Recurrence of Hepatic Encephalopathy after TIPS: Effective Prophylaxis with Combination of Lactulose and Rifaximin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. TIPS Procedure
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Risk Factors for HE
3.2. Prophylactic Regimens
3.3. Logistic Regression Analysis of Prophylactic Efficacy
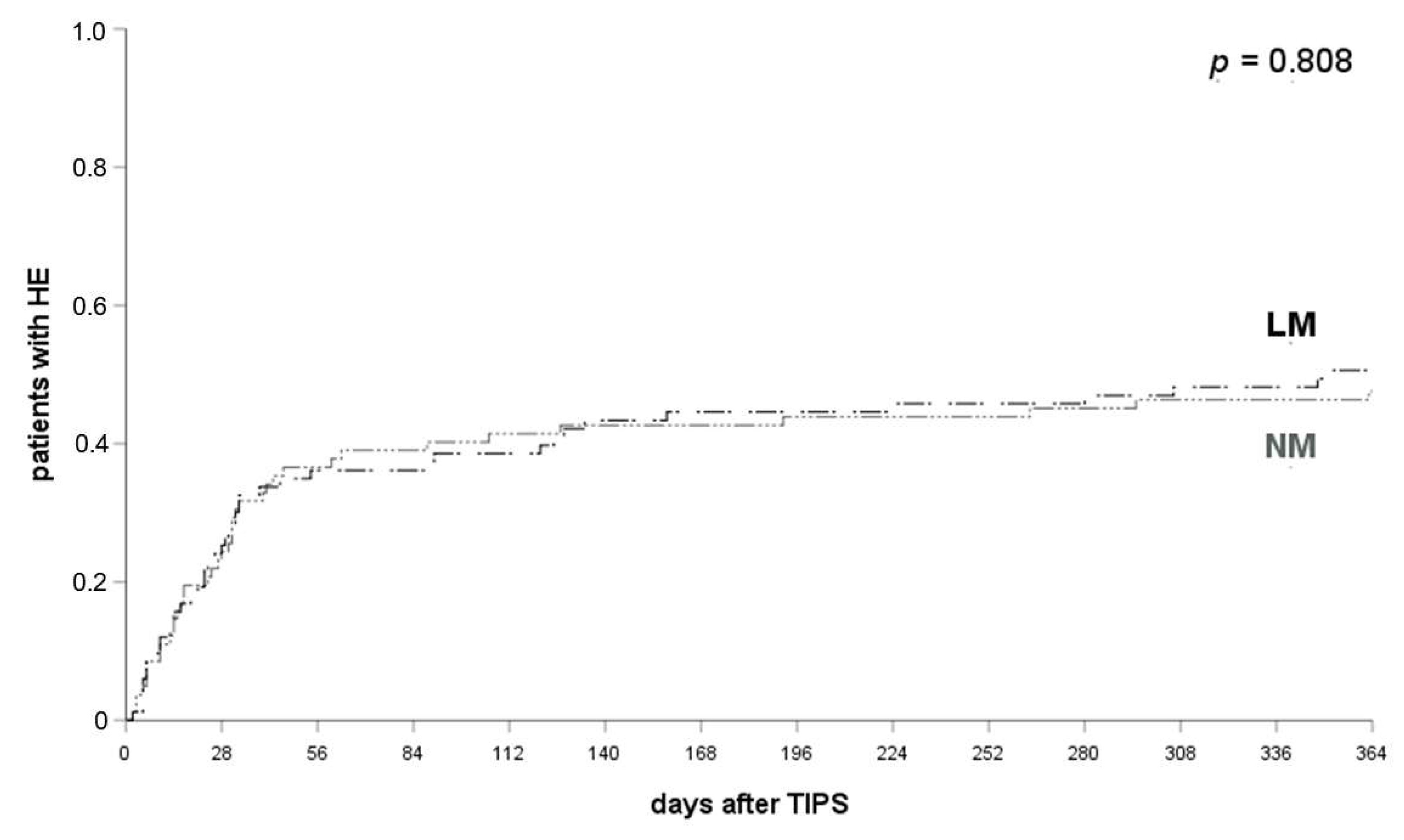
3.4. LM Has No Prophylactic Potency
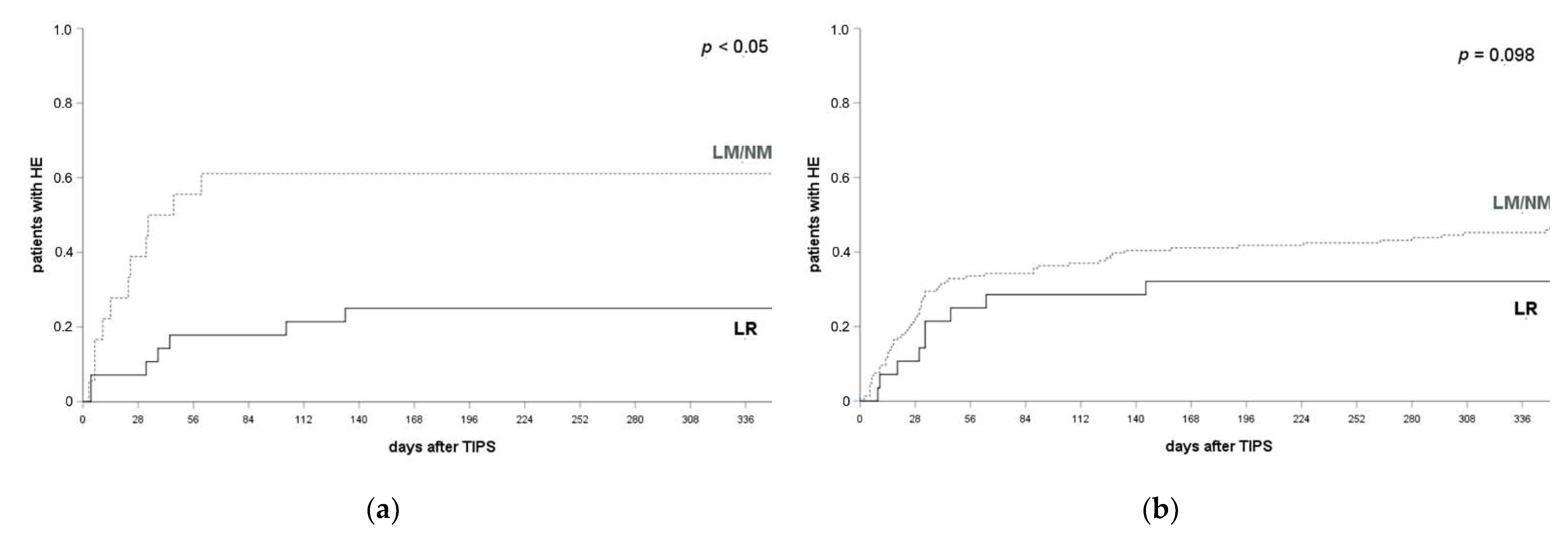
3.5. LR Prevents HE Compared to LM/NM
3.6. LR Prevents HE Recurrence and Not De Novo Occurrence Post TIPS Implantation
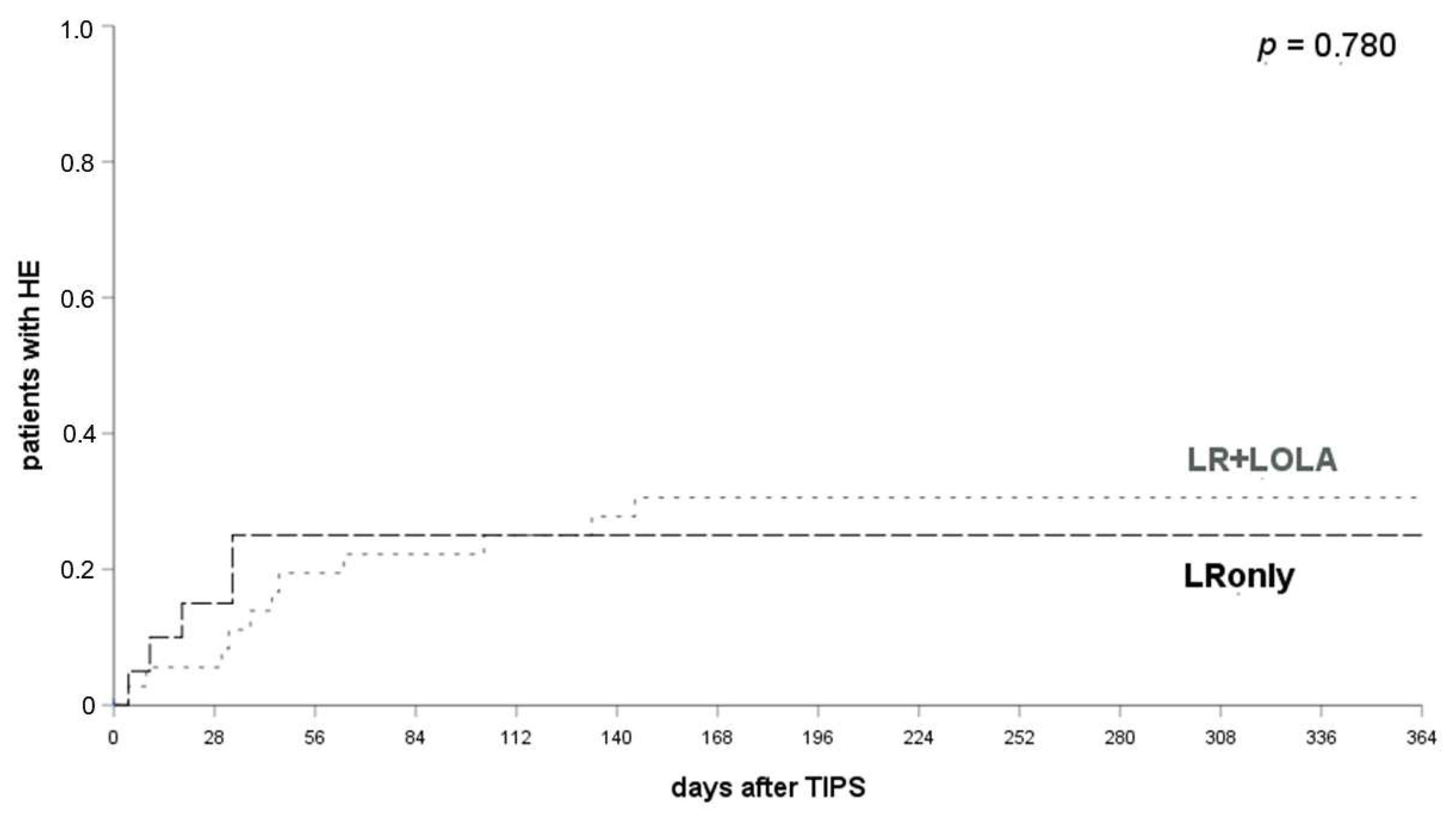
3.7. LOLA Provides No Additional Prophylactic Effect
3.8. Development of Chronic HE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schultheiß, M.; Bettinger, D.; Thimme, R.; Rössle, M. 30 Jahre transjugulärer intrahepatischer portosystemischer Shunt (TIPS)—Rückblick und Perspektive. Z. Gastroenterol. 2020, 58, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, K.; Lerrigo, R.; Liou, I.W.; Ioannou, G.N. Association Between Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt and Survival in Patients With Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Saffo, S.; Mandorfer, M.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Where does TIPS fit in the management of patients with cirrhosis? JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, C.F.; Amodio, P.; Bajaj, J.S.; Dhiman, R.K.; Montagnese, S.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Vilstrup, H.; Jalan, R. Hepatic encephalopathy: Novel insights into classification, pathophysiology and therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1526–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcovich, M.; Zocco, M.A.; Roccarina, D.; Ponziani, F.R.; Gasbarrini, A. Prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: Focusing on gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 6693–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjihambi, A.; Arias, N.; Sheikh, M.; Jalan, R. Hepatic encephalopathy: A critical current review. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilstrup, H.; Amodio, P.; Bajaj, J.; Cordoba, J.; Ferenci, P.; Mullen, K.D.; Weissenborn, K.; Wong, P. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study Of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014, 60, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenborn, K. Hepatic Encephalopathy: Definition, Clinical Grading and Diagnostic Principles. Drugs 2019, 79, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casadaban, L.C.; Parvinian, A.; Minocha, J.; Lakhoo, J.; Grant, C.W.; Ray, C.E.; Knuttinen, M.G.; Bui, J.T.; Gaba, R.C. Clearing the Confusion over Hepatic Encephalopathy After TIPS Creation: Incidence, Prognostic Factors, and Clinical Outcomes. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonio, P.; Discalzi, A.; Calandri, M.; Breatta, A.D.; Bergamasco, L.; Martini, S.; Ottobrelli, A.; Righi, D.; Gandini, G. Incidence of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) according to its severity and temporal grading classification. Radiol. Med. 2017, 122, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, O. Hepatic encephalopathy therapy: An overview. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 1, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, B.C. Management of overt hepatic encephalopathy. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2015, 5, S82–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schindler, P.; Seifert, L.; Masthoff, M.; Riegel, A.; Köhler, M.; Wilms, C.; Schmidt, H.H.; Heinzow, H.; Wildgruber, M. TIPS Modification in the Management of Shunt-Induced Hepatic Encephalopathy: Analysis of Predictive Factors and Outcome with Shunt Modification. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, M.; Yang, Z.; Qi, X.; Fan, D.; Han, G. L-ornithine-l-aspartate for hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnese, S.; Russo, F.P.; Amodio, P.; Burra, P.; Gasbarrini, A.; Loguercio, C.; Marchesini, G.; Merli, M.; Ponziani, F.R.; Riggio, O.; et al. Hepatic encephalopathy 2018: A clinical practice guideline by the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF). Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridola, L.; Riggio, O. Hepatic Encephalopathy in the 21st Century: Still an Emerging Topic. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steib, C.J.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Mayerle, J.; Ricke, J.; Gerbes, A.L.; Meyer, C.; Zipprich, A.; Trebicka, J. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for patients with liver cirrhosis: Survey evaluating indications, standardization of procedures and anticoagulation in 43 German hospitals. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 32, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, L.L.; Görlich, D.; Jansen, C.; Ortmann, O.; Schoster, M.; Praktiknjo, M.; Gu, W.; Schindler, P.; Köhler, M.; Maschmeier, M.; et al. Evaluation of impact of elective invasive examinations in patients with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the long-term follow up. Z. Gastroenterol. 