Oral Mucosa and Nails in Genodermatoses: A Diagnostic Challenge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Darier’s Disease
1.2. Dyschromatosis Universalis Hereditaria
1.3. Dyskeratosis Congenita
1.4. Epidermolysis Bullosa
1.5. Focal Dermal Hypoplasia
1.6. Pachyonychia Congenita
1.7. Papillon–Lefèvre Syndrome
1.8. Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)
2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilder, E.G.; Frieder, J.; Sulhan, S.; Michel, P.; Cizenski, J.D.; Wright, J.M.; Menter, M.A. Spectrum of orocutaneous disease associations: Genodermatoses and inflammatory conditions. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 809–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J.; Seebode, C.; Emmert, S. Research on genodermatoses using novel genome-editing tools. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2017, 15, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaffer, J.V. Practice and Educational Gaps in Genodermatoses. Dermatol. Clin. 2017, 34, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.J.; Atzmony, L.; Lim, Y.; McNiff, J.M.; Craiglow, B.G.; Antaya, R.J.; Choate, K.A. Review of genodermatoses with characteristic histopathology and potential diagnostic delay. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2019, 46, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandhi, D. Current status of genodermatoses: An Indian perspective. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2015, 81, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blentic, A.; Tandon, P.; Payton, S.; Walshe, J.; Carney, T.; Kelsh, R.N.; Mason, I.; Graham, A. The emergence of ectomesenchyme. Dev. Dyn. 2008, 237, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sprecher, E. Genetic hair and nail disorders. Clin. Dermatol. 2005, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamadar, A.C.; Palit, A. Nails: Diagnostic clue to genodermatoses. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2012, 78, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G. Nails in systemic disease. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2011, 77, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Shilpasree, A.S.; Chaudhary, M. Oral Manifestations and Molecular Basis of Oral Genodermatoses: A Review. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2016, 10, ZE08–ZE12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dika, E.; Starace, M.; Lambertini, M.; Patrizi, A.; Veronesi, G.; Alessandrini, A.; Piraccini, B.M. Oral and nail pigmentations: A useful parallelism for the clinician. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2020, 18, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, J.L.; Rogers, R.S., 3rd. Oral manifestations of genodermatoses. Dermatol. Clin. 2003, 21, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, A.; Stein, S.; Kenner-Bell, B. Acro-Dermato-Ungual-Lacrimal-Tooth Syndrome: An Uncommon Member of the Ectodermal Dysplasias. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2016, 33, e322–e326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, G.; Elbay, U. Rapp-Hodgkin syndrome: Clinical and dental findings. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2009, 34, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanda, N.; Anthonappa, R.; Al-Mulla, H.; King, N. Long-term dental management of a patient with features of Schöpf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome. Spec. Care Dent. 2017, 37, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.; Eid, E.; Hamieh, L.; Bardawil, T.; Moujaes, Z.; Khalil, W.; Abbas, O.; Kurban, M. Genodermatoses with teeth abnormalities. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.J.; Jagati, A.K.; Gupta, N.P.; Dhamale, S.S. Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome: A rare case. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2015, 6, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharati, A.; Navit, S.; Khan, S.A.; Jabeen, S.; Grover, N.; Upadhyay, M. Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal Dysplasia Clefting Syndrome: A Case Report of Its Dental Management with 2 Years Follow-Up. Case Rep. Dent. 2020, 8418725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, D.; Attuati, S.; Besana, M.; Rodilosso, G.; Quinzi, V.; Marzo, G.; Carinci, F. Oral and craniofacial manifestations of Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome: A systematic review. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2019, 20, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devadas, S.; Varma, B.; Mungara, J.; Joseph, T.; Saraswathi, T.R. Witkop tooth and nail syndrome: A case report. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2005, 15, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, N.; Graham-Brown, R.A. Nail dystrophy, an unusual presentation of incontinentia pigmenti. Br. J. Dermatol. 2003, 149, 1286–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.; Lurie, A.G.; Reichenberger, E. Clinical features of tricho-dento-osseous syndrome and presentation of three new cases: An addition to clinical heterogeneity. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2005, 100, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Reali, J.; Mendoza-Ramos, M.I.; Garrido-Guerrero, E.; Méndez-Catalá, C.F.; Méndez-Cruz, A.R.; Pozo-Molina, G. Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia: Clinical and molecular review. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wong, S.W.; He, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, D.; Feng, H. Distinct impacts of bi-allelic WNT10A mutations on the permanent and primary dentitions in odonto-onycho-dermal dysplasia. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2019, 179, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.; Kini, P.; Chopra, D.; Gupta, Y. Finlay-Marks syndrome: Report of two siblings and review of literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2012, 158A, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, D.C.; Limdi, P.K.; Parekh, N.V.; Gohil, N.R. Oculodentodigital dysplasia. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 64, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?lng=EN&Expert=2710 (accessed on 5 December 2020).
