The Role of Urinary N-Acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase in Cirrhotic Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Study Protocol
2.2. Data Collection and Measurement of Urine NAG
2.3. Definition, Management, Outcomes, and Follow-Up
2.4. Sample Size Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and AKI Phenotype
3.2. Relationship between Urine NAG and AKI Stage
3.3. Relationship of Urine NAG and Change of AKI Status
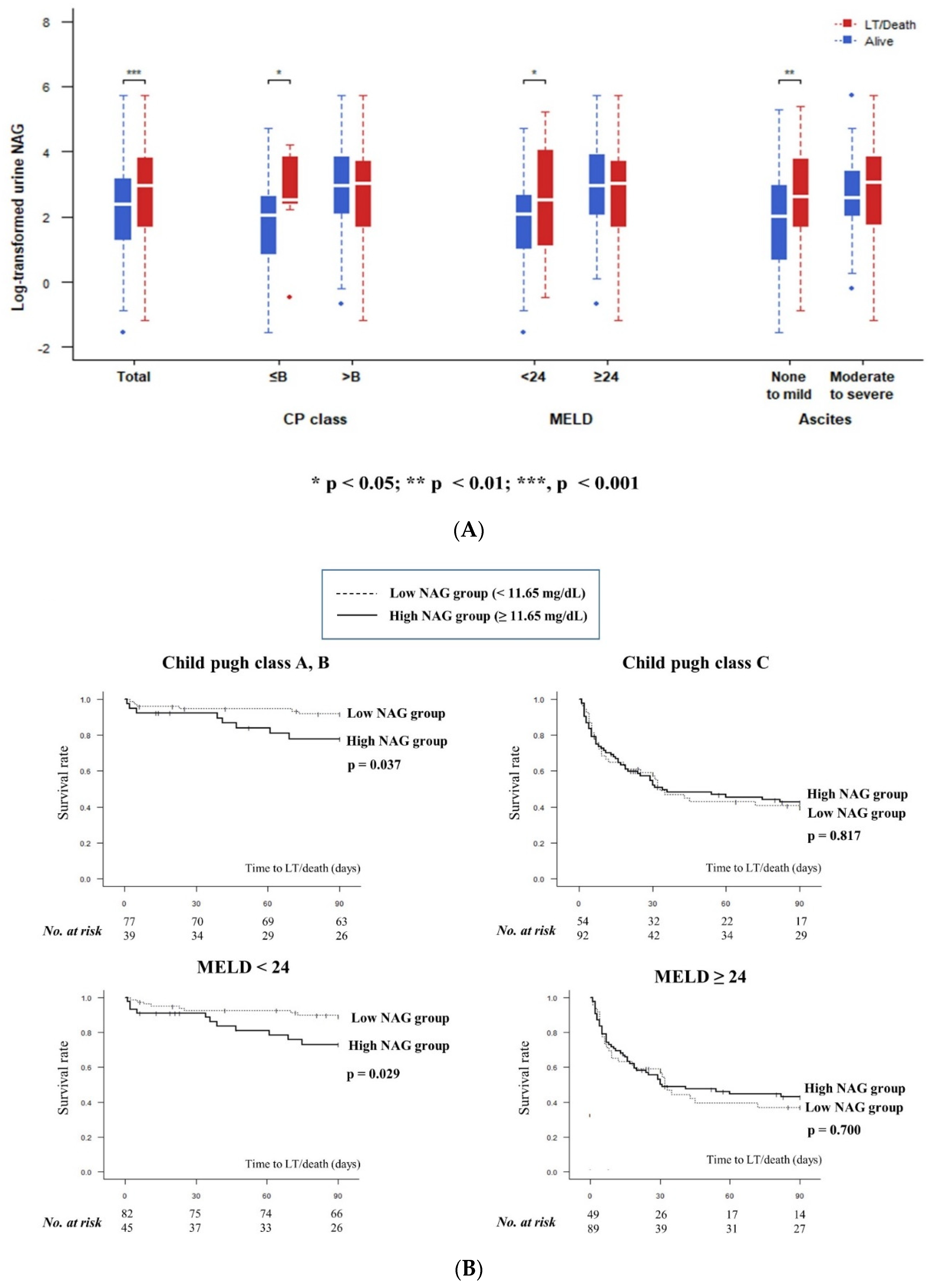
3.4. Relationship between Urine NAG and 3-Months Transplant-Free Survival
3.5. Urine NAG and Terlipressin Treatment Response in HRS-AKI
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biggins, S.W.; Angeli, P.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Gines, P.; Ling, S.C.; Nadim, M.K.; Wong, F.; Kim, W.R. Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Ascites, Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis and Hepatorenal Syndrome: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1014–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, P.; Kc, S.; Hamal, A.B.; Sharma, D.; Khadka, S.; Karki, N.; Jaishi, B.; Tiwari, P.S.; Vaidya, A.; Karki, A. Prevalence of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. JNMA J. Nepal Med. Assoc. 2020, 58, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F. Acute kidney injury in liver cirrhosis: New definition and application. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2016, 22, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belcher, J.M.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Sanyal, A.J.; Bhogal, H.; Lim, J.K.; Ansari, N.; Coca, S.G.; Parikh, C.R.; Consortium, T.-A. Association of AKI with mortality and complications in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2013, 57, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bucsics, T.; Krones, E. Renal dysfunction in cirrhosis: Acute kidney injury and the hepatorenal syndrome. Gastroenterol. Rep. (Oxf.) 2017, 5, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, P.; Gines, P.; Wong, F.; Bernardi, M.; Boyer, T.D.; Gerbes, A.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Sarin, S.K.; Piano, S.; et al. Diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: Revised consensus recommendations of the International Club of Ascites. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoo, J.J.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, B.; Lee, M.H.; Jeong, S.W.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, Y.D.; et al. Estimation of renal function in patients with liver cirrhosis: Impact of muscle mass and sex. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, P.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Nadim, M.K.; Parikh, C.R. News in pathophysiology, definition and classification of hepatorenal syndrome: A step beyond the International Club of Ascites (ICA) consensus document. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mindikoglu, A.L.; Pappas, S.C. Predictors of Response to Terlipressin in Hepatorenal Syndrome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ariza, X.; Sola, E.; Elia, C.; Barreto, R.; Moreira, R.; Morales-Ruiz, M.; Graupera, I.; Rodriguez, E.; Huelin, P.; Sole, C.; et al. Analysis of a urinary biomarker panel for clinical outcomes assessment in cirrhosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liangos, O.; Perianayagam, M.C.; Vaidya, V.S.; Han, W.K.; Wald, R.; Tighiouart, H.; MacKinnon, R.W.; Li, L.; Balakrishnan, V.S.; Pereira, B.J.; et al. Urinary N-acetyl-beta-(d)-glucosaminidase activity and kidney injury molecule-1 level are associated with adverse outcomes in acute renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, S.; Rosi, S.; Maresio, G.; Fasolato, S.; Cavallin, M.; Romano, A.; Morando, F.; Gola, E.; Frigo, A.C.; Gatta, A.; et al. Evaluation of the Acute Kidney Injury Network criteria in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis and ascites. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francoz, C.; Nadim, M.K.; Durand, F. Kidney biomarkers in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fagundes, C.; Barreto, R.; Guevara, M.; Garcia, E.; Sola, E.; Rodriguez, E.; Graupera, I.; Ariza, X.; Pereira, G.; Alfaro, I.; et al. A modified acute kidney injury classification for diagnosis and risk stratification of impairment of kidney function in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.R.; Anderson, R.J.; Linas, S.L.; Henrich, W.L.; Berns, A.S.; Gabow, P.A.; Schrier, R.W. Urinary diagnostic indices in acute renal failure: A prospective study. Ann. Intern. Med. 1978, 89, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, R.; Lebrec, D. Acute renal failure in patients with cirrhosis: Perspectives in the age of MELD. Hepatology 2003, 37, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.O.; Francoz, C. Global strategy for the diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury in patients with liver cirrhosis. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2021, 9, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.Y.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, J.K.; Hwang, S.D.; Lee, Y.W. Urinary cystatin C levels as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in patients with acute kidney injury. Nephrology 2013, 18, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazar, A.; Pereira, G.H.; Guevara, M.; Martin-Llahi, M.; Pepin, M.N.; Marinelli, M.; Sola, E.; Baccaro, M.E.; Terra, C.; Arroyo, V.; et al. Predictors of response to therapy with terlipressin and albumin in patients with cirrhosis and type 1 hepatorenal syndrome. Hepatology 2010, 51, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron, J.M.; Bureau, C.; Gonzalez, L.; Garcia-Ricard, F.; de Soyres, O.; Dupuis, E.; Alric, L.; Pourrat, J.; Vinel, J.P. Treatment of hepatorenal syndrome as defined by the international ascites club by albumin and furosemide infusion according to the central venous pressure: A prospective pilot study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 2702–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthumana, J.; Ariza, X.; Belcher, J.M.; Graupera, I.; Gines, P.; Parikh, C.R. Urine Interleukin 18 and Lipocalin 2 Are Biomarkers of Acute Tubular Necrosis in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1003–1013.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ariza, X.; Graupera, I.; Coll, M.; Sola, E.; Barreto, R.; Garcia, E.; Moreira, R.; Elia, C.; Morales-Ruiz, M.; Llopis, M.; et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is a biomarker of acute-on-chronic liver failure and prognosis in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huelin, P.; Sola, E.; Elia, C.; Sole, C.; Risso, A.; Moreira, R.; Carol, M.; Fabrellas, N.; Bassegoda, O.; Juanola, A.; et al. