Fibrosis Burden of Missed and Added Populations According to the New Definition of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Rationale for Abdominal Sonography and MRE as Health Check-Up
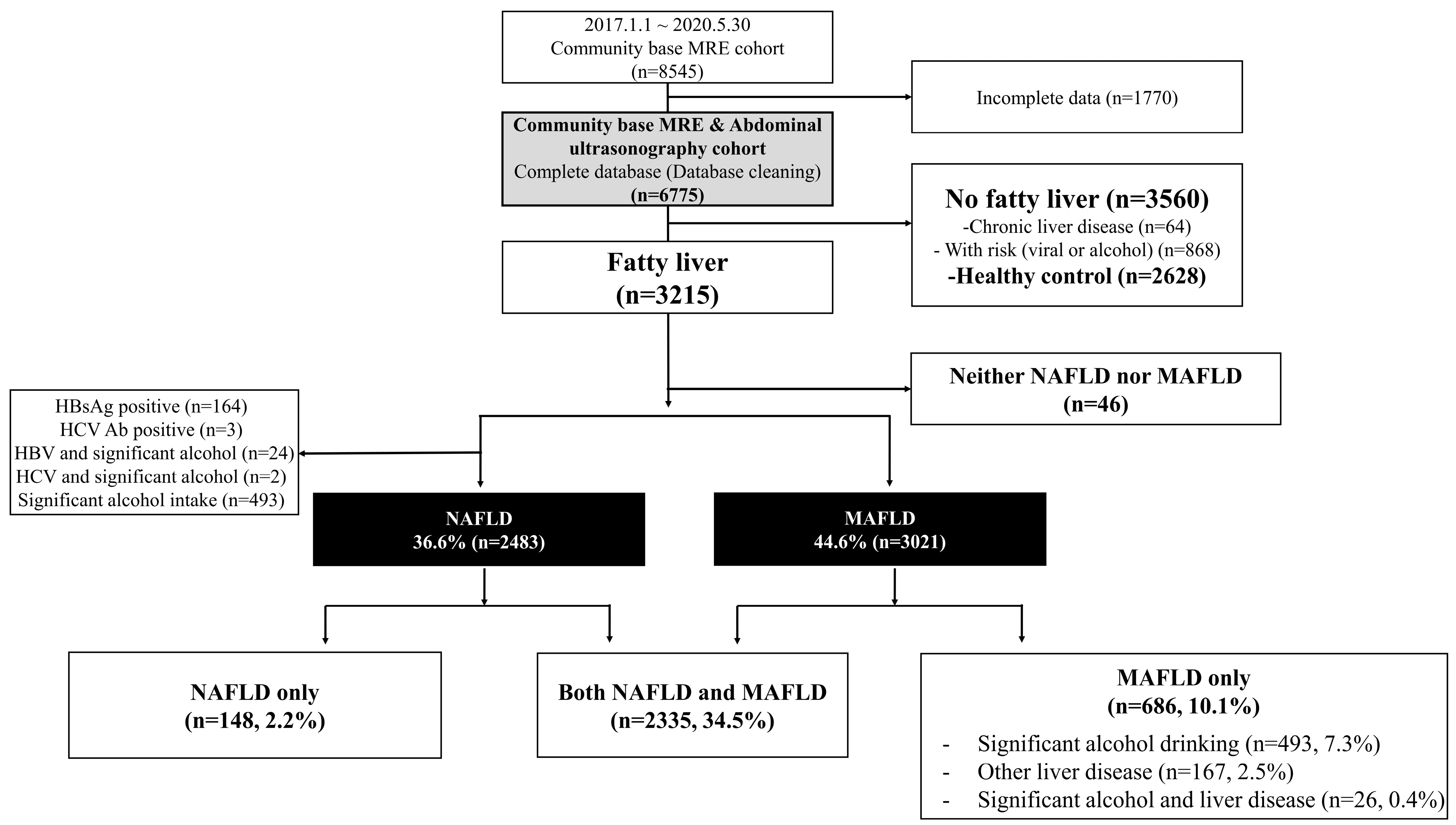
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Clinical Parameters of the Subjects
2.5. Definition of NAFLD and MAFLD
2.6. Assessment of Hepatic Fibrosis Severity
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Entire Population
3.2. Distribution of Fatty Liver According to NAFLD and MAFLD Definitions
3.3. Clinical Characteristics of the MAFLD-Only Group (Added Population)
3.4. Clinical Characteristics of the NAFLD-Only Group (Missed Population)
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis According to Various MRE Cut-Offs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J.; International Consensus, P. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kumar, R.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, S. MAFLD criteria overlooks a number of patients with severe steatosis: Is it clinically relevant? J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1265–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Kumar, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of MAFLD and NAFLD diagnostic criteria in real world. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, S.; Eslam, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nakano, D.; Yoshinaga, S.; Takahashi, H.; Anzai, K.; George, J.; Torimura, T. MAFLD identifies patients with significant hepatic fibrosis better than NAFLD. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 3018–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardullo, S.; Perseghin, G. Prevalence of NAFLD, MAFLD and associated advanced fibrosis in the contemporary United States population. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 1290–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.-Q.; Jin, Y.; Wang, T.-Y.; Zheng, K.I.; Rios, R.S.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Yuan, W.-J.; Zheng, M.-H. MAFLD and risk of CKD. Metabolism 2021, 115, 154433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.I.; Sun, D.Q.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, P.W.; Zheng, M.H. Clinical utility of the MAFLD definition. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 989–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, W.; Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, J.G.; An, J.; Jang, E.S.; Lee, D.H.; Sinn, D.H. A Survey of Liver Cancer Specialists’ Views on the National Liver Cancer Screening Program in Korea. J. Liver Cancer 2020, 20, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.-C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention; national heart, lung, and blood institute; American heart association; world heart federation; international atherosclerosis society; and international association for the study of obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, M.; Talwalkar, J.A.; Glaser, K.J.; Manduca, A.; Grimm, R.C.; Rossman, P.J.; Fidler, J.L.; Ehman, R.L. Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 1207–1213.e1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.; Caussy, C.; Imajo, K.; Chen, J.; Singh, S.; Kaulback, K.; Le, M.-D.; Hooker, J.; Tu, X.; Bettencourt, R. Magnetic resonance vs transient elastography analysis of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and pooled analysis of individual participants. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 630–637.e638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, G.; Zhu, S.; Xiao, X.; Yan, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, G. Comparison of laboratory tests, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance elastography to detect fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Shin, J.; Kim, G.-H.; Park, S.; Ihm, S.-H.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, K.-I.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.-M. 2018 Korean Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the management of hypertension: Part II-diagnosis and treatment of hypertension. Clin. Hypertens. 2019, 25, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Han, J.H.; Kim, D.J. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among Korean adults according to the criteria of the International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 933–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noh, J. The diabetes epidemic in Korea. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 31, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, H.C. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Incident Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Total (n = 6775) | Control (n = 2628) | Neither NAFLD nor MAFLD (n = 46) | NAFLD (n = 2483) | NAFLD Only (n = 148) | MAFLD Only (n = 686) | Both NAFLD and MAFLD (n = 2335) | p ‡ | p § | p ‖ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) † | 46.8 ± 10.3 | 46.4 ± 10.9 | 46.4 ± 10.4 | 47.4 ± 9.8 | 46.5 ± 10.2 | 46.9 ± 9.5 | 47.5 ± 9.8 | 0.875 | 0.228 | 0.636 |
| Male | 5460 (80.6) | 1941 (73.9) | 39 (84.8) | 2229 (89.8) | 116 (78.4) | 622 (90.7) | 2113 (90.5) | 0.222 | 0.487 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1895 (28) | 559 (21.3) | 4 (8.7) | 916 (36.9) | 11 (7.4) | 236 (34.4) | 905 (38.8) | <0.001 | 0.230 | <0.001 |
| Type 2 diabetes | 545 (8) | 103 (3.9) | 0 (0) | 312 (12.9) | 1 (0.7) | 81 (11.8) | 320 (13.7) | 0.043 | 0.435 | <0.001 |
| Alcohol consumption (g/week) † | 94 ± 166 | 53 ± 1 | 335 ± 229 | 34 ± 54 | 37 ± 57 | 304 ± 248 | 34 ± 54 | 0.391 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Number of metabolic risks † | 1.4 ± 1.3 | 0.9 ± 1 | 0.3 ± 0.4 | 2.1 ± 1.3 | 0.3 ± 0.5 | 2.2 ± 1.2 | 2 ± 1.2 | <0.001 | 0.654 | <0.001 |
| Metabolic syndrome | 1517 (22.4) | 243 (9.2) | 0 (0) | 946 (38.1) | 0 (0) | 250 (36.5) | 946 (40.5) | <0.001 | 0.427 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) † | 24.8 ± 3.2 | 23.4 ± 2.6 | 21.8 ± 0.8 | 26.4 ± 3 | 21.6 ± 1.1 | 26.6 ± 2.8 | 26.7 ± 2.8 | <0.001 | 0.076 | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) † | 85.3 ± 9.1 | 81.2 ± 8.1 | 79.3 ± 5.3 | 90 ± 7.6 | 78.9 ± 5.1 | 90.6 ± 7.3 | 90.7 ± 7.2 | 0.001 | 0.085 | <0.001 |
| Total fat mass (kg) † | 18.5 ± 5.8 | 16.2 ± 4.8 | 13.6 ± 2.6 | 21 ± 5.7 | 13.6 ± 2.7 | 21.6 ± 5.7 | 21.5 ± 5.5 | <0.001 | 0.020 | <0.001 |
| Lean mass (kg) † | 49.1 ± 8.9 | 46.9 ± 8.6 | 44.9 ± 8.2 | 51.8 ± 8.3 | 45.2 ± 6.5 | 52.4 ± 8 | 52.2 ± 8.2 | 0.022 | 0.082 | <0.001 |
| Lean mass * 100/BW | 68.6 | 70.1 | 70.5 | 67.1 | 72.5 | 67 | 66.8 | <0.001 | 0.563 | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) † | 116 ± 13 | 114 ± 13 | 112. ± 11 | 119 ± 13 | 113 ± 10 | 117 ± 13 | 119 ± 13 | 0.234 | 0.006 | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) † | 74 ± 9 | 73 ± 9 | 71 ± 7 | 76 ± 9 | 72 ± 7 | 75 ± 9 | 77 ± 9 | 0.103 | 0.015 | <0.001 |
