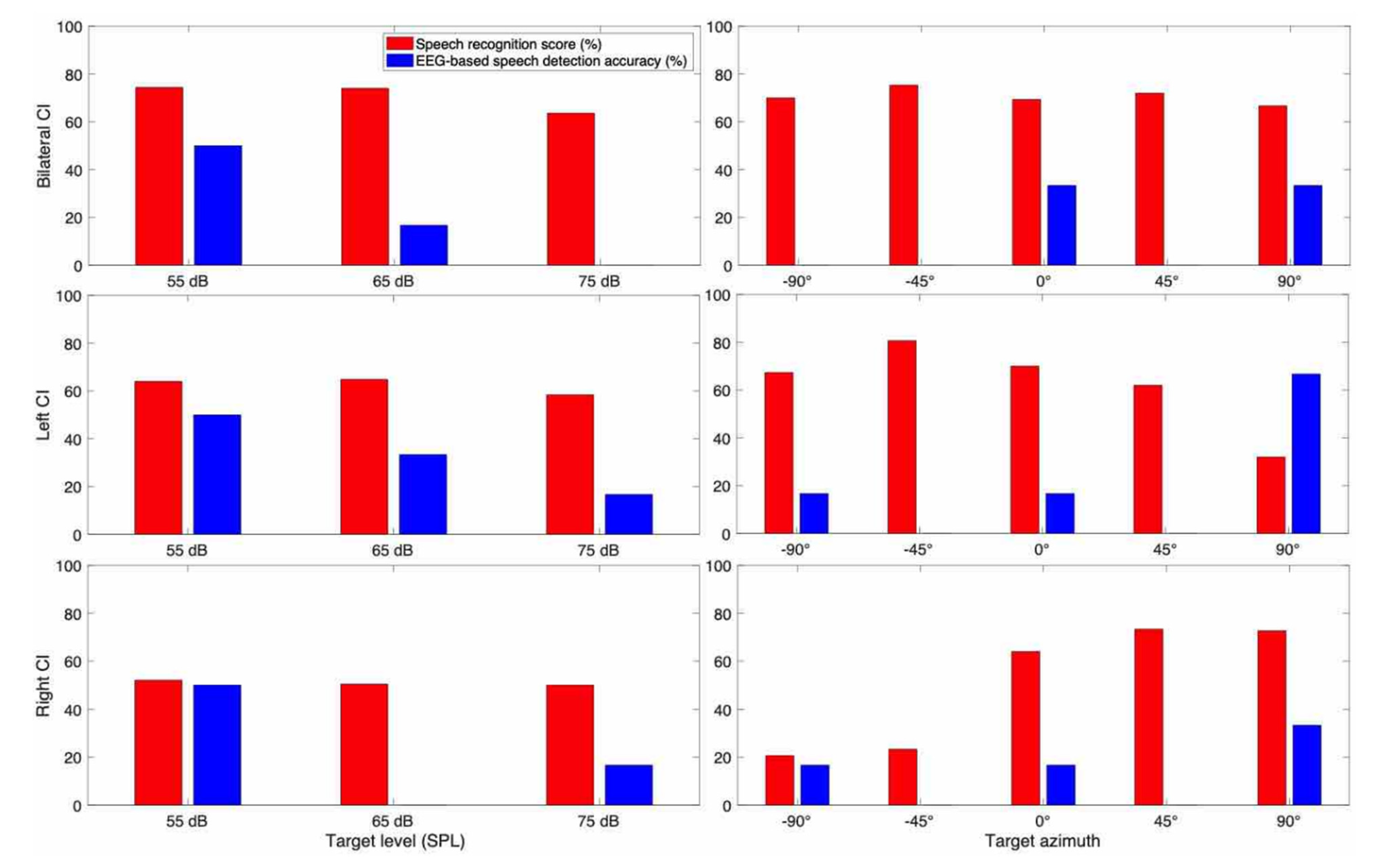
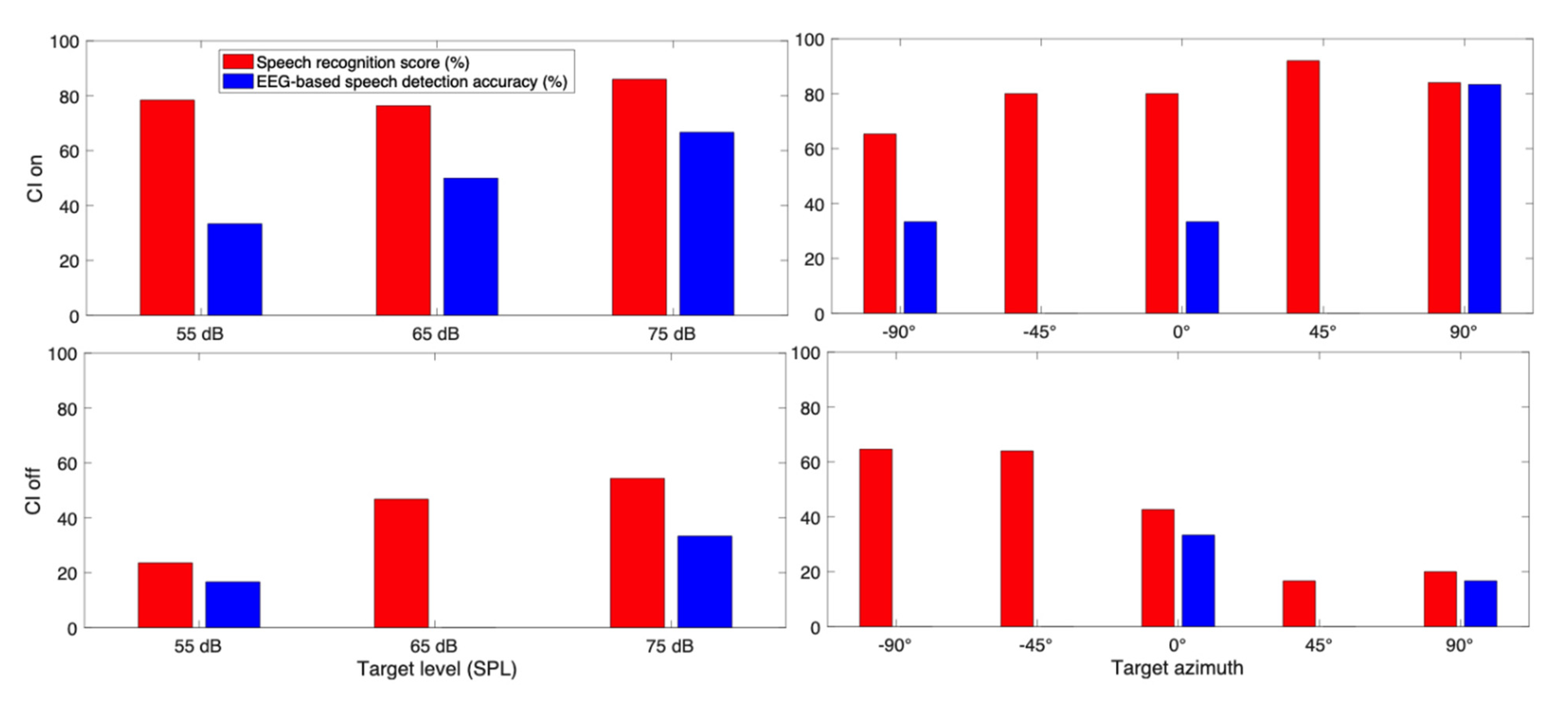
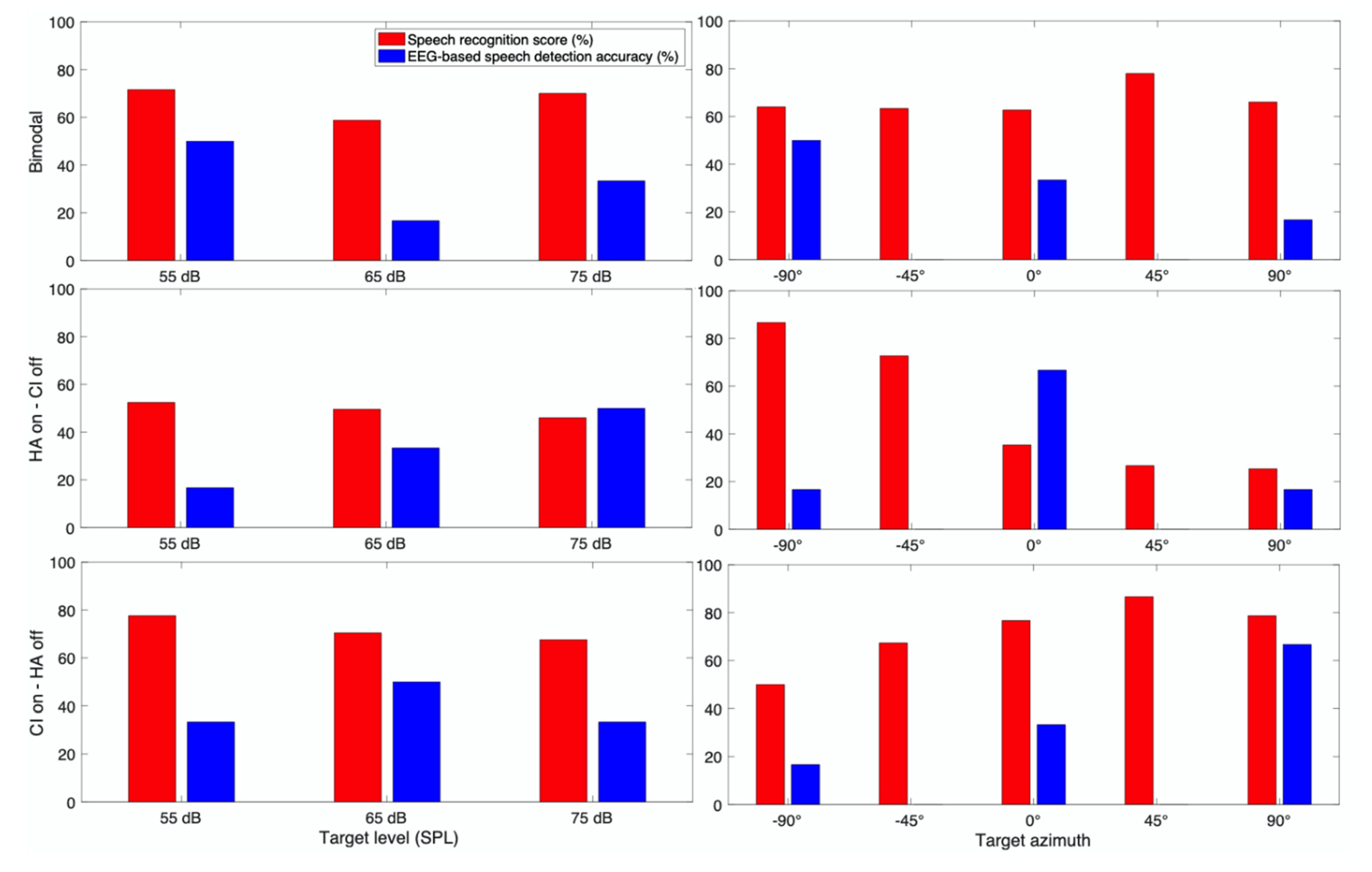
3. Results
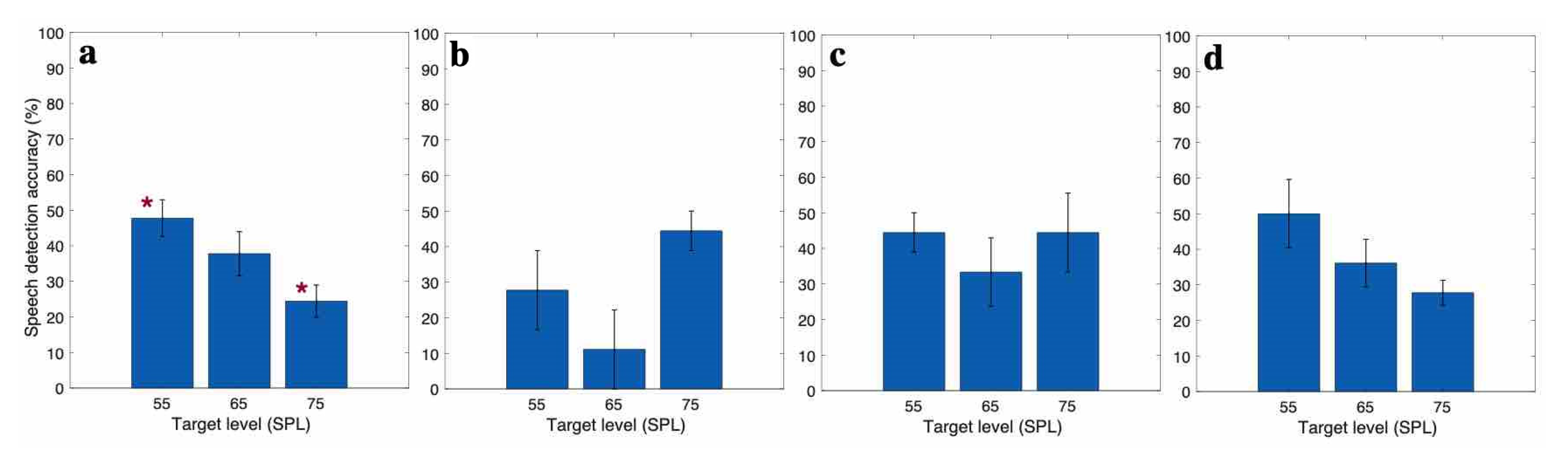
3.1. Behavioral Speech Recognition Score
3.2. EEG Based Speech Detection Accuracy
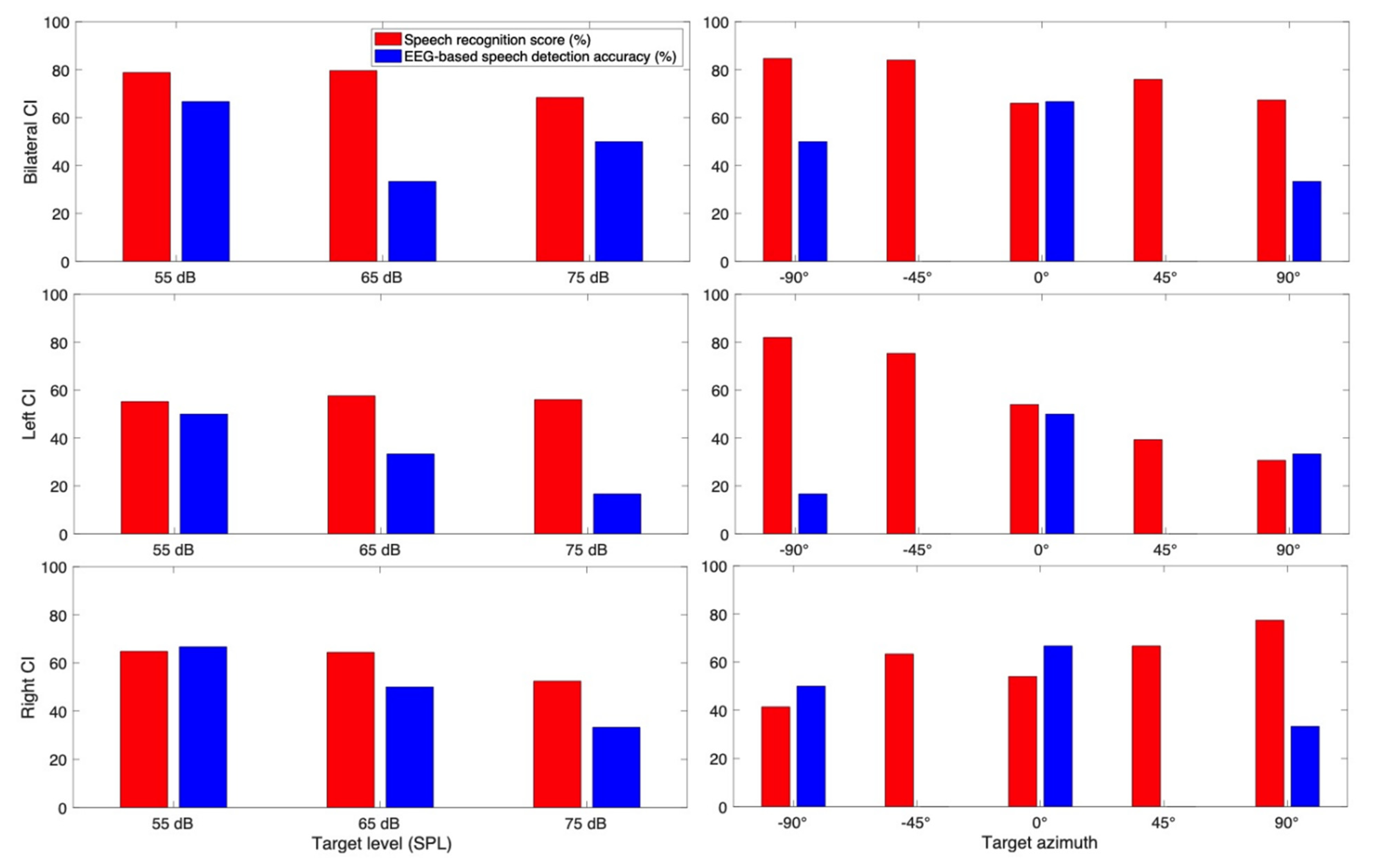
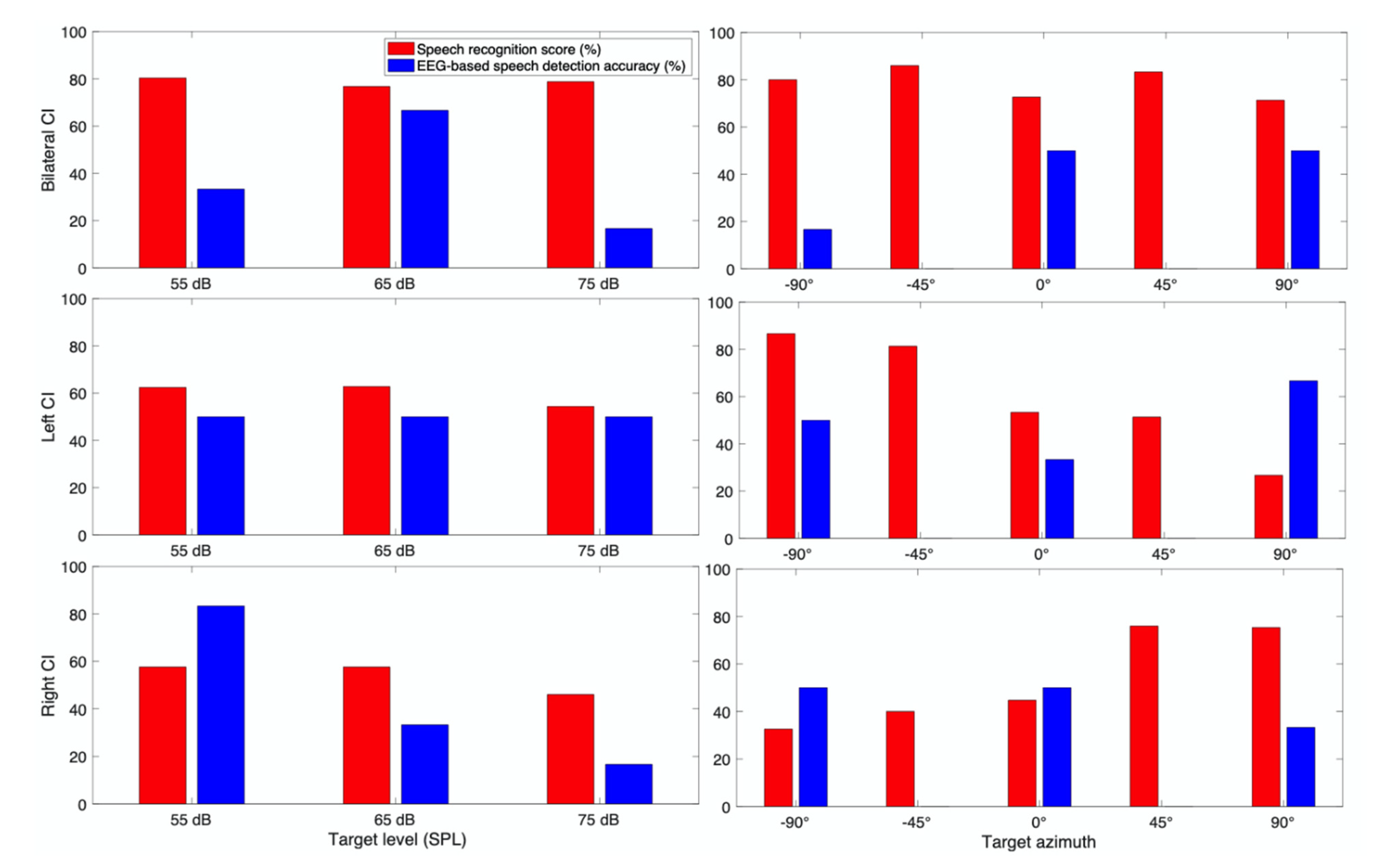
3.3. Case Report for Individual Subjects
3.3.1. Subject CI 1
3.3.2. Subject CI 2
3.3.3. Subject CI 3
3.3.4. Subject CI 4
3.3.5. Subject CI 6
3.3.6. Subject CI 7
3.3.7. Subject CI 9
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Subject Number | CI-1 | CI-2 | CI-3 | CI-4 | CI-6 | CI-7 | CI-9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λ | 101 | 105 | 101 | 105 | 10−1 | 103 | 101 |
References
- Shannon, R.V.; Zeng, F.G.; Kamath, V.; Wygonski, J.; Ekelid, M. Speech recognition with primarily temporal cues. Science 1995, 270, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinn-cunningham, B.G.; Best, V. Selective attention in normal and impaired hearing. Trends Amplif. 2008, 12, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackersie, C.L.; Prida, T.L.; Stiles, D. The role of sequential stream segregation and frequency selectivity in the perception of simultaneous sentences by listeners with sensorineural hearing loss. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2001, 44, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, N.; Mason, C.R.; Kidd, G. The effects of hearing loss and age on the benefit of spatial separation between multiple talkers in reverberant