Gallbladder Polyp Classification in Ultrasound Images Using an Ensemble Convolutional Neural Network Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
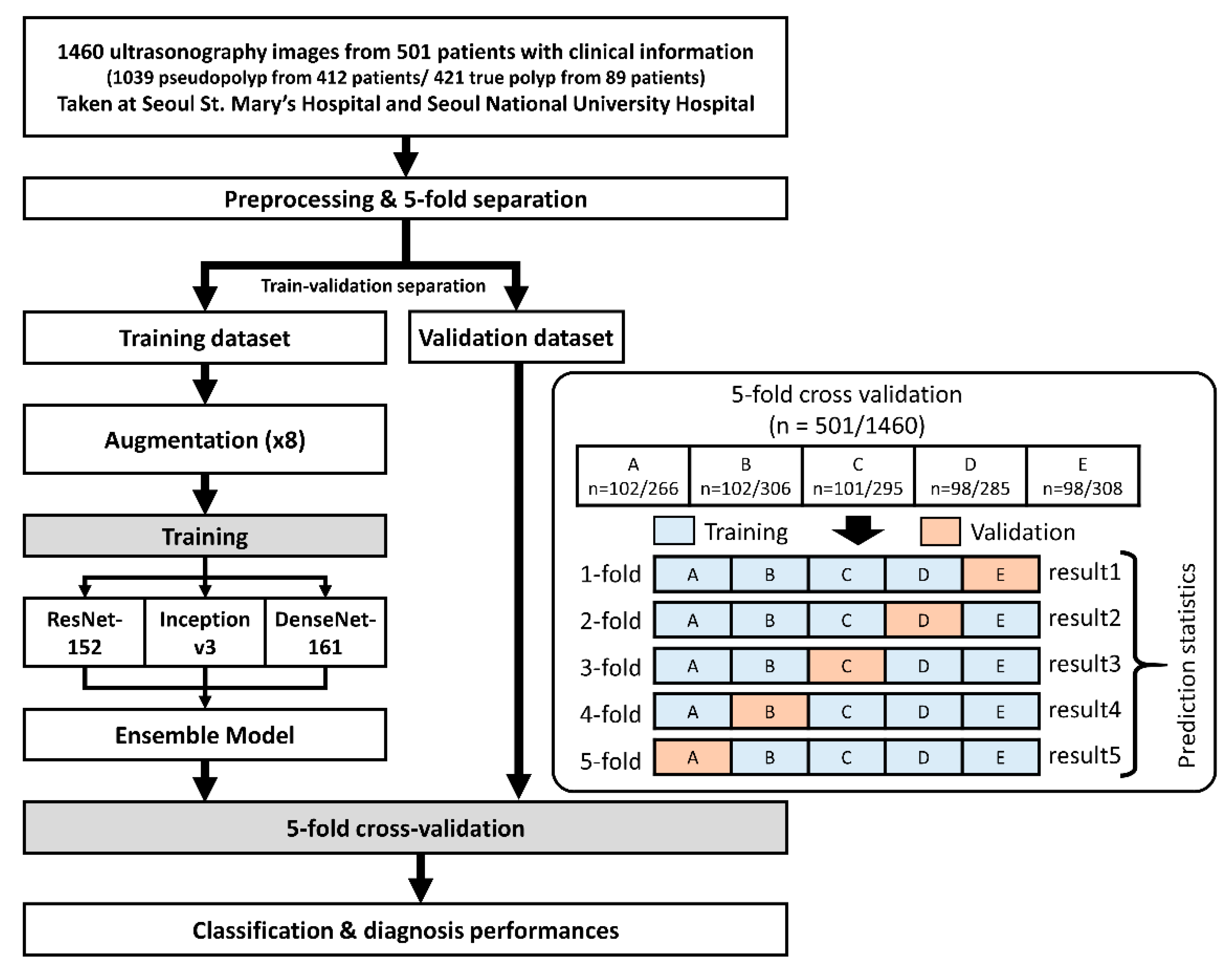
2.1. Patients and Dataset Preparation
2.2. Ensemble Convolutional Neural Network Model
2.3. Clinical Validation
2.4. Performance Measures and Statistics
3. Results
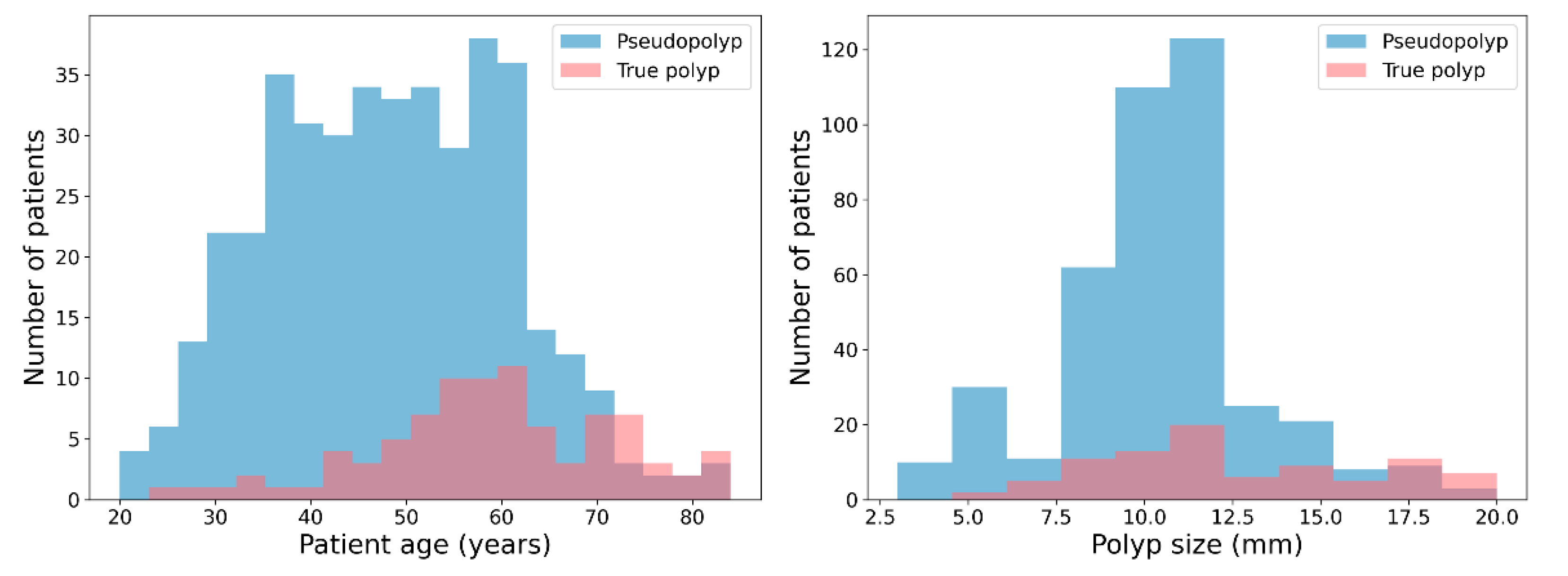
3.1. Dataset Composition and Characteristics
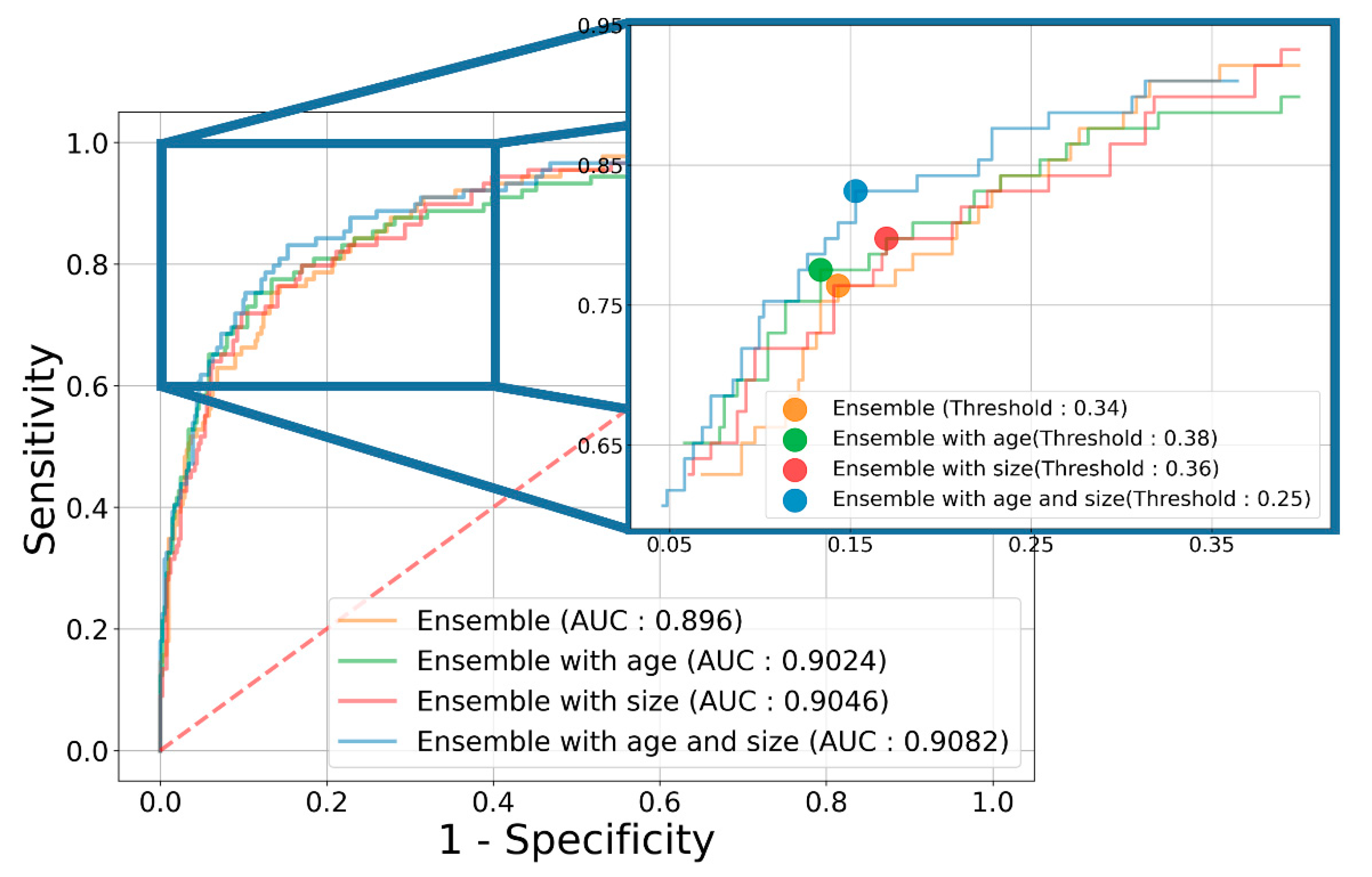
3.2. Diagnostic Performance of the Ensemble Model
3.3. Diagnostic Performance Based on the GB Polyp Size
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ito, H.; Hann, L.E.; D‘Angelica, M.; Allen, P.; Fong, Y.; Dematteo, R.P.; Klimstra, D.S.; Blumgart, L.H.; Jarnagin, W.R. Polypoid lesions of the gallbladder: Diagnosis and followup. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2009, 20, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Lan, X.; Tan, H. Neoplastic polyps in gallbladder: A retrospective study to determine risk factors and treatment strategy for gallbladder polyps. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2019, 8, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, B.I.; Dennison, A.R.; Garcea, G. Management and diagnosis of gallbladder polyps: A systematic review. