The Use of Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) in the Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Equipment and Current Technology
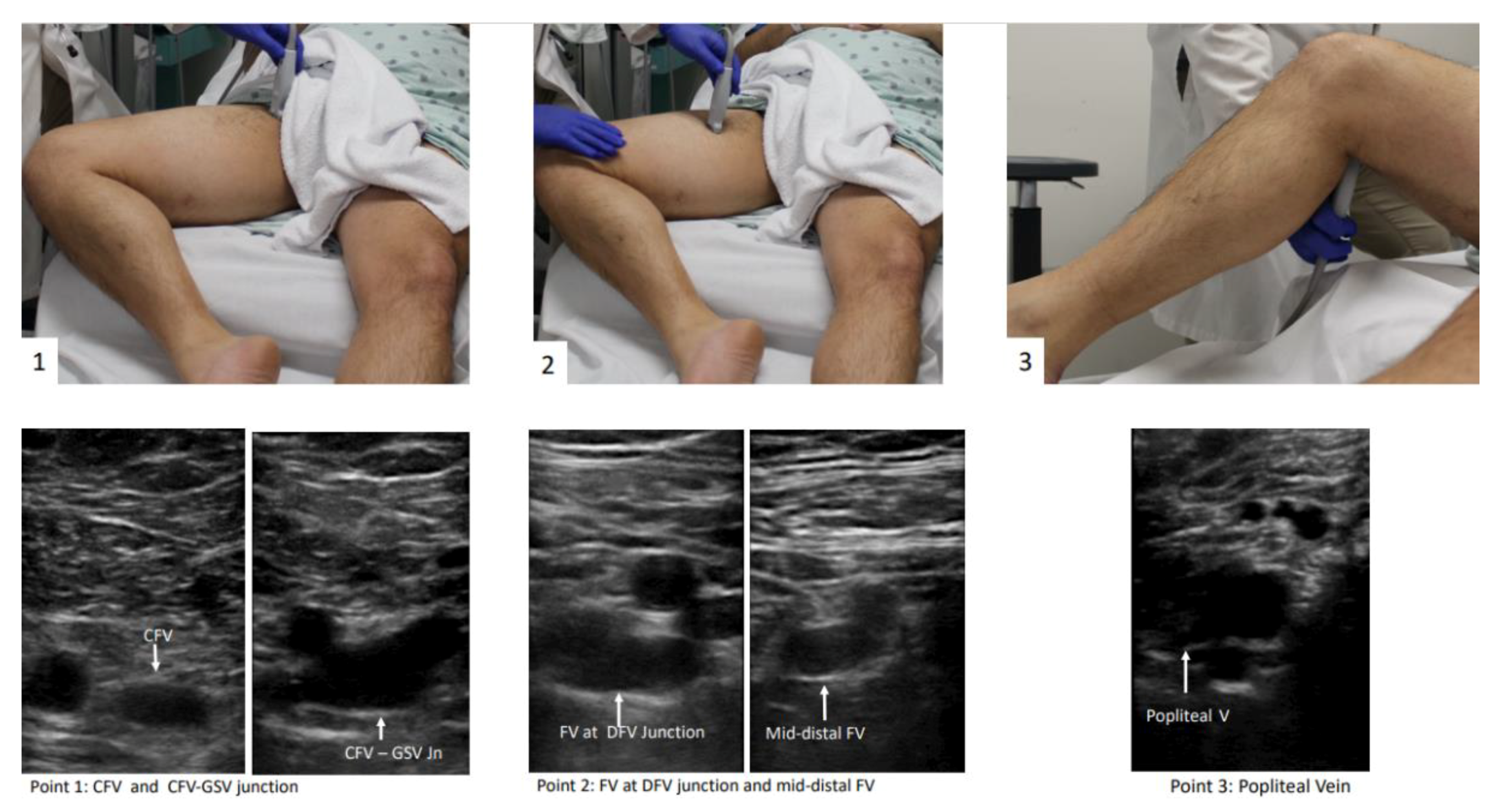
4. Patient Preparation
5. Protocols
6. Sensitivity and Specificity
7. Pre-Test Probability and D-Dimer
8. Time and Resources
9. Education
10. Limitations
11. Summary and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heit, J.A. Epidemiology of venous thromboembolism. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, K.K.; Herbert, M.; Henderson, S.O. The mortality of untreated pulmonary embolism in emergency department patients. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2005, 45, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Valois, J.; van Schaik, C.; Verzijlbergen, F.; van Ramshorst, B.; Eikelboom, B.; Meuwissen, O. Contrast venography: From gold standard to ‘golden backup’ in clinically suspected deep vein thrombosis. Eur. J. Radiol. 1990, 11, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomero, F.; Dentali, F.; Borretta, V.; Bonzini, M.; Melchio, R.; Douketis, J.D.; Fenoglioet, L.M. Accuracy of emergency physician-performed ultrasonography in the diagnosis of deep-vein thrombosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 109, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnside, P.R.; Brown, M.D.; Kline, J.A. Systematic review of emergency physician-performed ultrasonography for lower-extremity deep vein thrombosis. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2008, 15, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, S.; Chand, S.; Dieiev, V.; Fazzari, M.; Tanner, T.; Lewandowski, D.C.; Nalla, A.; AbdulFattah, O.; Aboodi, M.S.; Shiloh, A.L.; et al. Thromboembolic events and role of point of care ultrasound in hospitalized Covid-19 patients needing intensive care unit admission. J. Intensive Care Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrawalla, P.; Eisen, L.A.; Shiloh, A.L.; Shah, B.J.; Savenkov, O.; Wise, W.; Evans, L.; Mayo, P.H.; Szyld, D. Development and validation of an assessment tool for competency in critical care ultrasound. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2015, 7, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Emergency Physicians. ACEP emergency ultrasound guidelines—2001. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2001, 38, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultrasound guidelines: Emergency, point-of-care and clinical ultrasound guidelines in medicine. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2017, 69, e27–e54. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, T.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, J. DVT incidence and risk factors in critically ill patients with COVID-19. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 51, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.A.; Kinnear, B.; Sall, D.; Kelleher, M.; Sanchez, O.; Mathews, B.; Schnobrich, D.; Olson, A.P.J. Hospitalist-operated compression ultrasonography: A point-of-care ultrasound study (HOCUS-POCUS). J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2019, 34, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, N.J.; Arntfield, R.; Kory, P. Point of Care Ultrasound, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zuker-Herman, R.; Dangur, I.A.; Berant, R.; Cohen Sitt, E.; Baskin, L.; Shaya, Y.; Shiber, S. Comparison between two-point and three-point compression ultrasound for the diagnosis of deep vein throm-bosis. J. Thromb Thrombolysis 2018, 45, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.; Anjum, F.; dela Cruz, J. Deep Venous Thrombosis Ultrasound Evaluation; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shiloh, Lower Extremity Deep Venous Thrombosis. In Point of Care Ultrasound; Soni, N., Arntfield, R., Kory, P., Eds.; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 21–213. [Google Scholar]
