Long-Term Results of Kidney Transplantation in the Elderly: Comparison between Different Donor Settings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Deceased Donor Kidney Allocation
2.3. Operative Management
2.4. Perioperative Management
2.5. Clinical Outcomes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison between the Live Donor Group (LD) and the Two Deceased Donor Groups: Old-to-Old (DD-OTO) and Young-to-Old (DD-YTO) Recipients
3.2. Comparison between Patients 70 and Older to Patients 60–69 Years
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hart, A.; Smith, J.M.; Skeans, M.A.; Gustafson, S.K.; Wilk, A.R.; Castro, S.; Foutz, J.; Wainright, J.L.; Snyder, J.J.; Kasiske, B.L.; et al. OPTN/SRTR 2018 annual data report: Kidney. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 20–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasiske, B.L.; Cangro, C.B.; Hariharan, S.; Hricik, D.E.; Kerman, R.H.; Roth, D.; Rush, D.N.; Vazquez, M.A.; Weir, M.R.; American Society of Transplantation. The evaluation of renal transplantation candidates—Clinical practice guidelines. Am. J. Transplant. 2001, 1, 3–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, R.A.; Ashby, V.B.; Milford, E.L.; Ojo, A.O.; Ettenger, R.E.; Agodoa, L.Y.C.; Held, P.J.; Port, F.K. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, P.S.; Merion, R.M.; Ashby, V.B.; Port, F.K.; Wolfe, R.A.; Kayler, L.K. Renal transplantation in elderly patients older than 70 years of age: Results from the scientific registry of transplant recipients. Transplantation 2007, 83, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harhay, M.N.; Rao, M.K.; Woodside, K.J.; Johansen, K.L.; Lentine, K.L.; Tullius, S.G.; Parsons, R.F.; Alhamad, T.; Berger, J.; Cheng, X.S.; et al. An overview of frailty in kidney transplantation: Measurement, management and future considerations. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2020, 35, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolla, C.; Naso, E.; Mella, A. Impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on kidney transplant rates and clinical outcomes among waitlisted candidates in a single center European experience. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassal, S.V.; Krahn, M.; Naglie, G.; Zaltzman, J.S.; Roscoe, J.M.; Cole, E.H.; Redelmeier, D.A. Kidney transplantation in the elderly: A decision analysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heldal, K.; Hartmann, A.; Grootendorst, D.C.; de Jager, D.J.; Leivestad, T.; Foss, A.; Midtvedt, K. Benefit of kidney transplantation beyond 70 years of age. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 25, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosengard, B.R.; Feng, S.; Alfrey, E.J.; Zaroff, J.G.; Emond, J.C.; Henry, M.L.; Garrity, E.R.; Roberts, J.P.; Wynn, J.; Metzger, R.A.; et al. Report of the Crystal City meeting to maximize the use of organs recovered from the cadaver donor. Am. J. Transplant. 2002, 2, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlieper, G.; Ivens, K.; Voiculescu, A.; Luther, B.; Sandmann, W.; Grabensee, B. Eurotransplant senior program ‘old for old’: Results from 10 patients. Clin. Transpl. 2001, 15, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss-Salz, I.; Mandel, M.; Galai, N.; Boner, G.; Mor, E.; Nakache, R.; Simchen, E.; Israeli Transplantation Consortium. Negative impact of “old-to-old” donations on success of cadaveric renal transplants. Clin. Transpl. 2005, 19, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavee, J.; Ashkenazi, T.; Gurman, G.; Steinberg, D. A new law for allocation of donor organs in Israel. Lancet 2010, 375, 1131–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port, F.K.; Bragg-Gresham, J.L.; Metzger, R.A.; Dykstra, D.M.; Gillespie, B.W.; Young, E.W.; Delmonico, F.L.; Wynn, J.J.; Merion, R.M.; Wolfe, R.A.; et al. Donor characteristics associated with reduced graft survival: An approach to expanding the pool of kidney donors. Transplantation 2002, 74, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanriover, B.; Mohan, S.; Cohen, D.J. Kidneys at higher risk of discard: Expanding the role of dual kidney transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- A Guide to Calculating and Interpreting the Kidney Donor Profle Index (KDPI). 2020. Available online: https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/media/1512/guide_to_calculating_interpreting_kdpi.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2020).