rooms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 124, 3064–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Best, V.; Marrone, N.; Mason, C.R.; Kidd, G.; Shinn-Cunningham, B.G. Effects of Sensorineural Hearing Loss on Visually Guided Attention in a Multitalker Environment. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2008, 10, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, L.; Best, V.; Shinn-Cunningham, B.G. Sensorineural hearing loss degrades behavioral and physiological measures of human spatial selective auditory attention. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3286–E3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, J.; Summerfield, A.Q.; O’Donoghue, G.M.; Moore, D.R. Spatial hearing of normally hearing and cochlear implanted children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 75, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, M.; Galvin, K.; Dowell, R.C.; McKay, C.M. Spatial Unmasking and Binaural Advantage for Children with Normal Hearing, a Cochlear Implant and a Hearing Aid, and Bilateral Implants. Audiol. Neurotol. 2007, 12, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, E.E.; Litovsky, R.Y. Sound Localization in Toddlers with Normal Hearing and with Bilateral Cochlear Implants Revealed Through a Novel “Reaching for Sound” Task. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2020, 31, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, H.M.; Bulla, W.; Tarr, E.W. Spatial release from masking and sound localization using real-time sensorineural hearing loss and cochlear implant simulation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winn, M.B.; Won, J.H.; Moon, I.J. Assessment of spectral and temporal resolution in cochlear implant users using psychoacoustic discrimination and speech cue categorization. Ear Hear. 2016, 37, e377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seebacher, J.; Franke-Trieger, A.; Weichbold, V.; Zorowka, P.; Stephan, K. Improved interaural timing of acoustic nerve stimulation affects sound localization in single-sided deaf cochlear implant users. Hear. Res. 2019, 371, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francart, T.; Brokx, J.; Wouters, J. Sensitivity to Interaural Level Difference and Loudness Growth with Bilateral Bimodal Stimulation. Audiol. Neurotol. 2008, 13, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbogast, T.L.; Mason, C.R.; Kidd, G. The effect of spatial separation on informational and energetic masking of speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 2086–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glyde, H.; Hickson, L.; Cameron, S.; Dillon, H. Problems hearing in noise in older adults: A review of spatial processing disorder. Trends Amplif. 2011, 15, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Best, V.; Marrone, N.; Mason, C.R.; Kidd, G. The influence of non-spatial factors on measures of spatial release from masking. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 3103–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strelcyk, O.; Dau, T. Relations between frequency selectivity, temporal fine-structure processing, and speech reception in impaired hearing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 3328–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smoski, W.J.; Trahiotis, C. Discrimination of interaural temporal disparities by normal-hearing listeners and listeners with high-frequency sensorineural hearing loss. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1986, 79, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, D.B.; Wightman, F.L. Interaural Time Discrimination Ability of Listeners with Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Int. J. Audiol. 1980, 19, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, T.Y.C.; Van Wanrooy, E.; Dillon, H.; Carter, L. Spatial release from masking in normal-hearing children and children who use hearing aids. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallun, F.J.; Diedesch, A.C.; Kampel, S.D.; Jakien, K.M. Independent impacts of age and hearing loss on spatial release in a complex auditory environment. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbarzadeh, S.; Lee, S.; Chen, F.; Tan, C.-T. The effect of perceived sound quality of speech in noisy speech perception by normal hearing and hearing impaired listeners. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mesgarani, N.; Chang, E.F. Selective cortical representation of attended speaker in multi-talker speech perception. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 485, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Sullivan, J.A.; Power, A.J.; Mesgarani, N.; Rajaram, S.; Foxe, J.; Shinn-Cunningham, B.G.; Slaney, M.; Shamma, S.A.; Lalor, E.C. Attentional Selection in a Cocktail Party Environment Can Be Decoded from Single-Trial EEG. Cereb. Cortex 2015, 25, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, C.; Srinivasan, R.; D’Zmura, M. Envelope responses in single-trial EEG indicate attended speaker in a ‘cocktail party’. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 11, 046015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanthornhout, J.; Decruy, L.; Wouters, J.; Simon, J.; Francart, T. Speech Intelligibility Predicted from Neural Entrainment of the Speech Envelope. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2018, 19, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, G.; Best, V.; Mason, C.R. Listening to every other word: Examining the strength of linkage variables in forming streams of speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 124, 3793–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, R.M.; Genevieve, C.G.; Alexander, C. Development of the Connected Speech Test (CST).pdf. Ear Hear. 1987, 8, 119S–126S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, R.M.; McDaniel, D.M. Development of the speech intelligibility rating (SIR) test for hearing aid comparisons. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1989, 32, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.