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2015, 400, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, T.; Jensen, K.H. Polyps in the gallbladder. A prevalence study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1990, 25, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.; Gill, R.; Debru, E. Diagnostic accuracy of transabdominal ultrasonography for gallbladder polyps: Systematic review. Can. J. Surg. 2018, 61, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.Y.; Hong, S.P.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.M.; Cho, J.H.; Park, S.W.; Song, S.Y.; Chung, J.B.; Bang, S. Long-term follow up of gallbladder polyps. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, B.H.; Hwang, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.E.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.Y. Pre-operative factors that can predict neoplastic polypoid lesions of the gallbladder. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 2216–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.S.; Chen, T.; Gu, L.H.; Guo, Y.F.; Li, C.Y.; Li, F.H.; Wang, J. Ultrasound-based scoring system for differential diagnosis of polypoid lesions of the gallbladder. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiles, R.; Thoeni, R.F.; Barbu, S.T.; Vashist, Y.K.; Rafaelsen, S.R.; Dewhurst, C.; Arvanitakis, M.; Lahaye, M.; Soltes, M.; Perinel, J.; et al. Management and follow-up of gallbladder polyps: Joint guidelines between the European Society of Gastrointestinal and Abdominal Radiology (ESGAR), European Association for Endoscopic Surgery and other Interventional Techniques (EAES), International Society of Digestive Surgery - European Federation (EFISDS) and European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE). Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 3856–3866. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wennmacker, S.Z.; van Dijk, A.H.; Raessens, J.H.J.; van Laarhoven, C.; Drenth, J.P.H.; de Reuver, P.R.; Nagtegaal, I.D. Polyp size of 1 cm is insufficient to discriminate neoplastic and non-neoplastic gallbladder polyps. Surg. Endosc. 2019, 33, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujiwara, K.; Abe, A.; Masatsugu, T.; Hirano, T.; Sada, M. Effect of gallbladder polyp size on the prediction and detection of gallbladder cancer. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 5179–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, O.; Gersh, B.J.; Bhatt, D.L. Artificial intelligence in medical imaging: Switching from radiographic pathological data to clinically meaningful endpoints. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e486–e488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Guan, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, P.; Yu, A.; Long, X.; Liu, L.; et al. Adrenal incidentaloma: Machine learning-based quantitative texture analysis of unenhanced CT can effectively differentiate sPHEO from lipid-poor adrenal adenoma. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3577–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27 June–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, A.; Verma, G.K. Convolutional neural network: A review of models, methodologies and applications to object detection. Lect. Notes Artif. Int. 2020, 9, 85–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.-X.; Yu, Q.-H.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.-P. Ultrasound Radiomics Effective for Preoperative Identification of True and Pseudo Gallbladder Polyps Based on Spatial and Morphological Features. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Chae, H.-D.; Park, S.J.; Bae, J.S.; Joo, I.; Han, J.K. Deep learning-based decision support system for the diagnosis of neoplastic gallbladder polyps on ultrasonography: Preliminary results. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskin, O.C.; Basturk, O.; Reid, M.D.; Dursun, N.; Bagci, P.; Saka, B.; Balci, S.; Memis, B.; Bellolio, E.; Araya, J.C.; et al. Gallbladder polyps: Correlation of size and clinicopathologic characteristics based on updated definitions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennmacker, S.Z.; de Savornin Lohman, E.A.; Hasami, N.A.; Nagtegaal, I.D.; Boermeester, M.A.; Verheij, J.; Spillenaar Bilgen, E.J.; Meijer, J.W.H.; Bosscha, K.; van der Linden, J.C.; et al. Overtreatment of Nonneoplastic Gallbladder Polyps due to Inadequate Routine Ultrasound Assessment. Dig. Surg. 2021, 38, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Katanuma, A.; Hayashi, T.; Kin, T.; Takahashi, K. Role of endoscopic ultrasound for gallbladder disease. J. Med. Ultrason. 2021, 48, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
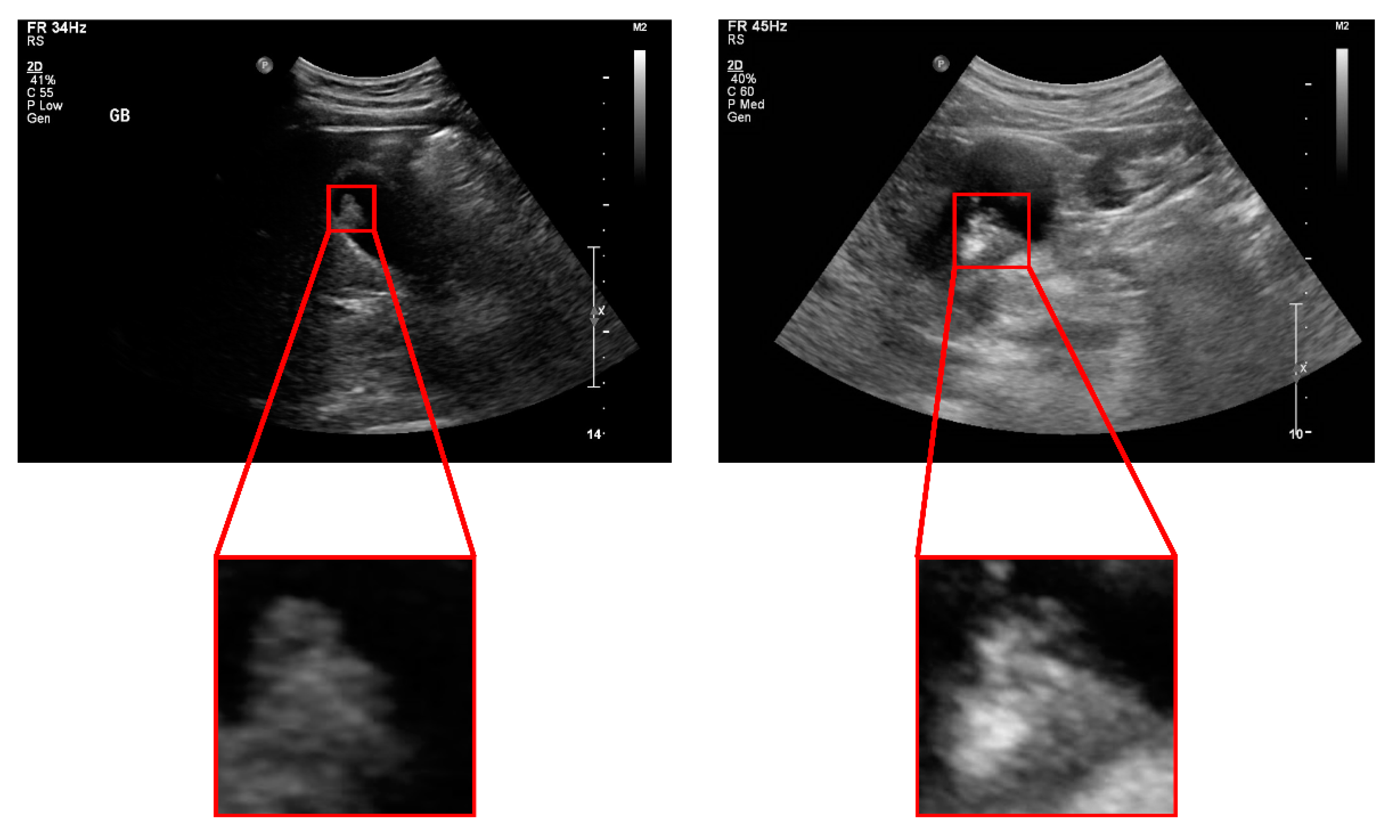

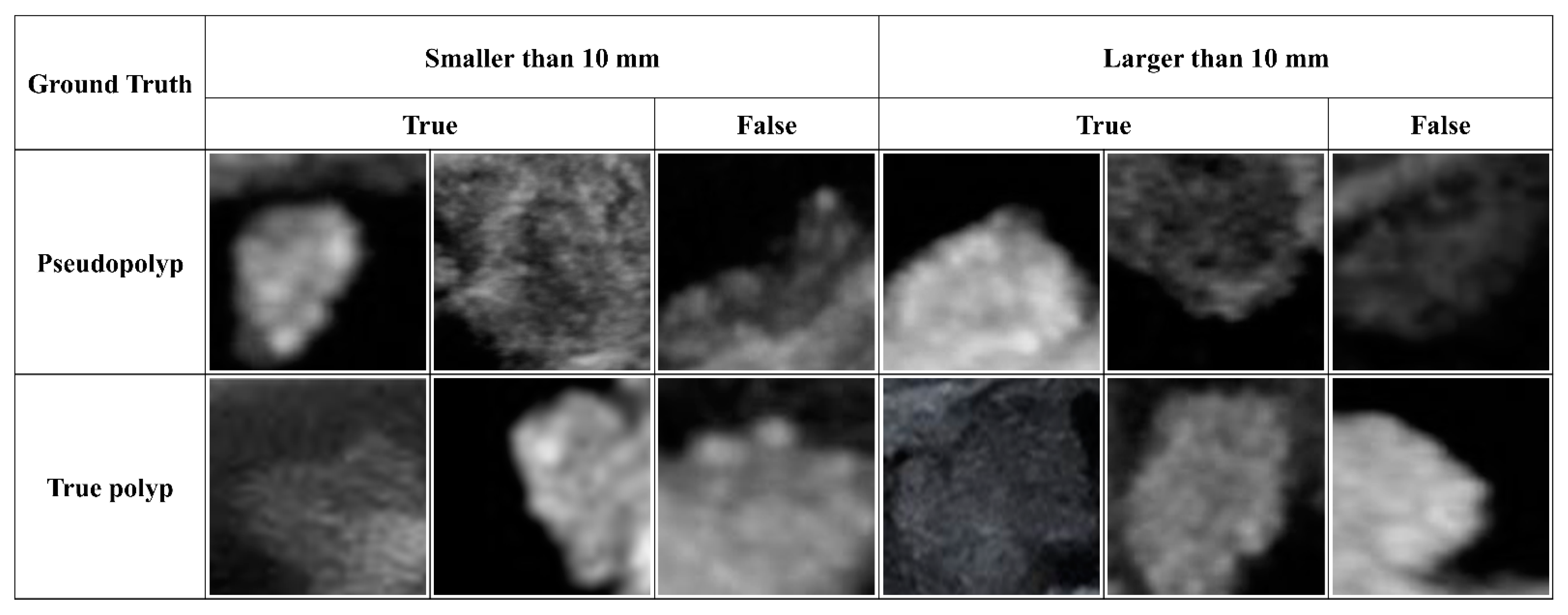