- Ojo, A.O.; Hanson, J.A.; Meier-Kriesche, H.-U.; Okechukwu, C.N.; Wolfe, R.A.; Leichtman, A.B.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Kaplan, B.; Port, F.K. Survival in recipients of marginal cadaveric donor kidneys compared with other recipients and wait-listed transplant candidates. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2001, 12, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, M.; Pascual, J. Strategies for an expanded use of kidneys from elderly donors. Transplantation 2017, 101, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloveras, J.; Arcos, E.; Comas, J.; Crespo, M.; Pascual, J. A paired survival analysis comparing hemodialysis and kidney transplantation from deceased elderly donors older than 65 years. Transplantation 2015, 99, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kriesche, H.-U.; Schold, J.D.; Gaston, R.S.; Wadstrom, J.; Kaplan, B. Kidneys from deceased donors: Maximizing the value of a scarce resource. Am. J. Transpl. 2005, 5, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.; Bunnapradist, S.; Danovitch, G.M.; Gjertson, D.; Gill, J.S.; Cecka, M. Outcomes of kidney transplantation from older living donors. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 52, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, M.Z.; Streja, E.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Shah, A.; Huang, E.; Bunnapradist, S.; Krishnan, M.; Kopple, J.D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Age and the associations of living donor and expanded criteria donor kidneys with kidney transplant outcomes. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 59, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berger, J.C.; Muzaale, A.D.; James, N.; Hoque, M.O.; Wang, J.M.G.; Montgomery, R.A.; Massie, A.B.; Hall, E.C.; Segev, D.L. Living kidney donors ages 70 and older: Recipient and donor outcomes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 2887–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.; Kim, S.J.; Speechley, M.R.; Huang, A.; Knoll, G.; Prasad, G.V.R.; Treleaven, D.; Diamant, M.; Garg, A.X.; for the Donor Nephrectomy Outcomes Research (DONOR) Network. Accepting kidneys from older living donors: Impact on transplant recipient outcomes. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Gill, J.; Dong, J.; Rose, C.; Yan, H.; Landsberg, D.; Cole, E.H.; Gill, J.S. Article living donor age and kidney allograft half-life: Implications for living donor paired exchange programs. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schold, J.D.; Meier-Kriesche, H.-U. Which renal transplant candidates should accept marginal kidneys in exchange for a shorter waiting time on dialysis? Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 1, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, P.F.; Cristelli, M.P.; Aldworth, C.A.R.; Freitas, T.V.D.S.; Felipe, C.R.; Júnior, H.T.S.; Pestana, J.O.M.D.A. Long-term outcomes of elderly kidney transplant recipients. J. Bras. Nefrol. 2015, 37, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Kidney Transplant Candidate Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Candidates for Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2020, 104, S11–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFalls, E.O.; Ward, H.B.; Moritz, T.E.; Goldman, S.; Krupski, W.C.; Littooy, F.; Pierpont, G.; Santilli, S.; Rapp, J.; Hattler, B.; et al. Coronary-artery revascularization before elective major vascular surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2795–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chadban, S.J.; Ahn, C.; Axelrod, D.A.; Foster, B.J.; Kasiske, B.L.; Kher, V.; Kumar, D.; Oberbauer, R.; Pascual, J.; Pilmore, H.L.; et al. Summary of the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) clinical practice guideline on the evaluation and management of candidates for kidney transplantation. Transplantation 2020, 104, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.N.; Murad, D.N.; Knoll, G.A. Thinking Outside the Box: Novel Kidney Protective Strategies in Kidney Transplantation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachtner, T.; Otto, N.M.; Reinke, P. Two decades of the Eurotransplant Senior Program: The gender gap in mortality impacts patient survival after kidney transplantation. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, C.L.; Washburn, K.; Dean, P.G.; Helmick, R.A.; Pugh, J.; Stegall, M.D. Survival benefit in older patients associated with earlier transplant with high KDPI kidneys. Transplantation 2017, 101, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- UNOS. Questions and Answers for Transplant Candidates about the Kidney Allocation System How Are Kidneys Classified? What Goes into a KDPI Score? Available online: www.unos.org (accessed on 13 October 2021).
