IgA Vasculitis with Nephritis in Adults: Histological and Clinical Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. IgAVN Patients
2.2. Clinical and Demographic Data
2.3. Kidney Pathology
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Clinical Data at the Time of Kidney Biopsy
3.2. Kidney Histopathology and Kidney Function
3.3. Histopathology of Kidney Biopsy Specimens with Different Intervals between Purpura Onset and Diagnostic Kidney Biopsy
3.4. Neutrophils in Peripheral Blood in Patients with Different Intervals between Purpura Onset and Diagnostic Kidney Biopsy
3.5. Association of Serum Total IgA Concentration and Mesangial Proliferation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saulsbury, F.T. Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2010, 22, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin, J.-C. Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis: Pathophysiology, treatment, and future strategy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davin, J.C.; Coppo, R. Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis in children. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, M. IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis. In Heptinstall’s Pathology of the Kidney; Jennette, J.C., Olson, J.L., Schwartz, M.M., Silva, F.G., Eds.; Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 423–486. [Google Scholar]
- Hastings, M.C.; Rizk, D.V.; Kiryluk, K.; Nelson, R.; Zahr, R.S.; Novak, J.; Wyatt, R.J. IgA vasculitis with nephritis: Update of pathogenesis with clinical implications. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin, J.C.; Ten Berge, I.J.; Weening, J.J. What is the difference between IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis? Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emancipator, S.N. IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein syndrome. In Heptinstall’s Pathology of the Kidney; Jennette, J.C., Olson, J.L., Schwartz, M.M., Silva, F.G., Eds.; Lippincott-Raven Publishers: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1998; pp. 479–539. [Google Scholar]
- Fervenza, F.C. Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2003, 42, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldo, F.B. Is Henoch-Schönlein purpura the systemic form of IgA nephropathy? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1988, 12, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, R.J.; Novak, J.; Gaber, L.W.; Lau, K.K. IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis. In Clinical Pediatric Nephrology, 2nd ed.; Kher, K.K., Schnapper, H.W., Makker, S.P., Eds.; Informa UK Ltd.: London, UK, 2006; pp. 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Szeto, C.C.; Choi, P.C.L.; To, K.F.; Li, P.K.T.; Hui, J.; Chow, K.M.; Leung, C.B.; Lui, S.F.; Lai, F.M.-M. Grading of acute and chronic renal lesions in Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Mod. Pathol. 2001, 14, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, I.S.; Cook, H.T.; Troyanov, S.; Alpers, C.E.; Amore, A.; Barratt, J.; Berthoux, F.; Bonsib, S.; Bruijn, J.A. The Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy: Pathology definitions, correlations, and reproducibility. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reamy, B.V.; Servey, J.T.; Williams, P.M. Henoch-Schönlein purpura (IgA vasculitis): Rapid evidence review. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 102, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Urizar, R.E.; Michael, A.; Sisson, S.; Vernier, R.L. Anaphylactoid purpura. II. Immunofluorescent and electron microscopic studies of the glomerular lesions. Lab. Investig. 