2021, 59, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordoba, J.; Ventura-Cots, M.; Simón-Talero, M.; Amorós, À.; Pavesi, M.; Vilstrup, H.; Angeli, P.; Domenicali, M.; Ginès, P.; Bernardi, M.; et al. Characteristics, risk factors, and mortality of cirrhotic patients hospitalized for hepatic encephalopathy with and without acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.C.; Maharshi, S. Prevention of hepatic encephalopathy recurrence. Clin. Liver Dis. 2015, 5, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tromm, A.; Griga, T.; Greving, I.; Hilden, H.; Hüppe, D.; Schwegler, U.; Micklefield, G.H.; May, B. Orthograde whole gut irrigation with mannite versus paromomycine + lactulose as prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding: Results of a controlled randomized trial. Hepatogastroenterology 2000, 47, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.C.; Sharma, P.; Agrawal, A.; Sarin, S.K. Primary prophylaxis of overt hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: An open labeled randomized controlled trial of lactulose versus no lactulose. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, E.; Lazare, F.; Treem, W.R.; Xu, J.; Iqbal, J.; Pan, X.; Josekutty, J.; Walsh, M.; Anderson, V.; Hussain, M.M.; et al. ω-3 fatty acids prevent hepatic steatosis, independent of PPAR-α activity, in a murine model of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, B.C.; Sharma, P.; Agrawal, A.; Sarin, S.K. Secondary Prophylaxis of Hepatic Encephalopathy: An Open-Label Randomized Controlled Trial of Lactulose Versus Placebo. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, M.; Schuchmann, M. Long-term management of hepatic encephalopathy with lactulose and/or rifaximin: A review of the evidence. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 31, 434–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, R.F.; McPhail, M.J.W. l-Ornithine l-Aspartate (LOLA) for Hepatic Encephalopathy in Cirrhosis: Results of Randomized Controlled Trials and Meta-Analyses. Drugs 2019, 79, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Les, I.; Doval, E.; Martinez, R.G.; Planas, M.; Cárdenas, G.; Gómez, P.; Flavià, M.; Jacas, C.; Mínguez, B.; Vergara, M.; et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids supplementation in patients with cirrhosis and a previous episode of hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varakanahalli, S.; Sharma, B.C.; Srivastava, S.; Sachdeva, S.; Dahale, A.S. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis of liver: A double-blind randomized controlled trial of l-ornithine l-aspartate versus placebo. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.; He, C.; Yin, Z.; Niu, J.; Wang, Z.; Qi, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, Z.; Guo, W.; Tie, J.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: L-ornithine-l-aspartate reduces significantly the increase of venous ammonia concentration after TIPSS. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riggio, O.; Masini, A.; Efrati, C.; Nicolao, F.; Angeloni, S.; Salvatori, F.M.; Bezzi, M.; Attili, A.F.; Merli, M. Pharmacological prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: A randomized controlled study. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, K.; Schaapman, J.J.; Nevens, F.; Verbeek, J.; Coenen, S.; Cuperus, F.J.C.; Kramer, M.; Tjwa, E.T.T.L.; Mostafavi, N.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.W.; et al. Prevention of hepatic encephalopathy by administration of rifaximin and lactulose in patients with liver cirrhosis undergoing placement of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS): A multicentre randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial (PEARL trial). BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020, 7, e000531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinger, D.; Sturm, L.; Pfaff, L.; Hahn, F.; Kloeckner, R.; Volkwein, L.; Praktiknjo, M.; Lv, Y.; Han, G.; Huber, J.P.; et al. Refining prediction of survival after TIPS with the novel Freiburg index of post-TIPS survival. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhang, F.; Guo, H.; Peng, C.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zou, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhuge, Y. A nomogram to predict the risk of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in Cirrhotic Patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Gan, C.; Wei, B.; Wang, Z.D.; Li, X.D.; Qian, S.J.; Huan, H.; Zhang, L.H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.L.; et al. Risk factors for overt hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation in patients with liver cirrhosis. J. Dig. Dis. 2021, 22, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamm, S.L. Complications of Cirrhosis in Primary Care: Recognition and Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 356, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, S.; Lattanzi, B.; Torrisi, S.; Greco, F.; Farcomeni, A.; Gioia, S.; Merli, M.; Riggio, O. Sarcopenia Is Risk Factor for Development of Hepatic Encephalopathy After Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Placement. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 934–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmassaoud, A.; Roccarina, D.; Arico, F.; Leandro, G.; Yu, B.; Cheng, F.; Yu, D.; Patch, D.; Tsochatzis, E. Sarcopenia Does Not Worsen Survival in Patients With Cirrhosis Undergoing Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt for Refractory Ascites. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter |
All Patients % (Total Number) or Median/Mean (SD or Range) |
HE Prior TIPS % (Total Number) or Median/Mean (SD or Range) |
No HE Prior TIPS % (Total Number) or Median/Mean (SD or Range) | p -Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n° of patients | 233 | 21.0 (49) | 79.0 (184) | - |
| sex | 0.798 | |||
| male | 60.9 (42) | 59.2 (29) | 61.4 (113) | |
| female | 39.1 (91) | 40.8 (20) | 38.6 (71) | |
| age (median, range, in y) | 58 (19–80) | 59 (41–77) | 58 (19–80) | 0.911 |
| PTFE-covered stent | 78.1 (182 | 77.6 (38) | 78.2 (144) | 0.944 |
| effective stent-diameter | 8.0 (6–12) | 8.0 (8–12) | 8.0 (6–12) | 0.984 |
| HE prior TIPS | 21.0 (49) | 100 (49) | - | - |
| HE grade | ||||
| I | 77.6 (38) | 77.6 (38) | ||
| II | 16.3 (8) | 16.3 (8) | ||
| III | 6.1 (3) | 6.1 (3) | ||
| IV | - | - | ||
| HE prophylaxis | ||||
| NM | 35.6 (83) | 16.3 (8) | 40.8 (75) | 0.002 |
| LM | 2.1 (5) | 20.4 (10) | 40.8 (75) | 0.298 |
| RM | 36.5 (85) | 4.1 (2) | 1.6 (3) | 0.008 |
| LR | 25.3 (59) | 59.2 (29) | 16.3 (30) | <0.001 |
| LR + LOLA | 16.3 (38) | 42.9 (21) | 9.2 (17) | <0.001 |
| LRonly | 9.0 (21) | 16.3 (8) | 7.1 (13) | 0.046 |
| etiology of liver disease | ||||
| alcoholic | 51.5 (120) | 55.1 (27) | 50.8 (93) | 0.594 |
| viral | 9.4 (22) | 8.2 (4) | 9.8 (18) | |
| NAFLD | 8.6 (20) | 10.2 (5) | 8.2 (15) | |
| other | 30.5 (71) | 26.5 (13) | 31.1 (57) | |
| Child–Pugh grade | <0.001 | |||
| A | 27.0 (63) | 8.2 (4) | 32.1 (59) | |
| B | 61.5 (143) | 65.3 (32) | 60.3 (111) | |
| C | 11.5 (27) | 26.5 (13) | 7.6 (14) | |
| indication for TIPS | ||||
| ascites | 49.4 (115) | 55.1 (27) | 47.8 (88) | 0.894 |
| variceal bleeding | 33.0 (77) | 20.4 (10) | 36.4 (67) | |
| secondary prophylaxis | 84.4 (65) | 80.0 (8) | 85.1 (57) | |
| pre-emptive TIPS | 9.1 (7) | 10.0 (1) | 9.0 (6) | |
| emergency TIPS | 6.5 (5) | 10.0 (1) | 5.9 (4) | |