- Bae, S.; Massie, A.B.; Thomas, A.G.; Bahn, G.; Luo, X.; Jackson, K.; Ottmann, S.E.; Brennan, D.C.; Desai, N.M.; Coresh, J.; et al. Who can tolerate a marginal kidney? Predicting survival after deceased-donor kidney transplantation by donor-recipient combination. Am. J. Transpl. 2019, 19, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
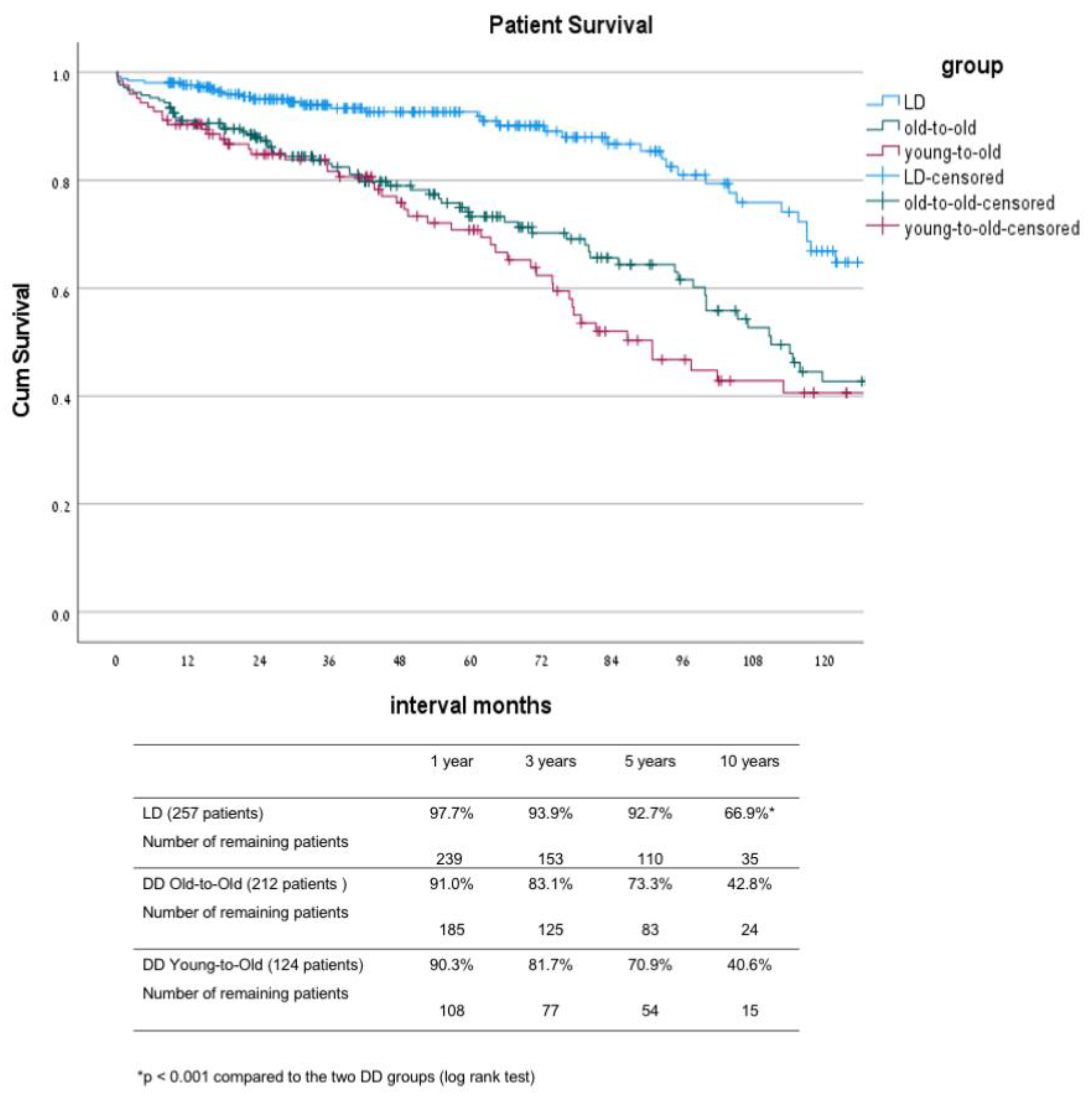
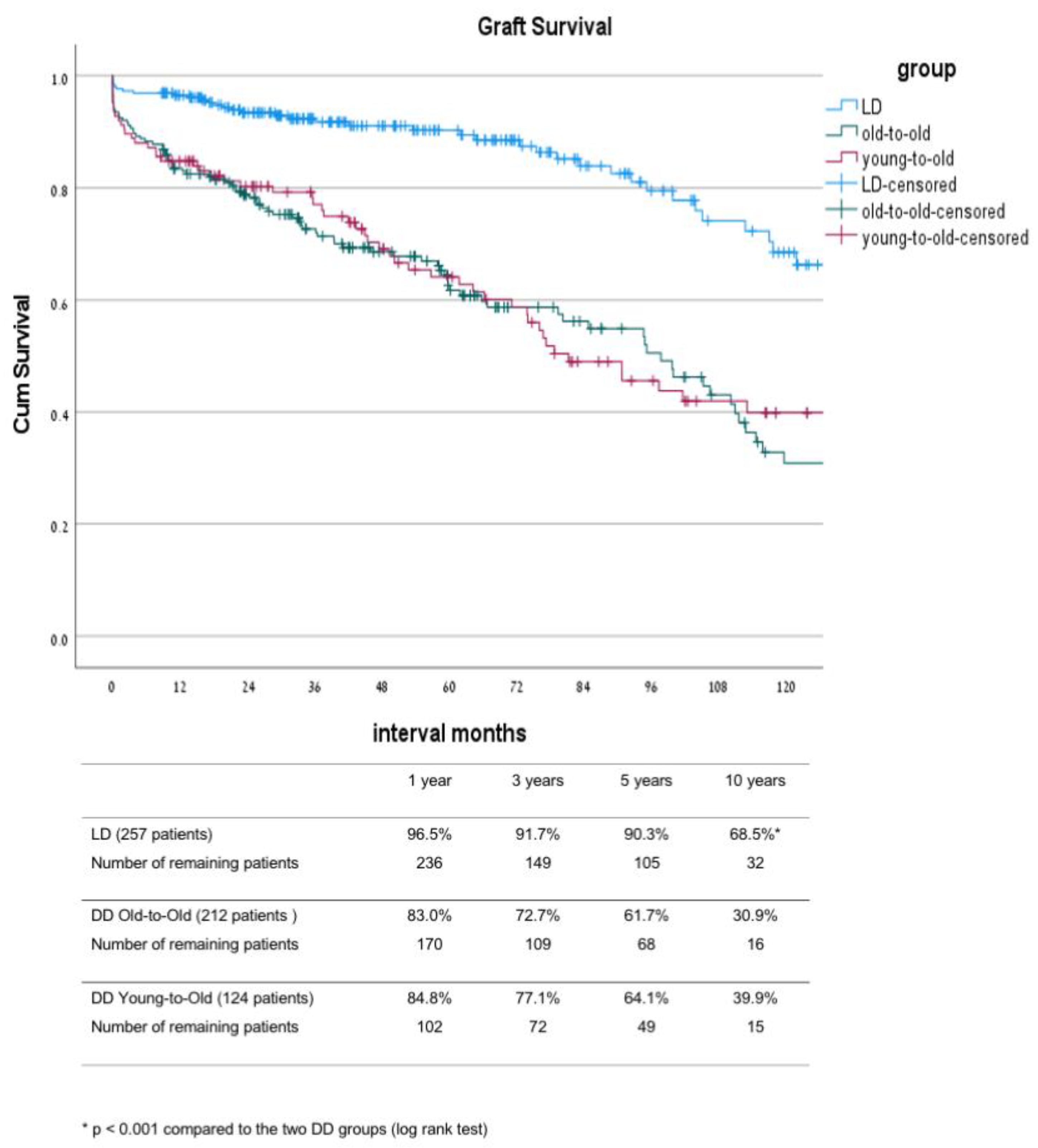

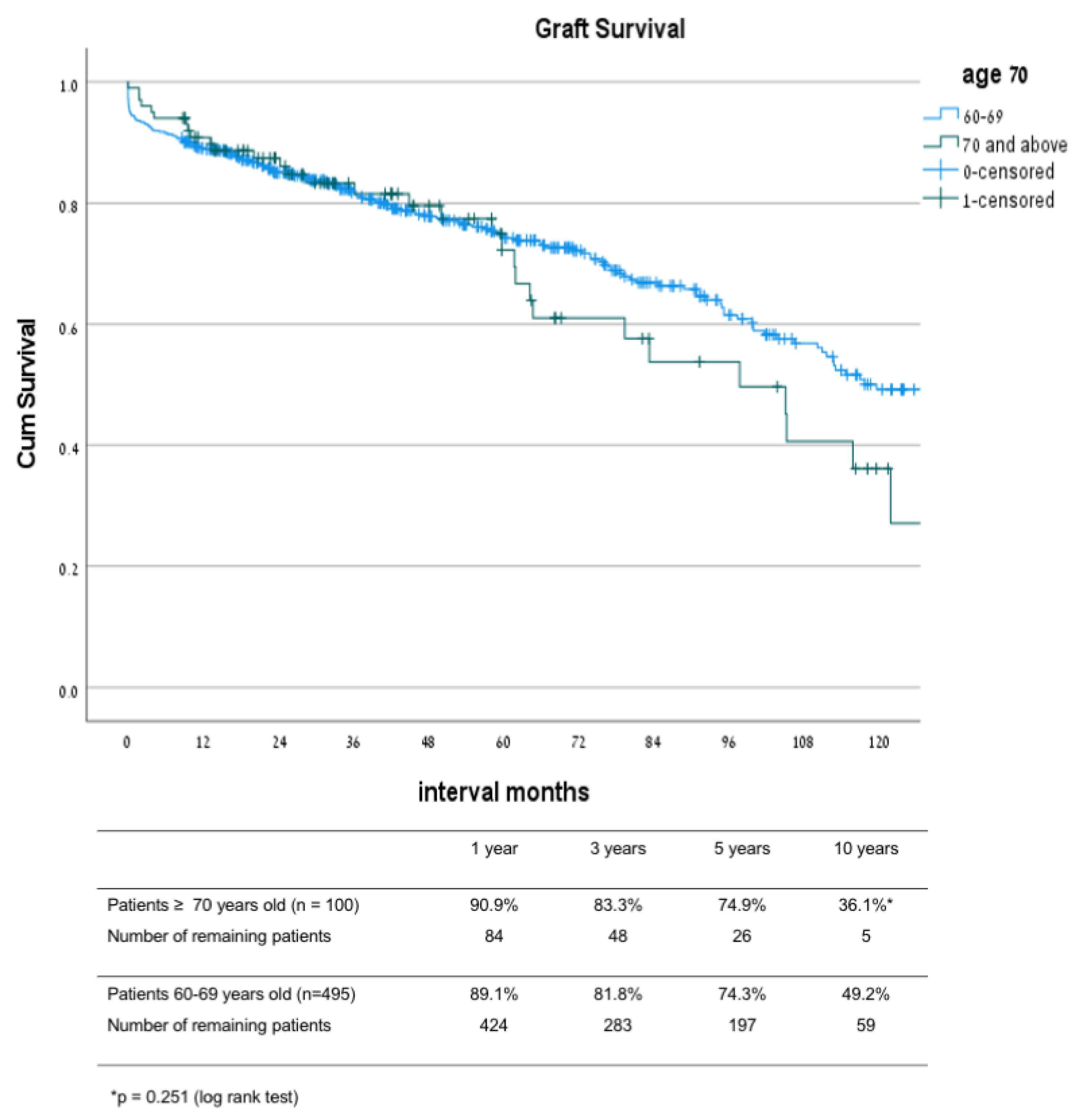


| Living Donor n = 257 | DD Old-to-Old n = 213 | DD Young-to-Old n = 123 | p Value LD vs. DD | p Value OTO vs. YTO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean follow-up (months) | 63.0 ± 49.5 | 59.4 ± 47.4 | 60.6 ± 49.2 | 0.714 | 0.082 |
| Recipient age (years) | 64.9 ± 3.8 | 65.7 ± 5.0 | 64.5 ± 3.6 | 0.036 | 0.012 |
| Recipient Gender M/F (%) | 76.4/23.1 | 78.4/21.6 | 69.6/30.4 | 0.180 | 0.480 |
| Primary Disease (%) | 0.014 | 0.133 | |||
| HTN | 10.1 | 15.5 | 9.6 | ||
| DM | 32.2 | 32.4 | 20.0 | ||
| PCKD | 12.4 | 12.7 | 11.2 | ||
| GN | 7.4 | 7.5 | 12.8 | ||
| Pyelonephritis | 3.9 | 2.3 | 5.6 | ||
| FSGS | 4.3 | 7.0 | 7.2 | ||
| IgA | 5.4 | 2.8 | 2.8 | ||
| Other | 10.5 | 6.1 | 14.4 | ||
| Unknown | 13.8 | 13.7 | 16.4 | ||
| Diabetes (%) | 49.6 | 45.1 | 34.2 | 0.020 | 0.093 |
