Sex Differences in Clinical Course and Intensive Care Unit Admission in a National Cohort of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Statistical Analysis
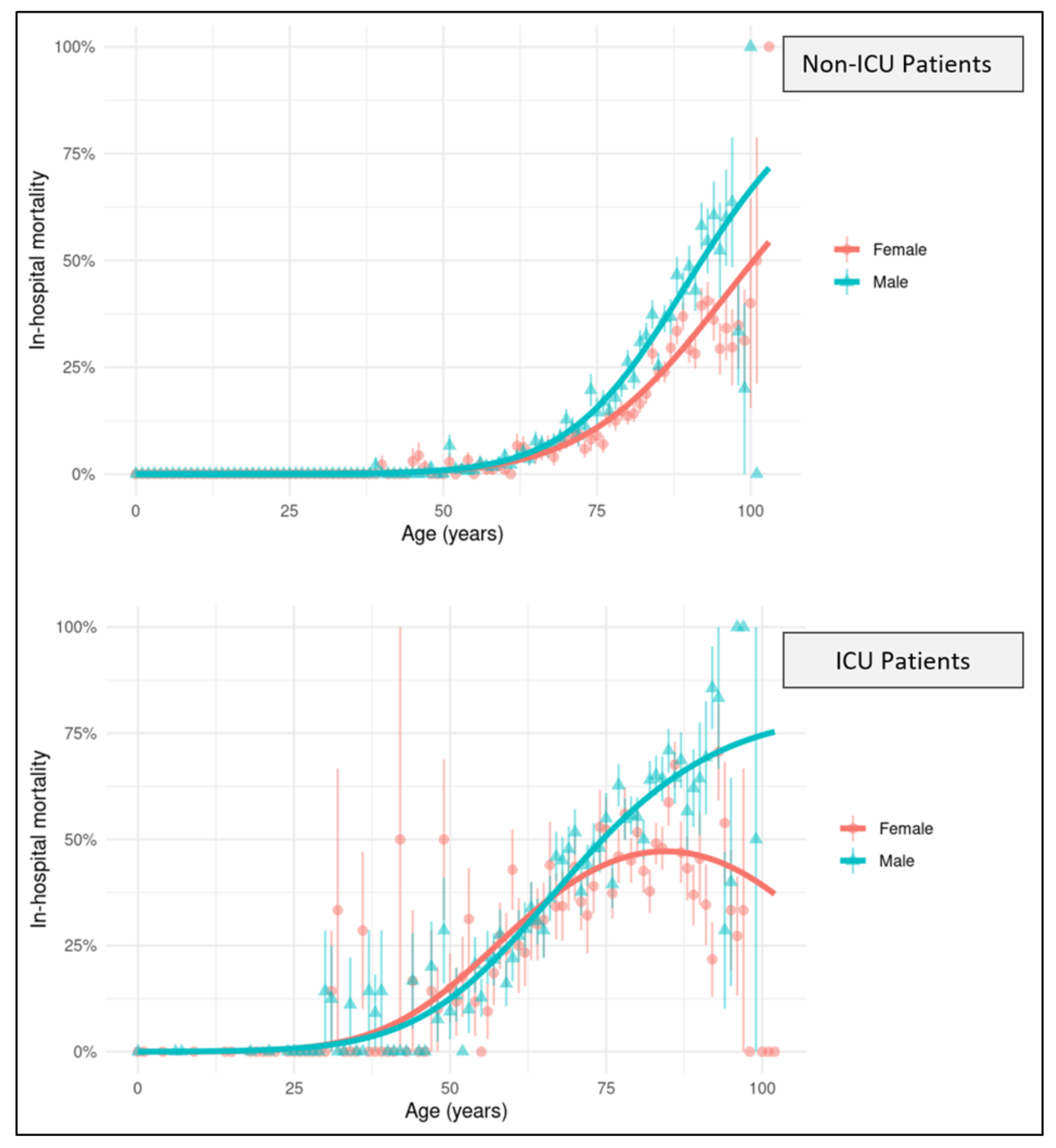
3. Results
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kremer, H.-J.; Thurner, W. Age dependence in COVID-19 mortality in Germany. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2020, 117, 432–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, E.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; Bacon, S.; Bates, C.; Morton, C.E.; Curtis, H.J.; Mehrkar, A.; Evans, D.; Inglesby, P. Opensafely: Factors associated with COVID-19-related hospital death in the linked electronic health records of 17 million adult NHS patients. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Health 50/50. The Sex, Gender and COVID-19 Project. Available online: https://globalhealth5050.org/the-sex-gender-and-covid-19-project/ (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Hoffmann, C.; Wolf, E. Older age groups and country-specific case fatality rates of COVID-19 in Europe, USA and Canada. Infection 2021, 49, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peckham, H.; de Gruijter, N.M.; Raine, C.; Radziszewska, A.; Ciurtin, C.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Rosser, E.C.; Webb, K.; Deakin, C.T. Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, F.S.; Papoila, A.L.; Machado, R.S.; Fidalgo, P. Age, sex, and comorbidities predict ICU admission or mortality in cases with SaRS-CoV2 infection: A population-based cohort study. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirhadi, R.; Talaulikar, V.S.; Onwude, J.; Manyonda, I. Could estrogen protect women from COVID-19? J. Clin. Med. Res. 2020, 12, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Vignera, S.; Cannarella, R.; Condorelli, R.A.; Torre, F.; Aversa, A.; Calogero, A.E. Sex-specific SaRS-CoV-2 mortality: Among hormone-modulated ace2 expression, risk of venous thromboembolism and hypovitaminosis D. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Wong, P.; Ellingson, M.; Lucas, C.; Klein, J.; Israelow, B.; Silva, J.; Oh, J.; Mao, T.; Tokuyama, M. Sex differences in immune responses to SaRS-CoV-2 that underlie disease outcomes. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Chowdhry, M.; Chatterjee, A.; Khan, A. Gender-based disparities in COVID-19 patient outcomes: A propensity-matched analysis. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Van Walraven, C.; Austin, P.C.; Jennings, A.; Quan, H.; Forster, A.J. A modification of the elixhauser comorbidity measures into a point system for hospital death using administrative data. Med. Care 2009, 47, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachtigall, I.; Lenga, P.; Jóźwiak, K.; Thürmann, P.; Meier-Hellmann, A.; Kuhlen, R.; Brederlau, J.; Bauer, T.; Tebbenjohanns, J.; Schwegmann, K.; et al. Clinical course and factors associated with outcomes among 1904 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Germany: An observational study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, B.B.; Kassie, A.M.; Kassaw, M.W.; Aragie, T.G.; Masresha, S.A. Sex difference in coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e040129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert Koch-Institut. COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://experience.arcgis.com/experience/478220a4c454480e823b17327b2bf1d4 (accessed on 26 March 2021).
- Sunden-Cullberg, J.; Nilsson, A.; Inghammar, M. Sex-based differences in ED management of critically ill patients with sepsis: A nationwide cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Todorov, A.; Kaufmann, F.; Arslani, K.; Haider, A.; Bengs, S.; Goliasch, G.; Zellweger, N.; Tontsch, J.; Sutter, R.; Buddeberg, B. Gender differences in the provision of intensive care: A bayesian approach. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zettersten, E.; Jäderling, G.; Larsson, E.; Bell, M. The impact of patient sex on intensive care unit admission: A blinded randomized survey. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, R.A.; Sabur, N.; Li, P.; Juurlink, D.N.; Pinto, R.; Hladunewich, M.A.; Adhikari, N.K.; Sibbald, W.J.; Martin, C.M. Sex-and age-based differences in the delivery and outcomes of critical care. Cmaj 2007, 177, 1513–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nachtigall, I.; Tafelski, S.; Rothbart, A.; Kaufner, L.; Schmidt, M.; Tamarkin, A.; Kartachov, M.; Zebedies, D.; Trefzer, T.; Wernecke, K.-D.; et al. Gender-related outcome difference is related to course of sepsis on mixed ICUs: A prospective, observational clinical study. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Phenotype | Weight |
|---|---|
