Esophageal Pressure and Clinical Assessments in the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Procedures
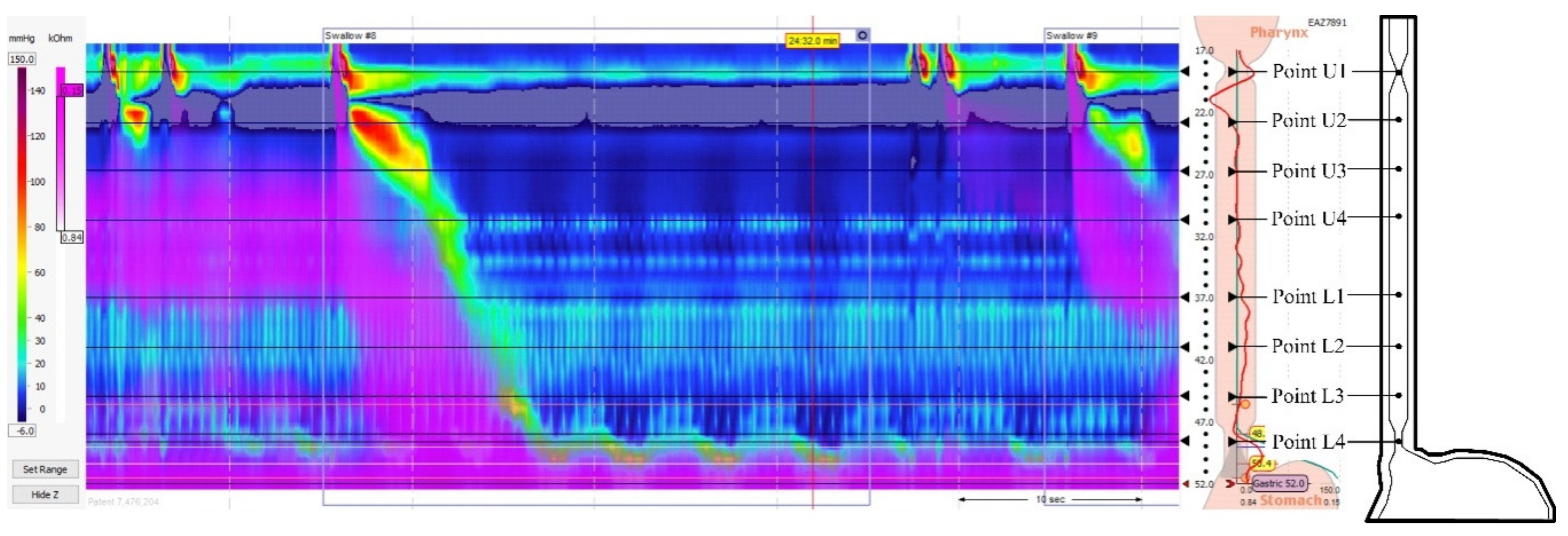
2.2. Esophageal Pressure Assessment
2.3. Clinical Assessments
2.3.1. Reflux Finding Score
2.3.2. Eating Assessment Tool-10
2.3.3. Reflux Symptom Index
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes on Esophageal Pressure in LRPD Patients with Various GERD Severity
3.2. Results of Comparing Sphincter Pressures across Age, Gender, and BMI
4. Discussion
Study Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LPRD | laryngopharyngeal reflux disease |
| GERD | gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| UES | upper esophageal sphincter |
| LES | lower esophageal sphincter |
| RFS | reflux finding scores |
| RSI | reflux symptom index |
| BMI | body mass index |
| EAT-10 | eating assessment tool-10 |
| LA | Los Angeles |
| PPIs | proton pump inhibitors |
| H2 | histamine-2 |
References
- Barrett, C.M.; Patel, D.; Vaezi, M.F. Laryngopharyngeal Reflux and Atypical Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 30, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Li, L.; Fan, X.; Liu, H.; Sun, Z.; Han, H.; Li, B.; Ding, R.; Wu, W. Relationship between laryngopharyngeal reflux disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease based on synchronous esophageal and oropharyngeal Dx-pH monitoring. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 41, 102441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Saussez, S.; Karkos, P.D. Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease: Clinical presentation, diagnosis and therapeutic challenges in 2018. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 26, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelardi, M.; Ciprandi, G. Focus on gastroesophageal reflux (GER) and laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR): New pragmatic insights in clinical practice. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, P.O.; Gerson, L.B.; Vela, M.F. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 308–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, R.O.; Cassiani, R.A. Upper esophageal sphincter dysfunction in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dysphagia 2019, 34, 942–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelmans, J.; Tack, J. Extraoesophageal manifestations of gastrooesophageal reflux. Gut 2005, 54, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinucci, I.; de Bortoli, N.; Savarino, E.; Nacci, A.; Romeo, S.O.; Bellini, M.; Savarino, V.; Fattori, B.; Marchi, S. Optimal treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux disease. Ther. Adv. Chronic. Dis. 2013, 4, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, E.J.; Choi, K.D.; Jung, H.K.; Youn, Y.H.; Min, B.H.; Song, K.H.; Huh, K.C. Quality of life, patient satisfaction, and disease burden in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease with or without laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, D.A., Jr.; Garrett, J.D.; Radionoff, S.L.; Reussner, L.A.; Stasney, C.R. The proximal probe in esophageal pH monitoring: Development of a normative database. J. Voice 2000, 14, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, N.; Bulmer, D.; Gill, G.A.; Panetti, M.; Ross, P.E.; Pearson, J.P.; Pignatelli, M.; Axford, S.E.; Dettmar, P.W.; Koufman, J.A. Cell biology of laryngeal epithelial defenses in health and disease: Further studies. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2003, 112, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.; Bennett, J.R.; Blum, A.L.; Dent, J.; De Dombal, F.T.; Galmiche, J.P.; Lundell, L.; Margulies, M.; Richter, J.E.; Spechler, S.J.; et al. The endoscopic assessment of esophagitis: A progress report on observer agreement. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, A.; Ding, A.; Mirza, F.; Gyawali, C.P. Optimizing the high-resolution manometry (HRM) study protocol. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belafsky, P.C.; Postma, G.N.; Koufman, J.A. The validity and reliability of the reflux finding score (RFS). Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belafsky, P.C.; Mouadeb, D.A.; Rees, C.J.; Pryor, J.C.; Postma, G.N.; Allen, J.; Leonard, R.J. Validity and reliability of the Eating Assessment Tool (EAT-10). Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2008, 117, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belafsky, P.C.; Postma, G.N.; Koufman, J.A. Validity and reliability of the reflux symptom index (RSI). J. Voice 2002, 16, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.Y.; Tsai, S.L.; Albu, J.B.; Lin, C.C.; Li, T.C.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Sung, P.K.; Huang, K.C. Body mass index and all-cause mortality in a large Chinese cohort. CMAJ 2011, 183, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guntinas-Lichius, O. Laryngopharyngeal reflux. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, D.; Zifan, A.; Mittal, R.K. Botox injection into the lower esophageal sphincter induces hiatal paralysis and gastroesophageal reflux. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, O.O.; Kaindlstorfer, A.; Antoniou, S.A.; Asche, K.U.; Granderath, F.A.; Pointner, R. Influence of the esophageal hiatus size on the lower esophageal sphincter, on reflux activity and on symptomatology. Dis. Esophagus 2012, 25, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.L. Laryngopharyngeal reflux: An update. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Muddana, S.; Slaughter, J.C.; Casey, S.; Hill, E.; Farrokhi, F.; Garrett, C.G.; Vaezi, M.F. A new pH catheter for laryngopharyngeal reflux: Normal values. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 1639–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczesniak, M.M.; Williams, R.B.; Brake, H.M.; Maclean, J.C.; Cole, I.E.; Cook, I.J. Upregulation of the esophago-UES relaxation response: A possible pathophysiological mechanism in suspected reflux laryngitis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, S.; Sana, M.; Johnston, N.; Mittal, S.K. Hoarseness and chronic cough: Would you suspect reflux? J. Fam. Pract. 2011, 60, 458–462. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, T.; Zackria, S.; Lopez, R.; Richter, J.; Thota, P.N. Upper esophageal sphincter abnormalities and high-resolution esophageal manometry findings in patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.Y.; Chang, W.C.; Wen, S.H.; Yi, C.H.; Liu, T.T.; Hung, J.S.; Wong, M.W.; Chen, C.L. Predicting factors of recurrence in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: A prospective follow-up analysis. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbella, F.A.; Andolfi, C.; Vigneswaran, Y.; Patti, M.G.; Pinna, B.R. Importance of esophageal manometry and pH monitoring for the evaluation of otorhinolaryngologic (ENT) manifestations of GERD. A multicenter study. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2016, 20, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braghetto, I.; Venturelli, F.; Rodríguez, A.; Brunetto, B.; Maass, J.; Henríquez, A. Association of gastroesophageal reflux with posterior laryngitis. Study of 43 patients. Rev. Chil. Cir. 2014, 66, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ylitalo, R.; Ramel, S.; Hammarlund, B.; Lindgren, E. Prevalence of extraesophageal reflux in patients with symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 131, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylitalo, R.; Lindestad, P.A.; Hertegard, S. Is pseudosulcus alone a reliable sign of gastroesophago-pharyngeal reflux? Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 2004, 29, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosli, M.; Alkhathlan, B.; Abumohssin, A.; Merdad, M.; Alherabi, A.; Marglani, O.; Jawa, H.; Alkhatib, T.; Marzouki, H.Z. Prevalence and clinical predictors of LPR among patients diagnosed with GERD according to the reflux symptom index questionnaire. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Dehom, S.; Sanders, S.; Murry, T.; Krishna, P.; Crawley, B.K. Treating laryngopharyngeal reflux: Evaluation of an anti-reflux program with comparison to medications. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2018, 39, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, K.A.; Ellerston, J.; Heller, A.; Houtz, D.R.; Zhang, C.; Presson, A.P. Objective measures of swallowing function applied to the dysphagia population: A one year experience. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheney, D.M.; Siddiqui, M.T.; Litts, J.K.; Kuhn, M.A.; Belafsky, P.C. The ability of the 10-item eating assessment tool (EAT-10) to predict aspiration risk in persons with dysphagia. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2015, 124, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, M.; Sundaram, A.; Mittal, S.K. Role of the lower esophageal sphincter on acid exposure revisited with high-resolution manometry. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2011, 213, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershcovici, T.; Mashimo, H.; Fass, R. The lower esophageal sphincter. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakiri, K. The role of excessive esophageal acid exposure in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 2, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.S.; Hagen, J.A.; Fein, M.; Bremner, C.G.; Dunst, C.M.; Demeester, S.R.; Lipham, J.; Demeester, T.R. The impact of reflux composition on mucosal injury and esophageal function. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2006, 10, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Items | Patients (n = 90) |