| IHD (%) | 32.9 | 39.7 | 42.2 | 0.159 | 0.770 |
| PRA class I (%) | 8.3 | 0.0 | 11.4 | 0.001 | 0.015 |
| PRA class II (%) | 6.6 | 0.0 | 3.9 | 0.002 | 0.016 |
| Time on dialysis (mo.) | 21.5 ± 22.7 | 63.3 ± 28.8 | 61.9 ± 33.8 | p < 0.001 | 0.486 |
| HLA-B full-match (%) | 6.7 | 1.2 | 4.2 | p < 0.001 | 0.273 |
| HLA-DR full-match (%) | 6.7 | 2.9 | 10.3 | p < 0.001 | 0.058 |
| Re-transplantation (%) | 8.1 | 3.8 | 9.6 | 0.205 | 0.086 |
| Donor age (years) | 45.9 ± 12.4 | 65.9 ± 4.4 | 47.1 ± 11.0 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Donor gender M/F (%) | 54.3/45.7 | 56.6/43.4 | 60.5/39.5 | 0.521 | 0.730 |
| Induction (%) | p < 0.001 | 0.828 | |||
| IL-2 inhibitor | 75.3 | 46.4 | 48.8 | ||
| ATG | 8.6 | 48.8 | 45.5 | ||
| Desensitization (IVIG + PP + Rituximab) | 8.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Cold ischemia time (hours) | 3.5 ± 1.8 | 10.1 ± 3.7 | 10.8 ± 3.8 | p < 0.001 | 0.524 |
| Living Donor n = 257 | DD Old-to-Old n = 213 | DD Young-to-Old n = 123 | p Value LD vs. DD | p Value OTO vs. YTO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGF (%) | 9.7 | 41.3 | 47.2 | p < 0.001 | 0.255 |
| PNF (%) | 0.4 | 2.3 | 1.6 | 0.001 | 0.366 |
| Graft Failure (%) | 4.7 | 18.8 | 11.2 | p < 0.001 | 0.531 |
| Death (%) | 15.5 | 36.2 | 40.8 | p < 0.001 | 0.395 |