| Congestive heart failure | 9 |
| Cardiac arrhythmias | 0 |
| Valvular disease | 0 |
| Pulmonary circulation disorders | 6 |
| Peripheral vascular disorders | 3 |
| Hypertension (combined uncomplicated and complicated) | −1 |
| Paralysis | 5 |
| Other neurological disorders | 5 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 3 |
| Diabetes, uncomplicated | 0 |
| Diabetes, complicated | −3 |
| Hypothyroidism | 0 |
| Renal failure | 6 |
| Liver disease | 4 |
| Peptic ulcer disease, excluding bleeding | 0 |
| AIDS/HIV | 0 |
| Lymphoma | 6 |
| Metastatic cancer | 14 |
| Solid tumour without metastasis | 7 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis/collagen vascular diseases | 0 |
| Coagulopathy | 11 |
| Obesity | −5 |
| Weight loss | 9 |
| Fluid and electrolyte disorders | 11 |
| Blood loss anaemia | −3 |
| Deficiency anaemia | −2 |
| Alcohol abuse | −1 |
| Drug abuse | −7 |
| Psychoses | −5 |
| Depression | −5 |
| Non-ICU Patients (n 17,133) | ICU Patients (Ventilated and Non-Ventilated) (n = 6102) | Ventilated ICU-Patients (n = 3654) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Females n (%) | Males n (%) | p-Value | Odds Ratio/Crude-Risk Ratio Males (95% CI) |
Females n (%) |
Males n (%) | p-Value |
Odds Ratio/Crude-risk Ratio Males (95% CI) |
Females n (%) |
Males n (%) | p-Value |
Odds Ratio/Crude-Risk Ratio Males (95% CI) | |
| 8884 (51.9) | 8249 (48.1) | <0.0001 | 0.93 (0.90–0.96) | 2411 (39.5) (21.3% of females) | 3691 (60.5) (30.9% of males) | <0.0001 | 1.53 (1.45–1.61) | 1278 (35.0) | 2376 (65.0) | <0.0001 | 1.86 (1.74–1.99) | |
| Age (years) | ||||||||||||
| Mean (SD) | 69.3 ± 20.9 | 67.3 ± 18.8 | <0.0001 | 72.9 ± 14.9 | 69.2 ± 13.7 | <0.0001 | 71.1 ± 13.8 | 69.2 ± 12.4 | <0.0001 | |||
| ≤59 | 2407 (27.1) | 2426 (29.4) | 0.0008 | 417 (17.3) | 807 (21.9) | <0.0001 | 241 (18.0) | 483 (20.3) | n.s. | |||
| 60−69 | 953 (10.7) | 1406 (17.0) | <0.0001 | 364 (15.1) | 887 (24.0) | <0.0001 | 236 (18.5) | 640 (26.9) | <0.0001 | |||
| 70−79 | 1650 (18.6) | 1736 (21,0) | <0.0001 | 634 (26.3) | 1034 (28.0) | n.s. | 390 (30.5) | 694 (29.2) | n.s. | |||
| ≥80 | 3874 (43.6) | 2681 (32.5) | <.0001 | 996 (41.3) | 963 (26.1) | <0.0001 | 411 (32.2) | 559 (23.5) | <0.0001 | |||
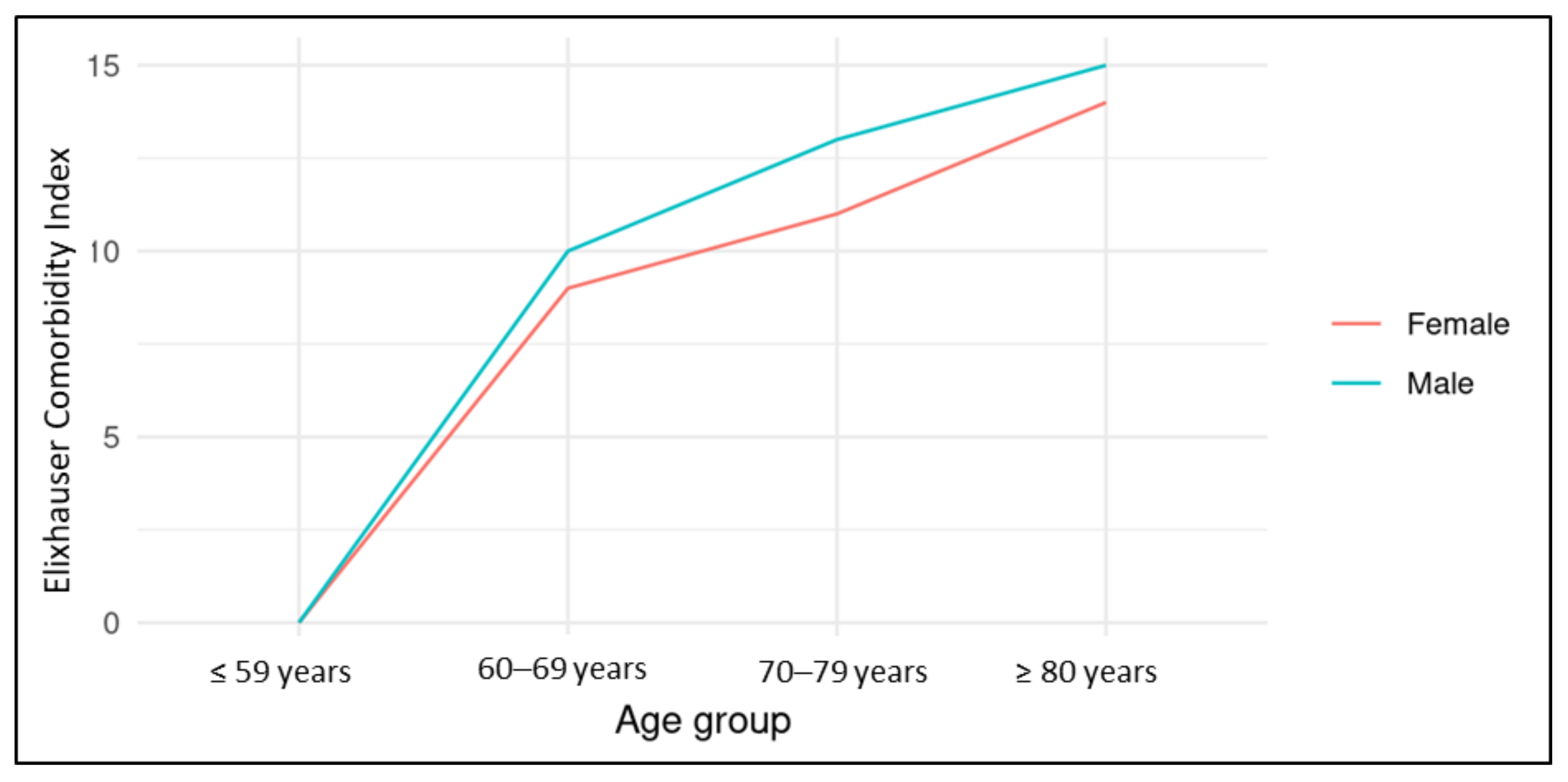
| Elixhauser Comorbidity Index | ||||||||||||
| Mean (SD) | 9.5 ±10.6 | 9.7 ± 11.0 | n.s. | 15.9 ± 12.4 | 16.1 ± 12.3 | n.s. | 16.8 ± 12.4 | 17.0 ±12.3 | n.s. | |||
