Serum Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis Staging in the Era of the Concept “Compensated Advanced Chronic Liver Disease”
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Liver Biopsy Examination
3. Serum Biomarkers for Liver Fibrosis
3.1. The Mechanisms of Liver Fibrosis with a Focus on Fibrosis Biomarkers
3.2. Fibrosis-4 Index
3.3. AST to Platelet Ratio Index
3.4. FibroTest
3.5. WFA+-M2BP
3.6. Enhanced Liver Fibrosis Score
3.7. Others
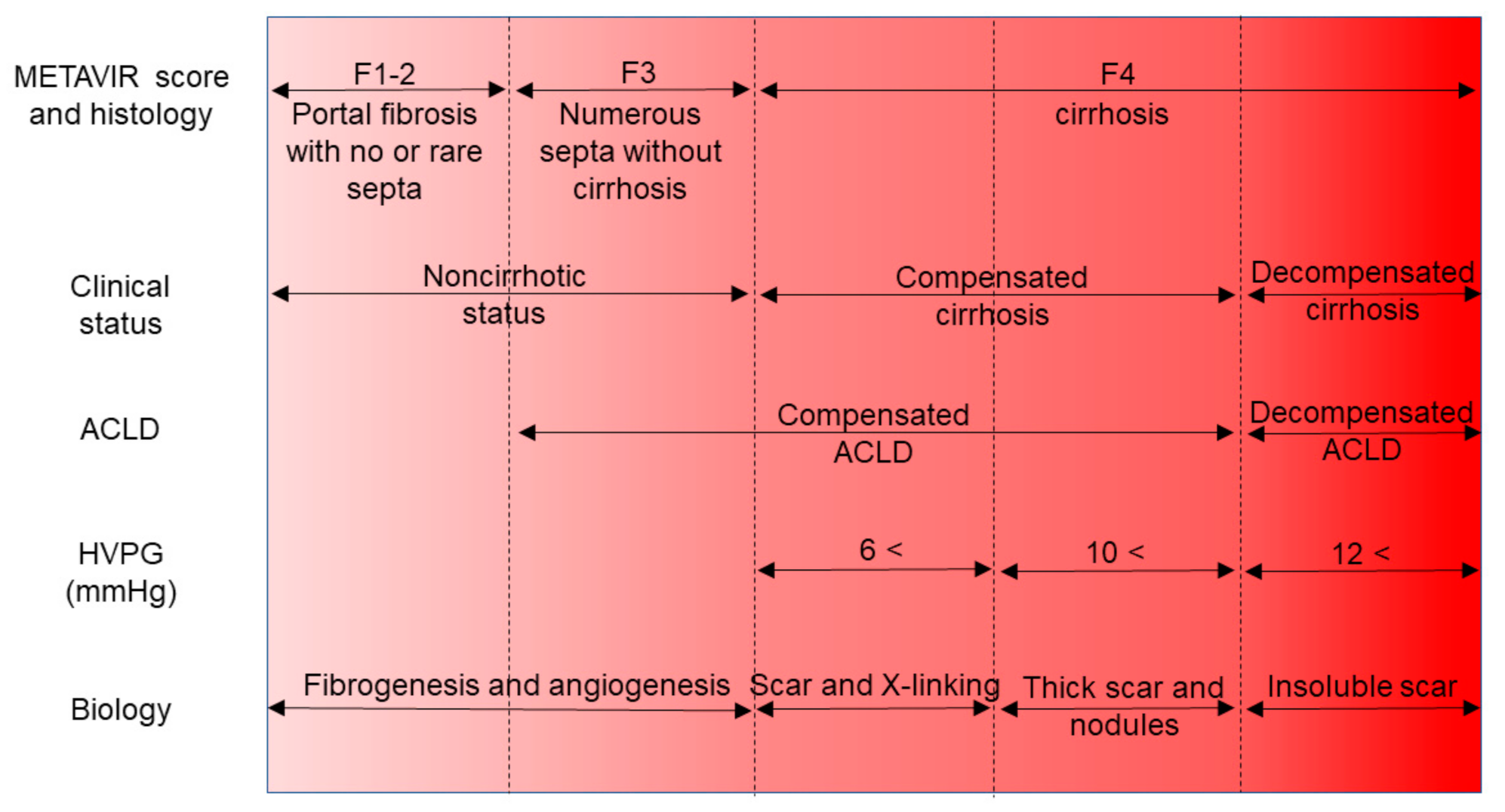
4. Revision of the Idea “Liver Cirrhosis”
4.1. Focus on the Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient
4.2. Concept of the Compensated Advanced Chronic Liver Disease
4.3. Fibrosis Staging by Noninvasive Biomarkers
4.4. Fibrosis Stage as a Surrogate for the Prognosis of Chronic Liver Diseases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Franchis, R.; Faculty, B.V. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lurie, Y.; Webb, M.; Cytter-Kuint, R.; Shteingart, S.; Lederkremer, G.Z. Non-invasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11567–11583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, G.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Pagliaro, L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: A systematic review of 118 studies. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsochatzis, E.A.; Bosch, J.; Burroughs, A.K. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2014, 383, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockey, D.C.; Caldwell, S.H.; Goodman, Z.D.; Nelson, R.C.; Smith, A.D. Diseases AAftSoL. liver biopsy. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1017–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, W.M.; Voelker, M.; Thiel, R.; Becka, M.; Burt, A.; Schuppan, D.; Hubscher, S.; Roskams, T.; Pinzani, M.; Arthur, J.P.M. Serum markers detect the presence of liver fibrosis: A cohort study. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL-ALEH Clinical practice guidelines: Non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 237–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The French METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Intraobserver and interobserver variations in liver biopsy interpretation in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 1994, 20, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, P.P.; Ishak, K.G.; Nayak, N.C.; Poulsen, H.E.; Scheuer, P.J.; Sobin, L.H. The morphology of cirrhosis: Definition, nomenclature, and classification. Bull. World Health Organ. 1977, 55, 521–540. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, P.P.; Ishak, K.G.; Nayak, N.C.; Poulsen, H.E.; Scheuer, P.J.; Sobin, L.H. The morphology of cirrhosis. Recommendations on definition, nomenclature, and classification by a working group sponsored by the World Health Organization. J. Clin. Pathol. 1978, 31, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castera, L.; Pinzani, M. Biopsy and non-invasive methods for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis: Does it take two to tango? Gut 2010, 59, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, E.B.; Lok, A.S.F. Use of liver imaging and biopsy in clinical practice. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2296–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saundby, R. Clinical lecture on cirrhosis of the liver. Br. Med. J. 1886, 1, 1210–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinzani, M.; Rosselli, M.; Zuckermann, M. Liver cirrhosis. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 25, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, A.A.; Sheth, S.G.; Chopra, S. Liver biopsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regev, A.; Berho, M.; Jeffers, L.J.; Milikowski, C.; Molina, E.G.; Pyrsopoulos, N.T.; Feng, Z.-Z.; Reddy, K.R.; Schiff, E.R. Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2614–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, M.; Palmentieri, B.; Vecchione, R.; Torella, R.; De Sio, I. Diagnosis of chronic liver disease: Reproducibility and validation of liver biopsy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 491–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedossa, P.; Dargère, D.; Paradis, V. Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 38, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, B.; Leary, W.; Naran, A.; Maharaj, R.; Cooppan, R.; Pirie, D.; Pudifin, D. Sampling variability and its influence on the diagnostic yield of percutaneous needle biopsy of the liver. Lancet 1986, 327, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousselet, M.-C.; Michalak, S.; Dupré, F.; Croué, A.; Bedossa, P.; Saint-André, J.-P.; Calès, P. Sources of variability in histological scoring of chronic viral hepatitis. Hepatology 2005, 41, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeff, L.B.; Everson, G.T.; Morgan, T.R.; Curto, T.M.; Lee, W.M.; Ghany, M.G.; Shiffman, M.L.; Fontana, R.J.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; et al. Complication rate of percutaneous liver biopsies among persons with advanced chronic liver disease in the HALT-C trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poynard, T.; Bedossa, P. CLINIVIR cooperative study groups Age and platelet count: A simple index for predicting the presence of histological lesions in patients with antibodies to hepatitis C virus. J. Viral Hepat. 1997, 4, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, V.J.; Gerber, M.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Manns, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Classification of chronic hepatitis: Diagnosis, grading and staging. Hepatology 1994, 19, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Tsao, G.; Friedman, S.; Iredale, J.; Pinzani, M. Now there are many (stages) where before there was one: In search of a pathophysiological classification of cirrhosis. Hepatology 2009, 51, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, C.; Greenson, J.K.; Fontana, R.J.; Kalbfleisch, J.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Lok, A.S.-F. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 38, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, K.; Kuroda, N.; Morishita, A.; Oura, K.; Tadokoro, T.; Nomura, T.; Yoneyama, H.; Arai, T.; Himoto, T.; Watanabe, S.; et al. Fibrosis staging using direct serum biomarkers is influenced by hepatitis activity grading in Hepatitis C virus infection. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, S.M.; Fernández-Varo, G.; Gonzalez, P.; Sampson, E.; Bruguera, M.; Navasa, M.; Jiménez, W.; Sánchez-Tapias, J.M.; Forns, X. Assessment of liver fibrosis before and after antiviral therapy by different serum marker panels in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 33, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.K.; Kim, D.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Chon, C.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Paik, Y.H.; Lee, K.S.; Park, Y.N.; Han, K.-H. Validation of FIB-4 and comparison with other simple noninvasive indices for predicting liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in hepatitis B virus-infected patients. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Zhu, S.; Xiao, X.; Yan, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, G. Comparison of laboratory tests, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance elastography to detect fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attallah, A.M.; El-Far, M.; Omran, M.M.; Farid, K.; Albannan, M.S.; El-Dosoky, I. Noninvasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in chronic sepatitis C patients. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2013, 27, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L. The gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-platelet ratio predicts liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in HBeAg-positive chronic HBV infection patients with high HBV DNA and normal or mildly elevated alanine transaminase levels in China. J. Viral. Hepat. 2016, 23, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfon, P.; Bourliere, M.; Deydier, R.; Botta-Fridlund, D.; Renou, C.; Tran, A.; Portal, I.; Allemand, I.; Bertrand, J.J.; Rosenthal-Allieri, A.; et al. Independent prospective multicenter validation of biochemical markers (Fibrotest-Actitest) for the prediction of liver fibrosis and activity in patients with chronic hepatitis C: The fibropaca Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.; Vergniol, J.; Guillet, A.; Hiriart, J.