The Combination of Albumin–Bilirubin Score and Prothrombin Time Is a Useful Tool for Predicting Liver Dysfunction after Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Child–Pugh Class A Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Up-to-Seven Criteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
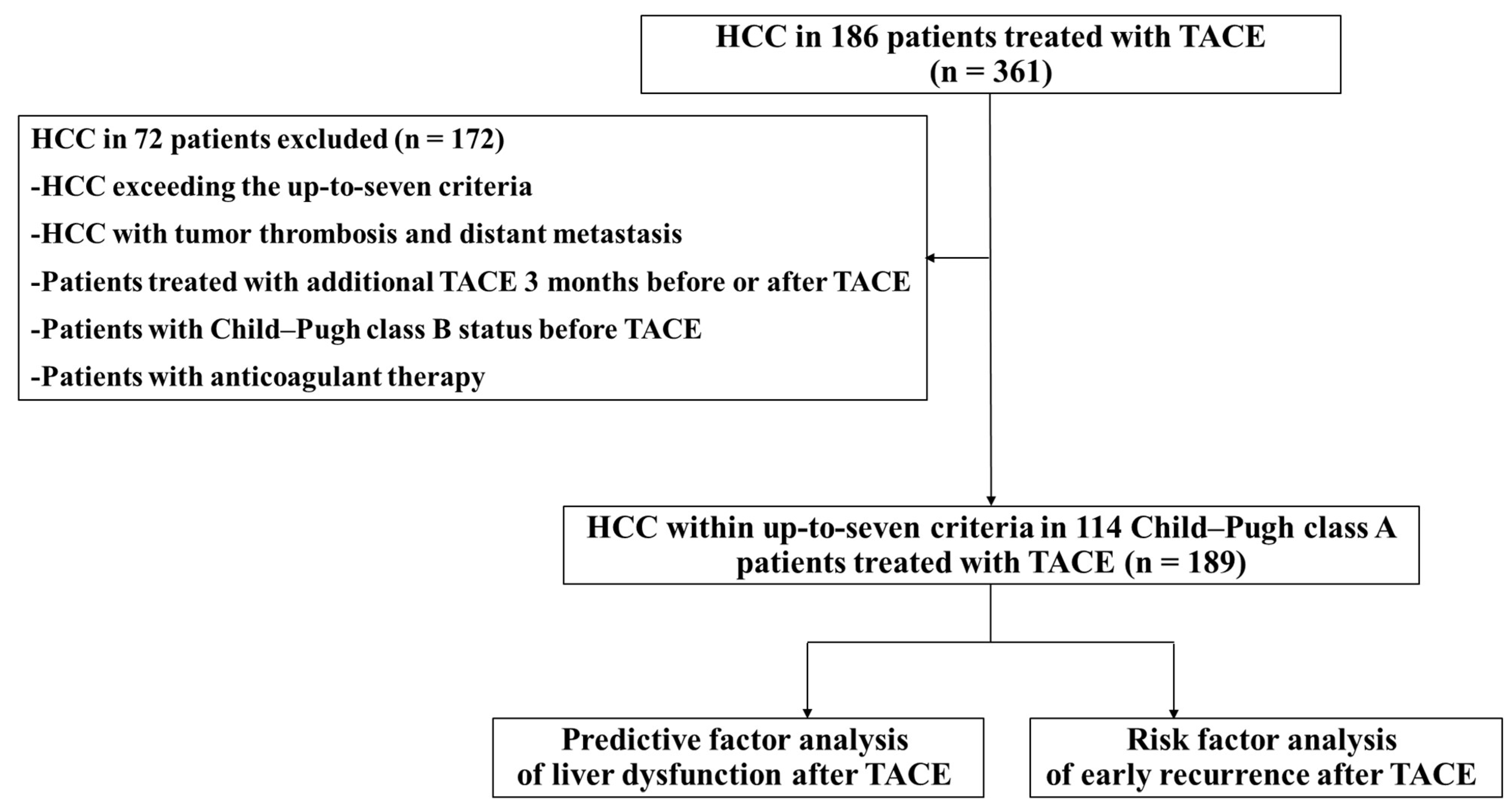
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. TACE
2.3. Follow-Up
2.4. ALBI Score
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of Patients and HCC
3.2. Change in Liver Function from Child–Pugh Class A to Class B after TACE
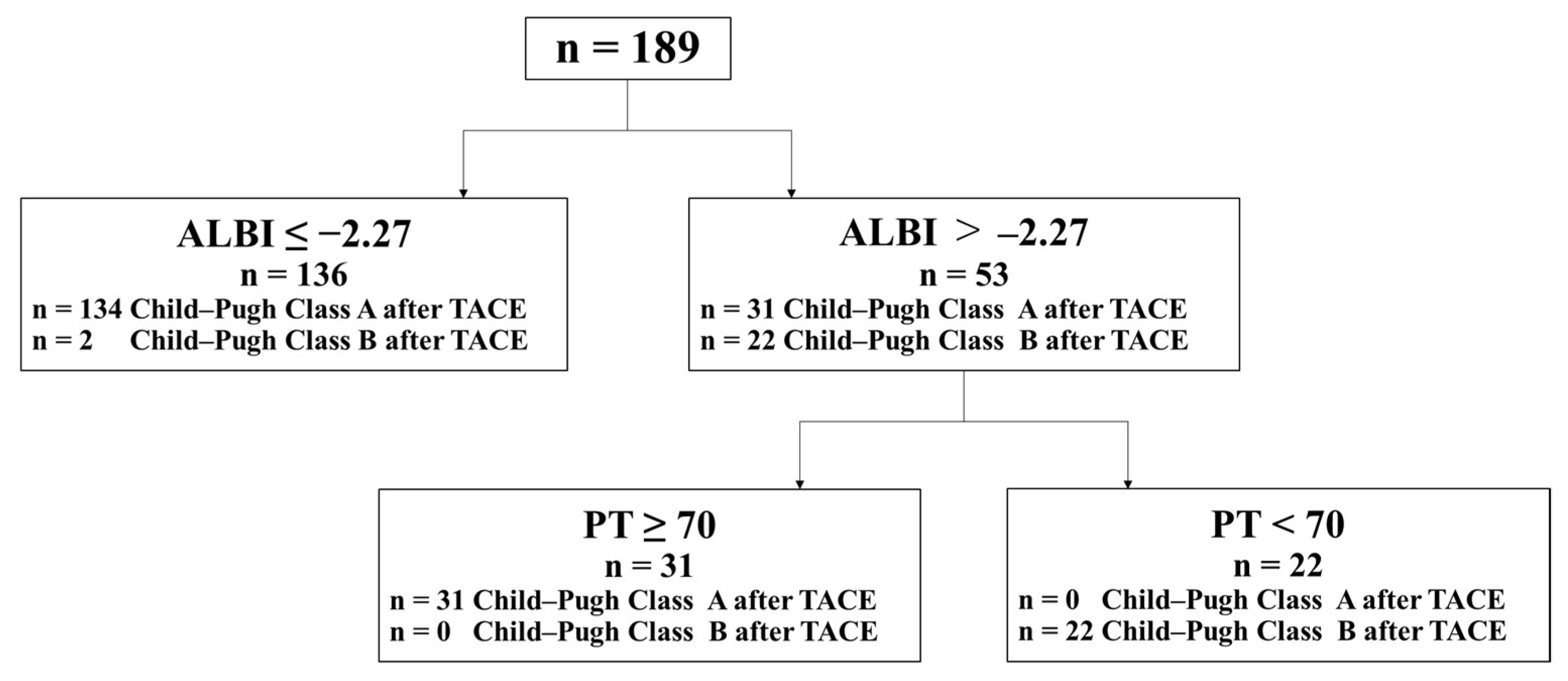
3.3. Risk Factors for Liver Dysfunction from Child–Pugh Class A to Class B after TACE
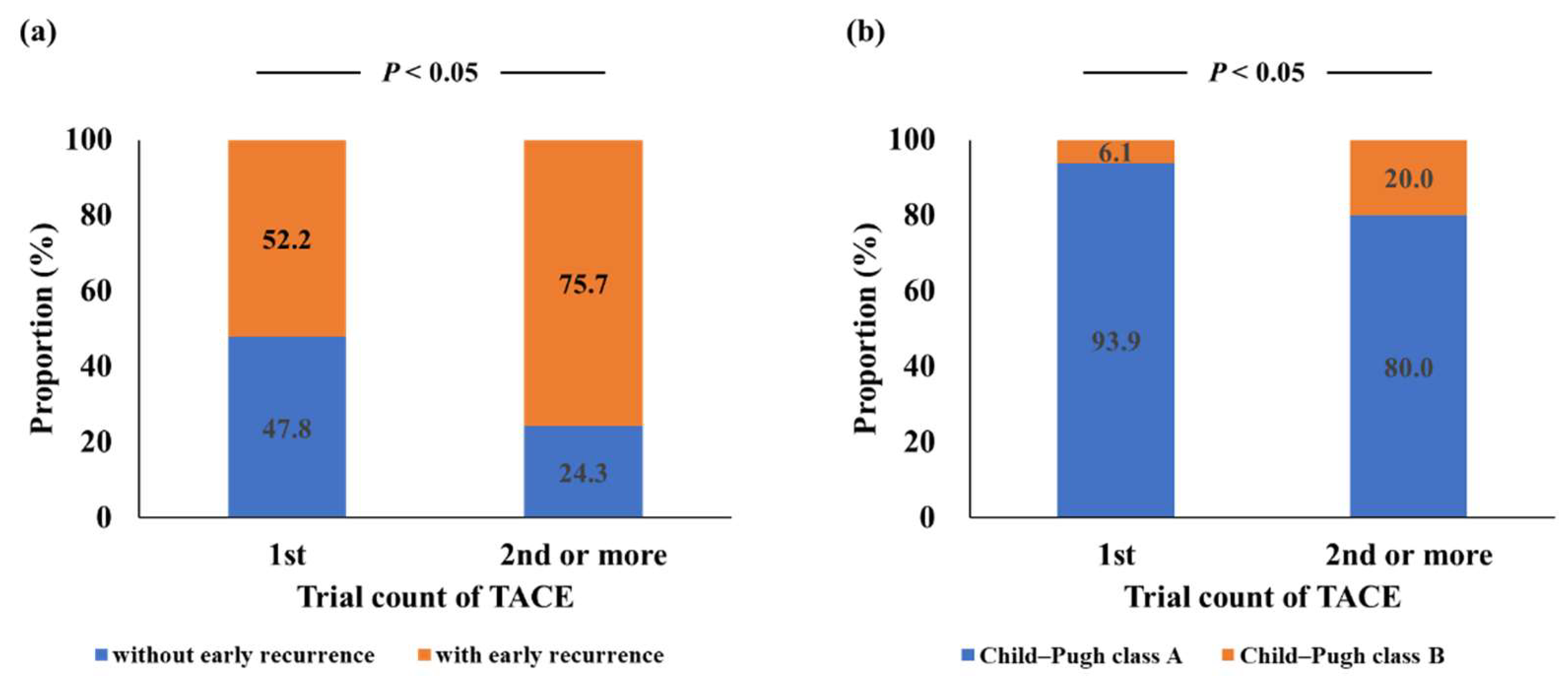
3.4. Risk Factors for Early Recurrence after TACE
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Saviano, A.; Erstad, D.J.; Hoshida, Y.; Fuchs, B.C.; Baumert, T.; Tanabe, K.K. Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prevention: Emphasis on Secondary Prevention and Its Translational Challenges. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kokudo, N.; Takemura, N.; Hasegawa, K.; Takayama, T.; Kubo, S.; Shimada, M.; Nagano, H.; Hatano, E.; Izumi, N.; Kaneko, S.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for hepatocellular carcinoma: The Japan Society of Hepatology 2017 (4th JSH-HCC guidelines) 2019 update. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Kudo, M.; Hirooka, M.; Koizumi, Y.; Hiasa, Y.; Tajiri, K.; Toyoda, H.; Tada, T.; Ochi, H.; et al. Hepatic Function during Repeated TACE Procedures and Prognosis after Introducing Sorafenib in Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Multicenter Analysis. Dig. Dis. 2017, 35, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Ueshima, K.; Chan, S.; Minami, T.; Chishina, H.; Aoki, T.; Takita, M.; Hagiwara, S.; Minami, Y.; Ida, H.; et al. Lenvatinib as an Initial Treatment in Patients with Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Beyond Up-To-Seven Criteria and Child-Pugh A Liver Function: A Proof-Of-Concept Study. Cancers 2019, 11, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Douhara, A.; Namisaki, T.; Moriya, K.; Kitade, M.; Kaji, K.; Kawaratani, H.; Takeda, K.; Okura, Y.; Takaya, H.; Noguchi, R.; et al. Predisposing factors for hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence following initial remission after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3028–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kudo, M.; Arizumi, T.; Ueshima, K.; Sakurai, T.; Kitano, M.; Nishida, N. Subclassification of BCLC B Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Treatment Strategies: Proposal of Modified Bolondi's Subclassification (Kinki Criteria). Dig. Dis. 2015, 33, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomonari, T.; Sato, Y.; Tani, J.; Hirose, A.; Ogawa, C.; Morishita, A.; Tanaka, H.; Tanaka, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Okamoto, K.; et al. Comparison of therapeutic outcomes of sorafenib and lenvatinib as primary treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma with a focus on molecular-targeted agent sequential therapy: A propensity score-matched analysis. