Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Treatment of Patients with Cleft Lip, Alveolus, and Palate: An Executive Summary
Abstract
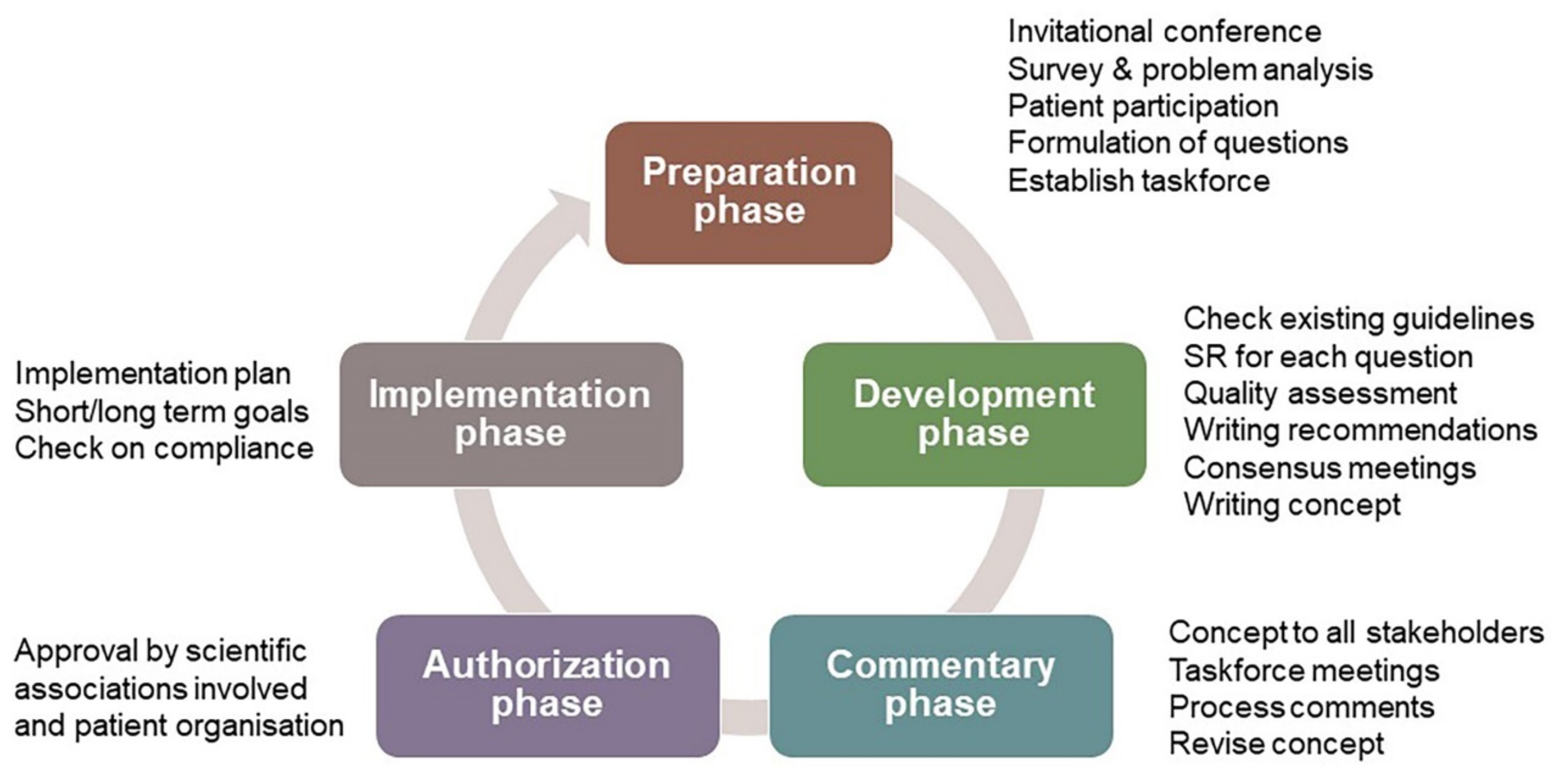
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Database Search
3.2. Clinical Questions and Recommendations
3.2.1. Genetic Testing
3.2.2. Administering Food
3.2.3. Lip and Palate Surgical Repair
Timing of Repair
Repair Technique
3.2.4. Hearing Problems
3.2.5. Hypernasality
Diagnosis
Surgical Treatment
3.2.6. Bone Grafting Procedures
Timing of Bone Grafts
Bone Graft Technique
3.2.7. Orthodontic Treatment
Nasoalveolar Molding (NAM)
Maxillary Protraction
Orthodontic Retention
3.2.8. Psychosocial Guidance
3.2.9. Dentistry
3.2.10. Osteotomy versus Distraction Osteogenesis
3.2.11. Rhinoplasty
4. Discussion
4.1. Guideline Principles
4.2. Findings
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luijsterburg, A.J.M.; Vermeij-Keers, C. Ten years recording common oral clefts with a new descriptive system. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2011, 48, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozendaal, A.M.; Luijsterburg, A.J.M.; Mohangoo, A.D.; Ongkosuwito, E.M.; Anthony, S.; Vermeij-Keers, C. Validation of the NVSCA registry for common oral clefts: Study design and first results. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2010, 47, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozendaal, A.M.; Luijsterburg, A.J.M.; Ongkosuwito, E.M.; Van Den Boogaard, M.J.H.; De Vries, E.; Hovius, S.E.R.; Vermeij-Keers, C. Delayed diagnosis and underreporting of congenital anomalies associated with oral clefts in the Netherlands: A national validation study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2012, 65, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.J.; Marazita, M.L.; Beaty, T.H.; Murray, J.C. Cleft lip and palate: Understanding genetic and environmental influences. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leslie, E.J.; Marazita, M.L. Genetics of cleft lip and cleft palate. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2013, 163, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rittler, M.; Cosentino, V.; López-Camelo, J.S.; Murray, J.C.; Wehby, G.; Castilla, E.E. Associated anomalies among infants with oral clefts at birth and during a 1-year follow-up. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2011, 155, 1588–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setó-Salvia, N.; Stanier, P. Genetics of cleft lip and/or cleft palate: Association with other common anomalies. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 57, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, E.J.; Koboldt, D.C.; Kang, C.J.; Ma, L.; Hecht, J.T.; Wehby, G.L.; Christensen, K.; Czeizel, A.E.; Deleyiannis, F.W.B.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. IRF6 mutation screening in non-syndromic orofacial clefting: Analysis of 1521 families. Clin. Genet. 2016, 90, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brito, L.A.; Yamamoto, G.L.; Melo, S.; Malcher, C.; Ferreira, S.G.; Figueiredo, J.; Alvizi, L.; Kobayashi, G.S.; Naslavsky, M.S.; Alonso, N.; et al. Rare Variants in the Epithelial Cadherin Gene Underlying the Genetic Etiology of Nonsyndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarse, W.; Rozendaal, A.M.; Pajkrt, E.; Vermeij-Keers, C.; van der Molen, A.B.M.; van den Boogaard, M.J.H. A systematic review of associated structural and chromosomal defects in oral clefts: When is prenatal genetic analysis indicated? J. Med. Genet. 2012, 49, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, F.; Oti, M.; Dixon, J.; Carels, C.E.L.; Rubini, M.; Zhou, H. Systematic analysis of copy number variants of a large cohort of orofacial cleft patients identifies candidate genes for orofacial clefts. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basha, M.; Demeer, B.; Revencu, N.; Helaers, R.; Theys, S.; Bou Saba, S.; Boute, O.; Devauchelle, B.; Francois, G.; Bayet, B.; et al. Whole exome sequencing identifies mutations in 10% of patients with familial non-syndromic cleft lip and/or palate in genes mutated in well-known syndromes. J. Med. Genet. 