|---|---|
| Male/Female | 41/49 |
| Age (years) | 51.57 ± 13.63 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.75 ± 7.51 |
| No. of BMI ≥ 28, n (%) | 22 (24.4%) |
| No. of patients with gastritis, n (%) | 82 (91.1%) |
| No. of patients with esophagitis, n (%) | 81 (90.0%) |
| RFS | 11.05 ± 3.64 |
| EAT-10 | 6.08 ± 7.35 |
| RSI | 20.76 ± 7.35 |
| Grade A (n = 27) | Grade B (n = 33) | Grade C (n = 17) | Grade D (n = 13) | F Value | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFS | 10.25 ± 5.64 | 13.41 ± 7.02 | 11.01 ± 8.74 | 11.09 ± 9.65 | 1.01 | 0.39 |
| EAT-10 | 5.73 ± 6.34 | 6.64 ± 8.36 | 7.38 ± 8.34 | 7.52 ± 9.12 | 0.22 | 0.87 |
| RSI | 21.26 ± 6.83 | 20.76 ± 6.83 | 21.83 ± 8.95 | 23.92 ± 9.87 | 0.54 | 0.65 |
| UES duration (s) | 2.42 ± 0.55 | 2.44 ± 0.71 | 3.27 ± 0.72 | 3.67 ± 0.34 | 19.21 | 0.001 * |
| UES Pressure (mmHg) | ||||||
| Point U1 | 140.12 ± 39.37 | 127.05 ± 36.53 | 114.28 ± 40.57 | 113.06 ± 32.50 | 2.02 | 0.11 |
| Point U2 | 126.34 ± 29.68 | 95.57 ± 37.51 | 93.05 ± 35.38 | 88.08 ± 23.53 | 4.54 | 0.01 * |
| Point U3 | 104.22 ± 37.40 | 64.55 ± 21.67 | 64.06 ± 20.76 | 40.05 ± 24.72 | 19.32 | 0.001 * |
| Point U4 | 102.67 ± 29.96 | 39.08 ± 26.38 | 37.02 ± 19.57 | 32.01 ± 18.89 | 33.31 | 0.001 * |
| LES duration (s) | 1.51 ± 0.65 | 2.26 ± 0.62 | 4.73 ± 1.50 | 6.75 ± 1.87 | 87.67 | 0.001 * |
| LES Pressure (mmHg) | ||||||
| Point L1 | 77.05 ± 21.26 | 62.05 ± 18.32 | 60.03 ± 27.16 | 43.34 ± 19.90 | 22.74 | 0.001 * |
| Point L2 | 79.03 ± 21.63 | 70.08 ± 19.05 | 66.08 ± 27.17 | 52.56 ± 25.95 | 7.21 | 0.001 * |
| Point L3 | 87.06 ± 32.62 | 76.51 ± 37.78 | 62.24 ± 30.98 | 60.09 ± 28.12 | 2.61 | 0.06 |
| Point L4 | 92.01 ± 35.19 | 83.04 ± 32.09 | 82.11 ± 34.01 | 69.12 ± 36.09 | 1.35 | 0.26 |
| Grade A vs. Grade D | Grade B vs. Grade A | Grade C vs. Grade B | Grade D vs. Grade C | Comparison | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFS | 0.72 | 0.06 | 0.30 | 0.98 | B > D > C > A |
| EAT-10 | 0.47 | 0.64 | 0.76 | 0.96 | C > D > B > A |
| RSI | 0.32 | 0.77 | 0.63 | 0.54 | B < A < C < D |
| UES duration (s) | 0.001 * | 0.90 | 0.001 * | 0.07 | A < B < C < D |
| UES Pressure (mmHg) | |||||
| Point U1 | 0.03 * | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.92 | A > B > C > D |
| Point U2 | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | 0.81 | 0.66 | A > B > C > D |
| Point U3 | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | 0.93 | 0.007 * | A > B > C > D |
| Point U4 | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | 0.77 | 0.48 | A > B > C > D |
| LES duration (s) | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | 0.002 * | A < B < C < D |
| LES Pressure (mmHg) | |||||
| Point L1 | 0.001 * | 0.004 * | 0.78 | 0.04 * | A > B > C >D |
| Point L2 | 0.001 * | 0.09 | 0.50 | 0.17 | A > B > C >D |
| Point L3 | 0.01 * | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.84 | A > B > C > D |
| Point L4 | 0.02 * | 0.30 | 0.92 | 0.32 | A > B > C > D |