1968, 19, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berger, J. IgA glomerular deposits in renal disease. Transplant. Proc. 1969, 1, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.J.; Williams, D.G.; Peters, D.K.; Sissons, J.G.P.; Boulton-Jones, J.M.; Ogg, C.S.; Cameron, J.S.; Hoffbrand, B.I. Glomerular deposition of properdin in Henoch-Schönlein syndrome and idiopathic focal nephritis. Br. Med. J. 1973, 3, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selewski, D.T.; Ambruzs, J.M.; Appel, G.B.; Bomback, A.S.; Matar, R.B.; Cai, Y.; Cattran, D.C.; Chishti, A.S.; D’Agati, V.D.; D’Alessandri-Silva, C.J.; et al. Clinical characteristics and treatment patterns of children and adults with IgA nephropathy or IgA vasculitis: Findings from the CureGN study. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pillebout, E.; Jamin, A.; Ayari, H.; Housset, P.; Pierre, M.; Sauvaget, V.; Viglietti, D.; Deschenes, G.; Monteiro, R.C.; Berthelot, L.; et al. Biomarkers of IgA vasculitis nephritis in children. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conley, E.M.; Cooper, M.; Michael, A.F. Selective deposition of immunoglobulin A1 in immunoglobulin A nephropathy, anaphylactoid purpura nephritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 66, 1432–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Yasutake, J.; Makita, Y.; Tanbo, Y.; Yamasaki, K.; Sofue, T.; Kano, T.; Suzuki, Y. IgA nephropathy and IgA vasculitis with nephritis have a shared feature involving galactose-deficient IgA1-oriented pathogenesis. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saulsbury, F.T. Alterations in the O-linked glycosylation of IgA1 in children with Henoch-Schönlein purpura. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 2246–2249. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, A.C.; Willis, F.R.; Beattie, T.J.; Feehally, J. Abnormal IgA glycosylation in Henoch-Schönlein purpura restricted to pa-tients with clinical nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1998, 13, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, K.K.; Wyatt, R.J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Tomana, M.; Julian, B.J.; Hogg, R.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Huang, W.-Q.; Mestecky, J.; Novak, J. Serum levels of galactose-deficient IgA in children with IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schoenlein purpura. Ped. Nephrol. 2007, 22, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizerska-Wasiak, M.; Gajewski, Ł.; Cichoń-Kawa, K.; Małdyk, J.; Dziedzic-Jankowska, K.; Leszczyńska, B.; Szuminska, A.A.R.; Wasilewska, A.; Pukajło-Marczyk, A.; Zwolińska, D.; et al. Serum GDIgA1 levels in children with IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein nephritis. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 43, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, S.; Imamura, R.; Kawamura, M.; Kato, T.; Abe, T.; Iwatani, H.; Yamanaka, K.; Uemura, M.; Kishikawa, H.; Nishimura, K.; et al. Evaluation of IgA1 O-glycosylation in Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis using mass spectrometry. Transplant. Proc. 2019, 51, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Renfrow, M.B.; Yanagihara, T.; Suzuki, H.; Raska, M.; Hall, S.; Brown, R.; Huang, W.-Q.; Goepfert, A.; et al. IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schoenlein purpura nephritis: Aberrant glycosylation of IgA1, formation of IgA1-containing immune complexes, and activation of mesangial cells. Contrib. Nephrol. 2007, 157, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldoveanu, Z.; Wyatt, R.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Tomana, M.; Julian, B.A.; Mestecky, J.; Huang, W.