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin for Assessment of Acute Kidney Injury in Cirrhosis: A Prospective Study. Hepatology 2019, 70, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzi, C.; Petrini, C.; Rizza, V.; Arrigo, G.; Napodano, P.; Paparella, M.; D’Amico, G. Urinary N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase excretion is a marker of tubular cell dysfunction and a predictor of outcome in primary glomerulonephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2002, 17, 1890–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, W.K.; Waikar, S.S.; Johnson, A.; Betensky, R.A.; Dent, C.L.; Devarajan, P.; Bonventre, J.V. Urinary biomarkers in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, W.K.; Bonventre, J.V. Biologic markers for the early detection of acute kidney injury. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2004, 10, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, D.; Doi, K.; Honda, K.; Negishi, K.; Fujita, T.; Hisagi, M.; Ono, M.; Matsubara, T.; Yahagi, N.; Iwagami, M.; et al. Combination of two urinary biomarkers predicts acute kidney injury after adult cardiac surgery. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 93, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Lee, H.A.; Seo, Y.S.; Lee, Y.R.; Yim, S.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Suh, S.J.; Jung, Y.K.; Kim, J.H.; An, H.; et al. Assessment and prediction of acute kidney injury in patients with decompensated cirrhosis with serum cystatin C and urine N-acetyl-beta-d-glucosaminidase. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Amico, G.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Pagliaro, L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: A systematic review of 118 studies. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellwood, J.M.; Ellis, B.G.; Price, R.G.; Hammond, K.; Thompson, A.E.; Jones, N.F. Urinary N-acetyl-beta-d-glucosaminidase activities in patients with renal disease. Br. Med. J. 1975, 3, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.K.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, B.H.; Om, A.S.; Hong, J.H.; Koh, H.C.; Lee, C.H.; Shin, I.C.; Kang, J.S. Urinary N-acetyl-beta-d-glucosaminidase and malondialdehyde as a markers of renal damage in burned patients. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2001, 16, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address, e.e.e.; European Association for the Study of the, L. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 406–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyer, T.D.; Sanyal, A.J.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Blei, A.; Carl, D.; Bexon, A.S.; Teuber, P.; Terlipressin Study, G. Predictors of response to terlipressin plus albumin in hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) type 1: Relationship of serum creatinine to hemodynamics. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinit, S.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, P.; Bansal, R.; Tyagi, P.; Bansal, N.; Singla, V.; Kumar, M.; Ranjan, P.; Sachdeva, M.; et al. Predictors of Response and Outcome to Terlipressin in Patients With Hepatorenal Syndrome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, M.N.; Bouchard, J.; Legault, L.; Ethier, J. Diagnostic performance of fractional excretion of urea and fractional excretion of sodium in the evaluations of patients with acute kidney injury with or without diuretic treatment. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 50, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, J.; Arroyo, V.; Ballesta, A.M.; Rimola, A.; Gual, J.; Elena, M.; Rodes, J. Aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity in cirrhosis. Value of urinary beta 2-microglobulin to discriminate functional renal failure from acute tubular damage. Gastroenterology 1982, 82, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, J.M.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Sanyal, A.J.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Peixoto, A.J.; Perazella, M.A.; Ansari, N.; Lim, J.; Coca, S.G.; Parikh, C.R.; et al. Urinary biomarkers and progression of AKI in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvounis, C.P.; Nisar, S.; Guro-Razuman, S. Significance of the fractional excretion of urea in the differential diagnosis of acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 2223–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gines, P.; Sola, E.; Angeli, P.; Wong, F.; Nadim, M.K.; Kamath, P.S. Hepatorenal syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Total (N = 262) | Pre-Renal (N = 119) | ATN (N = 52) | Miscellaneous (N = 18) | HRS-AKI (N = 73) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 58.8 ± 12.9 | 59.0 ± 13.1 | 60.6 ± 13.7 | 62.6 ± 13.0 | 56.1 ± 11.6 | 0.121 |
| Male (n, %) | 190 (72.5%) | 96 (80.7%) | 38 (73.1%) | 10 (55.6%) | 46 (63.0%) | 0.020 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.0 ± 4.2 | 24.0 ± 4.1 | 23.7 ± 4.6 | 24.0 ± 4.3 | 24.2 ± 4.1 | 0.931 |
| Etiology (n, %) | 0.418 | |||||
| Viral | 44 (16.8%) | 15 (12.6%) | 10 (19.2%) | 4 (22.2%) | 15 (20.5%) | |
| Non-viral | 218 (83.2%) | 104 (87.4%) | 42 (80.8%) | 14 (77.8%) | 58 (79.5%) | |
| Current alcohol drinking (n, %) | 100 (38.1%) | 42 (35.3%) | 14 (26.9%) | 6 (33.3%) | 25 (34.2%) | 0.209 |
| Diabetes (n, %) | 87 (33.2%) | 38 (31.9%) | 21 (40.4%) | 4 (22.2%) | 24 (32.9%) | 0.517 |
| Prior use of diuretics (n, %) | 152 (58.0%) | 71 (59.7%) | 27 (51.9%) | 13 (72.2%) | 41 (56.2%) | 0.472 |
| Prior use of beta blocker (n, %) | 55 (20.9%) | 27 (22.7%) | 12 (23.1%) | 3 (16.7%) | 13 (17.8%) | 0.803 |
| AKI stage (n, %) | <0.001 | |||||
| Stage I | 135 (51.5%) | 75 (63.0%) | 25 (48.1%) | 13 (72.2%) | NA | |
| Stage II | 79 (30.1%) | 30 (25.2%) | 19 (36.5%) | 4 (22.2%) | NA | |
| Stage III | 48 (18.4%) | 14 (11.8%) | 8 (15.4%) | 1 (5.6%) | NA | |
| HRS-AKI (n, %) | 73 (27.8%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 73 (100%) | <0.001 |
| Ascites (n, %) | 0.081 | |||||
| No | 84 (32.1%) | 36 (30.3%) | 25 (48.1%) | 6 (33.3%) | 17 (23.3%) | |
| Mild | 47 (17.9%) | 21 (17.6%) | 10 (19.2%) | 4 (22.2%) | 12 (16.4%) | |
| Moderate to severe | 131 (50.0%) | 62 (52.1%) | 17 (32.7%) | 8 (44.4%) | 44 (60.3%) | |
| Hepatic encephalopathy (n, %) | 0.125 | |||||
| No | 199 (76.0%) | 88 (73.9%) | 46 (88.5%) | 16 (88.9%) | 49 (67.1%) | |
| Grade I to II | 26 (9.9%) | 14 (11.8%) | 2 (3.8%) | 1 (5.6%) | 9 (12.3%) | |
| Grade III to IV | 37 (14.1%) | 17 (14.3%) | 4 (7.7%) | 1 (5.6%) | 15 (20.5%) | |
| Child–Pugh class (n, %) | 0.002 | |||||
| A | 28 (10.7%) | 10 (8.4%) | 11 (21.2%) | 5 (27.8%) | 2 (2.7%) | |
| B | 88 (33.6%) | 43 (36.1%) | 20 (38.5%) | 3 (16.7%) | 22 (30.1%) | |
| C | 146 (55.7%) | 66 (55.5%) | 21 (40.4%) | 10 (55.6%) | 49 (67.1%) | |