| Symptoms at admission * | ||||||||||||
| Fever | 1953 (25.9) | 2352 (33.5) | <0.0001 | 1.51 (1.40–1.63) | 608 (29.0) | 1217 (38.1) | <0.0001 | 1.54 (1.36–1.75) | 418 (37.3) | 911 (43.4) | 0.0002 | 1.36 (1.16–1.60) |
| Dyspnea | 1561 (20.7) | 1807 (25.7) | <0.0001 | 1.37 (1.26–1.49) | 647 (30.8) | 1248 (39.0) | <0.0001 | 1.46 (1.29–1.66) | 505 (45.0) | 973 (46.3) | n.s. | 1.07 (0.91–1.25) |
| Cough | 1700 (22.5) | 1844 (26.2) | <0.0001 | 1.24 (1.13–1.35) | 467 (22.2) | 820 (25.6) | 0.0046 | 1.22 (1.06–1.39) | 306 (27.3) | 588 (28.0) | n.s. | 1.05 (0.89–1.24) |
| Diarrhea | 619 (8.2) | 476 (6.8) | 0.0008 | 0.81 (0.71–0.91) | 128 (6.1) | 215 (6.7) | n.s. | 1.11 (0.88–1.39) | 62 (5.5) | 158 (7.5) | 0.0254 | 1.41 (1.04–1.91) |
| Length of hospital stay (nights) | ||||||||||||
| Mean (SD) | 10.1 ± 10.6 | 9.8 ±9.8 | n.s. | 18.8 ± 17.3 | 19.4 ± 16.4 | 0.0238 | 19.8 ± 18.6 | 20.7 ± 16.9 | 0.0052 | |||
| ICU stay (days) | ||||||||||||
| Mean (SD) | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 8.0 ± 10.9 | 10.4 ± 12.2 | <0.0001 | 12.1 ± 13.1 | 14.1 ± 13.5 | <0.0001 | ||
| Proportion (n/N) | Gender | Comparison with Non-ICU | Interaction | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | Females and Males | Females | Males | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value |
| Total (N = 21,346) | 21.1% (4509/21,346) | 18.8% (1969/10,488) | 23.4% (2540/10,858) | 1.31 (1.22–1.40) | <0.0001 | ||||
| non-ICU (N = 16,197) | 14.8% (2391/16,197) | 13.7% (1152/8399) | 15.9% (1239/7798) | 1.19 (1.09–1.30) | 0.0001 | ||||
| ICU (N = 5149) | 41.1% (2118/5149) | 39.1% (817/2089) | 42.5% (1301/3060) | 1.14 (1.02–1.28) | 0.0259 | 4.17 (3.87–4.49) | <0.0001 | 0.97 (0.84–1.13) | 0.7217 |
| ICU and ventilated (N = 2959) | 58.4% (1728/2959) | 59.5% (633/1064) | 57.8% (1095/1895) | 0.93 (0.80–1.09) | 0.3996 | 8.55 (7.81–9.35) | <0.0001 | 0.79 (0.67–0.95) | 0.0109 |
| ICU and not ventilated (N = 2190) | 17.8% (390/2190) | 18.0% (184/1025) | 17.7% (206/1165) | 0.98 (0.79–1.22) | 0.8487 | 1.32 (1.17–1.48) | <0.0001 | 0.83 (0.65–1.05) | 0.1124 |
| Variable | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Male sex | 1.588 (1.491–1.692) | <0.0001 |
| Age (years) | 0.997 (0.995–0.999) | 0.0050 |
| Interaction sex × age | 0.996 (0.993–1.000) | 0.0319 |
| Elixhauser Comorbidity Index | 1.053 (1.050–1.056) | <0.0001 |