| both | 17.6 (41) | 24.5 (12) | 15.8 (29) | |
| LTX prior TIPS | 4.7 (11) | 2.0 (1) | 5.4 (10) | 0.319 |
| HE after TIPS | 54.5 (127) | 61.2 (30) | 52.7 (97) | 0.337 |
| HE grade | ||||
| I | 60.6 (77) | 76.7 (23) | 55.7 (54) | 0.521 |
| II | 19.7 (25) | 13.3 (4) | 21.6 (21) | |
| III | 14.2 (18) | 3.3 (1) | 17.5 (17) | |
| IV | 5.5 (7) | 6.6 (2) | 5.2 (5) | |
| TIPS revision | 3.0 (7) | 2.0 (1) | 3.3 (6) | 0.649 |
| TIPS occlusion | 0.9 (2) | - | 1.1 (2) | 0.461 |
| diabetes | 28.8 (67) | 28.6 (14) | 28.8 (53) | 0.940 |
| MELD-score | 14 (7.2) | 18.9 (6.4) | 13.6 (7.0) | <0.001 |
| bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.30 (2.46) | 2.0 (4.23) | 1.20 (1.31) | <0.001 |
| albumin (g/dL) | 3.23 (0.64) | 3.16 (0.56) | 3.32 (0.66) | 0.287 |
| creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.33 (0.88) | 1.61 (1.27) | 1.21 (0.67) | 0.009 |
| INR | 1.31 (0.34) | 1.43 (0.30) | 1.28 (0.35) | 0.053 |
| platelets (ths/µL) | 139 (102) | 131 (81) | 143 (110) | 0.892 |
| hemoglobin (mg/dL) | 10.1 (4.8) | 9.2 (3.6) | 10.4 (2.2) | 0.002 |
| PSG (mmHg) | 18.0 (5.8) | 19.0 (5.8) | 16.9 (5.7) | 0.044 |
| Parameter | ß | SE | HR | 95% CI for HR | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate Model | |||||
| age | 0.035 | 0.013 | 1.035 | 1.010–1.061 | 0.006 |
| HE prior TIPS | 1.446 | 0.448 | 4.245 | 1.765–10.212 | 0.001 |
| PSG before TIPS | 0.033 | 0.026 | 1.034 | 0.983–1.087 | 0.191 |
| PSG after TIPS | −0.008 | 0.042 | 0.992 | 0.913–1.078 | 0.847 |
| ∆PSG | −0.062 | 0.034 | 0.940 | 0.879–1.005 | 0.171 |
| bilirubin | 0.146 | 0.140 | 1.157 | 0.878–1.523 | 0.300 |
| INR | −0.948 | 0.697 | 0.387 | 0.099–1.519 | 0.387 |
| creatinine | 0.074 | 0.246 | 1.076 | 0.664–1.744 | 0.765 |
| hemoglobin | −0.027 | 0.073 | 0.973 | 0.843–1.124 | 0.711 |
| platelet count | 0.002 | 0.002 | 1.002 | 0.998–1.006 | 0.260 |
| diabetes | 0.209 | 0.157 | 1.233 | 0.906–1.678 | 0.184 |
| indication | 0.325 | 0.233 | 1.384 | 0.877–2.185 | 0.162 |
| etiology of liver disease | −0.026 | 0.065 | 0.974 | 0.857–1.107 | 0.687 |
| Child–Pugh score | 0.118 | 0.275 | 1.126 | 0.657–1.929 | 0.666 |
| effective stent-dameter | 0.136 | 0.119 | 1.146 | 0.907–1.447 | 0.253 |
| multivariate model | |||||
| age | 0.038 | 0.013 | 1.039 | 1.013–1.066 | 0.003 |
| HE prior TIPS | 1.307 | 0.449 | 3.695 | 1.531–8.917 | 0.004 |
| HE Prior TIPS | No HE Prior TIPS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regimen | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| 1 month post TIPS | ||||||