-B.; Lannes, A.; Le Bail, B.; Michalak, S.; Chermak, F.; Bertrais, S.; Foucher, J.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic significance of blood fibrosis tests and liver stiffness measurement by FibroScan in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, C. Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2-binding protein as a diagnostic biomarker in liver cirrhosis: An updated meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trembling, P.M.; Lampertico, P.; Parkes, J.; Tanwar, S.; Viganò, M.; Facchetti, F.; Colombo, M.; Rosenberg, W. Performance of enhanced liver fibrosis test and comparison with transient elastography in the identification of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2013, 21, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Lawitz, E.J.; Alkhouri, N.; Wong, V.W.; Romero-Gómez, M.; Okanoue, T.; Trauner, M.; Kersey, K.; Li, G.; Han, L.; et al. Noninvasive tests accurately identify advanced fibrosis due to NASH: Baseline data from the STELLAR trials. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.A.M.; Myers, R.P. Diagnostic accuracy of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the prediction of hepatitis C–related fibrosis: A systematic review. Hepatology 2007, 46, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Lin, Z.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X.; Dong, Q.; Xuan, S. Diagnostic accuracy of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the prediction of hepatitis B-related fibrosis: A leading meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaheen, A.A.M.; Wan, A.F.; Myers, R.P. FibroTest and FibroScan for the prediction of hepatitis C-related fibrosis: A systematic review of diagnostic test accuracy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2589–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkic, N.; Jovanovic, P.; Hauser, G.; Brcic, M. FibroTest/Fibrosure for significant liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis B: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, T.; Friedman, S.L.; Hoshida, Y. Hepatic stellate cells as key target in liver fibrosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 121, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochatzis, E.A.; Crossan, C.; Longworth, L.; Gurusamy, K.; Rodríguez-Perálvarez, M.; Mantzoukis, K.; O’Brien, J.; Thalassinos, E.; Papastergiou, V.; Noel-Storr, A.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of noninvasive liver fibrosis tests for treatment decisions in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2014, 60, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.; Gulbis, B.; Moreno, C.; Evrard, S.; Verset, G.; Golstein, P.; Frotscher, B.; Nagy, N.; Thiry, P. The predictive value of FIB-4 versus FibroTest, APRI, FibroIndex and Forns index to noninvasively estimate fibrosis in hepatitis C and nonhepatitis C liver diseases. Hepatology 2008, 47, 762–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Pichard, A.; Mallet, V.; Nalpas, B.; Verkarre, V.; Nalpas, A.; Dhalluin-Venier, V.; Fontaine, H.; Pol, S. FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology 2007, 46, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.-C.; Liu, C.-J.; Su, T.-H.; Yang, W.-T.; Chen, C.-L.; Yang, H.-C.; Kuo, S.F.-T.; Liu, C.-H.; Chen, P.-J.; Chen, D.-S.; et al. Fibrosis-4 index predicts cirrhosis risk and liver-related mortality in 2075 patients with chronic HBV infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peleg, N.; Issachar, A.; Sneh-Arbib, O.; Shlomai, A. AST to Platelet Ratio Index and fibrosis 4 calculator scores for non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, S.; Hardy, T.; Dufour, J.-F.; Petta, S.; Romero-Gómez, M.; Allison, M.; Oliveira, C.P.; Francque, S.; Van Gaal, L.