| Variable | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Total cohort | ||
| Male sex | 1.415 (1.281–1.563) | <0.0001 |
| Age (years) | 1.064 (1.061–1.068) | <0.0001 |
| Interaction sex × age | 1.015 (1.008–1.022) | <0.0001 |
| Elixhauser Comorbidity Index | 1.051 (1.047–1.054) | <0.0001 |
| ICU cohort | ||
| Male sex | 1.277 (1.122–1.454) | 0.0002 |
| Age (years) | 1.053 (1.047–1.058) | <0.0001 |
| Interaction sex × age | 1.032 (1.021–1.044) | <0.0001 |
| Elixhauser Comorbidity Index | 1.041 (1.035–1.047) | <0.0001 |
| Non-ICU cohort | ||
| Male sex | 1.312 (1.096–1.570) | 0.0031 |
| Age (years) | 1.097 (1.091–1.104) | <0.0001 |
| Interaction sex × age | 1.016 (1.005–1.027) | 0.0053 |
| Elixhauser Comorbidity Index | 1.037 (1.032–1.042) | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nachtigall, I.; Bonsignore, M.; Thürmann, P.; Hohenstein, S.; Jóźwiak, K.; Hauptmann, M.; Eifert, S.; Dengler, J.; Bollmann, A.; Groesdonk, H.V.; et al. Sex Differences in Clinical Course and Intensive Care Unit Admission in a National Cohort of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4954. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214954
Nachtigall I, Bonsignore M, Thürmann P, Hohenstein S, Jóźwiak K, Hauptmann M, Eifert S, Dengler J, Bollmann A, Groesdonk HV, et al. Sex Differences in Clinical Course and Intensive Care Unit Admission in a National Cohort of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(21):4954. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214954
Chicago/Turabian StyleNachtigall, Irit, Marzia Bonsignore, Petra Thürmann, Sven Hohenstein, Katarzyna Jóźwiak, Michael Hauptmann, Sandra Eifert, Julius Dengler, Andreas Bollmann, Heinrich V. Groesdonk, and et al. 2021. "Sex Differences in Clinical Course and Intensive Care Unit Admission in a National Cohort of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 21: 4954. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214954
APA StyleNachtigall, I., Bonsignore, M., Thürmann, P., Hohenstein, S., Jóźwiak, K., Hauptmann, M., Eifert, S., Dengler, J., Bollmann, A., Groesdonk, H. V., Kuhlen, R., & Meier-Hellmann, A. (2021). Sex Differences in Clinical Course and Intensive Care Unit Admission in a National Cohort of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(21), 4954. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214954