- Read, H.; Holdgate, A.; Watkins, S. Simple external rotation of the leg increases the size and accessibility of the femoral vein. Emerg. Med. Australas. 2012, 24, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koksoy, C.; Cetinkaya, O.A. Popliteal access in the supine position for endovenous management of deep vein thrombosis. EJVES Short Rep. 2020, 46, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, S.; Zeger, W.; Thom, C.; Fields, J.M. Isolated deep venous thrombosis: Implications for 2-point compression ultrasonography of the lower extremity. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2015, 66, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahmand, S.; Farnia, M.; Shahriaran, S.; Khashayar, P. The accuracy of limited B-mode compression technique in diagnosing deep venous thrombosis in lower extremities. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 29, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacoby, J.; Cesta, M.; Axelband, J.; Melanson, S.; Heller, M.; Reed, J. Can emergency medicine residents detect acute deep venous thrombosis with a limited, two-site ultrasound examination? J. Emerg. Med. 2007, 32, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoro, D.; Blaivas, M.; Duggal, S.; Snyder, G.; Lucas, M. Real-time B-mode ultrasound in the ED saves time in the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2004, 22, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, T.; Docherty, M.; Aubin, C.; Polites, G. Resident-performed compression ultrasonography for the detection of proximal deep vein thrombosis: Fast and accurate. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2004, 11, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, J.A.; O’Malley, P.M.; Tayal, V.S.; Snead, G.R.; Mitchell, A.M. Emergency clinician-performed compression ultrasonography for deep venous thrombosis of the lower extremity. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2008, 52, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, B.T.; Massarin, E.; Pigman, E.C. Color Doppler ultrasonography by emergency physicians for the diagnosis of acute deep ve-nous thrombosis. Acad. Emerg. Med. 1997, 4, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaivas, M. Point-of-care ultrasonographic deep venous thrombosis evaluation after just ten minutes’ training: Is this offer too good to be true? Ann. Emerg. Med. 2010, 56, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magazzini, S.; Vanni, S.; Toccafondi, S.; Paladini, B.; Zanobetti, M.; Giannazzo, G.; Federico, R.; Grifoni, S. Duplex ultrasound in the emergency department for the diagnostic management of clinically suspected deep vein thrombosis. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2007, 14, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kory, P.D.; Pellecchia, C.M.; Shiloh, A.L.; Mayo, P.H.; DiBello, C.; Koenig, S. Accuracy of ultrasonography performed by critical care physicians for the diagnosis of DVT. Chest 2011, 139, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, J.P.; Alonso, J.V.; García, P.C.; Rodríguez, F.R.; López, M.A.; Muñoz-Villanueva, M.D.C. Comparison of the accuracy of emergency department-performed point-of-care-ultrasound (POCUS) in the diagnosis of lower-extremity deep vein thrombosis. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 54, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Yun, S.J. Comparison of 2-point and 3-point point-of-care ultrasound techniques for deep vein thrombosis at the emergency department: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e15791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caronia, J.; Sarzynski, A.; Tofighi, B.; Mahdavi, R.; Allred, C.; Panagopoulos, G.; Mina, B. Resident performed two-point compression ultrasound is inadequate for diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis in the critically III. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2014, 37, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needleman, L.; Cronan, J.; Lilly, M.; Merli, G.; Adhikari, S.; Hertzberg, B. Ultrasound for lower extremity deep venous thrombosis: Multidisciplinary recommendations from the Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound Consensus Conference. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2019, 7, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.M.; Jaeschke, R.; Stevens, S.M.; Goodacre, S.; Wells, P.S.; Stevenson, M.D.; Kearon, C.; Schunemann, H.J.; Crowther, M.; Pauker, S.G.; et al. Diagnosis of DVT: Antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2012, 141 (Suppl. 2), e351S–e418S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, P.S.; Anderson, D.R.; Rodger, M.; Forgie, M.; Kearon, C.; Dreyer, J.; Kovacs, G.; Mitchell, M.; Lewandowski, B.; Kovacs, M.J. Evaluation of D-Dimer in the diagnosis of suspected deep-vein thrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaseem, A.; Snow, V.; Barry, P.; Hornbake, E.R.; Rodnick, J.E.; Tobolic, T.; Ireland, B.; Segal, J.; Bass, E.; Weiss, K.B. Current diagnosis of venous thromboembolism in primary care: A clinical practice guideline from the American Academy of Family Physicians and the American College of Physicians. Ann. Fam. Med. 2007, 5, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazerian, P.; Volpicelli, G.; Gigli, C.; Becattini, C.; Papa, G.F.S.; Grifoni, S.; Vanni, S.; the Ultrasound Wells Study Group. Ultrasound Wells Study Group diagnostic performance of wells score combined with point-of-care lung and venous ultrasound in suspected pulmonary embolism. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2017, 24, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.D.; Murray, P.K. Cost-effectiveness of screening for deep vein thrombosis by ultrasound at admission to stroke rehabilitation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1941–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.M.; Yassin, M.; Galang, G. Cost-effectiveness analysis of routine venous doppler ultrasound for diagnosis of deep ve-nous thrombosis at admission to inpatient rehabilitation. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 97, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.A.; Brodersen, J.; Davidsen, A.S.; Graumann, O.; Jensen, M.B.B. Use and impact of point-of-care ultrasonography in general practice: A prospective observational study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e037664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Situ-LaCasse, E.; Guirguis, H.; Friedman, L.; Patanwala, A.E.; Cohen, S.E.; Adhikari, S. Can emergency physicians perform extended compression ultrasound for the diagnosis of lower extremity deep vein thrombosis? World J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 10, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, K.; Fukuda, S.; Yamashita, H.; Uetsuhara, T.; Sakamoto, A.; Yamasaki, K.; Kosaka, M.; Shirai, N.; Uono, H.; Yoshikawa, J.; et al. Detection of deep venous thrombosis using a pocket-size ultrasound examination device. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 897–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squizzato, A.; Galli, L.; Gerdes, V.E.A. Point-of-care ultrasound in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. Crit. Ultrasound J. 2015, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahner, D.; Blaivas, M.; Cohen, H.; Fox, J.C.; Hoffenberg, S.; Kendall, J.; Langer, J.; McGahan, J.P.; Sierzenski, P.; Tayal, V.S.; et al. AIUM practice guideline for the performance of the focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) examination. J. Ultrasound Med. 2008, 27, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Hockberger, R.S.; Binder, L.S.; Chisholm, C.D.; Cushman, J.; Hayden, S.R.; Sklar, D.P.; Stern, S.A.; Strauss, R.W.; Thomas, H.A.; Viravec, D.R. The model of the clinical practice of emergency medicine: A 2-Year update. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2005, 45, 659–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaivas, M.; Lambert, M.J.; Harwood, M.A.; Wood, J.P.; Konickiet, J. Lower-extremity Doppler for deep venous thrombosis—Can emergency physicians be accurate and fast? Acad. Emerg. Med. 2000, 7, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.C.; Bertoglio, K.C. Emergency physician performed ultrasound for DVT evaluation. Thrombosis 2011, 2011, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mumoli, N.; Vitale, J.; Giorgi-Pierfranceschi, M.; Sabatini, S.; Tulino, R.; Cei, M.; Bucherini, E.; Bova, C.; Mastroiacovo, D.; Camaiti, A.; et al. General practitioner-performed compression ultrasonography for diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis of the leg: A multicenter, prospective cohort study. Ann. Fam. Med. 2017, 15, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.A.; Hedegård, H.S.; Løkkegaard, T.; Frølund, J.; Jensen, M.B. Education of general practitioners in the use of point-of-care ultrasonography: A systematic review. Fam. Pract. 2020, 38, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Jung, J.Y.; Kwon, H. Effectiveness of education in point-of-care ultrasound-assisted physical examinations in an emer-gency department: A before-and-after study. Medicine 2017, 96, e7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitek, T.; Baydoun, J.; Yepez, S.; Forred, W.; Slattery, D.E. Mistakes and pitfalls associated with two-point compression ultrasound for deep vein thrombosis. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 17, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledsoe, J.R.; Woller, S.C.; Stevens, S.M.; Aston, V.; Patten, R.; Allen, T.; Horne, B.D.; Dong, L.; Lloyd, J.; Snow, G.; et al. Management of low-risk pulmonary embolism patients without hospitalization: The low-risk pulmonary embolism prospective management study. Chest 2018, 154, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaye, B.; Noukoua, C.T.; Dondelinger, R.F.; Nchimi, A. Incidence and distribution of lower extremity deep venous thrombosis at indirect computed tomography venography in patients suspected of pulmonary embolism. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 97, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, A.; Mallard, L.; Elias, M.; Alquier, C.; Guidolin, F.; Gauthier, B.; Viard, A.; Mahouin, P.; Vinel, A.; Boccalon, H. A single complete ultrasound investigation of the venous network for the diagnostic management of patients with a clini-cally suspected first episode of deep venous thrombosis of the lower limbs. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 89, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aleva, F.E.; Voets, L.W.L.M.; Simons, S.O.; de Mast, Q.; van der Ven, A.J.A.M.; Heijdra, Y.F. Prevalence and localization of pulmonary embolism in unexplained acute exacerbations of COPD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest 2017, 151, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P.M.; Penaloza, A.; Hugli, O.; Klok, F.A.; Arnoux, A.; Elias, A.; Couturaud, F.; Joly, L.