- Tirali, R.E.; Sar, C.; Cehreli, S.B. Oro-facio-dental findings of rubinstein-taybi syndrome as a useful diagnostic feature. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2014, 8, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, A.; Daniel, R.; Piraccini, B.A.; Iorizzo, M. Color Atlas of Nails; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Coto, A.; Rojas-Solano, L.F.; Hidalgo-Hidalgo, H.; Solano-Aguilar, E.; Esquivel-Chinchilla, J.M. Erythropoietic porphyria. Report of the 1st case in Costa Rica. Med. Cutan. Ibero Lat. Am. 1983, 11, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Dharman, S.; Arvind, M. Darier’s disease—Oral, general and histopathological features in a 7 year old child. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2016, 34, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, S.J.; Rosario-Collazo, J.A. Keratosis Follicularis (Darier Disease). In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal, V.N.; Srivastava, G. Darier’s (Darier-White) disease/keratosis follicularis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2005, 44, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katta, R.; Reed, J.; Wolf, J.E. Cornifying Darier’s disease. Int. J. Dermatol. 2000, 39, 844–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanway, A. Darier Disease. DermNet NZ. Available online: http://www.dermnetnz.org/scaly/darier.html (accessed on 18 August 2020).
- Korman, A.M.; Milani-Nejad, N. Darier Disease. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwetha, V.; Sujatha, S.; Yashoda Devi, B.K.; Rakesh, N.; Pavan Kumar, T.; Priyadharshini, R.; Krishnamurthy, Y. Spectrum of features in Darier’s disease: A case report with emphasis on differential diagnosis. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2019, 9, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online:https://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?lng=en&Expert=241 (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Yao, Z. Updated review of genetic reticulate pigmentary disorders. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sharma, Y.; Dash, K.N.; Verma, S.; Natarajan, V.T.; Singh, A. Ultrastructural Investigations in an Autosomal Recessively Inherited Case of Dyschromatosis Universalis Hereditaria. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2015, 95, 738–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.W.; Asan, S.J.; Vano-Galvan, S.; Liu, F.X.; Wei, X.X.; Ma, D.L. Differential Diagnosis of Two Chinese Families with Dyschromatoses by Targeted Gene Sequencing. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojhirunsakool, S.; Vachiramon, V. Dyschromatosis universalis hereditaria with renal failure. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2015, 7, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirka, C.S.; Sahu, K.; Rout, A.N. Dyschromatosis Universalis Hereditaria with Hypospadias: A Rare Association. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 11, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, N.S.; Anandan, V.; Jameela, W.A.; Kumar, V.S.; Lavanya, P. A Case Report of Dyschromatosis Universalis Hereditaria (DUH) with Primary Ovarian Failure (POF). J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2016, 10, WD1–WD2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.L.; Wang, H.J.; Lin, Z.M.; Yang, Y. Novel mutations in SASH1 associated with dyschromatosis universalis hereditaria. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2019, 85, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethuraman, G.; Srinivas, C.R.; D’Souza, M.; Thappa, D.M.; Smiles, L. Dyschromatosis universalis hereditaria. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2002, 27, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Rajendra, O.; Prasad, H. Dyschromatosis universalis hereditaria: A case report. Int. J. Dermatol. 2014, 53, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Kumagai, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Yamamoto, E. Cole-Engman syndrome associated with leukoplakia of the tongue: A case report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1999, 57, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auluck, A. Dyskeratosis congenita. Report of a case with literature review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2017, 12, E369–E373. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Karim, A.; Frezzini, C.; Viggor, S.; Davidson, L.E.; Thornhill, M.H.; Yeoman, C.M. Dyskeratosis congenita: A case report. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2009, 108, e20–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, S.V.; Boggio, P.A.; Fezzi, F.A.; Sebastião, A.L.; Nico, M.M. Dyskeratosis congenita--report of a case with emphasis on gingival aspects. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2009, 26, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández García, M.S.; Teruya-Feldstein, J. The diagnosis and treatment of dyskeratosis congenita: A review. J. Blood Med. 2014, 5, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noto, Z.; Tomihara, K.; Furukawa, K.; Noguchi, M. Dyskeratosis congenita associated with leukoplakia of the tongue. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.C.; Harvey, K.E.; Domingo, D.L.; Trujillo, M.I.; Guadagnini, J.P.; Gollins, S.; Giri, N.; Hart, T.C.; Alter, B.P. Oral and dental phenotype of dyskeratosis congenita. Oral Dis. 2008, 14, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofola, C.; Nassereddin, A.; Gross, G.P. Dyskeratosis Congenita. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507710/ (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Baran, I.; Nalcaci, R.; Kocak, M. Dyskeratosis congenita: Clinical report and review of the literature. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2010, 8, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, S.A. Dyskeratosis Congenita. 12 November 2009 [Updated 21 November 2019]. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, K.; Tripathi, S.; Agarwal, N.; Bareth, A. Dyskeratosis congenita presenting with dysphagia. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2016, 7, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckner, A.L.; Losow, M.; Wisk, J.; Patel, N.; Reha, A.; Lagast, H.; Gault, J.; Gershkowitz, J.; Kopelan, B.; Hund, M.; et al. The challenges of living with and managing epidermolysis bullosa: Insights from patients and caregivers. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inherited epidermolysis bullosa. Available online: https://www.orpha.net/consor/www/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?lng=EN&Expert=79361 (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- Mariath, L.M.; Santin, J.T.; Schuler-Faccini, L.; Kiszewski, A.E. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: Update on the clinical and genetic aspects. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2020, 95, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Jimeno, C.; Escámez, M.J.; Ayuso, C.; Trujillo-Tiebas, M.J.; Del Río, M.; En Representación de la Cátedra de la Fundación Jiménez Díaz de Medicina Regenerativa y Bioingeniería Tisular, DEBRA-España y de Otros Profesionales Sanitarios. Genetic diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa: Recommendations from an expert Spanish research group. [Diagnóstico genético de la epidermólisis bullosa: Recomendaciones de un grupo español de expertos]. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. 2018, 109, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubail, A.R.; Belkharoeva, R.K.; Tepluk, N.P.; Grabovskaya, O.V. A case of a patient with severe epidermolysis bullosa surviving to adulthood. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2018, 11, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Has, C.; Bauer, J.W.; Bodemer, C.; Bolling, M.C.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Diem, A.; Fine, J.D.; Heagerty, A.; Hovnanian, A.; Marinkovich, M.P.; et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfendner, E.G.; Bruckner, A.L. Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex. 7 October 1998 [Updated 13 October 2016]. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1369/ (accessed on 31 August 2020).
- Bergman, R.; Harel, A.; Sprecher, E. Dyskeratosis as a histologic feature in epidermolysis bullosa simplex-Dowling Meara. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 57, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfendner, E.G.; Lucky, A.W. Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa. 22 February 2008 [Updated 20 Decemer 2018]. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1125/ (accessed on 31 August 2020).
- Serrano-Martínez, M.C.; Bagán, J.V.; Silvestre, F.J.; Viguer, M.T. Oral lesions in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Oral Dis. 2003, 9, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfendner, E.G.; Lucky, A.W. Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. 21 August 2006 [Updated 13 September 2018]. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/ (accessed on 31 August 2020).