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. Age as a Confounding Factor for the Accurate Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Advanced NAFLD Fibrosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.A.; Wallace, M.C.; Friedman, S.L. Pathobiology of liver fibrosis: A translational success story. Gut 2015, 64, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viganò, M.; Andreoni, M.; Perno, C.F.; Craxì, A.; Aghemo, A.; Alberti, A.; Andreone, P.; Babudieri, S.; Bonora, S.; Brunetto, M.R.; et al. Real life experiences in HCV management in 2018. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2018, 17, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.S.Y.; Covert, E.; Wilson, E.; Kottilil, S. Chronic hepatitis B infection: A Review. JAMA 2018, 319, 1802–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, L.-C.; Chen, E.-Q.; Chen, X.-B.; Chen, L.-Y.; Liu, L.; Lei, X.-Z.; Liu, C.; Tang, H. Prospective evaluation of FibroScan for the diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis compared with liver biopsy/AST Platelet ratio index and FIB-4 in patients with chronic HBV infection. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 2742–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbert-Bismut, F.; Ratziu, V.; Pieroni, L.; Charlotte, F.; Benhamou, Y.; Poynard, T. Biochemical markers of liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C virus infection: A prospective study. Lancet 2001, 357, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveau, S.; Gaudé, G.; Asnacios, A.; Agostini, H.; Abella, A.; Barri-Ova, N.; Dauvois, B.; Prévot, S.; Ngo, Y.; Munteanu, M.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic values of noninvasive biomarkers of fibrosis in patients with alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2008, 49, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Tateyama, M.; Abiru, S.; Komori, A.; Nagaoka, S.; Saeki, A.; Hashimoto, S.; Sasaki, R.; Bekki, S.; Kugiyama, Y.; et al. Elevated serum levels of Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive human Mac-2 binding protein predict the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C patients. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narimatsu, H.; Sato, T. Wisteria floribunda agglutinin positive glycobiomarkers: A unique lectin as a serum biomarker probe in various diseases. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2017, 15, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshima, T.; Shirabe, K.; Ikegami, T.; Yoshizumi, T.; Kuno, A.; Togayachi, A. Gotoh, M.; Narimatsu, H.; Korenaga, M.; Mizokami, M.; et al. A novel serum marker, glycosylated Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein (WFA(+)-M2BP), for assessing liver fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuno, A.; Ikehara, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Ito, K.; Matsuda, A.; Sekiya, S.; Hige, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Kage, M.; Mizokami, M.; et al. A serum “sweet-doughnut” protein facilitates fibrosis evaluation and therapy assessment in patients with viral hepatitis. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura, K.; Furusyo, N.; Ogawa, E.; Hayashi, T.; Mukae, H.; Shimizu, M.; Toyoda, K.; Murata, M. Serum WFA+-M2BP is a non-invasive liver fibrosis marker that can predict the efficacy of direct-acting anti-viral-based triple therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 43, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nobili, V.; Parkes, J.; Bottazzo, G.; Marcellini, M.; Cross, R.; Newman, D.; Vizzutti, F.; Pinzani, M.; Rosenberg, W. Performance of ELF Serum Markers in Predicting Fibrosis Stage in Pediatric Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsdal, M.; Nielsen, S.; Leeming, D.; Langholm, L.L.; Nielsen, M.; Manon-Jensen, T.; Siebuhr, A.; Gudmann, N.; Rønnow, S.R.; Sand, J.; et al. The good and the bad collagens of fibrosis—Their role in signaling and organ function. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 121, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnans, C.; Chou, J.; Werb, Z. Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 786–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.M.; Mei, R. Basement Membrane Type IV Collagen and Laminin: An Overview of Their Biology and Value as Fibrosis Biomarkers of Liver Disease. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2017, 300, 1371–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojkind, M.; Ponce-Noyola, P. The Extracellular Matrix of the Liver. Collagen Relat. Res. 1982, 2, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T.; Inuzuka, S.; Torimura, T.; Oohira, H.; Ko, H.; Obata, K.; Sata, M.; Yoshida, H.; Tanikawa, K. Significance of serum type-IV collagen levels in various liver diseases. Measurement with a one-step sandwich enzyme immunoassay using monoclonal antibodies with specificity for pepsin-solubilized type-IV collagen. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1992, 27, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köpke-Aguiar, L.A.; Martins, J.R.; Passerotti, C.C.; Toledo, C.F.; Nader, H.B.; Borges, D.R. Serum hyaluronic acid as a comprehensive marker to assess severity of liver disease in schistosomiasis. Acta. Trop. 2002, 84, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, L. Hyaluronan, a truly “youthful” polysaccharide. Its medical applications. Pathol. Biol. 2015, 63, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.S.; Gibson, P.R. Effects of eating on plasma hyaluronan in patients with cirrhosis: Its mechanism and influence on clinical interpretation. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1998, 13, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, M.G.; Cohen, L.B.; Nanau, R.M. Hyaluronic acid as a non-invasive biomarker of liver fibrosis. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 49, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meeteren, L.A.; Moolenaar, W.H. Regulation and biological activities of the autotaxin-LPA axis. Prog. Lipid Res. 2007, 46, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, S.; Andries, M.; Vekemans, K.; Vanbilloen, H.; Verbruggen, A.; Bollen, M. Rapid clearance of the circulating metastatic factor autotaxin by the scavenger receptors of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Cancer Lett. 2009, 284, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Ikeda, H.; Nakamura, K.; Ohkawa, R.; Kume, Y.; Aoki, J.; Hama, K.; Okudaira, S.; Tanaka, M.; Tomiya, T.; et al. Both plasma lysophosphatidic acid and serum autotaxin levels are increased in chronic hepatitis C. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Ikeda, H.; Nakamura, K.; Ohkawa, R.; Masuzaki, R.; Tateishi, R.; Yoshida, H.; Watanabe, N.; Tejima, K.; Kume, Y.; et al. Autotaxin as a novel serum marker of liver fibrosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshita, S.; Umemura, T.; Usami, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Norman, G.L.; Sugiura, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Fujimori, N.; Kimura, T.; Matsumoto, A.; et al. Serum Autotaxin Is a Useful Disease Progression Marker in Patients with Primary Biliary Cholangitis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melato, M.; Mucli, E. Something new in liver cirrhosis epidemiology. Lancet 1989, 334, 395–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, A.E. Cirrhosis of the liver. Br. Med. J. 1968, 1, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poynard, T.; McHutchison, J.; Manns, M.; Trepo, C.; Lindsay, K.; Goodman, Z.; Ling, M.; Albrecht, J. Impact of pegylated interferon alfa-2b and ribavirin on liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dienstag, J.L.; Goldin, R.; Heathcote, E.; Hann, H.; Woessner, M.; Stephenson, S.L.; Gardner, S.; Gray, D.; Schiff, E.R. Histological outcome during long-term lamivudine therapy. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czaja, A.J.; Carpenter, H.A. Decreased fibrosis during corticosteroid therapy of autoimmune hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falize, L.; Guillygomarc’H, A.; Perrin, M.; Laine, F.; Guyader, D.; Brissot, P.; Turlin, B.; Deugnier, Y. Reversibility of hepatic fibrosis in treated genetic hemochromatosis: A study of 36 cases. Hepatology 2006, 44, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hytiroglou, P.; Snover, D.C.; Alves, V.; Balabaud, C.; Bhathal, P.S.