| Child–Pugh score | 9.8 ± 2.4 | 9.9 ± 2.3 | 8.6 ± 2.5 | 8.8 ± 2.6 | 10.6 ± 2.2 | <0.001 |
| MELD score | 25.2 ± 9.1 | 24.1 ± 7.9 | 22.4 ± 8.6 | 21.1 ± 9.1 | 30.2 ± 9.3 | <0.001 |
| Vital sign | ||||||
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 116 ± 19 | 114 ± 18 | 120 ± 20 | 119 ± 17 | 114 ± 19 | 0.255 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 69 ± 14 | 69 ± 12 | 70 ± 11 | 74 ± 12 | 69 ± 17 | 0.486 |
| Mean blood pressure (mmHg) | 85 ± 14 | 84 ± 13 | 87 ± 14 | 89 ± 13 | 84 ± 17 | 0.435 |
| Heart rate (beats per minute) | 86 ± 17 | 87 ± 18 | 83 ± 17 | 86 ± 17 | 85 ± 16 | 0.517 |
| Laboratory findings | ||||||
| White blood cell (/μL) | 9748 ± 6898 | 10,727 ± 7691 | 8589 ± 6606 | 6173 ± 3228 | 9860 ± 3562 | 0.032 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 9.7 ± 2.2 | 9.7 ± 2.3 | 9.9 ± 2.6 | 10.2 ± 1.4 | 9.5 ± 2.1 | 0.542 |
| Platelet (103/μL) | 104 ± 60 | 105 ± 63 | 113 ± 61 | 104 ± 64 | 98 ± 55 | 0.602 |
| hs-CRP (mg/dL) | 3.2 ± 4.3 | 3.5 ± 3.8 | 2.8 ± 4.9 | 2.4 ± 4.2 | 3.1 ± 4.5 | 0.676 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.7 ± 0.6 | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 3.0 ± 0.7 | 2.8 ± 0.8 | 2.5 ± 0.4 | 0.002 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 42 ± 23 | 40 ± 22 | 35 ± 17 | 31 ±15 | 55 ±25 | <0.001 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 8.4 ± 10.1 | 8.2 ± 10.1 | 6.6 ± 9.0 | 3.9 ± 5.0 | 11.1 ± 11.3 | 0.016 |
| AST (U/L) | 162 ± 621 | 136 ± 192 | 296 ± 1320 | 169 ± 474 | 107 ± 177 | 0.363 |
| ALT (U/L) | 84 ± 349 | 64 ± 117 | 149 ± 708 | 64 ± 120 | 75 ± 240 | 0.510 |
| Serum sodium (mmol/L) | 132 ± 7 | 132 ± 8 | 133 ± 5 | 133 ± 6 | 130 ± 6 | 0.112 |
| Creatinine_baseline (mg/dL) | 1.05 ± 0.36 | 1.01 ± 0.26 | 0.92 ± 0.22 | 1.06 ± 0.29 | 1.19 ± 0.51 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine_enrollment (mg/dL) | 2.27 ± 0.87 | 1.99 ± 0.52 | 2.01 ± 0.58 | 1.89 ± 0.76 | 3.02 ±1.07 | <0.001 |
| Prothrombin time (INR) | 1.85 ± 0.85 | 1.78 ± 0.69 | 1.71 ± 0.75 | 1.78 ±1.20 | 2.06 ± 0.99 | 0.078 |
| Urine NAG (mg/dL) | 28.31 ± 45.23 | 26.36 ± 37.06 | 16.06 ± 23.40 | 13.22 ± 16.52 | 43.92 ± 65.52 | 0.002 |
| Variable | LT/Death in 3-Months (N = 95) | Alive (N = 167) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 60.32 ± 12.66 | 57.96 ± 13.04 | 0.157 |
| Male (n, %) | 71 (74.74%) | 119 (71.26%) | 0.644 |
| Liver transplantation (n, %) | 13 (13.68%) | 0 | 0.999 |
| Death (n, %) | 82 (86.31%) | 0 | 0.999 |
| AKI stage (n, %) | 0.001 | ||
| Stage I | 35 (36.84%) | 100 (59.88%) | |
| Stage II | 36 (37.89%) | 43 (25.75%) | |
| Stage III | 24 (25.26%) | 24 (14.37%) | |
| HRS-AKI (n, %) | 36 (37.89%) | 37 (22.16%) | 0.010 |
| Ascites (n, %) | 0.021 | ||
| No | 22 (23.16%) | 62 (37.13%) | |
| Mild | 15 (15.79%) | 32 (19.16%) | |
| Moderate to severe | 58 (61.05%) | 73 (43.71%) | |
| Hepatic encephalopathy (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| No | 59 (62.11%) | 140 (83.83%) | |
| Grade I to II | 15 (15.79%) | 11 (6.59%) | |
| Grade III to IV | 21 (22.11%) | 16 (9.58%) | |
| Child–Pugh class (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| A | 3 (3.16%) | 25 (14.97%) | |
| B | 11 (11.58%) | 77 (46.11%) | |
| C | 81 (85.26%) | 65 (38.92%) | |
| Child–Pugh score | 11.37 ± 2.11 | 8.90 ± 2.23 | <0.001 |
| MELD score | 31.30 ± 8.48 | 21.84 ± 7.56 | <0.001 |
| Laboratory findings | |||
| White blood cell (/μL) | 12,270.20 ± 7648.55 | 8314.59 ± 5999.27 | <0.001 |