-Q.; Anreddy, S.R.; Hall, S.; Hastings, M.C.; et al. Patients with IgA nephropathy have increased serum galactose-deficient IgA1 levels. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiryluk, K.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Sanders, J.T.; Eison, T.M.; Suzuki, H.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J.; Gharavi, A.G.; Wyatt, R.J. Aberrant glycosylation of IgA1 is inherited in both pediatric IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Julian, B.A.; Wyatt, R.J.; Novak, J. Autoantibodies specific for galactose-deficient IgA1 in IgA vasculitis with nephritis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomana, M.; Novak, J.; Julian, B.A.; Matousovic, K.; Konecny, K.; Mestecky, J. Circulating immune complexes in IgA nephropathy consist of IgA1 with galactose-deficient hinge region and antiglycan antibodies. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Fan, R.; Zhang, Z.; Brown, R.; Hall, S.; Julian, B.A.; Chatham, W.W.; Suzuki, Y.; Wyatt, R.J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; et al. Aberrantly glycosylated IgA1 in IgA nephropathy patients is recognized by IgG antibodies with restricted heterogeneity. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.Q.; Raska, M.; Stewart, T.J.; Reily, C.; King, R.G.; Crossman, D.K.; Crowley, M.R.; Hargett, A.; Zhang, Z.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Somatic mutations modulate autoantibodies against galactose-deficient IgA1 in IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 3278–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizk, D.V.; Saha, M.K.; Hall, S.; Novak, L.; Brown, R.; Huang, Z.-Q.; Fatima, H.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J. Glomerular immunodeposits of patients with IgA nephropathy are enriched for IgG autoantibodies specific for galactose-deficient IgA1. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 2017–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, Z.; Suzuki, H.; Reily, C.; Satake, K.; Novak, L.; Xu, N.; Huang, Z.-Q.; Knoppova, B.; Khan, A.; Hall, S.; et al. Experimental evidence of pathogenic role of IgG autoantibodies in IgA nephropathy. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 118, 102593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, J.; Tomana, M.; Brown, R.; Hall, S.; Novak, L.; Julian, B.A.; Wyatt, R.J.; Mestecky, J.; Matousovic, K. IgA1-containing immune complexes in IgA nephropathy differentially affect proliferation of mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Novak, J.; Kafkova, L.R.; Suzuki, H.; Tomana, M.; Matousovic, K.; Brown, R.; Hall, S.; Sanders, J.T.; Eison, T.M.; Moldoveanu, Z.; et al. IgA1 immune complexes from pediatric patients with IgA nephropathy activate cultured human mesangial cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3451–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moura, I.C.; Arcos-Fajardo, M.; Sadaka, C.; Leroy, V.; Benhamou, M.; Novak, J.; Vrtovsnik, F.; Haddad, E.; Chintalacharuvu, K.R.; Monteiro, R.C. Glycosylation and size of IgA1 are essential for interaction with mesangial transferrin receptor in IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maillard, N.; Wyatt, R.J.; Julian, B.A.; Kiryluk, K.; Gharavi, A.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Novak, J. Current Understanding of the role of complement in IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coppo, R.; Andrulli, S.; Amore, A.; Gianoglio, B.; Conti, G.; Peruzzi, L.; Locatelli, F.; Cagnoli, L. Predictors of outcome in Henoch-Schönlein nephritis in children and adults. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 47, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppo, R.; Basolo, B.; Martina, G.; Rollino, C.; De Marchi, M.; Giacchino, F.; Mazzucco, G.; Messina, M.; Piccoli, G. Circulating immune complexes containing IgA, IgG and IgM in patients with primary IgA nephropathy and with Henoch-Schönlein nephritis. Correlation with clinical and histologic signs of activity. Clin. Nephrol. 1982, 18, 230–239. [Google Scholar]