| Pseudopolyp | True Polyp | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 412 | 89 | |
| Number of images | 1039 | 421 | |
| Age (years) | 48.3 ± 12.3 | 59.1 ± 12.6 | <0.001 |
| Polyp size (mm) | 10.5 ± 2.8 | 12.6 ± 3.8 | <0.001 |
| Clinical Information | Model | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Diagnosis | |||||||
| None | ResNet 152 | 80.39 (74.48~86.30) | 84.28 (74.64~93.92) | 79.59 (71.41~87.78) | 48.37 (35.94~60.80) | 96.00 (93.81~98.19) | 0.8710 (0.8335~0.9084) |
| Inception v3 | 81.76 (65.42~98.09) | 84.47 (72.67~96.28) | 81.29 (59.47~100.0) | 56.84 (33.48~80.21) | 96.37 (93.78~98.95) | 0.8625 (0.7991~0.9260) | |
| DenseNet 161 | 83.84 (77.07~90.62) | 81.78( 72.36~91.20) | 84.23 (74.71~93.76) | 54.89 (41.86~67.91) | 95.67 (93.91~97.44) | 0.8776 (0.8449~0.9103) | |
| Ensemble | 83.63 (77.34~89.93) | 84.08 (74.58~93.58) | 83.49 (74.61~92.37) | 54.48 (40.97~68.00) | 96.18 (94.27~98.09) | 0.8960 (0.8599~0.9321) | |
| Age | ResNet 152 | 80.35 (72.55~88.14) | 84.47 (74.26~94.69) | 79.57 (68.59~90.54) | 49.14 (34.99~63.28) | 96.07 (93.76~98.38) | 0.8701 (0.8394~0.9008) |
| Inception v3 | 81.97 (73.19~90.76) | 88.22 (77.70~98.75) | 80.81 (68.51~93.10) | 52.05 (38.02~66.07) | 97.02 (94.34~99.69) | 0.8761 (0.8314~0.9208) | |
| DenseNet161 | 77.91 (67.64~88.18) | 92.89 (83.10~100.0) | 74.56 (61.12~88.00) | 45.75 (34.25~57.24) | 98.20 (95.86~100.0) | 0.8825 (0.8330~0.9320) | |
| Ensemble | 84.99 (73.37~96.61) | 86.38 (75.30~97.46) | 84.70 (69.35~100.0) | 60.81 (37.52~84.10) | 96.83 (94.70~98.95) | 0.9024 (0.8495~0.9554) | |