- Lai-Cheong, J.E.; McGrath, J.A. Kindler syndrome. Dermatol. Clin. 2010, 28, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Sato, M.; Ban, M.; Kitajima, Y.; Ishizaki, S.; Harada, T.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Fine, J.D.; Burgeson, R.; Kon, A.; et al. Immunohistochemical, ultrastructural, and molecular features of Kindler syndrome distinguish it from dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Arch. Dermatol. 1997, 133, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssefian, L.; Vahidnezhad, H.; Uitto, J. Kindler Syndrome. 3 March 2016. [Updated 1 December 2016]. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gysin, S.; Itin, P. Blaschko Linear Enamel Defects—A Marker for Focal Dermal Hypoplasia: Case Report of Focal Dermal Hypoplasia. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2015, 7, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.T.; Puranik, C.P.; Farrington, F. Oral phenotype and variation in focal dermal hypoplasia. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2016, 172C, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostwick, B.; Van den Veyver, I.B.; Sutton, V.R. Focal Dermal Hypoplasia. 15 May 2008 [Updated 21 July 2016]. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Krakowski, A.C.; Ozog, D.M.; Ginsberg, D.; Cheng, C.; Chaffins, M.L. Laser-Induced Neocollagenesis in Focal Dermal Hypoplasia Associated With Goltz Syndrome in a Girl. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bree, A.F.; Grange, D.K.; Hicks, M.J.; Goltz, R.W. Dermatologic findings of focal dermal hypoplasia (Goltz syndrome). Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2016, 172C, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jin, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, D.; Hu, T.; Li, W.; Jiang, L.; Dan, H.; Zeng, X.; Chen, Q. Focal dermal hypoplasia: Updates. Oral Dis. 2014, 20, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Dutta, A.; Sarkar, S.; Nag, S.S.; Biswas, S.K.; Mandal, P. Focal Dermal Hypoplasia (Goltz Syndrome): A Cross-sectional Study from Eastern India. Indian J. Dermatol. 2017, 62, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karen, J.K.; Schaffer, J.V. Pachyonychia congenita associated with median rhomboid glossitis. Dermatol. Online J. 2007, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, A.; Rusu, C.; Murgu, A.; Chiriac, A.E.; Wilson, N.J.; Smith, F. First Report of Pachyonychia Congenita Type PC-K6a in the Romanian Population. Maedica 2017, 12, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Pradeep, A.R.; Nagaraja, C. Pachyonychia congenita with unusual dental findings: A case report. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2007, 104, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sravanthi, A.; Srivalli, P.; Gopal, K.V.; Rao, T.N. Pachyonychia congenita with late onset (PC tarda). Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2016, 7, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daroach, M.; Dogra, S.