| Death with functioning graft (%) | 11.6 | 25.8 | 33.6 | p < 0.001 | 0.066 |
| Length of stay (days) | 12.5 ± 23.7 | 15.7 ± 11.6 | 15.9 ± 12.2 | 0.081 | 0.201 |
| Cr 30 days (mg/dL) | 1.36 ± 0.67 | 2.90 ± 1.29 | 1.91 ± 1.28 | p < 0.001 | 0.668 |
| Cr 1 year (mg/dL) | 1.22 ± 0.37 | 1.74 ± 1.12 | 1.79 ± 1.49 | p < 0.001 | 0.717 |
| Cr 5 years (mg/dL) | 1.35 ± 1.14 | 2.29 ± 2.19 | 1.79 ± 1.49 | p < 0.001 | 0.124 |
| Risk Factors for Death | Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p Value |
| Age | 1.060 | 1.019–1.101 | 0.004 |
| DM | 1.773 | 1.241–2.532 | 0.002 |
| IHD | 1.510 | 1.063–2.145 | 0.021 |
| Donor type (DD/LD) | 2.865 | 1.910–3.800 | p < 0.001 |
| Risk Factors for Graft Loss | |||
| IHD | 1.782 | 1.045–3.038 | 0.034 |
| Donor age | 1.025 | 1.000–1.051 | 0.050 |
| Donor type DD/LD | 6.064 | 2.315–15.881 | p < 0.001 |
| Patients 60–69 Years Old n = 493 | Patients ≥ 70 Years Old n = 100 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recipient age (years) | 63.7 ± 2.8 | 72.3 ± 2.4 | p < 0.001 |
| Recipient Gender M/F (%) | 77.4/22.6 | 67/33 | 0.027 |
| Primary Disease (%) | 0.359 | ||
| HTN | 11.1 | 16.0 | |
| DM | 30.2 | 27.0 | |
| PCKD | 12.5 | 11.0 | |
| GN | 8.5 | 9.0 | |
| Pyelonephritis | 4.0 | 2.0 | |
| FSGS | 6.0 | 5.0 | |