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Crawford, J.M.; Dhillon, A.P.; Ferrell, L.; Guido, M.; et al. Beyond “cirrhosis”: A proposal from the International Liver Pathology Study Group. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 137, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burroughs, A.K. The natural history of varices. J. Hepatol. 1993, 17 (Suppl. 2), S10–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groszmann, R.J.; Bosch, J.; Grace, N.D.; Conn, H.O.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Navasa, M.; Alberts, J.; Rodes, J.; Fischer, R.; Bermann, M.; et al. Hemodynamic events in a prospective randomized trial of propranolol versus placebo in the prevention of a first variceal hemorrhage. Gastroenterology 1990, 99, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagula, S.; Jain, D.; Groszmann, R.J.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Histological-hemodynamic correlation in cirrhosis—A histological classification of the severity of cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Maiwall, R.; Bihari, C.; Ahuja, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, T.; Wani, Z.A.; Sarin, S.K. Cirrhosis histology and Laennec staging system correlate with high portal pressure. Histopathology 2013, 62, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión, J.A.; Navasa, M.; Bosch, J.; Bruguera, M.; Gilabert, R.; Forns, X. Transient elastography for diagnosis of advanced fibrosis and portal hypertension in patients with hepatitis C recurrence after liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2006, 12, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzutti, F.; Arena, U.; Romanelli, R.G.; Rega, L.; Foschi, M.; Colagrande, S.; Petrarca, A.; Moscarella, S.; Belli, G.; Zignego, A.L.; et al. Liver stiffness measurement predicts severe portal hypertension in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis. Hepatology 2007, 45, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franchis, R.; Pascal, J.P.; Ancona, E.; Burroughs, A.K.; Henderson, M.; Fleig, W.; Groszmann, R.; Bosch, J.; Sauerbruch, T.; Soederlund, C. Definitions, methodology and therapeutic strategies in portal hypertension. A Consensus Development Workshop, Baveno, Lake Maggiore, Italy, April 5 and 6, 1990. J. Hepatol. 1992, 15, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franchis, R. Developing consensus in portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 1996, 25, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franchis, R. Updating consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno III Consensus Workshop on definitions, methodology and therapeutic strategies in portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2000, 33, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franchis, R. Evolving consensus in portal hypertension. Report of the Baveno IV consensus workshop on methodology of diagnosis and therapy in portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franchis, R.; Faculty, B.V. Revising consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno V consensus workshop on methodology of diagnosis and therapy in portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishak, K.; Baptista, A.; Bianchi, L.; Callea, F.; De Groote, J.; Gudat, F.; Denk, H.; Desmet, V.; Korb, G.; Macsween, R.N.; et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 1995, 22, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedossa, P.; Carrat, F. Liver biopsy: The best, not the gold standard. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poynard, T.; Morra, R.; Halfon, P.; Castera, L.; Ratziu, V.; Imbert-Bismut, F.; Naveau, S.; Thabut, D.; Lebrec, D.; Zoulim, F.; et al. Meta-analyses of FibroTest diagnostic value in chronic liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2007, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berzigotti, A.; Tsochatzis, E.; Boursier, J.; Castera, L.; Cazzagon, N.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Petta, S.; Thiele, M. Easl Clinical Practice Guidelines (Cpgs) on non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis—2020 Update. J. Hepatol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morling, J.R.; Guha, I.N. Biomarkers of liver fibrosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 7, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, S.H.; Lau, B.; Afdhal, N.H.; Thomas, D.L. Exceeding the limits of liver histology markers. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peery, A.F.; Crockett, S.D.; Murphy, C.C.; Lund, J.L.; Dellon, E.S.; Williams, J.L.; Jensen, E.T.; Shaheen, N.J.; Barritt, A.S.; Lieber, S.R.; et al. Burden and cost of gastrointestinal, liver, and pancreatic diseases in the United States: Update 2018. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 254–272.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pimpin, L.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Negro, F.; Corbould, E.; Lazarus, J.; Webber, L.; Sheron, N. Burden of liver disease in Europe: Epidemiology and analysis of risk factors to identify prevention policies. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 718–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, T.; Serin, A.; Emek, E.; Bozkurt, B.; Arikan, B.T.; Tokat, Y. Effectiveness of noninvasive fibrosis markers for the prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis B+D induced cirrhosis. Transplant. Proc. 2019, 51, 2397–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Brú, C.; Bruix, J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin. Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach—The ALBI grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinchoc, M.; Kamath, P.S.; Gordon, F.D.; Peine, C.J.; Rank, J.; Ter Borg, P.C.J. A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology 2000, 31, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castera, L.; Forns, X.; Alberti, A. Non-invasive evaluation of liver fibrosis using transient elastography. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| F3-4 vs. F1-2 | HCV | HBV | NASH |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIB-4 | 0.87 (0.83–0.91), n = 340 [30] | 0.91 (0.89–0.93), n = 699 [31] | 0.80 (0.77–0.84), n = 8245 [32] |
| APRI | 0.68 (-), n= 324 [33] | 0.65 (0.56–0.73), n = 1521 [34] | 0.75 (0.72–0.77), n = 6746 [32] |
| Fibrotest | 0.73 (0.69–0.77), n = 504 [35] | - | 0.74 (–), n = 452 [36] |
| WFA+-M2BP | 0.78 (0.74–0.82), n = 1609 [37] | 0.75 (0.71–0.79), n = 1602 [37] | 0.77 (0.73–0.81), n = 701 [37] |
| ELF score | 0.83 (0.79–0.87), n = 340 [30] | 0.80 (0.73–0.87), n = 182 [38] | 0.80 (0.80-0.80), n = 3173 [39] |
| F4 vs. F1-3 | |||
| FIB-4 | 0.89 (0.85-0.92), n = 340 [30] | 0.93 (0.91–0.95), n = 699 [31] | 0.85 (0.81–0.89), n = 1872 [32] |
| APRI | 0.83 (0.78-0.88), n= 4266 [40] | 0.75 (-), n= 1798 [41] | 0.75 (0.70–0.80), n = 2196 [32] |
| Fibrotest | 0.90 (–), n = 1679 [42] | 0.87 (0.85–0.90), n = 1754 [43] | 0.76 (–), n = 452 [36] |
| WFA+-M2BP | 0.87 (0.83–0.89), n = 859 [37] | 0.81 (0.77–0.84), n = 1283 [37] | 0.85 (0.82–0.88) n = 728 [37] |
| ELF score | 0.82 (0.78-0.87), n = 340 [30] | 0.83 (0.76–090), n = 182 [38] | 0.76 (0.76-0.77), n = 3173 [39] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujita, K.; Masaki, T. Serum Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis Staging in the Era of the Concept “Compensated Advanced Chronic Liver Disease”. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153340
Fujita K, Masaki T. Serum Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis Staging in the Era of the Concept “Compensated Advanced Chronic Liver Disease”. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(15):3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153340
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujita, Koji, and Tsutomu Masaki. 2021. "Serum Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis Staging in the Era of the Concept “Compensated Advanced Chronic Liver Disease”" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 15: 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153340
APA StyleFujita, K., & Masaki, T. (2021). Serum Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis Staging in the Era of the Concept “Compensated Advanced Chronic Liver Disease”. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(15), 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153340