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Tp, A.; Smith, F.; Mahajan, R. Pachyonychia congenita responding favorably to a combination of surgical and medical therapies. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieman, A.G.; Coulombe, P.A. Pathophysiology of pachyonychia congenita-associated palmoplantar keratoderma: New insights into skin epithelial homeostasis and avenues for treatment. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 182, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, F.J.D.; Hansen, C.D.; Hull, P.R.; Kaspar, R.L.; McLean, W.H.I.; O’Toole, E.; Sprecher, E. Pachyonychia Congenita. Pachyonychia Congenita. 27 January 2006 [updated 30 November 2017]. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Leachman, S.A.; Kaspar, R.L.; Fleckman, P.; Florell, S.R.; Smith, F.J.; McLean, W.H.; Lunny, D.P.; Milstone, L.M.; van Steensel, M.A.; Munro, C.S.; et al. Clinical and pathological features of pachyonychia congenita. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2005, 10, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caputo, R.; Tadini, G. Atlas of Genodermatoses; Taylor & Francis e-Library: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, P.; Chhaperwal, M.K.; Singh, A.; Verma, A.; Nijhawan, M.; Singh, K.; Mathur, D. Pachyonychia congenita: A rare genodermatosis. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2013, 4, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachyonychia congenita. Available online: https://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?Expert=2309&lng=EN (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- Sreeramulu, B.; Shyam, N.D.; Ajay, P.; Suman, P. Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome: Clinical presentation and management options. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2015, 7, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, S.M.; Metkari, S.B.; Shetty, S.; Thakkannavar, S.; Sarode, S.C.; Sarode, G.S.; Sengupta, N.; Patil, S. Dental prosthetic rehabilitation of Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome: A case report. Clin. Pract. 2020, 10, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Chedid, J.C.; Salameh, M.; El-Outa, A.; Noujeim, Z. Papillon-Lefèvre Syndrome: Diagnosis, Dental Management, and a Case Report. Case Rep. Dent. 2019, 2019, 4210347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portocarrero, L.; Quental, K.N.; Samorano, L.P.; Oliveira, Z.; Rivitti-Machado, M. Tuberous sclerosis complex: Review based on new diagnostic criteria. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2018, 93, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araujo, L.; Lima, L.S.; Alvarenga, T.M.; Martelli-Júnior, H.; Coletta, R.D.; de Aquino, S.N.; Bonan, P.R. Oral and neurocutaneous phenotypes of familial tuberous sclerosis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2011, 111, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, E.A.; Aeddula, N.R. Tuberous Sclerosis. 7 May 2020. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Volpi, A.; Sala, G.; Lesma, E.; Labriola, F.; Righetti, M.; Alfano, R.M.; Cozzolino, M. Tuberous sclerosis complex: New insights into clinical and therapeutic approach. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northrup, H.; Koenig, M.K.; Pearson, D.A.; Au, K.S. Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. 13 July 1999 [updated 16 April 2020]. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nico, M.M.; Hammerschmidt, M.; Lourenço, S.V. Oral mucosal manifestations in some genodermatoses: Correlation with cutaneous lesions. Eur. J. Dermatol. EJD 2013, 23, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafont, J.; Catherine, J.H.; Lejeune, M.; Ordioni, U.; Lan, R.; Campana, F. Oral and skin manifestations of tuberous sclerosis complex. J. Oral Med. Oral Surg. 2019, 25, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Darling, T.; Moss, J.; Lee, C.C. Histologic variants of periungual fibromas in tuberous sclerosis complex. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 64, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

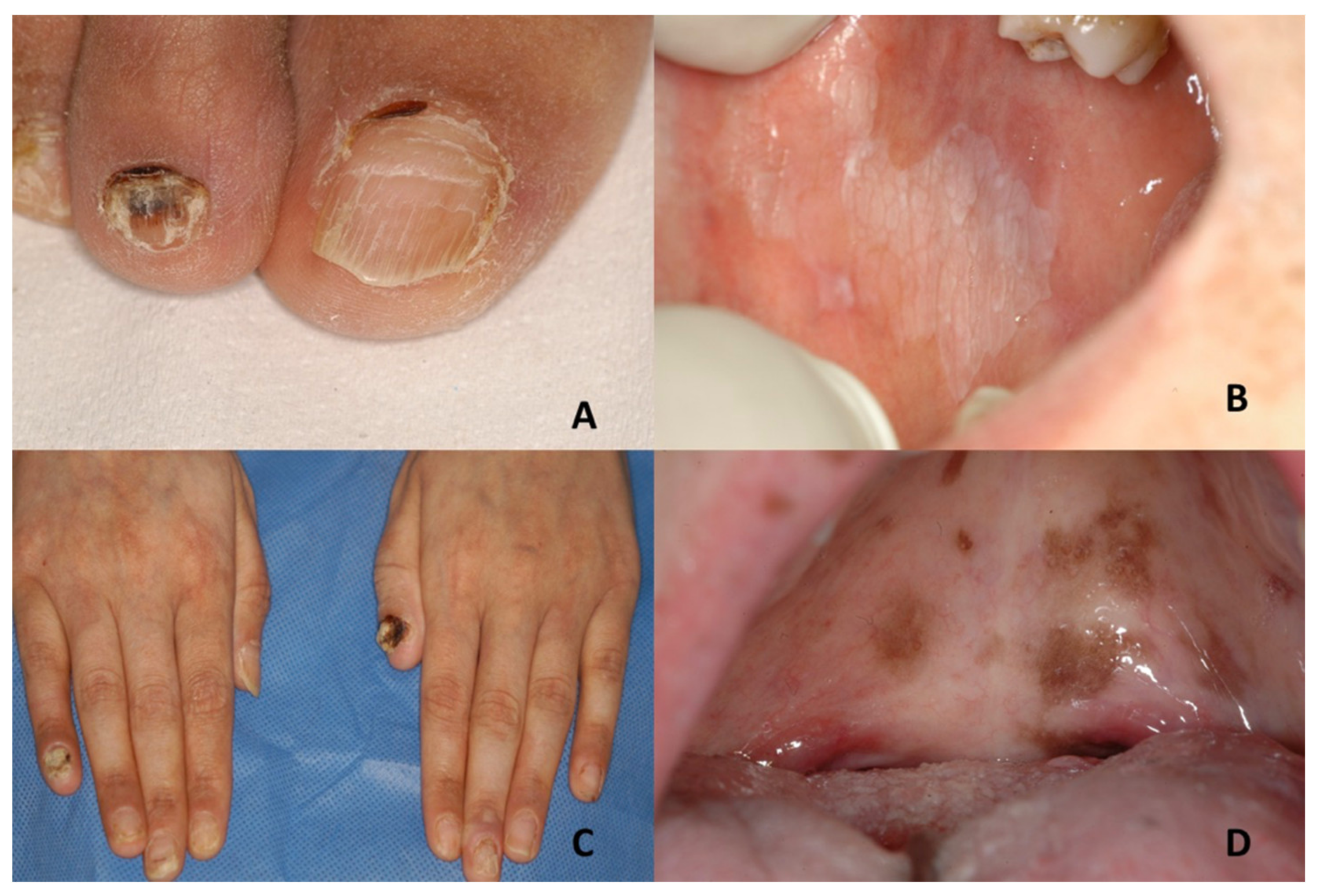

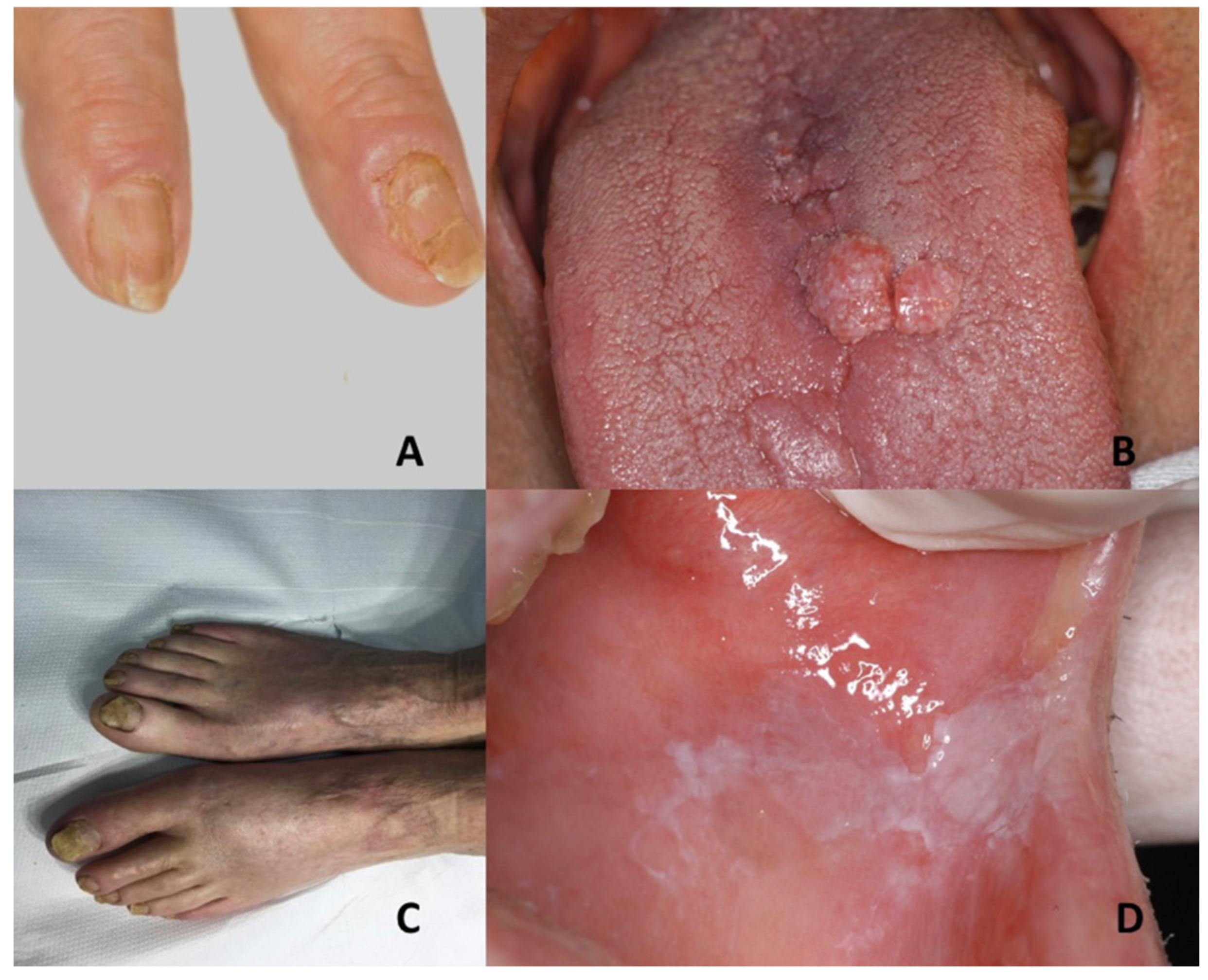

| Genodermatoses | Dental Features | Nails Features | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acro–dermato–ungual–lacrimal–tooth syndrome (ADULT syndrome) | Hypodontia | Dysplastic nails | Whittington et al., 2016 [13] |
| Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome (also known as: Ankyloblepharon-ectodermal defects-cleft lip/palate syndrome (AEC syndrome); Hay–Wells syndrome) | Hypodontia, abnormal tooth shape, dental caries and delayed dental eruption | Dystrophic nails | Tosun and Elbay, 2009 [14] |
| Schopf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome | Hypodontia | Dystrophic nails | Manchanda et al., 2017 [15] Khalil et al., 2020 [16] |
| Naegeli–Franceschetti–Jadassohn syndrome | Yellowish discoloration, abnormal dentition and enamel defects | Dystrophic nails | Shah et al., 2015 [17] Khalil et al., 2020 [16] |
| Ectrodactyly Ectodermal Dysplasia–Clefting syndrome (EEC syndrome) | Hypodontia and hypoplasia | Dystrophic nails | Bharati et al., 2020 [18] |
| Ellis–van Creveld syndrome | Conical teeth, enamel hypoplasia, hypodontia and natal teeth | Hypoplastic, dystrophic and friable nails | Lauritano et al., 2019 [19] |
| Witkop syndrome | Hypodontia | Spoon-shaped, rigid, slow-growing and friable nails | Devadas et al., 2005 [20] |
| Incontinentia Pigmenti | Dental shape anomalies, hypodontia and delayed dentition | Dystrophic nails | Khalil et al., 2020 [16] Nicolaou and Graham-Brown, 2003 [21] |
| Tricho-Dento-Osseous syndrome | Severe enamel hypomineralization and hypoplasia and taurodontic teeth | Thin, brittle nails | Khalil et al., 2020 [16] Islam et al., 2005 [22] |
| Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia | Hypodontia or anodontia, small, conical and bulbous or taurodontic teeth | Thin nails | Reyes-Reali et al., 2018 [23] |