-G.; Grant, G.; Niparko, J.; Galvin, J.; Shannon, R.; Opie, J.; Segel, P. Speech dynamic range and its effect on cochlear implant performance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 111, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firszt, J.B.; Holden, L.K.; Skinner, M.W.; Tobey, E.A.; Peterson, A.; Gaggl, W.; Runge-Samuelson, C.L.; Wackym, P.A. Recognition of Speech Presented at Soft to Loud Levels by Adult Cochlear Implant Recipients of Three Cochlear Implant Systems. Ear Hear. 2004, 25, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, S.; Lee, S.; Singh, S.; Tuan-Tan, C. Implication of speech level control in noise to sound quality judgement. In Proceedings of the 2018 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–15 November 2018; pp. 388–392. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarzadeh, S.; Lee, S.; Chen, F.; Tuan-Tan, C. The effect of speech and noise levels on the quality perceived by cochlear implant and normal hearing listeners. Speech Commun. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesmans, W.; Das, N.; Francart, T.; Bertrand, A. Auditory-Inspired Speech Envelope Extraction Methods for Improved EEG-Based Auditory Attention Detection in a Cocktail Party Scenario. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkovic, B.; Debener, S.; Jaeger, M.; De Vos, M. Decoding the attended speech stream with multi-channel EEG: Implications for online, daily-life applications. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 046007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosse, M.J.; Di Liberto, G.M.; Bednar, A.; Lalor, E.C. The Multivariate Temporal Response Function (mTRF) Toolbox: A MATLAB Toolbox for Relating Neural Signals to Continuous Stimuli. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oostenveld, R.; Fries, P.; Maris, E.; Schoffelen, J.-M. FieldTrip: Open Source Software for Advanced Analysis of MEG, EEG, and Invasive Electrophysiological Data. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2010, 2011, 156869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Subject Number | Age (years) | Gender | CI Ear | CI Model | CI Use (years) | Speech Processing Strategy | Duration of HL (years) | Pure Tone Average of 500, 1000, and 2000 Hz (dB HL) | Etiology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bilateral CI | |||||||||
| 1 | 75 | Male | Both | Medel/Sonnet | 7 | FS4 | 33 | Right: NR Left: NR | Meniere’s Disease |
| 2 | 40 | Female | Both | Medel/Sonnet | 4 | FS4 | 38.5 | Right: NR Left: NR | unknown |
| 3 | 68 | Male | Both | Medel/Sonnet | 10 | FS4 | 38 | Right: NR Left: NR | unknown |
| 4 | 25 | Female | Both | Cochlear/Nucleus 6 | 21 | ACE | 25 | Right: NR Left: NR | unknown |
| 5 * | 77 | Female | Both | Medel/Sonnet | 70 | FS4 | 6 | Right: NR Left: NR | meningitis |
| Unilateral CI | |||||||||
| 6 | 67 | Male | Right | Cochlear/Nucleus 6 | 11 | ACE | 11 | Right: NR Left: 70 | Noise induced |
| 7 | 67 | Male | Right | Medel/Sonnet | 10 | FS4 | 24 | Right: NR Left: 71.6 | Meniere’s Disease |
| 8 * | 24 | Female | Right | Cochlear/Nucleus 7 | 1 | ACE | 23 | Right: NR Left: NR | Genetic |
| Bimodal hearing | |||||||||
| 9 | 77 | Male | Right | Medel/Sonnet | 2 | FS4 | 20 | Right: 82.5 Left: 66.6 | Noise induced |
| Name | Verb | Number | Adjective | Noun |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jane | Took | Two | New | Toys |
| Gene | Gave | Three | Old | Hats |
| Pat | Lost | Four | Big | Shoes |
| Bob | Found | Five | Small | Cards |
| Sue | Bought | Six | Red | Pens |
| Mike | Sold | Seven | Blue | Socks |
| Lynn | Held | Eight | Cold | Bags |
| Jill | Saw | Nine | Hot | Gloves |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akbarzadeh, S.; Lee, S.; Tan, C.-T. The Spatial Selective Auditory Attention of Cochlear Implant Users in Different Conversational Sound Levels. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143078
Akbarzadeh S, Lee S, Tan C-T. The Spatial Selective Auditory Attention of Cochlear Implant Users in Different Conversational Sound Levels. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(14):3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143078
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkbarzadeh, Sara, Sungmin Lee, and Chin-Tuan Tan. 2021. "The Spatial Selective Auditory Attention of Cochlear Implant Users in Different Conversational Sound Levels" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 14: 3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143078
APA StyleAkbarzadeh, S., Lee, S., & Tan, C.-T. (2021). The Spatial Selective Auditory Attention of Cochlear Implant Users in Different Conversational Sound Levels. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(14), 3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143078





