Diffusion–Based Virtual MR Elastography of the Liver: Can It Be Extended beyond Liver Fibrosis?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
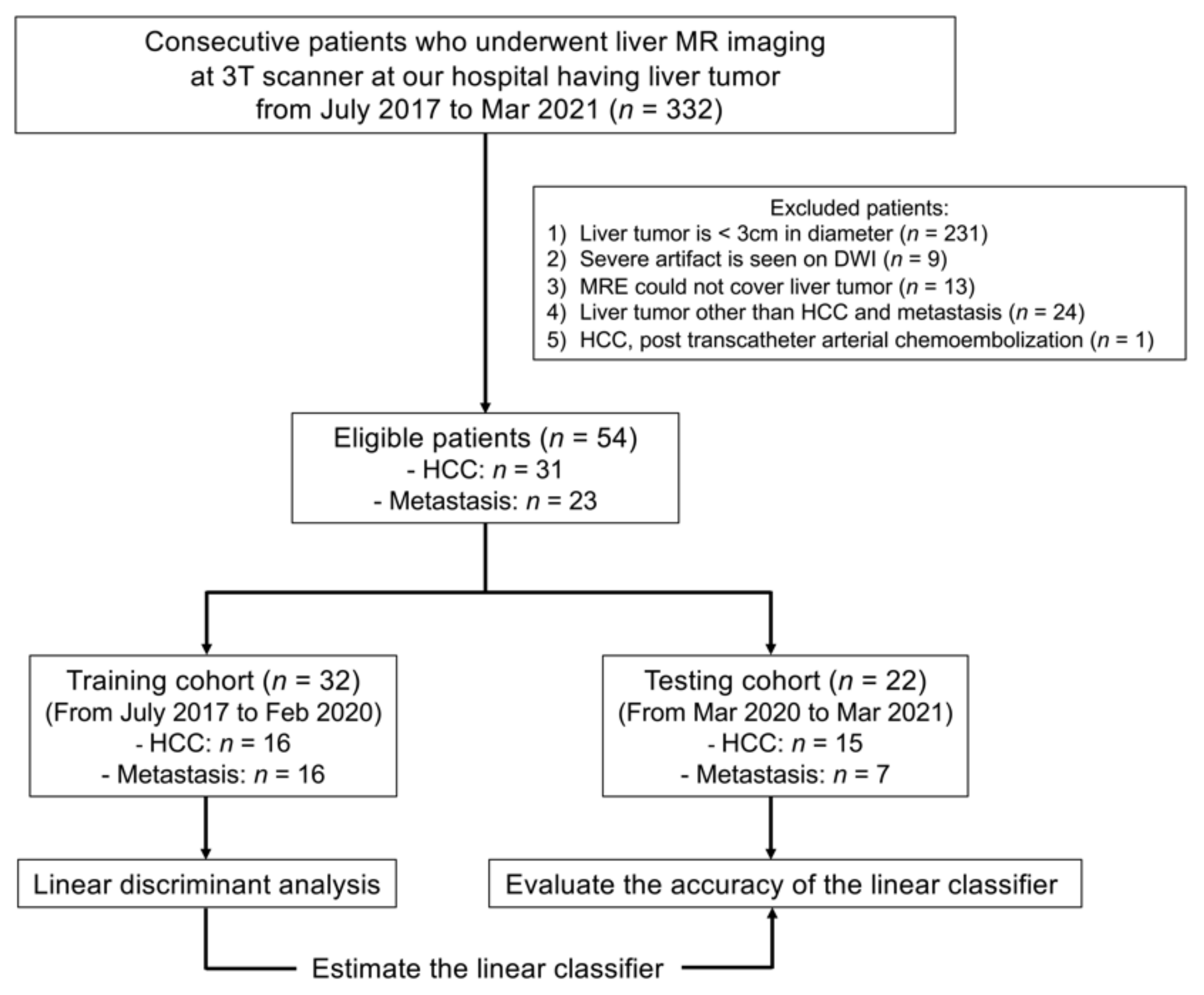
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. MR Imaging Acquisition and Analysis
2.3. MR Elastography
2.4. Diffusion MRI
2.5. Image Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Inter-Reader Reliability
3.3. Diffusion MRI and MRE Shear Modulus
3.4. Relationships between Shear Modulus (µMRE) and ADC Values (sADC and ADC)
3.5. Virtual Shear Modulus (µdiff)
3.6. ROC, Discriminant Analyses and Diagnostic Values
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Bihan, D.; Ichikawa, S.; Motosugi, U. Diffusion and Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MR Imaging-based Virtual Elastography: A Hypothesis-generating Study in the Liver. Radiology 2017, 285, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kromrey, M.L.; Le Bihan, D.; Ichikawa, S.; Motosugi, U. Diffusion-weighted MRI-based Virtual Elastography for the Assessment of Liver Fibrosis. Radiology 2020, 295, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, S.K.; Yin, M.; Glockner, J.F.; Takahashi, N.; Araoz, P.A.; Talwalkar, J.A.; Ehman, R.L. MR Elastography of Liver Tumors: Preliminary Results. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 190, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hennedige, T.P.; Hallinan, J.T.; Leung, F.P.; Teo, L.L.; Iyer, S.; Wang, G.; Chang, S.; Madhavan, K.K.; Wee, A.; Venkatesh, S.K. Comparison of magnetic resonance elastography and diffusion-weighted imaging for differentiating benign and malignant liver lesions. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garteiser, P.; Doblas, S.; Daire, J.L.; Wagner, M.; Leitao, H.; Vilgrain, V.; Sinkus, R.; Van Beers, B.E. MR elastography of liver tumours: Value of viscoelastic properties for tumour characterisation. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 2169–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.W.; Shin, S.; Park, C.M. Differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma from its various mimickers in liver magnetic resonance imaging: What are the tips when using hepatocyte-specific agents? World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyak, V.; Fowler, K.J.; Kamaya, A.; Kielar, A.Z.; Elsayes, K.M.; Bashir, M.R.; Kono, Y.; Do, R.K.; Mitchell, D.G.; Singal, A.G.; et al. Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) Version 2018: Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in At-Risk Patients. Radiology 2018, 289, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, A.D. The cost of developing imaging agents for routine clinical use. Investig. Radiol. 2006, 41, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guglielmo, F.F.; Venkatesh, S.K.; Mitchell, D.G. Liver MR Elastography Technique and Image Interpretation: Pearls and Pitfalls. Radiographics 2019, 39, 1983–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthupillai, R.; Lomas, D.J.; Rossman, P.J.; Greenleaf, J.F.; Manduca, A.; Ehman, R.L. Magnetic resonance elastography by direct visualization of propagating acoustic strain waves. Science 1995, 269, 1854–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.M.; Wang, J.; Chandan, V.S.; Glaser, K.J.; Roberts, L.R.; Ehman, R.L.; Venkatesh, S.K. MR elastography of hepatocellular carcinoma: Correlation of tumor stiffness with histopathology features-Preliminary findings. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 37, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKnight, A.L.; Kugel, J.L.; Rossman, P.J.; Manduca, A.; Hartmann, L.C.; Ehman, R.L. MR elastography of breast cancer: Preliminary results. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2002, 178, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinkus, R.; Tanter, M.; Xydeas, T.; Catheline, S.; Bercoff, J.; Fink, M. Viscoelastic shear properties of in vivo breast lesions measured by MR elastography. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2005, 23, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunevicius, A.; Schregel, K.; Sinkus, R.; Golby, A.; Patz, S. REVIEW: MR elastography of brain tumors. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 25, 102109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackl, C.; Neumann, P.; Gerken, M.; Loss, M.; Klinkhammer-Schalke, M.; Schlitt, H.J. Treatment of colorectal liver metastases in Germany: A ten-year population-based analysis of 5772 cases of primary colorectal adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ratziu, V.; Charlotte, F.; Heurtier, A.; Gombert, S.; Giral, P.; Bruckert, E.; Grimaldi, A.; Capron, F.; Poynard, T. Sampling variability of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagrini, E.; Renzulli, M.; Pecorelli, A.; Stefanini, F.; Piscaglia, F. Imaging of Liver Tumors in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease. Curr. Radiol. Rep. 2014, 2, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Parameter | Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 54 | ||
| Men | 37 | ||
| Women | 17 | ||
| Mean age (years) | 69.4 ± 9.3 years | ||
| Number of liver tumors | 56 | Histology | Imaging features |
| HCC 1 | 31 | 30 | 1 |
| Type of HCC | |||
| Well differentiated | 8 | ||
| Moderately differentiated | 17 | ||
| Poorly differentiated | 2 | ||
| Combined type HCC–ICC 2 | 2 | ||
| Unknown | 2 | ||
| Metastasis | 25 | 10 | 15 |
| Primary tumor | |||
| Colorectal cancer | 17 | ||
| Anal cancer | 1 | ||
| Esophageal cancer | 1 | ||
| Adrenal cancer | 1 | ||
| Neuroendocrine tumor | 1 | ||
| Liposarcoma | 1 | ||
| ICC | 2 | ||
| Submandibular cancer | 1 |
| MR-System | Discovery 750 | ||
| MR Sequence | MRE | DWI (b = 0, 800) | DWI (b = 200, 1500) |
| Respiration pattern | Breath-hold | Respiratory-triggered | Breath-hold |
| Acoustic vibration (Hz) | 60 | N/A | N/A |
| TR/TE (msec) | 600/62.4 | 6000–10,000/50.7 | 3500/60.5 |
| FOV (cm) | 42 × 42 | 36 × 27 | 36 × 27 |
| Matrix | 64 × 64 | 128 × 128 | 64 × 64 |
| Thickness (mm) | 10 | 5 | 7 |
| Slice spacing (mm) | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Bandwidth (kHz) | 250 | 250 | 250 |
| NEX | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Acquisition time | 14 s | 3–4 min | 25 s |
| MR-System | Discovery 750 w | ||
| MR Sequence | MRE | DWI (b = 0, 800) | DWI (b = 200, 1500) |
| Respiration pattern | Breath-hold | Respiratory-triggered | Breath-hold |
| Acoustic vibration (Hz) | 60 | N/A | N/A |
| TR/TE (msec) | 600/63.4 | 6000–10,000/63.7 | 3500/77.9 |
| FOV (cm) | 42 × 42 | 36 × 27 | 36 × 27 |
| Matrix | 64 × 64 | 128 × 128 | 64 × 64 |