| Odonto-onychodermal dysplasia | Hypodontia, peg-shaped incisors and enamel hypoplasia | Dysplastic nails | Yu et al., 2019 [24] Khalil et al., 2020 [16] |
| Monilethrix (also known as: Moniliform hair syndrome) | Hypodontia and cone shaped teeth | Dystrophic nails | Khalil et al., 2020 [16] |
| Scalp–ear–nipple syndrome | Oligodontia and small peg-like teeth | Dystrophic nails | Naik et al., 2012 [25] Khalil et al., 2020 [16] |
| Oculodentodigital dysplasia | Hypodontia, defective enamel, abnormally small teeth and premature tooth loss | Brittle nails | Doshi et al., 2016 [26] Khalil et al., 2020 [16] Orphanet [27] |
| Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome | Talon-like cingulum on maxillary central incisors and hyperdontia | Racquet nails | Tirali et al., 2014 [28] Tosti et al., 2009 [29] |
| Porphyrias | Erythrodontia | Photo-onycholysis and marked koilonychias | Inamadar and Palit, 2012 [30] |
| Genodermatosis | Oral Findings | Nails Findings | Differential Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Darier’s disease | Asymptomatic multiple white papules with a cobblestone appearance | V-shaped notching at the distal end of the nail plate; subungual hyperkeratosis; red and white lines, longitudinally oriented over the nail | Acne vulgaris, seborrheic dermatitis, acanthosis nigricans, confluent reticulate papillomatosis, prurigo pigmentosa, reticulate erythematomucinous syndrome and acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf |
| Dyschromatosis universalis hereditaria | Mottled pigmentation | Dystrophic nails with a few showing pterygium formation | Xeroderma pigmentosum, dyskeratosis congenita, dyschromatosis symmetrica hereditaria, dyschromic amyloidosis, generalized Dowling-Degos disease, incontinentia pigmenti, Naegeli–Franceschetti–Jadassohn syndrome |
| Dyskeratosis congenita | Leukoplakia; evolution into squamous cell carcinoma | Nail dystrophy with ridging and longitudinal splitting. Gradual atrophy, thinning, pterygium and deformation, leading to small, undeveloped or missing nails | Nail-patella syndrome, twenty-nail dystrophy, keratoderma with nail dystrophy and motor-sensory neuropathy, poikiloderma with neutropenia, Fanconi anemia, Diamond-Blackfan anemia, Shwachman-Diamond syndrome, acquired aplastic anaemia, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| Epidermolysis bullosa | Epidermolysis bullosa simplex Large blisters grouped in an arch-shaped distribution Junctional epidermolysis bullosa Several symmetrically distributed granulation tissue in the mouth; blisters; microstomia; ankyloglossia Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa Large size subepithelial blisters; microstomia; ankyloglossia; loss of the vestibular fundus; lingual depapillation; atrophy of the palatal folds Kindler syndrome Hemorrhagic mucositis; gingivitis; periodontitis; gingival hyperplasia; early dental loss; labial leukokeratosis | Epidermolysis bullosa simplex Nail dystrophy Junctional epidermolysis bullosa Dystrophic or absent nails Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa Dystrophic or absent nails Kindler syndrome Dystrophic nails | Incontinentia pigmenti; ichthyosiform bullous erythroderma; epidemic pemphigus in new-borns; bullous ichthyosis of Siemens; toxic epidermal necrolysis; congenital porphyria |