| Size | ResNet152 | 79.01 (70.61~87.42) | 90.59 (79.58~100.0) | 76.45 (65.78~87.12) | 46.78 (34.56~59.00) | 97.61 (94.73~100.0) | 0.8848 (0.8303~0.9393) |
| Inception v3 | 83.26 (78.72~87.80) | 81.97 (70.87~93.08) | 83.49 (76.16~90.82) | 52.77 (45.54~60.00) | 95.68 (93.12~98.23) | 0.8779 (0.8496~0.9061) | |
| DenseNet 161 | 78.40 (66.12~90.67) | 89.93 (80.46~99.41) | 75.97 (59.57~92.36) | 47.58 (33.76~61.40) | 97.45 (95.27~99.64) | 0.8736 (0.8442~0.9030) | |
| Ensemble | 81.20 (69.71~92.69) | 92.04 (87.89~96.19) | 78.89 (64.70~93.09) | 51.34 (33.94~68.74) | 97.91 (97.12~98.71) | 0.9046 (0.8537~0.9555) | |
| Age + Size | ResNet 152 | 79.63 (70.94~88.33) | 88.88 (84.57~93.19) | 77.68 (66.75~88.60) | 47.81 (36.06~59.56) | 97.01 (95.86~98.16) | 0.8814 (0.8432~0.9196) |
| Inception v3 | 81.63 (70.86~92.40) | 82.63 (68.58~96.68) | 81.34 (66.28~96.40) | 52.99 (33.97~72.01) | 95.94 (92.92~98.96) | 0.8756 (0.8358~0.9153) | |
| DenseNet 161 | 84.63 (81.01~88.25) | 85.33 (77.68~92.98) | 84.47 (79.94~89.00) | 54.64 (46.76~62.52) | 96.43 (94.56~98.30) | 0.8991 (0.8602~0.9380) | |
| Ensemble | 87.61 (81.03~94.18) | 84.28 (72.79~95.76) | 88.35 (81.24~95.46) | 62.42 (45.42~79.43) | 96.31 (93.70~98.92) | 0.9082 (0.8550~0.9614) | |
| Model (With Clinical Info) | Size | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Diagnosis | |||||||
| Ensemble (age + size) | - | 87.61 (81.03~94.18) | 84.28 (72.79~95.76) | 88.35 (81.24~95.46) | 62.42 (45.42~79.43) | 96.31 (93.70~98.92) | 0.9082 (0.8550~0.9614) |
