Drug Policies Skyline during COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
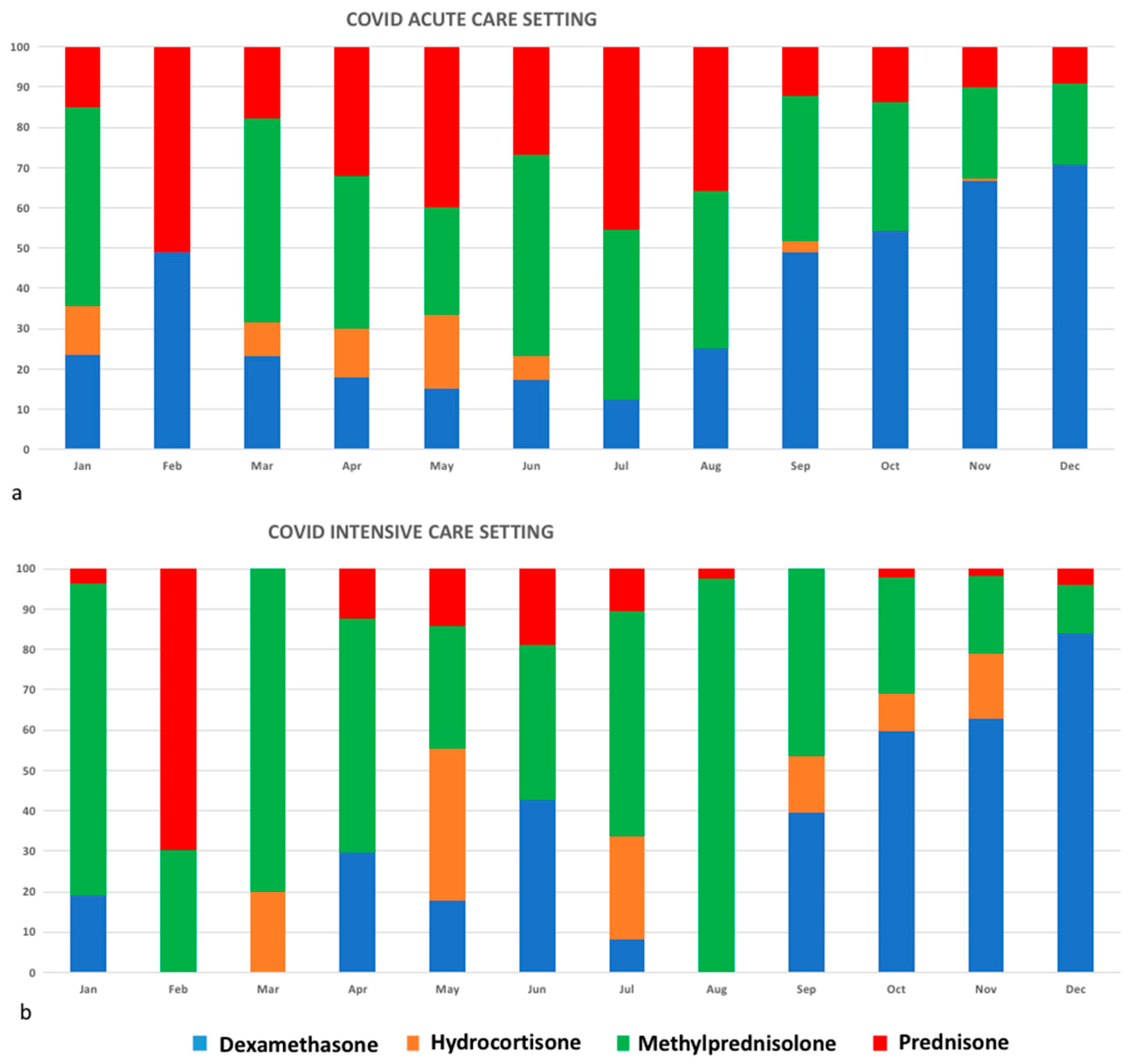
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Danion, F.; Ruch, Y.; Fourtage, M.; Kaeuffer, C.; Greigert, V.; Lefebvre, N.; Muller, J.; Nai, T.; Hansmann, Y. The good, the bad, and the hoax: When publication instantaneously impacts treatment strategies for COVID-19. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.-J.; Ni, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.-H.; Ou, C.-Q.; He, J.-X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.-L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Wang, Y.; Wen, D.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Fan, G.; Ruan, L.; Song, B.; Cai, Y.; Wei, M.; et al. A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautret, P.; Lagier, J.C.; Parola, P.; Hoang, V.T.; Meddeb, L.; Mailhe, M.; Courjon, J.; Giordanengo, V.; Vieira, V.E.; Dupont, H.T.; et al. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: Results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, J.M.; Delaugerre, C.; Le Goff, J.; Mela-Lima, B.; Ponscarme, D.; Goldwirt, L.; de Castro, N. No evidence of rapid antiviral clearance or clinical benefit with the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in patients with severe COVID-19 infection. Med. Mal. Infect. 2020, 50, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Chen, R.; Liu, C.; Liang, W.; Guan, W.; Tang, R.; Tang, C.; Zhang, N.; Zhong, N.; Li, S. Attention should be paid to venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in the management of COVID-19. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e362–e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Han, M.; Li, T.; Sun, W.; Wang, D.; Fu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 10970–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Recovery Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19—Preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Corticosteroids for COVID-19: Living Guidance, 2 September 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2020/03/17/20A01706/SG (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Available online: https://www.aifa.gov.it/-/covid-19-sospensione-d-uso-anche-per-la-clorochina (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Michau, K.; Wipfler, K.; Shaw, Y.; Simon, T.A.; Cornish, A.; England, B.R.; Ogdie, A.; Katz, P. Experiences of patients with rheumatic diseases in the United States during early days of the COVID-19 pandemic. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020, 2, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Owens, B. Hydroxychloroquine side-effects raise concerns for rheumatology patients. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, A.; Bernatsky, S.; Askanase, A.; Bae, S.C.; Clarke, A.E.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Gladman, D.D.; Gordon, C.; Hanly, J. Hydroxychloroquine shortages among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus during the COVID-19 pandemic: Experience of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziadé, N.; Hmamouchi, I.; El Kibbi, L.; Abdulateef, N.; Halabi, H.; Abutiban, F.; Hamdi, W.; El Rakawi, M.; Eissa, M.; Masri, B. The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on rheumatology practice: A cross-sectional multinational study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 3205–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grein, J.; Ohmagari, N.; Shin, D.; Diaz, G.; Asperges, E.; Castagna, A.; Feldt, T.; Green, G.; Green, M.L.; Lescure, F.-X.; et al. Compassionate use of remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Du, G.; Du, R.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Y.; Fu, S.; Gao, L.; Cheng, Z.; Lu, Q.; et al. Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—Preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, N.; Bai, H.; Chen, X.; Gong, J.; Li, D.; Sun, Z. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vita, S.; Forliano, D.; De Luca, A.; Beccacece, A.; Marchioni, L.; Nicastri, E.; on behalf of the COVID-19 INMI Study Group. Drug Policies Skyline during COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143117
Vita S, Forliano D, De Luca A, Beccacece A, Marchioni L, Nicastri E, on behalf of the COVID-19 INMI Study Group. Drug Policies Skyline during COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(14):3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143117
Chicago/Turabian StyleVita, Serena, Dora Forliano, Aldo De Luca, Alessia Beccacece, Luisa Marchioni, Emanuele Nicastri, and on behalf of the COVID-19 INMI Study Group. 2021. "Drug Policies Skyline during COVID-19 Pandemic" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 14: 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143117
APA StyleVita, S., Forliano, D., De Luca, A., Beccacece, A., Marchioni, L., Nicastri, E., & on behalf of the COVID-19 INMI Study Group. (2021). Drug Policies Skyline during COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(14), 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143117