- Coppo, R.; Basolo, B.; Piccoli, G.; Mazzucco, G.; Bulzomì, M.R.; Roccatello, D.; De Marchi, M.; Carbonara, A.O.; Di Belgiojoso, G.B. IgA1 and IgA2 immune complexes in primary IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein nephritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1984, 57, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coppo, R.; Mazzucco, G.; Cagnoli, L.; Lupo, A.; Schena, F.P. Long-term prognosis of Henoch-Schönlein nephritis in adults and children. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1997, 12, 2277–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Counahan, R.; Winterborn, M.H.; White, R.H.; Heaton, J.M.; Meadow, S.R.; Bluett, N.H.; Swetschin, H.; Cameron, J.S.; Chantler, C. Prognosis of Henoch-Schönlein nephritis in children. BMJ 1977, 2, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Kiryluk, K.; Novak, J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Herr, A.; Renfrow, M.B.; Wyatt, R.; Scolari, F.; Mestecky, J.; Gharavi, A.G.; et al. The pathophysiology of IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, N.; Hou, P.; Lv, J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Li, Y.; Kiryluk, K.; Gharavi, A.G.; Novak, J.; Zhang, H. The level of galactose-deficient IgA1 in the sera of patients with IgA nephropathy is associated with disease progression. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berthoux, F.; Suzuki, H.; Thibaudin, L.; Yanagawa, H.; Maillard, N.; Mariat, C.; Tomino, Y.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J. Autoantibodies targeting galactose-deficient IgA1 associate with progression of IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maixnerová, D.; Ling, C.; Hall, S.; Reily, C.; Brown, R.; Neprasova, M.; Suchanek, M.; Honsova, E.; Zima, T.; Novak, J.; et al. Galactose-deficient IgA1 and the corresponding IgG autoantibodies predict IgA nephropathy progression. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen, A.C.; Bailey, E.M.; Brenchley, P.; Buck, K.S.; Barratt, J.; Feehally, J. Mesangial IgA1 in IgA nephropathy exhibits aberrant O-glycosylation: Observations in three patients. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiki, Y.; Odani, H.; Takahashi, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Nishimoto, A.; Iwase, H.; Shinzato, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Maeda, K. Mass spectrometry proves under-O-glycosylation of glomerular IgA1 in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Hall, S.; Brown, R.; Vu, H.L.; Novak, L.; Julian, B.A.; Tomana, M.; Wyatt, R.J.; Edberg, J.C.; et al. IgA1-secreting cell lines from patients with IgA nephropathy produce aberrantly glycosylated IgA1. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Raska, M.; Yamada, K.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Julian, B.A.; Wyatt, R.J.; Tomino, Y.; Gharavi, A.G.; Novak, J. Cytokines alter IgA1 O-glycosylation by dysregulating C1GalT1 and ST6GalNAc-II enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 5330–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 36.5 ± 16.0 |
| Males (%) | 50 (45) |
| Subjects with hypertension (%) | 23 (21) |