| Focal Dermal Hypoplasia | Verrucoid papillomas | Longitudinal ridging of the nail plate associated with nail splitting; V-shaped notches at the distal free edge of the nail plate; micronychia; anonychia | Microphthalmia with linear skin defects, incontinentia pigmenti, TP63-related disorders, oculocerebrocutaneous syndrome, Rothmund-Thomson syndrome |
| Pachyonychia congenita | Oral leukokeratosis | Hypertrophic nail dystrophy | Onychomycosis, epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Clouston syndrome, amilial onychogryphosis, twenty-nail dystrophy, dyskeratosis congenita, palmoplantar keratoderma striata, Olmsted syndrome |
| Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome | Severe gingivostomatitis and periodontitis | Nail dystrophy | Haim-Munk syndrome, prepubertal/aggressive periodontitis, keratosis punctate, Greither’s syndrome, keratoderma hereditarium mutilans, leukemia, Takahara’s syndrome, localized epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma, Meleda disease, Howel–Evans syndrome |
| Tuberous sclerosis complex | Oral fibromas | Ungual fibromas | Vitiligo, nevus depigmentus, nevus anemicus, piebaldism, Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada syndrome, hypomelanosis of Ito, cardiac myxoma, isolated brain tumors, pulmonary emphysema, acne vulgaris, acne rosacea, or multiple trichoepithelioma |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cantile, T.; Coppola, N.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Russo, D.; Bucci, P.; Spagnuolo, G.; Mignogna, M.D.; Leuci, S. Oral Mucosa and Nails in Genodermatoses: A Diagnostic Challenge. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5404. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225404
Cantile T, Coppola N, Caponio VCA, Russo D, Bucci P, Spagnuolo G, Mignogna MD, Leuci S. Oral Mucosa and Nails in Genodermatoses: A Diagnostic Challenge. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(22):5404. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225404
Chicago/Turabian StyleCantile, Tiziana, Noemi Coppola, Vito Carlo Alberto Caponio, Daniela Russo, Paolo Bucci, Gianrico Spagnuolo, Michele Davide Mignogna, and Stefania Leuci. 2021. "Oral Mucosa and Nails in Genodermatoses: A Diagnostic Challenge" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 22: 5404. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225404
APA StyleCantile, T., Coppola, N., Caponio, V. C. A., Russo, D., Bucci, P., Spagnuolo, G., Mignogna, M. D., & Leuci, S. (2021). Oral Mucosa and Nails in Genodermatoses: A Diagnostic Challenge. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(22), 5404. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225404







