Nocturnal Blood Pressure Fluctuations in Patients with Rapid Eye Movement-Related Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Questionnaires
2.3. Polysomnography
2.4. Blood Pressure Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics, Sleep Quality, and PSG Findings
3.2. PTT Index and Blood Pressure Using PTT
3.3. Nocturnal Blood Pressure Fluctuations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Conwell, W.; Patel, B.; Doeing, D.; Pamidi, S.; Knutson, K.L.; Ghods, F.; Mokhlesi, B. Prevalence, clinical features, and CPAP adherence in REM-related sleep-disordered breathing: A cross-sectional analysis of a large clinical population. Sleep Breath 2012, 16, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, C.; Thornley, K.S.; Hanly, P.J. Gender differences in the polysomnographic features of obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haba-Rubio, J.; Janssens, J.P.; Rochat, T.; Sforza, E. Rapid eye movement-related disordered breathing: Clinical and polysomnographic features. Chest 2005, 128, 3350–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, B.B.; Patel, S.R.; Strohl, K.; Hoffstein, V. Rapid eye movement-related sleep-disordered breathing: Influence of age and gender. Chest 2008, 134, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, M.; Hoshino, T.; Sasanabe, R.; Murotani, K.; Nomura, A.; Hori, R.; Konishi, N.; Baku, M.; Shiomi, T. Impact of gender and age on rapid eye movement-related obstructive sleep apnea: A clinical study of 3234 Japanese OSA patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Somers, V.K.; Dyken, M.E.; Mark, A.L.; Abboud, F.M. Sympathetic-nerve activity during sleep in normal subjects. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findley, L.J.; Wilhoit, S.C.; Suratt, P.M. Apnea duration and hypoxemia during REM sleep in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 1985, 87, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppard, P.E.; Ward, N.R.; Morrell, M.J. The impact of obesity on oxygen desaturation during sleep-disordered breathing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pansani, A.P.; Schoorlemmer, G.H.; Ferreira, C.B.; Rossi, M.V.; Angheben, J.M.M.; Ghazale, P.P.; Gomes, K.P.; Cravo, S.L. Chronic apnea during REM sleep increases arterial pressure and sympathetic modulation in rats. Sleep 2021, 44, zsaa249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somers, V.K.; Dyken, M.E.; Clary, M.P.; Abboud, F.M. Sympathetic neural mechanisms in obstructive sleep apnea. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 1897–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuspidi, C.; Tadic, M.; Sala, C.; Gherbesi, E.; Grassi, G.; Mancia, G. Blood pressure non-dipping and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mokhlesi, B.; Finn, L.A.; Hagen, E.W.; Young, T.; Hla, K.M.; Van Cauter, E.; Peppard, P.E. Obstructive sleep apnea during REM sleep and hypertension. results of the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, S.L.; Vakulin, A.; Martin, S.A.; Lang, C.J.; Wittert, G.A.; Taylor, A.W.; McEvoy, R.D.; Antic, N.A.; Catcheside, P.G.; Adams, R.J. Hypertension is associated with undiagnosed OSA during rapid eye movement sleep. Chest 2016, 150, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Castro, P.; Hirotsu, C.; Marti-Soler, H.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Tobback, N.; Andries, D.; Waeber, G.; Preisig, M.; Vollenweider, P.; Haba-Rubio, J.; et al. REM-associated sleep apnoea: Prevalence and clinical significance in the HypnoLaus cohort. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1702484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaldi, D.; Beccuti, G.; Touma, C.; Van Cauter, E.; Mokhlesi, B. Association of obstructive sleep apnea in rapid eye movement sleep with reduced glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: Therapeutic implications. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chami, H.A.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Redline, S.; Punjabi, N.M. Association between glucose metabolism and sleep-disordered breathing during REM sleep. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, B.B.; Dostal, J.; Ioachimescu, O.; Budur, K. The effects of gender and age on REM-related sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Breath 2008, 12, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, T.; Sasanabe, R.; Murotani, K.; Hori, R.; Mano, M.; Nomura, A.; Konishi, N.; Baku, M.; Arita, A.; Kuczynski, W.; et al. Insomnia as a symptom of rapid eye movement-related obstructive sleep apnea. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geckil, A.A.; Ermis, H. The relationship between anxiety, depression, daytime sleepiness in the REM-related mild OSAS and the NREM-related mild OSAS. Sleep Breath 2020, 24, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, T.; Sasanabe, R.; Murotani, K.; Hori, R.; Mano, M.; Nomura, A.; Konishi, N.; Baku, M.; Nishio, Y.; Kato, C.; et al. Estimated respiratory arousal threshold in patients with rapid eye movement obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zung, W.W. A SELF-RATING DEPRESSION SCALE. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1965, 12, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, M.W. Reliability and factor analysis of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 1992, 15, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F., 3rd; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilo, G.; Zorzi, C.; Ochoa Munera, J.E.; Torlasco, C.; Giuli, V.; Parati, G. Validation of the Somnotouch-NIBP noninvasive continuous blood pressure monitor according to the European Society of Hypertension International Protocol revision 2010. Blood Press. Monit. 2015, 20, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitson, D.J.; Stradling, J.R. Value of beat-to-beat blood pressure changes, detected by pulse transit time, in the management of the obstructive sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 12, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gehring, J.; Gesche, H.; Drewniok, G.; Küchler, G.; Patzak, A. Nocturnal blood pressure fluctuations measured by using pulse transit time in patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath 2018, 22, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzak, A.; Mendoza, Y.; Gesche, H.; Konermann, M. Continuous blood pressure measurement using the pulse transit time: Comparison to intra-arterial measurement. Blood Press 2015, 24, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesche, H.; Grosskurth, D.; Küchler, G.; Patzak, A. Continuous blood pressure measurement by using the pulse transit time: Comparison to a cuff-based method. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, D.J. Phenotypic approaches to obstructive sleep apnoea—New pathways for targeted therapy. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 37, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamidi, S.; Knutson, K.L.; Ghods, F.; Mokhlesi, B. Depressive symptoms and obesity as predictors of sleepiness and quality of life in patients with REM-related obstructive sleep apnea: Cross-sectional analysis of a large clinical population. Sleep Med. 2011, 12, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedner, J.; Bengtsson-Boström, K.; Peker, Y.; Grote, L.; Råstam, L.; Lindblad, U. Hypertension prevalence in obstructive sleep apnoea and sex: A population-based case–control study. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Yin, G.; Zhang, P.; Song, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Hu, W. Distinct associations between hypertension and obstructive sleep apnea in male and female patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawatari, H.; Chishaki, A.; Ando, S. The epidemiology of sleep disordered breathing and hypertension in various populations. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2016, 12, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoncini, G.; Viazzi, F.; Storace, G.; Deferrari, G.; Pontremoli, R. Blood pressure variability and multiple organ damage in primary hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2013, 27, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhlesi, B.; Hagen, E.W.; Finn, L.A.; Hla, K.M.; Carter, J.R.; Peppard, P.E. Obstructive sleep apnoea during REM sleep and incident non-dipping of nocturnal blood pressure: A longitudinal analysis of the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort. Thorax 2015, 70, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seif, F.; Patel, S.R.; Walia, H.K.; Rueschman, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Quan, S.F.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Lewis, E.F.; Patil, S.P.; et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and diurnal nondipping hemodynamic indices in patients at increased cardiovascular risk. J. Hypertens. 2014, 32, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hla, K.M.; Young, T.; Finn, L.; Peppard, P.E.; Szklo-Coxe, M.; Stubbs, M. Longitudinal association of sleep-disordered breathing and nondipping of nocturnal blood pressure in the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort Study. Sleep 2008, 31, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Guilleminault, C.; Otsuka, K.; Shiomi, T. Blood pressure “dipping” and “non-dipping” in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome patients. Sleep 1996, 19, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aurora, R.N.; Crainiceanu, C.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Kim, J.S.; Punjabi, N.M. Obstructive Sleep Apnea during REM Sleep and Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Overall | Males | Females | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 27 | 17 | 10 | - |
| Demographics | ||||
| Age (year) | 46.0 ± 11.7 | 47.9 ± 13.1 | 42.6 ± 8.3 | 0.2587 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.4 ± 3.6 | 24.4 ± 2.6 | 24.4 ± 5.1 | 0.7252 |
| Smoking (N) | 8 | 6 | 2 | - |
| Antihypertensive (N) | 6 | 5 | 1 | - |
| Hypnotics (N) | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
| Antidepressants (N) | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
| Questionnaire | ||||
| ESS (points) | 10.2 ± 6.3 | 8.4 ± 6.1 | 13.4 ± 5.4 | 0.04 * |
| SDS (points) | 46.8 ± 10.2 | 43.8 ± 7.9 | 52.0 ± 11.6 | 0.038 * |
| PSQI (points) | 8.3 ± 4.1 | 7.9 ± 3.9 | 8.8 ± 4.5 | 0.6056 |