| Subjects with diabetes mellitus (%) | 4 (4) |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) mean (95% CI) | 0.85 (0.78, 0.92) |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2, mean ± SD) | 110 ± 43 |
| Subjects on ACEi/ARB before kidney biopsy (%) | 27 (25) |
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Mesangial score: mean (95% CI) | 1.1 (1.02–1.17) |
| Segmental sclerosis (%) | 18 |
| Global sclerosis (%) | 4 |
| Glomerular adhesion (%) | 26 |
| Glomerular leukocytes (%) | 20 |
| Tubular atrophy (%) | 43 |
| Interstitial fibrosis (%) | 40 |
| Interstitial leukocytes (%) | 39 |
| Crescents (%) | 9 |
| Characteristics | Group 1 a | Group 2 | Group 3 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 14) | (n = 58) | (n = 38) | ||
| Age (yr) c, (mean ± SD) | 40.5 ± 19.3 | 36.8 ± 16.0 | 34.5 ± 14.9 | 0.47 b |
| Male gender (% male) | 6 (43) | 28 (48) | 16 (42) | 0.82 |
| Hypertension (%) | 4 (29) | 12 (21) | 7 (18) | 0.73 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 2 (14) | 1 (2) | 1 (3) | 0.07 |
| ACEi/ARB before biopsy (%) | 10 (19) | 6 (32) | 11 (28) | 0.74 |
| Proteinuria (g/24 h) (range) | 2.23 (1.11, 4.68) | 1.39 (0.87, 2.29) | 1.13 (0.59, 1.93) | 0.08 |
| Urinary RBC (number/μL; mean ± SD) | 667 ± 885 | 369 ± 602 | 405 ± 660 | 0.29 |
| SCr (mg/dL; mean ± SD) | 0.97 ± 0.34 | 0.83 ± 0.40 | 0.83 ± 0.29 | 0.42 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2; mean ± SD) | 91 ± 29 | 113 ± 49 | 112 ± 36 | 0.28 |
| WBC (×109/L; mean ± SD) | 11.1 ± 7.0 | 9.3 ± 3.6 | 8.5 ± 3.4 | 0.13 |
| Neutrophils (% of WBC; mean ± SD) | 71 ± 8 | 68 ± 11 | 60 ± 12 | 1 vs. 2 = 0.3067 1 vs. 3 = 0.0039 2 vs. 3 = 0.0008 |
| Eosinophils (% of total WBC; mean ± SD) | 2 ± 4 | 1 ± 2 | 2 ± 3 | 0.40 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL; mean ± SD) | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 0.6 | 3.7 ± 0.5 | 0.14 |
| Serum total IgA (g/L; mean ± SD) | 3.1 ± 1.2 | 3.0 ± 1.3 | 2.9 ± 1.0 | 0.86 |
| Serum C3 (g/L; mean ± SD) | 1.17 ± 0.30 | 1.09 ± 0.24 | 1.10 ± 0.25 | 0.57 |
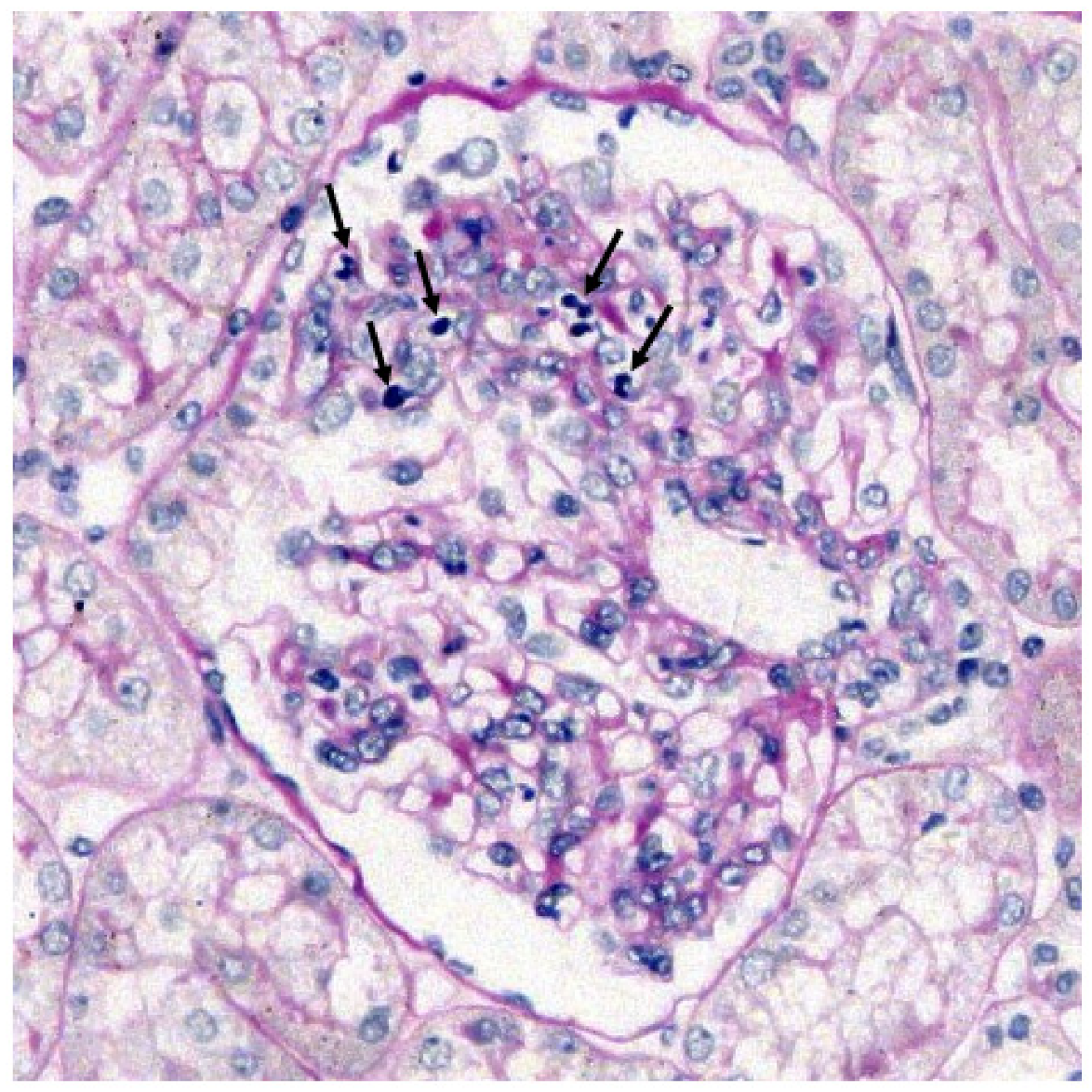
| Glomeruli with leukocytes (%) | 8 (57) | 6 (10) | 8 (21) | 0.0008 b |
| NLR (mean ± SD) c | 2.7 ± 0.8 | 2.6 ± 1.5 | 2.1 ± 1.4 | 0.09 b |
| MEST-C score | ||||
| M1 (%) | 71 | 68 | 95 | 0.0075 b 2 vs. 3 = 0.006 |
| E1 (%) | 14 | 42 | 30 | 0.106 b |
| S1 (%) | 21 | 14 | 24 | 0.397 b |
| T1/T2 (%) | 7 | 5 | 14 | 0.344 b |
| C1/C2 (%) | 57 | 49 | 60 | 0.598 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, L.; Liu, S.; Azrad, M.; Hall, S.; Hao, C.; Novak, J.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, L. IgA Vasculitis with Nephritis in Adults: Histological and Clinical Assessment. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4851. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214851
Lai L, Liu S, Azrad M, Hall S, Hao C, Novak J, Julian BA, Novak L. IgA Vasculitis with Nephritis in Adults: Histological and Clinical Assessment. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(21):4851. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214851
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Lingyun, Shaojun Liu, Maria Azrad, Stacy Hall, Chuanming Hao, Jan Novak, Bruce A. Julian, and Lea Novak. 2021. "IgA Vasculitis with Nephritis in Adults: Histological and Clinical Assessment" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 21: 4851. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214851
APA StyleLai, L., Liu, S., Azrad, M., Hall, S., Hao, C., Novak, J., Julian, B. A., & Novak, L. (2021). IgA Vasculitis with Nephritis in Adults: Histological and Clinical Assessment. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(21), 4851. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214851