| AST (IU/L) † | 30 ± 19 | 26 ± 13 | 27 ± 9 | 34 ± 22 | 29 ± 22 | 34 ± 25 | 34 ± 22 | 0.016 | 0.846 | 0.022 |
| ALT (IU/L) † | 32 ± 33 | 23 ± 21 | 27 ± 16 | 41 ± 35 | 28 ± 26 | 42 ± 46 | 42 ± 36 | 0.006 | 0.463 | <0.001 |
| GGT (U/L) † | 55 ± 84 | 43 ± 54 | 43 ± 45 | 72 ± 112 | 57 ± 142 | 62 ± 63 | 73 ± 110 | 0.007 | 0.023 | 0.559 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) † | 142 ± 113 | 112 ± 76 | 102 ± 52 | 181 ± 129 | 105 ± 55 | 180 ± 160 | 186 ± 131 | 0.314 | 0.815 | <0.001 |
| HDL (mg/dL) † | 53 ± 12 | 59 ± 13 | 55 ± 11 | 48 ± 10 | 56 ± 12 | 48 ± 10 | 48 ± 10 | 0.772 | 0.465 | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) † | 98 ± 20 | 94 ± 16 | 92 ± 7 | 103 ± 24 | 92 ± 9 | 103 ± 24 | 104 ± 24 | 0.051 | 0.657 | <0.001 |
| Liver stiffness (kPa) † | 2.34 ± 0.56 | 2.26 ± 0.51 | 2.36 ± 0.4 | 2.38 ± 0.54 | 2.26 ± 0.51 | 2.43 ± 0.62 | 2.38 ± 0.54 | 0.99 | 0.014 | 0.002 |
| Significant fibrosis | 554 (8.2) | 153 (5.8) | 2 (4.3) | 219 (8.8) | 9 (6.1) | 90 (13.1) | 210 (9) | 0.896 | 0.001 | 0.016 |
| Advanced fibrosis | 151 (2.2) | 37 (1.4) | 1 (2.2) | 58 (2.3) | 4 (2.7) | 18 (2.6) | 54 (2.3) | 0.204 | 0.663 | 0.957 |
| Cut-Off Values (KPa) | Total (n = 6775) | Control (n = 2628) | NAFLD Group (n = 2483) | NAFLD-Only Group (n = 148) | MAFLD-Only Group (n = 686) | p † | p ‡ | p § | p ‖ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥3.0 | 554 (8.2) | 153 (5.8) | 219 (8.8) | 9 (6.1) | 90 (13.1) | 0.896 | 0.001 | 0.016 | <0.001 |
| ≥3.2 | 340 (5) | 84 (3.2) | 136 (5.5) | 6 (4.1) | 54 (7.9) | 0.556 | 0.019 | 0.103 | <0.001 |
| ≥3.4 | 220 (3.2) | 51 (1.9) | 91 (3.7) | 5 (3.4) | 32 (4.7) | 0.226 | 0.230 | 0.491 | <0.001 |
| ≥3.6 | 151 (2.2) | 37 (1.4) | 58 (2.3) | 4 (2.7) | 18 (2.6) | 0.204 | 0.663 | 0.957 | 0.026 |
| ≥3.8 | 111 (1.6) | 24 (0.9) | 47 (1.9) | 3 (2) | 13 (1.9) | 0.179 | 0.997 | 0.915 | 0.029 |
| ≥4.2 | 72 (1.1) | 17 (0.6) | 29 (1.2) | 2 (1.4) | 10 (1.5) | 0.312 | 0.542 | 0.921 | 0.035 |
| ≥4.6 | 46 (0.7) | 7 (0.3) | 16 (0.6) | 0 (0) | 8 (1.2) | 0.53 | 0.163 | 0.187 | 0.002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.; Yoon, E.L.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, S.; Jun, D.W.; Nah, E.-H. Fibrosis Burden of Missed and Added Populations According to the New Definition of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194625
Park H, Yoon EL, Kim M, Kim J-H, Cho S, Jun DW, Nah E-H. Fibrosis Burden of Missed and Added Populations According to the New Definition of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(19):4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194625
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Huiyul, Eileen L. Yoon, Mimi Kim, Jung-Hwan Kim, Seon Cho, Dae Won Jun, and Eun-Hee Nah. 2021. "Fibrosis Burden of Missed and Added Populations According to the New Definition of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 19: 4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194625
APA StylePark, H., Yoon, E. L., Kim, M., Kim, J. -H., Cho, S., Jun, D. W., & Nah, E. -H. (2021). Fibrosis Burden of Missed and Added Populations According to the New Definition of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(19), 4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194625