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 51, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Hung, Y.; Liu, C.; Lee, R.; Su, C.; Huo, T.; Li, C.; Chao, Y.; Lin, H.; Hou, M.; et al. A new ALBI-based model to predict survival after transarterial chemoembolization for BCLC stage B hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, A.; Michitaka, K.; Kumada, T.; Kudo, M. ALBI Score as a Novel Tool in Staging and Treatment Planning for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Advantage of ALBI Grade for Universal Assessment of Hepatic Function. Liver Cancer 2017, 6, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Michitaka, K.; Toyoda, H.; Tada, T.; Ueki, H.; Kaneto, M.; Aibiki, T.; Okudaira, T.; Kawakami, T.; et al. Usefulness of albumin-bilirubin grade for evaluation of prognosis of 2584 Japanese patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Michitaka, K.; Kudo, M. Newly Proposed ALBI Grade and ALBI-T Score as Tools for Assessment of Hepatic Function and Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Liver Cancer 2018, 8, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, S.; Tsuchiya, K.; Yasui, Y.; Inada, K.; Kirino, S.; Yamashita, K.; Osawa, L.; Hayakawa, Y.; Sekiguchi, S.; Higuchi, M.; et al. Strategy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma based on liver function and portal vein tumor thrombosis. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Tsuji, K.; Hiraoka, A.; Michitaka, K.; Deguchi, A.; Ishikawa, T.; Imai, M.; Ochi, H.; et al. Impact of albumin–bilirubin grade on survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who received sorafenib: An analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristic. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 34, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Jiao, D.; Han, X.; Si, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, X. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with simultaneous DynaCT-guided microwave ablation in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, G.; Xie, X.; Gu, W.; Huang, J.; Zhu, D.; Hu, W.; Hou, Q.; Shi, C.; Li, T.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Drug-Eluting Beads Transarterial Chemoembolization by CalliSpheres® in 275 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients: Results from the Chinese CalliSpheres® Transarterial Chemoembolization in Liver Cancer (CTILC) Study. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2019, 28, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miksad, R.A.; Ogasawara, S.; Xia, F.; Fellous, M.; Piscaglia, F. Liver function changes after transarterial chemoembolization in US hepatocellular carcinoma patients: The LiverT study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) Assessment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 052–060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukushima, T.; Morimoto, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Ueno, M.; Sano, Y.; Kawano, K.; Asama, H.; Nagashima, S.; Maeda, S. Repeated transarterial chemoembolization with epirubicin-loaded superabsorbent polymer microspheres vs. conventional transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.M.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.-L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takaya, H.; Namisaki, T.; Shimozato, N.; Kaji, K.; Kitade, M.; Moriya, K.; Sato, S.; Kawaratani, H.; Akahane, T.; Matsumoto, M.; et al. ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand factor are useful biomarkers for sorafenib treatment efficiency in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 11, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, I.S.; Sinn, D.H.; Kang, T.W.; Lee, M.W.; Kang, W.; Gwak, G.-Y.; Paik, Y.-H.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, K.C.; et al. Liver Function Assessment Using Albumin–Bilirubin Grade for Patients with Very Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Radiofrequency Ablation. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 3235–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, E.; Bai, W.; Xia, D.; Ding, R.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Sun, J.; Mu, W.; et al. Exploratory Analysis to Identify Candidates Benefitting from Combination Therapy of Transarterial Chemoembolization and Sorafenib for First-Line Treatment of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Observational Study. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 308–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, B.-Y.; Yan, Z.-P.; Sun, J.-H.; Zhang, L.; Hou, Z.-H.; Yang, M.-J.; Zhou, G.-H.; Wang, W.-S.; Li, Z.; Huang, P.; et al. Prognostic Performance of Albumin–Bilirubin Grade With Artificial Intelligence for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated With Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined With Sorafenib. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Yuan, J.; Tang, B.; Zhang, F.; Lu, S.; Chen, R.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Z.; Yin, X. Albumin-bilirubin index and platelet-albumin-bilirubin index contribute to identifying survival benefit candidates in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh grade A undergoing transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with sorafenib treatment. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kurosaki, M.; Takeguchi, T.; Takeguchi, Y.; Okada, M.; Wang, W.; Kubota, Y.; Goto, T.; Komiyama, Y.; et al. Up-to-seven criteria as a useful predictor for tumor downstaging to within Milan criteria and Child-Pugh grade deterioration after initial conventional transarterial chemoembolization. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granito, A.; Bolondi, L. Non-transplant therapies for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh-Turcotte class B cirrhosis. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e101–e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Michitaka, K.; Kumada, T.; Izumi, N.; Kadoya, M.; Kokudo, N.; Kubo, S.; Matsuyama, Y.; Nakashima, O.; Sakamoto, M.; et al. Validation and Potential of Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Prognostication in a Nationwide Survey of 46,681 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients in Japan: The Need for a More Detailed Evaluation of Hepatic Function. Liver Cancer 2017, 6, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-P.; Mao, M.J.; He, Z.-L.; Zhang, L.; Chi, P.-D.; Su, J.-R.; Dai, S.-Q.; Liu, W.-L. A retrospective discussion of the prognostic value of combining prothrombin time(PT) and fibrinogen(Fbg) in patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2079–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mao, M.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Sheng, H.; Han, R.; Lin, W.; Dai, S. Novel Prognostic Scores Based on Plasma Prothrombin Time and Fibrinogen Levels in Patients With AFP-Negative Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Control. J. Moffitt Cancer Cent. 2020, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Guo, R.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Mei, J.; Feng, S.; et al. Lack of Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization for Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Abandon or Repeat? Radiology 2021, 298, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaya, H.; Namisaki, T.; Moriya, K.; Shimozato, N.; Kaji, K.; Ogawa, H.; Ishida, K.; Tsuji, Y.; Kaya, D.; Takagi, H.; et al. Association between ADAMTS13 activity–VWF antigen imbalance and the therapeutic effect of HAIC in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 7232–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaya, H.; Kawaratani, H.; Tsuji, Y.; Nakanishi, K.; Saikawa, S.; Sato, S.; Sawada, Y.; Kaji, K.; Okura, Y.; Shimozato, N.; et al. von Willebrand factor is a useful biomarker for liver fibrosis and prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with hepatitis B and C. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takaya, H.; Namisaki, T.; Kitade, M.; Shimozato, N.; Kaji, K.; Tsuji, Y.; Nakanishi, K.; Noguchi, R.; Fujinaga, Y.; Sawada, Y.; et al. Acylcarnitine: Useful biomarker for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in non-steatohepatitis patients. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 11, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocan, T.; Simão, A.L.; Castro, R.E.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Słomka, A.; Wang, B.; Strassburg, C.; Wöhler, A.; Willms, A.G.; Kornek, M. Liquid Biopsies in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Are We Winning? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, L.; Garuti, F.; Lenzi, B.; Pecorelli, A.; Farinati, F.; Giannini, E.; Granito, A.; Ciccarese, F.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Di Marco, M.; et al. The evolutionary scenario of hepatocellular carcinoma in Italy: An update. Liver Int. 2016, 37, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 73.7 ± 8.84 |
| Sex (male/female) | 88/26 |
| Etiology (HBV/HCV/alcohol/NASH/others) | 18/46/26/17/7 |
| Variable | |
|---|---|
| AFP (ng/mL) | 44.2 ± 98.3 |
| Trial count of TACE (1st/2nd/ 3rd and above) | 99/36/54 |
| Maximum tumor size (cm) | 1.92 ± 0.89 |
| Tumor number (1/2/3/4/5) | 73/54/28/30/4 |
| Tumor location (both lobes/one lobe) | 61/128 |
| Early recurrence after TACE (+/−) | 116/73 |
| Variable | Before TACE | 3 Months after TACE | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.89 ± 0.499 | 3.75 ± 0.520 | <0.05 |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 83.3 ± 13.0 | 80.5 ± 15.4 | NS |
| Total bilirubin > 1.5 mg/dL | 1.00 ± 0.458 | 1.08 ± 0.540 | NS |
| ALBI score | −2.53 ± 0.45 | −2.39 ± 0.48 | <0.05 |
| Child–Pugh score | 5.29 ± 0.453 | 5.59 ± 0.824 | <0.05 |
| Child–Pugh class A/B | 189/0 | 165/24 | <0.05 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p |
| Age > 70 years old | 0.541 (0.224–1.30) | 0.171 | ||
| Sex (male vs. female) | 0.393 (0.112–1.38) | 0.145 | ||
| Albumin < 3.5 g/dL | 9.79 (3.82–25.1) | <0.05 | 4.34 (0.716–26.3) | 0.110 |
| Prothrombin time < 70% | 5.39 (1.96–14.8) | <0.05 | 12.4 (1.84–83.4) | <0.05 |
| Total bilirubin > 2 mg/dL | 4.91 (0.777–31.0) | 0.0908 | ||
| Child–Pugh score 6 vs. 5 | 18.6 (5.96–57.9) | <0.05 | 1.32 (0.254–6.87) | 0.741 |
| ALBI score > −2.27 | 19.3 (6.17–60.1) | <0.05 | 9.08 (1.93–42.8) | <0.05 |
| AFP > 20 ng/mL | 1.64 (0.684–3.95) | 0.267 | ||
| Maximum tumor size > 3 cm | 0.73 (0.203–2.62) | 0.630 | ||
| Tumor number > 3 | 1.56 (0.571–4.28) | 0.385 | ||
| Tumor location (both lobes/one lobe) | 1.95 (0.816–4.64) | 0.133 | ||
| Trial count of TACE ≥ 2 | 0.943 (0.329–2.70) | 0.913 | ||
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p |
| Age > 70 years old | 0.839 (0.439–1.60) | 0.594 | ||
| Sex (male vs. female) | 0.715 (0.366–1.40) | 0.326 | ||
| Albumin < 3.5 g/dL | 0.999 (0.500–2.00) | 0.999 | ||