| IgA nephropathy | 4.2 | 0.0 | |
| Other | 9.3 | 12.0 | |
| Unknown | 14.2 | 18.0 | |
| Diabetes (%) | 42.9 | 43.0 | 0.942 |
| IHD (%) | 38.0 | 33.3 | 0.392 |
| PRA class I (%) | 8.0 | 5.3 | 0.355 |
| PRA class II (%) | 3.7 | 3.7 | 1.000 |
| Time on dialysis (mo.) | 52.5 ± 31.3 | 46.4 ± 34.8 | 0.115 |
| HLA-B full-match (%) | 5.3 | 0.0 | 0.013 |
| HLA-DR full-match (%) | 7.0 | 2.6 | 0.108 |
| Re-transplantation (%) | 7.3 | 5.1 | 0.558 |
| Donor age (years) | 52.4 ± 13.8 | 57.8 ± 12.2 | p < 0.001 |
| Donor gender M/F (%) | 55.2/44.8 | 63/37 | 0.230 |
| Donor type LD (%) | 19.8 | 12.8 | 0.016 |
| Induction (%) | 0.129 | ||
| IL-2 inhibitor | 59.2 | 61.0 | |
| ATG | 29.5 | 36.0 | |
| Desensitization | 4.3 | 1.0 | |
| (PP ± Rituximab) | 7.0 | 2.0 | |
| Cold ischemia time (hours) | 10.0 ± 3.5 | 10.7 ± 4.1 | 0.263 |
| Patients 60–69 Years Old n = 493 | Patients ≥ 70 Years Old n = 100 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DGF (%) | 28.5 | 32.0 | 0.746 |
| PNF (%) | 1.4 | 1.0 | 0.672 |
| Graft failure (%) | 32.5 | 32.0 | 0.929 |
| Death (%) | 27.6 | 31.0 | 0.493 |
| Death with functioning graft (%) | 17.9 | 26.0 | 0.054 |
| Length of stay (days) | 14.4 ± 19.4 | 14.0 ± 9.2 | 0.847 |
| Cr 30 days (mg/dL) | 1.76 ± 1.18 | 1.55 ± 0.67 | 0.084 |
| Cr 1 year (mg/dL) | 1.55 ± 1.09 | 1.38 ± 0.38 | 0.068 |
| Cr 5 years (mg/dL) | 1.77 ± 1.75 | 1.61 ± 0.78 | 0.668 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yemini, R.; Rahamimov, R.; Ghinea, R.; Mor, E. Long-Term Results of Kidney Transplantation in the Elderly: Comparison between Different Donor Settings. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5308. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225308
Yemini R, Rahamimov R, Ghinea R, Mor E. Long-Term Results of Kidney Transplantation in the Elderly: Comparison between Different Donor Settings. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(22):5308. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225308
Chicago/Turabian StyleYemini, Renana, Ruth Rahamimov, Ronen Ghinea, and Eytan Mor. 2021. "Long-Term Results of Kidney Transplantation in the Elderly: Comparison between Different Donor Settings" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 22: 5308. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225308
APA StyleYemini, R., Rahamimov, R., Ghinea, R., & Mor, E. (2021). Long-Term Results of Kidney Transplantation in the Elderly: Comparison between Different Donor Settings. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(22), 5308. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225308