| PSG findings | ||||
| Total sleep time (minutes) | 395 ± 93 | 377 ± 111 | 426 ± 38 | 0.0926 |
| Sleep efficiency (%) | 84.6 ± 8.1 | 86.0 ± 7.6 | 82.3 ± 8.8 | 0.2566 |
| Sleep latency (minutes) | 15.0 ± 22.9 | 8.8 ± 7.5 | 25.4 ± 35.0 | 0.0699 |
| REM-sleep latency (minutes) | 88.0 ± 47.2 | 82.3 ± 44.5 | 97.6 ± 52.4 | 0.4264 |
| Stage N1 (%) | 18.0 ± 6.5 | 18.7 ± 6.9 | 16.7 ± 5.8 | 0.4386 |
| Stage N2 (%) | 61.2 ± 7.1 | 62.0 ± 7.6 | 59.8 ± 6.2 | 0.4297 |
| Stage N3 (%) | 4.5 ± 5.2 | 3.0 ± 4.2 | 7.0 ± 6.0 | 0.0518 |
| Stage REM (%) | 16.3 ± 5.2 | 16.2 ± 5.1 | 16.6 ± 5.5 | 0.8738 |
| AHI (/h) | 13.5 ± 4.7 | 14.7 ± 4.6 | 11.6 ± 4.4 | 0.0967 |
| REM-AHI (/h) | 31.9 ± 12.1 | 35.1 ± 12.0 | 26.4 ± 10.6 | 0.0687 |
| NREM-AHI (/h) | 9.7 ± 3.2 | 10.5 ± 3.0 | 8.4 ± 3.1 | 0.1076 |
| Lowest O2 saturation (%) | 86.3 ± 4.5 | 85.6 ± 4.5 | 87.4 ± 4.5 | 0.3405 |
| CT90 (minutes) | 3.9 ± 10.5 | 5.7 ± 13.0 | 0.8 ± 1.5 | 0.0922 |
| PLMI (/h) | 5.1 ± 7.7 | 5.1 ± 8.7 | 5.2 ± 6.0 | 0.9732 |
| Arousal index (/h) | 10.9 ± 4.1 | 10.9 ± 4.0 | 10.9 ± 4.6 | 0.9983 |
| REM-arousal index (/h) | 10.2 ± 6.2 | 11.3 ± 7.1 | 8.4 ± 4.2 | 0.252 |
| NREM-arousal index (/h) | 12.2 ± 7.2 | 12.8 ± 8.3 | 11.3 ± 5.2 | 0.6147 |
| Overall | Male | Female | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTT index | ||||
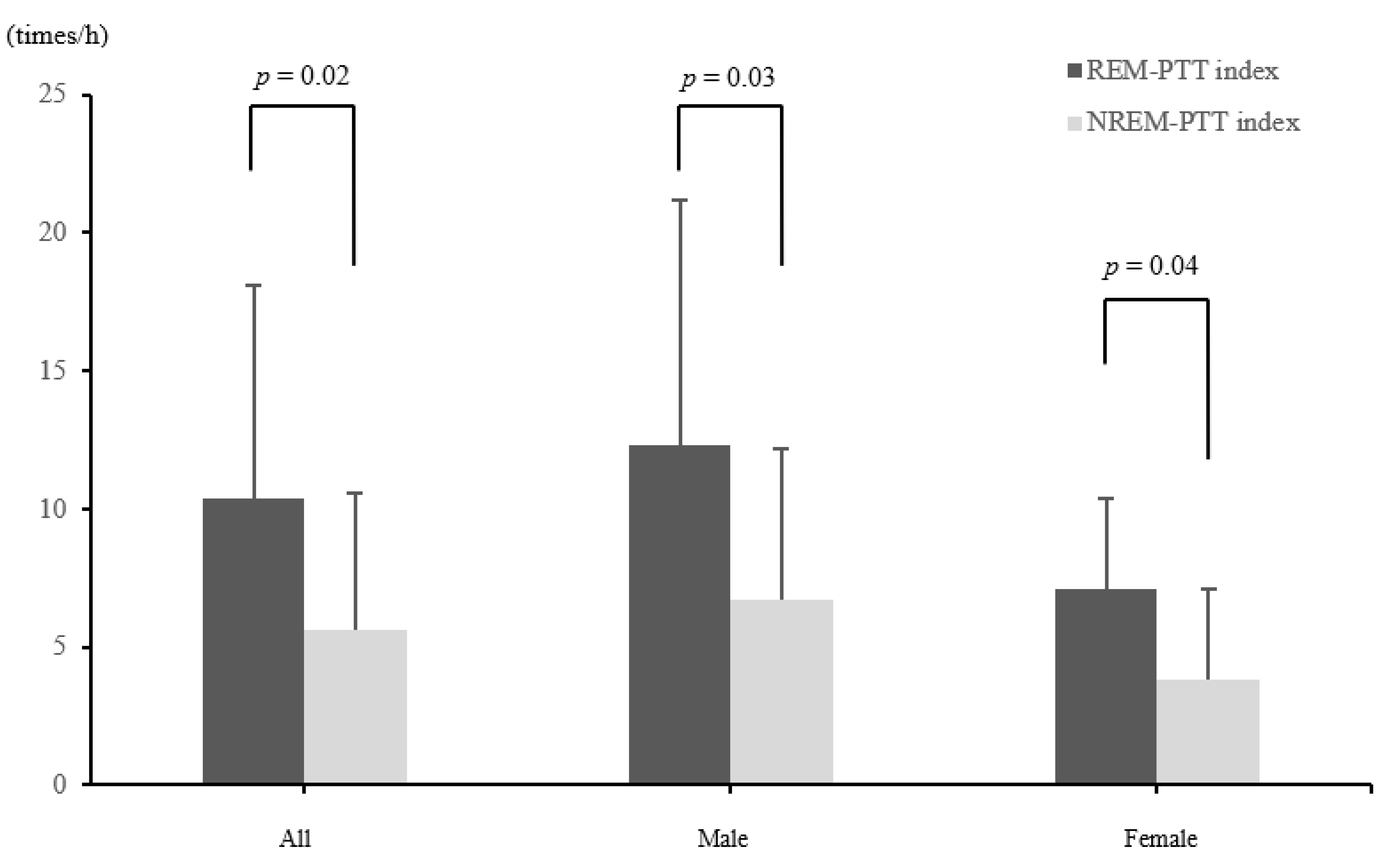
| PTT index (/h) | 6.5 ± 5.6 | 7.9 ± 6.4 | 4.2 ± 3.0 | 0.183 |
| REM-PTT index (/h) | 10.4 ± 7.7 | 12.3 ± 8.9 | 7.1 ± 3.3 | 0.1385 |
| NREM-PTT index (/h) | 5.6 ± 5.0 | 6.7 ± 5.5 | 3.8 ± 3.3 | 0.3397 |
| Blood pressure using PTT | ||||
| Maximum increase in nocturnal SBP (mmHg) | 23.3 ± 7.8 | 25.7 ± 8.9 | 19.3 ± 2.4 | 0.0032 * |
| Average nocturnal SBP (mmHg) | 119.6 ± 19.5 | 126.9 ± 16.4 | 107.1 ± 18.7 | 0.0082 * |
| Average nocturnal DBP (mmHg) | 76.3 ± 12.1 | 79.2 ± 12.4 | 71.3 ± 10.2 | 0.0999 |
| Average nocturnal heart rate (beat/min) | 67.4 ± 9.3 | 65.6 ± 7.4 | 70.6 ± 11.5 | 0.1798 |
| Blood pressure fluctuation pattern (N) | ||||
| Dipping | 8 | 5 | 3 | |
| Non-dipping | 19 | 12 | 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumagai, H.; Sawatari, H.; Hoshino, T.; Konishi, N.; Kiyohara, Y.; Kawaguchi, K.; Tsuda, H.; Haseda, Y.; Sasanabe, R.; Shiomi, T. Nocturnal Blood Pressure Fluctuations in Patients with Rapid Eye Movement-Related Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215023
Kumagai H, Sawatari H, Hoshino T, Konishi N, Kiyohara Y, Kawaguchi K, Tsuda H, Haseda Y, Sasanabe R, Shiomi T. Nocturnal Blood Pressure Fluctuations in Patients with Rapid Eye Movement-Related Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(21):5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215023
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumagai, Hajime, Hiroyuki Sawatari, Tetsuro Hoshino, Noriyuki Konishi, Yuka Kiyohara, Kengo Kawaguchi, Hiroko Tsuda, Yoko Haseda, Ryujiro Sasanabe, and Toshiaki Shiomi. 2021. "Nocturnal Blood Pressure Fluctuations in Patients with Rapid Eye Movement-Related Obstructive Sleep Apnea" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 21: 5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215023
APA StyleKumagai, H., Sawatari, H., Hoshino, T., Konishi, N., Kiyohara, Y., Kawaguchi, K., Tsuda, H., Haseda, Y., Sasanabe, R., & Shiomi, T. (2021). Nocturnal Blood Pressure Fluctuations in Patients with Rapid Eye Movement-Related Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(21), 5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215023