| Prothrombin time < 70% | 1.12 (0.443–2.81) | 0.817 | ||
| Total bilirubin > 2 mg/dL | 2.57 (0.282–23.5) | 0.403 | ||
| Child–Pugh score 6 vs. 5 | 1.28 (0.665–2.46) | 0.461 | ||
| ALBI score > −2.27 | 1.23 (0.637–2.37) | 0.539 | ||
| AFP > 20 ng/mL | 1.73 (0.902–3.33) | 0.0985 | ||
| Maximum tumor size > 3 cm | 0.793 (0.360–1.75) | 0.564 | ||
| Tumor number > 3 | 4.74 (1.75–12.9) | <0.05 | 4.73 (1.73–13.0) | <0.05 |
| Tumor location (both lobes/one lobe) | 2.01 (1.04–3.89) | 0.077 | ||
| Trial count of TACE ≥ 2 | 2.71 (1.21–6.08) | <0.05 | 2.70 (1.18–6.16) | <0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takaya, H.; Namisaki, T.; Takeda, S.; Kaji, K.; Ogawa, H.; Ishida, K.; Tsuji, Y.; Takagi, H.; Ozutsumi, T.; Fujinaga, Y.; et al. The Combination of Albumin–Bilirubin Score and Prothrombin Time Is a Useful Tool for Predicting Liver Dysfunction after Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Child–Pugh Class A Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Up-to-Seven Criteria. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214838
Takaya H, Namisaki T, Takeda S, Kaji K, Ogawa H, Ishida K, Tsuji Y, Takagi H, Ozutsumi T, Fujinaga Y, et al. The Combination of Albumin–Bilirubin Score and Prothrombin Time Is a Useful Tool for Predicting Liver Dysfunction after Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Child–Pugh Class A Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Up-to-Seven Criteria. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(21):4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214838
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakaya, Hiroaki, Tadashi Namisaki, Soichi Takeda, Kosuke Kaji, Hiroyuki Ogawa, Koji Ishida, Yuki Tsuji, Hirotetsu Takagi, Takahiro Ozutsumi, Yukihisa Fujinaga, and et al. 2021. "The Combination of Albumin–Bilirubin Score and Prothrombin Time Is a Useful Tool for Predicting Liver Dysfunction after Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Child–Pugh Class A Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Up-to-Seven Criteria" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 21: 4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214838
APA StyleTakaya, H., Namisaki, T., Takeda, S., Kaji, K., Ogawa, H., Ishida, K., Tsuji, Y., Takagi, H., Ozutsumi, T., Fujinaga, Y., Furukawa, M., Kitagawa, K., Nishimura, N., Sawada, Y., Shimozato, N., Kawaratani, H., Moriya, K., Akahane, T., Mitoro, A., & Yoshiji, H. (2021). The Combination of Albumin–Bilirubin Score and Prothrombin Time Is a Useful Tool for Predicting Liver Dysfunction after Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Child–Pugh Class A Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Up-to-Seven Criteria. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(21), 4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214838