-M.; Lopez, R.; Faber, L.M.; et al. Triaging acute pulmonary embolism for home treatment by Hestia or simplified PESI criteria: The HOME-PE randomized trial. Eur. Heart J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naringrekar, H.; Sun, J.; Ko, C.; Rodgers, S.K. It’s not all deep vein thrombosis: Sonography of the painful lower extremity with multimodality correlation. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 1075–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dihn, V. DVT ultrasound made easy step by step guide. Available online: www.pocus101.com (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Montorfano, M.A.; Pla, F.; Vera, L.; Cardillo, O.; Nigra, S.G.; Montorfano, L.M. Point-of-care ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound evaluation of vascular injuries in penetrating and blunt trauma. Crit. Ultrasound J. 2017, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dihn, V. DVT Ultrasound Made Easy: Step-By-Step Guide. 2008. Available online: https://www.pocus101.com/dvt-ultrasound-made-easy-step-by-step-guide/ (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Blanco, P.; Volpicelli, G. Common pitfalls in point-of-care ultrasound: A practical guide for emergency and critical care physicians. Crit. Ultrasound J. 2016, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palareti, G.; Cosmi, B.; Lessiani, G.; Rodorigo, G.; Guazzaloca, G.; Brusi, C.; Valdré, L.; Conti, E.; Sartori, M.; Legnani, C. Evolution of untreated calf deep-vein thrombosis in high risk symptomatic outpatients: The blind, prospective CALTHRO study. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 104, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinede, L.; Ninet, J.; Duhaut, P.; Chabaud, S.; Demolombe-Rague, S.; Durieu, I.; Nony, P.; Sanson, C.; Boissel, J.-P. Comparison of 3 and 6 months of oral anticoagulant therapy after a first episode of proximal deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism and comparison of 6 and 12 weeks of therapy after isolated calf deep vein thrombosis. Circulation 2001, 103, 2453–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Van Rooden, C.J.; Westerbeek, R.E.; Huisman, M.V. Diagnostic management of clinically suspected acute deep vein thrombosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 146, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, M.V.; Klok, F.A. Diagnostic management of acute deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varrias, D.; Palaiodimos, L.; Balasubramanian, P.; Barrera, C.A.; Nauka, P.; Arfaras-Melainis, A.; Zamora, C.; Zavras, P.; Napolitano, M.; Gulani, P.; et al. The Use of Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) in the Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173903
Varrias D, Palaiodimos L, Balasubramanian P, Barrera CA, Nauka P, Arfaras-Melainis A, Zamora C, Zavras P, Napolitano M, Gulani P, et al. The Use of Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) in the Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(17):3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173903
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarrias, Dimitrios, Leonidas Palaiodimos, Prasanth Balasubramanian, Christian A Barrera, Peter Nauka, Angelos Arfaras-Melainis, Christian Zamora, Phaedon Zavras, Marzio Napolitano, Perminder Gulani, and et al. 2021. "The Use of Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) in the Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 17: 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173903
APA StyleVarrias, D., Palaiodimos, L., Balasubramanian, P., Barrera, C. A., Nauka, P., Arfaras-Melainis, A., Zamora, C., Zavras, P., Napolitano, M., Gulani, P., Ntaios, G., Faillace, R. T., & Galen, B. (2021). The Use of Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) in the Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(17), 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173903