| LM | 0.171 | 0.020–1.436 | 0.153 | 1.018 | 0.516–2.011 | 1.000 |
| LR | 0.048 | 0.006–0.366 | 0.003 | 0.490 | 0.177–1.362 | 0.234 |
| LRonly | 0.057 | 0.004–0.817 | 0.041 | 0.940 | 0.258–3.430 | 1.000 |
| LR + LOLA | 0.044 | 0.005–0.400 | 0.005 | 0.251 | 0.053–1.185 | 0.119 |
| 3 months post TIPS | ||||||
| LM | 0.133 | 0.011–1.611 | 0.145 | 1.036 | 0.530–2.023 | 1.000 |
| LR | 0.042 | 0.004–0.429 | 0.003 | 0.647 | 0.249–1.678 | 0.483 |
| LR only | 0.024 | 0.001–0.468 | 0.010 | 0.768 | 0.211–2.793 | 0.759 |
| LR + LOLA | 0.051 | 0.005–0.563 | 0.009 | 0.558 | 0.162–1.929 | 0.397 |
| 12 months post TIPS implantation | ||||||
| LM | 0.111 | 0.009–1.309 | 0.134 | 1.086 | 0.566–2.083 | 0.869 |
| LR | 0.056 | 0.006–0.545 | 0.006 | 0.450 | 0.181–1.121 | 0.121 |
| LRonly | 0.024 | 0.001–0.468 | 0.010 | 0.500 | 0.138–1.809 | 0.358 |
| LR + LOLA | 0.071 | 0.007–0.729 | 0.024 | 0.417 | 0.133–1.304 | 0.177 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seifert, L.L.; Schindler, P.; Schoster, M.; Weller, J.F.; Wilms, C.; Schmidt, H.H.; Maschmeier, M.; Masthoff, M.; Köhler, M.; Heinzow, H.; et al. Recurrence of Hepatic Encephalopathy after TIPS: Effective Prophylaxis with Combination of Lactulose and Rifaximin. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10204763
Seifert LL, Schindler P, Schoster M, Weller JF, Wilms C, Schmidt HH, Maschmeier M, Masthoff M, Köhler M, Heinzow H, et al. Recurrence of Hepatic Encephalopathy after TIPS: Effective Prophylaxis with Combination of Lactulose and Rifaximin. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(20):4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10204763
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeifert, Leon Louis, Philipp Schindler, Martin Schoster, Jan Frederic Weller, Christian Wilms, Hartmut H. Schmidt, Miriam Maschmeier, Max Masthoff, Michael Köhler, Hauke Heinzow, and et al. 2021. "Recurrence of Hepatic Encephalopathy after TIPS: Effective Prophylaxis with Combination of Lactulose and Rifaximin" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 20: 4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10204763
APA StyleSeifert, L. L., Schindler, P., Schoster, M., Weller, J. F., Wilms, C., Schmidt, H. H., Maschmeier, M., Masthoff, M., Köhler, M., Heinzow, H., & Wildgruber, M. (2021). Recurrence of Hepatic Encephalopathy after TIPS: Effective Prophylaxis with Combination of Lactulose and Rifaximin. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(20), 4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10204763