| Thickness (mm) | 10 | 5 | 7 |
| Slice spacing (mm) | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Bandwidth (kHz) | 250 | 250 | 250 |
| NEX | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Acquisition time | 14 s | 3–4 min | 25 s |
| MR-System | Signa Architect | ||
| MR Sequence | MRE | DWI (b = 0, 800) | DWI (b = 200, 1500) |
| Respiration pattern | Breath-hold | Respiratory-triggered | Breath-hold |
| Acoustic vibration (Hz) | 60 | N/A | N/A |
| TR/TE (msec) | 600/63.4 | 6000–10,000/63.7 | 3500/77.9 |
| FOV (cm) | 42 × 42 | 36 × 27 | 36 × 27 |
| Matrix | 64 × 64 | 128 × 128 | 64 × 64 |
| Thickness (mm) | 10 | 5 | 7 |
| Slice spacing (mm) | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Bandwidth (kHz) | 250 | 250 | 250 |
| NEX | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Acquisition time | 14 s | 3–4 min | 25 s |
| n | sADC (b = 200, 1500 s/mm2) Mean ± SD (95% C.I.) | ADC (b = 0, 800 s/mm2) Mean ± SD (95% C.I.) | MRE (kPa) Mean ± SD (95% C.I.) | VMRE (kPa) Mean ± SD (95% C.I.) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC | 31 | 0.83 ± 0.11 (0.80−0.87) | 1.14 ± 0.20 (1.06−1.21) | 5.83 ± 2.21 (5.02−6.64) | 3.37 ± 1.35 (2.88−3.87) |
| Metastasis | 25 | 0.86 ± 0.22 (0.77−0.95) | 1.10 ± 0.26 (1.00−1.21) | 11.37 ± 3.54 (9.90−12.83) | 3.02 ± 2.79 (1.86−4.17) |
| µdiff (kPa) = α ln (S200/S1500) + β | ||
|---|---|---|
| α | β | |
| Liver parenchyma | −9.7 ± 0.7 | 13.9 ± 0.7 |
| HCC and Metastases | −8.1 ± 2.2 | 17.2 ± 2.5 |
| HCC | −10.8 ± 2.2 | 17.5 ± 2.4 |
| Metastases | −8.8 ± 1.8 | 21.2 ± 2.1 |
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | PPV | NPV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C (cut-off: 0) | 100% (31/31) | 92% * (23/25) | 96.4% (54/56) | 93.9% (31/33) | 100% (23/23) |
| MRE (kPa) (cut-off: 9.12 kPa) | 93.5% (29/31) | 76% * (19/25) | 85.7% (48/56) | 82.9% (29/35) | 90.5% (19/21) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ota, T.; Hori, M.; Le Bihan, D.; Fukui, H.; Onishi, H.; Nakamoto, A.; Tsuboyama, T.; Tatsumi, M.; Ogawa, K.; Tomiyama, N. Diffusion–Based Virtual MR Elastography of the Liver: Can It Be Extended beyond Liver Fibrosis? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194553
Ota T, Hori M, Le Bihan D, Fukui H, Onishi H, Nakamoto A, Tsuboyama T, Tatsumi M, Ogawa K, Tomiyama N. Diffusion–Based Virtual MR Elastography of the Liver: Can It Be Extended beyond Liver Fibrosis? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(19):4553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194553
Chicago/Turabian StyleOta, Takashi, Masatoshi Hori, Denis Le Bihan, Hideyuki Fukui, Hiromitsu Onishi, Atsushi Nakamoto, Takahiro Tsuboyama, Mitsuaki Tatsumi, Kazuya Ogawa, and Noriyuki Tomiyama. 2021. "Diffusion–Based Virtual MR Elastography of the Liver: Can It Be Extended beyond Liver Fibrosis?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 19: 4553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194553
APA StyleOta, T., Hori, M., Le Bihan, D., Fukui, H., Onishi, H., Nakamoto, A., Tsuboyama, T., Tatsumi, M., Ogawa, K., & Tomiyama, N. (2021). Diffusion–Based Virtual MR Elastography of the Liver: Can It Be Extended beyond Liver Fibrosis? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(19), 4553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194553