| Factors (No. of Patient) | LES Duration (s) | LES Pressure (mmHg) | UES Duration (s) | UES Pressure (mmHg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point L1 | Point L2 | Point L3 | Point L4 | Point U1 | Point U2 | Point U3 | Point U4 | |||
| Gender (n = 90) | ||||||||||
| Female (n = 49) | 2.51 ± 2.33 | 61.42 ± 50.45 | 63.87 ± 66.32 | 80.85 ± 80.12 | 87.67 ± 90.55 | 2.63 ± 2.44 | 127.42 ± 100.23 | 97.40 ± 89.32 | 55.75 ± 58.32 | 36.35 ± 38.34 |
| Male (n = 41) | 2.56 ± 2.76 | 69.46 ± 60.11 | 68.85 ± 63.21 | 74.15 ± 80.77 | 76.86 ± 69.28 | 2.54 ± 2.45 | 112.35 ± 89.32 | 97.69 ± 91.33 | 65.19 ± 64.78 | 44.31 ± 56.32 |
| p = 0.75 | p = 0.13 | p = 0.34 | p = 0.07 | p = 0.64 | p = 0.85 | p = 0.14 | p = 0.63 | p = 0.45 | p = 0.17 | |
| Age (n = 90) | ||||||||||
| <39 (n = 18) | 2.73 ± 2.33 | 70.53 ± 79.87 | 74.03 ± 69.56 | 86.82 ± 71.21 | 96.37 ± 90.12 | 2.63 ± 2.38 | 128.52 ± 101.78 | 119.42 ± 97.89 | 70.09 ± 72.32 | 53.23 ± 60.21 |
| 40~49 (n = 23) | 1.84 ± 3.01 | 64.12 ± 57.91 | 66.85 ± 66.01 | 84.61 ± 90.12 | 85.83 ± 78.34 | 2.87 ± 2.56 | 126.60 ± 102.52 | 101.86 ± 98.87 | 56.98 ± 47.21 | 35.56 ± 36.77 |
| 50~59 (n = 28) | 2.63 ± 2.89 | 62.87 ± 61.23 | 66.12 ± 62.89 | 80.16 ± 79.28 | 84.22 ± 80.23 | 2.33 ± 2.32 | 123.10 ± 98.35 | 99.74 ± 98.22 | 54.66 ± 47.55 | 38.19 ± 36.70 |
| >60 (n = 21) | 2.67 ± 3.21 | 58.29 ± 55.22 | 59.07 ± 62.45 | 74.81 ± 76.56 | 78.33 ± 69.43 | 2.97 ± 3.32 | 109.66 ± 70.21 | 88.67 ± 90.32 | 46.09 ± 50.44 | 28.51 ± 47.56 |
| p = 0.82 | p = 0.72 | p = 0.67 | p = 0.49 | p = 0.85 | p = 0.94 | p = 0.50 | p = 0.35 | p = 0.56 | p = 0.41 | |
| BMI (n = 90) | ||||||||||
| <28 (n = 55) | 2.35 ± 2.66 | 60.72 ± 58.46 | 63.17 ± 62.38 | 74.82 ± 69.76 | 80.21 ± 79.33 | 2.67 ± 2.35 | 115.82 ± 89.45 | 97.59 ± 85.39 | 66.25 ± 50.19 | 37.42 ± 35.77 |
| ≥28 (n = 35) | 1.86 ± 3.01 | 68.75 ± 59.32 | 71.81 ± 69.88 | 75.62 ± 72.43 | 94.25 ± 87.56 | 2.70 ± 2.76 | 105.60 ± 70.32 | 96.40 ± 88.24 | 58.21 ± 55.84 | 44.23 ± 46.93 |
| p = 0.52 | p = 0.21 | p = 0.90 | p = 0.88 | p = 0.62 | p = 0.12 | p = 0.42 | p = 0.64 | p = 0.89 | p = 0.88 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsou, Y.-A.; Chen, S.-H.; Wu, W.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Bassa, D.; Shih, L.-C.; Chang, W.-D. Esophageal Pressure and Clinical Assessments in the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225262
Tsou Y-A, Chen S-H, Wu W-C, Tsai M-H, Bassa D, Shih L-C, Chang W-D. Esophageal Pressure and Clinical Assessments in the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(22):5262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225262
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsou, Yung-An, Sheng-Hwa Chen, Wen-Chieh Wu, Ming-Hsui Tsai, David Bassa, Liang-Chun Shih, and Wen-Dien Chang. 2021. "Esophageal Pressure and Clinical Assessments in the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 22: 5262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225262
APA StyleTsou, Y.-A., Chen, S.-H., Wu, W.-C., Tsai, M.-H., Bassa, D., Shih, L.-C., & Chang, W.-D. (2021). Esophageal Pressure and Clinical Assessments in the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(22), 5262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225262