| ≥10 mm | 87.15 (80.62~93.69) | 85.30 (70.69~99.91) | 87.64 (80.65~94.64) | 63.46 (50.20~76.72) | 96.13 (92.25~100.0) | 0.9131 (0.8523~0.9740) | |
| <10 mm | 86.61 (67.88~100.0) | 93.33 (74.82~100.0) | 85.57 (64.33~100.0) | 59.24 (29.11~89.37) | 99.26 (97.20~100.0) | 0.8942 (0.7867~1.000) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.; Choi, Y.H.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, I.S. Gallbladder Polyp Classification in Ultrasound Images Using an Ensemble Convolutional Neural Network Model. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163585
Kim T, Choi YH, Choi JH, Lee SH, Lee S, Lee IS. Gallbladder Polyp Classification in Ultrasound Images Using an Ensemble Convolutional Neural Network Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(16):3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163585
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Taewan, Young Hoon Choi, Jin Ho Choi, Sang Hyub Lee, Seungchul Lee, and In Seok Lee. 2021. "Gallbladder Polyp Classification in Ultrasound Images Using an Ensemble Convolutional Neural Network Model" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 16: 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163585
APA StyleKim, T., Choi, Y. H., Choi, J. H., Lee, S. H., Lee, S., & Lee, I. S. (2021). Gallbladder Polyp Classification in Ultrasound Images Using an Ensemble Convolutional Neural Network Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(16), 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163585