2018, 55, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaty, T.H.; Marazita, M.L.; Leslie, E.J. Genetic factors influencing risk to orofacial clefts: Today’s challenges and tomorrow’s opportunities. F1000Research 2016, 5, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L.L.; Cox, T.C.; Moreno Uribe, L.M.; Zhu, Y.; Richter, C.T.; Nidey, N.; Standley, J.M.; Deng, M.; Blue, E.; Chong, J.X.; et al. Mutations in the Epithelial Cadherin-p120-Catenin Complex Cause Mendelian Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bessell, A.; Hooper, L.; Shaw, W.C.; Reilly, S.; Reid, J.; Glenny, A.-M. Feeding interventions for growth and development in infants with cleft lip, cleft palate or cleft lip and palate. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, M.; Chopra, R.; Bansal, K.; Marwaha, M. Role of obturators and other feeding interventions in patients with cleft lip and palate: A review. Eur. Arch. Paediatr. Dent. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augsornwan, D.; Surakunprapha, P.; Pattangtanang, P.; Pongpagatip, S.; Jenwitheesu, K.; Chowchuen, B.; Augsornwan, D.; Surakunprapha, P.; Pattangtanang, P.; Pongpagatip, S.; et al. Comparison of wound dehiscence and parent’s satisfaction between spoon/syringe feeding and breast/bottle feeding in patients with cleft lip repair. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2013, 96 (Suppl. S4), S61–S70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.; Lindup, M.; Wright, S.; Naik, M.; Dhesi, R.; Howard, R.; Sommerlad, B.; Kangesu, L.; Sury, M. Does nasogastric feeding reduce distress after cleft palate repair in infants? Nurs. Child. Young People 2013, 25, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ize-Iyamu, I.N.; Saheeb, B.D. Feeding intervention in cleft lip and palate babies: A practical approach to feeding efficiency and weight gain. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Lee, T.J.; Chae, S.W. Effect of unrestricted bottle-feeding on early postoperative course after cleft palate repair. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2009, 20, 1886–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, W.B. Weight gain and feeding in the neonate with cleft: A three-center study. Cleft Palate J. 1988, 25, 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, L.; Jacobsen, C.; Humenczuk, M.; Singhal, V.K.; Moore, D.; Bell, H. The effects of lactation education and a prosthetic obturator appliance on feeding efficiency in infants with cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2001, 38, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, W.C.; Semb, G.; Nelson, P.; Brattström, V.; Mølsted, K.; Prahl-Andersen, B.; Gundlach, K.K.H. The Eurocleft project 1996-2000: Overview. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 29, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, I.Y.; Liao, Y.F. The effect of 1-stage versus 2-stage palate repair on facial growth in patients with cleft lip and palate: A review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundlach, K.K.H.; Bardach, J.; Filippow, D.; Stahl-De Castrillon, F.; Lenz, J.H. Two-stage palatoplasty, is it still a valuable treatment protocol for patients with a cleft of lip, alveolus, and palate? J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 41, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, R.E.; Randall, P.; Wang, P.; Jawad, A.F.; Duran, M.; Huang, K.; Solot, C.; Cohen, M.; LaRossa, D. Cleft palate repair at 3 to 7 months of age. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2000, 105, 2127–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landheer, J.A.; Breugem, C.C.; Van Mink Der Molen, A.B. Fistula incidence and predictors of fistula occurrence after cleft palate repair: Two-stage closure versus one-stage closure. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2010, 47, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.F.; Cole, T.J.; Mars, M. Hard palate repair timing and facial growth in unilateral cleft lip and palate: A longitudinal study. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2006, 43, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolet, P.J.P.M.; Katsaros, C.; Van’t Hof, M.A.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. Treatment outcome in unilateral cleft lip and palate evaluated with the GOSLON yardstick: A meta-analysis of 1236 patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 116, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fudalej, P.; Katsaros, C.; Bongaarts, C.; Dudkiewicz, Z.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. Dental arch relationship in children with complete unilateral cleft lip and palate following one-stage and three-stage surgical protocols. Clin. Oral Investig. 