| Platelet (103/μL) | 96.21 ± 58.20 | 109.65 ± 61.75 | 0.047 |
| hs-CRP (mg/dL) | 4.08 ± 4.52 | 2.73 ± 4.13 | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.52 ± 0.54 | 2.86 ± 0.69 | <0.001 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 51.18 ± 25.12 | 38.21 ± 21.38 | <0.001 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 13.25 ± 11.34 | 5.70 ± 8.31 | <0.001 |
| AST (U/L) | 159.09 ± 273.73 | 164.76 ± 750.93 | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 89.84 ± 234.14 | 81.07 ± 401.41 | 0.003 |
| Serum sodium (mmol/L) | 129.79 ± 8.25 | 133.51 ± 6.21 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine_baseline (mg/dL) | 1.03 ± 0.37 | 1.06 ± 0.36 | 0.392 |
| Creatinine_enrollment (mg/dL) | 2.46 ± 0.87 | 2.17 ± 0.86 | 0.010 |
| Prothrombin time (INR) | 2.37 ± 1.03 | 1.55 ± 0.52 | <0.001 |
| Urine NAG (mg/dL) | 38.80 ± 55.90 | 22.34 ± 36.73 | 0.005 |
| Category | N | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | ||
| LT/Death in 3-months | |||||
| Total | 262 | 1.008 (1.002–1.015) ** | 1.010 (1.004–1.017) ** | 1.003 (0.997–1.010) | 1.003 (0.996–1.010) |
| MELD | |||||
| <24 | 127 | 1.028 (1.010–1.052) ** | 1.039 (1.016–1.065) ** | 1.036 (1.011–1.063) ** | 1.034 (1.008–1.062) * |
| ≥24 | 135 | 1.000 (0.994–1.007) | 1.002 (0.996–1.009) | 1.000 (0.993–1.007) | 1.000 (0.993–1.007) |
| Child–Pugh class | |||||
| ≤B | 116 | 1.022 (1.001–1.044) * | 1.033 (1.009–1.059) ** | 1.029 (1.003–1.055) * | 1.028 (1.002–1.054) * |
| >B | 146 | 1.002 (0.996–1.008) | 1.004 (0.997–1.011) | 1.001 (0.994–1.008) | 1.001 (0.994–1.008) |
| Ascites | |||||
| None to mild | 131 | 1.008 (0.999–1.018) | 1.009 (0.999–1.019) | 1.000 (0.988–1.012) | 1.000 (0.988–1.012) |
| Moderate to severe | 131 | 1.007 (1.000–1.017) | 1.009 (1.001–1.020) * | 1.004 (0.995–1.016) | 1.003 (0.994–1.013) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, J.-J.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Nam, S.W.; Park, J.W.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, C.W.; Shin, S.K.; Chon, Y.E.; Jang, E.S.; et al. The Role of Urinary N-Acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase in Cirrhotic Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194328
Yoo J-J, Kwon JH, Kim YS, Nam SW, Park JW, Kim HY, Kim CW, Shin SK, Chon YE, Jang ES, et al. The Role of Urinary N-Acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase in Cirrhotic Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(19):4328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194328
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Jeong-Ju, Jung Hyun Kwon, Young Seok Kim, Soon Woo Nam, Ji Won Park, Hee Yeon Kim, Chang Wook Kim, Seung Kak Shin, Young Eun Chon, Eun Sun Jang, and et al. 2021. "The Role of Urinary N-Acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase in Cirrhotic Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 19: 4328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194328
APA StyleYoo, J.-J., Kwon, J. H., Kim, Y. S., Nam, S. W., Park, J. W., Kim, H. Y., Kim, C. W., Shin, S. K., Chon, Y. E., Jang, E. S., Jeong, S.-H., Lee, J. W., Song, D. S., Yang, J. M., Lee, S. W., Lee, H. L., Jung, Y. K., Yim, H. J., Lee, B., ... Kim, J. H. (2021). The Role of Urinary N-Acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase in Cirrhotic Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(19), 4328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194328