2011, 15, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ysunza, A.; Pamplona, M.C.; Mendoza, M.; García-Velasco, M.; Aguilar, M.P.; Guerrero, M.E. Speech outcome and maxillary growth in patients with unilateral complete cleft lip/palate operated on at 6 versus 12 months of age. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1998, 102, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartzela, T.; Katsaros, C.; Shaw, W.C.; Rønning, E.; Rizell, S.; Bronkhorst, E.; Okada, T.O.; Pinheiro, F.H.D.S.L.; Dominguez-Gonzalez, S.; Hagberg, C.; et al. A longitudinal three-center study of dental arch relationship in patients with bilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2010, 47, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, B.; Russell, J.; McMahon, S.; Pigott, R. Results of Randomized Controlled Trial of Soft Palate First versus Hard Palate First Repair in Unilateral Complete Cleft Lip and Palate. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2006, 43, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, W.N.; Seagle, M.B.; Pegoraro-Krook, M.I.; Souza, T.V.; Garla, L.; Silva, M.L.; MacHado Neto, J.S.; Dutka, J.C.R.; Nackashi, J.; Boggs, S.; et al. Prospective clinical trial comparing outcome measures between furlow and von langenbeck palatoplasties for UCLP. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2011, 66, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friede, H.; Enemark, H. Long-term evidence for favorable midfacial growth after delayed hard palate repair in UCLP patients. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2001, 38, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.; Ghandour, H. Comparative study between V-Y pushback technique and Furlow technique in cleft soft palate repair. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2011, 34, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, K.O.; Dieckmann, A.; Dieckmann, O.; Lenz, J.H.; Gundlach, K.K.H. Veloplasty Using the Wave-Line Technique Versus Classic Intravelar Veloplasty. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2004, 41, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobbelaar, A.O.; Hudso, D.A.; Fernandes, D.B.; Lentin, R. Speech results after repair of the cleft soft palate. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1995, 95, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.E.; Askar, S. Does palatal muscle reconstruction affect the functional outcome of cleft palate surgery? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 119, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, P.D.; Cohen, D.T.; Muntz, H.R.; Grames, L.M.; Pilgram, T.K.; Marsh, J.L. Long-term stability of postpalatoplasty perceptual speech ratings: A prospective study. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1999, 43, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWilliams, B.J.; Randall, P.; LaRossa, D.; Cohen, S.; Yu, J.; Cohen, M.; Solot, C. Speech characteristics associated with the Furlow palatoplasty as compared with other surgical techniques. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1996, 98, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.L.; Tsao, Y.H.; Cheng, H.M.; Lien, C.F.; Hsu, C.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Shiao, A.S. Grommets for otitis media with effusion in children with cleft palate: A systematic review. Pediatrics 2014, 134, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ponduri, S.; Bradley, R.; Ellis, P.E.; Brookes, S.T.; Sandy, J.R.; Ness, A.R. The management of otitis media with early routine insertion of grommets in children with cleft palate-a systematic review. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2009, 46, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Specialisten FM Otitis Media Bij Kinderen in de tweede Lijn. Available online: https://richtlijnendatabase.nl/index.php/richtlijn/otitis_media_bij_kinderen_in_de_tweede_lijn/otitis_media_bij_kinderen_-_korte_beschrijving.html (accessed on 10 July 2021).
- Gani, B.; Kinshuck, A.J.; Sharma, R. A Review of Hearing Loss in Cleft Palate Patients. Int. J. Otolaryngol. 2012, 2012, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maheshwar, A.A.; Milling, M.A.P.; Kumar, M.; Clayton, M.I.; Thomas, A. Use of hearing aids in the management of children with cleft palate. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2002, 66, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, S.; Payne, K.; Fenwick, E.; O’Brien, K.; Bruce, I. A model-based cost-effectiveness analysis of a grommets-led care pathway for children with cleft palate affected by otitis media with effusion. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2015, 16, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klintö, K.; Salameh, E.K.; Svensson, H.; Lohmander, A. The impact of speech material on speech judgement in children with and without cleft palate. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2011, 46, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askar, S.M.; Abou-Elsaad, T.S. A speech nasoendoscopy-based surgeon’s decision for correction of velopharyngeal insufficiency following adenotonsillectomy. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2014, 271, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnell, M.P. Instrumental assessment of velopharyngeal closure for speech. Semin. Speech Lang. 2011, 32, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummer, A.W. Perceptual assessment of resonance and velopharyngeal function. Semin. Speech Lang. 2011, 32, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, A.; Hönig, F.; Bocklet, T.; Nöth, E.; Stelzle, F.; Nkenke, E.; Schuster, M. Automatic detection of articulation disorders in children with cleft lip and palate. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 126, 2589–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuster, M.; Maier, A.; Haderlein, T.; Nkenke, E.; Wohlleben, U.; Rosanowski, F.; Eysholdt, U.; Nöth, E. Evaluation of speech intelligibility for children with cleft lip and palate by means of automatic speech recognition. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 70, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Sell, D.; Sweeney, T.; Harding-Bell, A.; Williams, A. The cleft audit protocol for speech-augmented: A validated and reliable measure for auditing cleft speech. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2006, 43, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åbyholm, F.; D’Antonio, L.; Ward, S.L.D.; Kjøll, L.; Saeed, M.; Shaw, W.C.; Sloan, G.; Whitby, D.; Worthington, H.; Wyatt, R. Pharyngeal flap and sphincterplasty for velopharyngeal insufficiency have equal outcome at 1 year postoperatively: Results of a randomized trial. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2005, 42, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ysunza, A.; Pamplona, M.C.; Molina, F.; Drucker, M.; Felemovicius, J.; Ramírez, E.; Patiño, C. Surgery for speech in cleft palate patients. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2004, 68, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawashdeh, M.A.; Al Nimri, K.S. Outcome of secondary alveolar bone grafting before and after eruption of the canine in Jordanian patients with cleft lip and palate. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2007, 18, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freihofer, H.P.M.; Borstlap, W.A.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M.; Voorsmit, R.A.C.A.; van Damme, P.A.; Heidbüchel, K.L.W.M.; Borstlap-Engels, V.M.F. Timing and transplant materials for closure of alveolar clefts. A clinical comparison of 296 cases. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 1993, 21, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.L.; Fu, M.K.; Ma, L. Long-term outcome of secondary alveolar bone grafting in patients with various types of cleft. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 44, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.L.; Kauffmann, D.; St., John, D.; Wang, D.; Grant, J.H.; Waite, P.D. Retrospective Review of 99 Patients With Secondary Alveolar Cleft Repair. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, K.; Nozoe, E.; Maeda, A.; Hirahara, N.; Okawachi, T.; Miyawaki, S.; Nakamura, N. Original article outcome following secondary autogenous bone grafting before and after canine eruption in patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2014, 51, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindet-Pedersen, S. Comparative study of secondary and late secondary bone-grafting in patients with residual cleft defects. Short-term evaluation. Int. J. Oral Surg. 1985, 14, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempf, R.; Teltzrow, T.; Kramer, F.J.; Hausamen, J.E. Alveolar bone grafting in patients with complete clefts: A comparative study between secondary and tertiary bone grafting. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2002, 39, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trindade-Suedam, I.K.; Da Silva Filho, O.G.; Carvalho, R.M.; De Souza Faco, R.A.; Calvo, A.M.; Ozawa, T.O.; Trindade, A.S.; Kiemle Trindade, I.E. Timing of alveolar bone grafting determines different outcomes in patients with unilateral cleft palate. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2012, 23, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enemark, H.; Jensen, J.; Bosch, C. Mandibular bone graft material for reconstruction of alveolar cleft defects: Long-term results. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2001, 38, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuaksuban, N.; Nuntanaranont, T.; Pripatnanont, P. A comparison of autogenous bone graft combined with deproteinized bovine bone and autogenous bone graft alone for treatment of alveolar cleft. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canan, L.W.; Da Silva Freitas, R.; Alonso, N.; Tanikawa, D.Y.S.; Rocha, D.L.; Coelho, J.C.U. Human bone morphogenetic protein-2 Use for maxillary reconstruction in cleft lip and palate patients. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2012, 23, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, N.; Tanikawa, D.Y.S.; Freitas, R.D.S.; Canan, L.; Ozawa, T.O.; Rocha, D.L. Evaluation of maxillary alveolar reconstruction using a resorbable collagen sponge with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in cleft lip and palate patients. Tissue Eng.—Part C Methods 2010, 16, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Yao, J.; Chen, P.K.T.; Zheng, C.; Yang, J. Effect of Presurgical Nasoalveolar Molding on Nasal Symmetry in Unilateral Complete Cleft Lip/Palate Patients after Primary Cheiloplasty without Concomitant Nasal Cartilage Dissection: Early Childhood Evaluation. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2018, 55, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, V.; Agrawal, R.K.; Sailer, H.F. Long-term effect of presurgical nasoalveolar molding on growth of maxillary arch in unilateral cleft lip and palate: Randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzabadi-Farahani, A.; Lane, C.J.; Yen, S.L.K. Late maxillary protraction in patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate: A retrospective study. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2014, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susami, T.; Okayasu, M.; Inokuchi, T.; Ohkubo, K.; Uchino, N.; Uwatoko, K.; Takahashi-Ichikawa, N.; Nagahama, K.; Takato, T. Maxillary protraction in patients with cleft lip and palate in mixed dentition: Cephalometric evaluation after completion of growth. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2014, 51, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcusson, A.; Paulin, G. Changes in occlusion and maxillary dental arch dimensions in adults with treated unilateral complete cleft lip and palate: A follow-up study. Eur. J. Orthod. 2004, 26, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McComb, H.K. Primary repair of the bilateral cleft lip nose: A long-term follow-up. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 1610–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComb, H.K.; Coghlan, B.A. Primary repair of the unilateral cleft lip nose: Completion of a longitudinal study. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 1996, 33, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, A.; Persson, M.; Stock, N.; Rumsey, N.; Sandy, J.; Waylen, A.; Edwards, Z.; Hammond, V.; Partridge, L.; Ness, A. The effectiveness of psychosocial intervention for individuals with cleft lip and/or palate. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2015, 52, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, O.; Burden, D.; Hepper, P.; Johnston, C. The psychosocial effects of cleft lip and palate: A systematic review. Eur. J. Orthod. 2005, 27, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonarakis, G.S.; Palaska, P.K.; Herzog, G. Caries prevalence in non-syndromic patients with cleft lip and/or palate: A meta-analysis. Caries Res. 2013, 47, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Worth, V.; Perry, R.; Ireland, T.; Wills, A.K.; Sandy, J.; Ness, A. Are people with an orofacial cleft at a higher risk of dental caries? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. Dent. J. 2017, 223, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, L.L.; Moor, S.L.; Ho, C.T.C. Predisposing factors to dental caries in children with cleft lip and palate: A review and strategies for early prevention. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2007, 44, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, A.; Muthu, M.S.; Orenuga, O.O.; Mossey, P.; Ousehal, L.; Yan, S.; Campodonico, M.; England, R.; Taylor, S.; Sheeran, P. Systematic Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines for Oral Health in Children With Cleft Lip and Palate. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, A.G.; Buchalla, W.; Huysmans, M.C.D.N.J.M.; Amaechi, B.T.; Sampaio, F.; Vougiouklakis, G.; Pitts, N.B. A survey on education in cariology for undergraduate dental students in Europe. Eur. J. Dent. Educ. 2011, 15 (Suppl. S1), 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Winkelhoff, A.J.; Van der Weijden, G.A. (Eds.) Preventieve Tandheelkunde, 2nd ed.; Bohn Stafleu van Loghum: Houten, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, H.D.P.; Whitehill, T.L.; Samman, N.; Cheung, L.K. Maxillary distraction versus orthognathic surgery in cleft lip and palate patients: Effects on speech and velopharyngeal function. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloukos, D.; Fudalej, P.; Sequeira-Byron, P.; Katsaros, C. Maxillary distraction osteogenesis versus orthognathic surgery for cleft lip and palate patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 9, CD010403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luijsterburg, A.J.M.; Rozendaal, A.M.; Vermeij-Keers, C. Classifying common oral clefts: A new approach after descriptive registration. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2014, 51, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.; Dobbs, T.; Swan, M.C.; Weinstein, G.S.; Goodacre, T.E.E. Trans-oral robotic cleft surgery (TORCS) for palate and posterior pharyngeal wall reconstruction: A feasibility study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2016, 69, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mink van der Molen, A.B.; van Breugel, J.M.M.; Janssen, N.G.; Admiraal, R.J.C.; van Adrichem, L.N.A.; Bierenbroodspot, F.; Bittermann, D.; van den Boogaard, M.-J.H.; Broos, P.H.; Dijkstra-Putkamer, J.J.M.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Treatment of Patients with Cleft Lip, Alveolus, and Palate: An Executive Summary. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4813. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214813
Mink van der Molen AB, van Breugel JMM, Janssen NG, Admiraal RJC, van Adrichem LNA, Bierenbroodspot F, Bittermann D, van den Boogaard M-JH, Broos PH, Dijkstra-Putkamer JJM, et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Treatment of Patients with Cleft Lip, Alveolus, and Palate: An Executive Summary. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(21):4813. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214813
Chicago/Turabian StyleMink van der Molen, Aebele B., Johanna M. M. van Breugel, Nard G. Janssen, Ronald J. C. Admiraal, Leon N. A. van Adrichem, Frank Bierenbroodspot, Dirk Bittermann, Marie-José H. van den Boogaard, Pieter H. Broos, Janet J. M. Dijkstra-Putkamer, and et al. 2021. "Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Treatment of Patients with Cleft Lip, Alveolus, and Palate: An Executive Summary" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 21: 4813. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214813
APA StyleMink van der Molen, A. B., van Breugel, J. M. M., Janssen, N. G., Admiraal, R. J. C., van Adrichem, L. N. A., Bierenbroodspot, F., Bittermann, D., van den Boogaard, M.-J. H., Broos, P. H., Dijkstra-Putkamer, J. J. M., van Gemert-Schriks, M. C. M., Kortlever, A. L. J., Mouës-Vink, C. M., Swanenburg de Veye, H. F. N., van Tol-Verbeek, N., Vermeij-Keers, C., de Wilde, H., & Kuijpers-Jagtman, A. M. (2021). Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Treatment of Patients with Cleft Lip, Alveolus, and Palate: An Executive Summary. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(21), 4813. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214813






