Inaccurate Risk Assessment by the ACS NSQIP Risk Calculator in Aortic Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Discrimination—ROC Curve
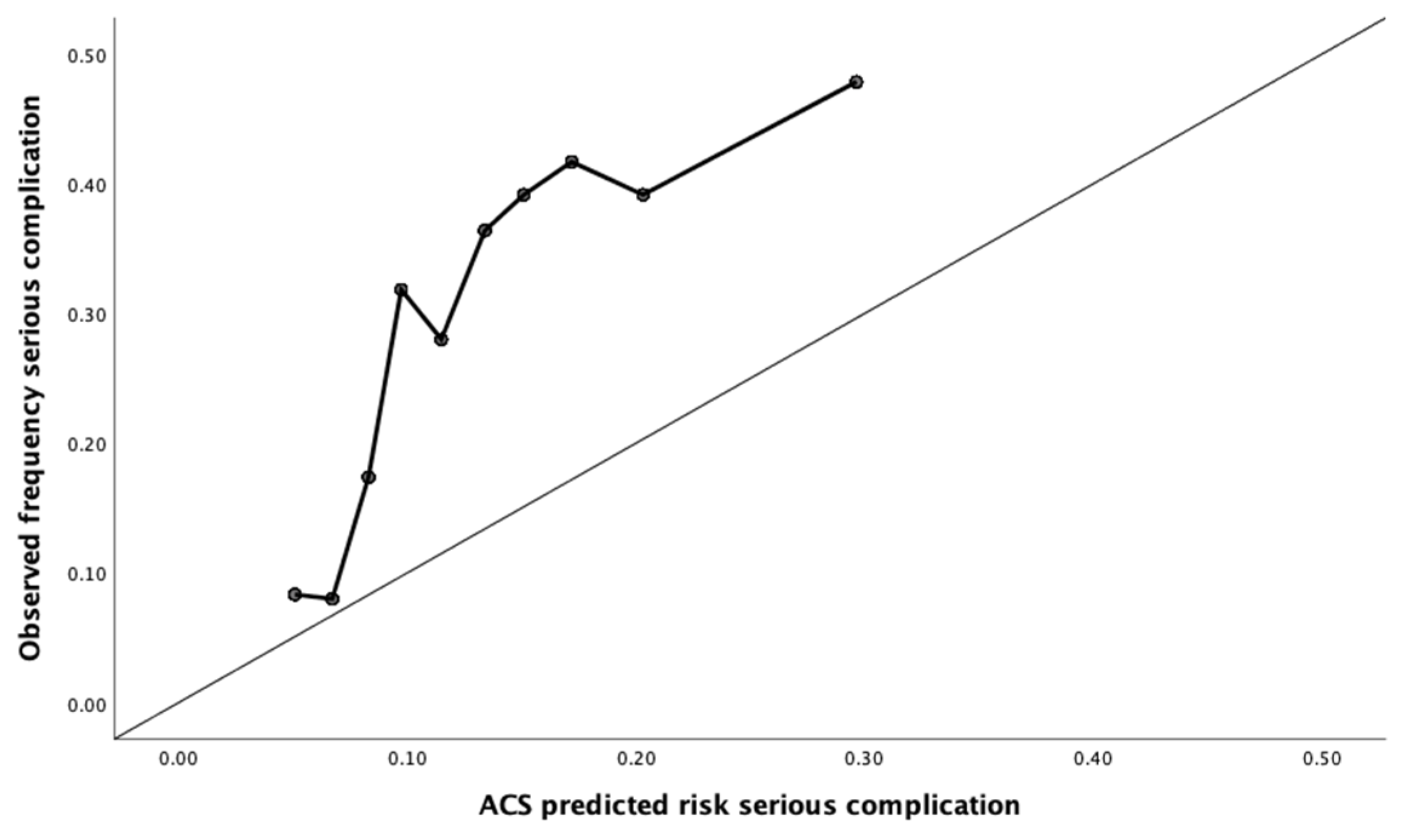
2.4. Calibration
2.5. Brier Score and Index of Prediction Accuracy (IPA) Values
2.6. Length of Hospital Stay
3. Results
3.1. Discrimination
3.2. Calibration
3.3. Brier Score and IPA Values
3.4. Length of Hospital Stay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. A Declaration on The Promotion of the Rights of Patients in Europe. In European Journal of Health Law; Brill Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Last, J.M. A Dictonary of Epidemiology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq, W.K.; Keulers, B.J.; Scheltinga, M.R.; Spauwen, P.H.; van der Wilt, G.J. A review of surgical informed consent: Past, present, and future. A quest to help patients make better decisions. World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Schaik, J.; Hers, T.M.; van Rijswijk, C.S.P.; Schooneveldt, M.S.; Putter, H.; Eefting, D.; van der Vorst, J.R. Risk assessment in aortic aneurysm repair by medical specialists versus the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program risk calculator outcomes. JRSM Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 10, 20480040211006582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilimoria, K.Y.; Liu, Y.; Paruch, J.; Zhou, L.; Kmiecik, T.E.; Ko, C.Y.; Cohen, M.E. Development and Evaluation of the Universal ACS NSQIP Surgical Risk Calculator: A Decision Aid and Informed Consent Tool for Patients and Surgeons. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2013, 217, 833–842.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McMillan, M.; Allegrini, V.; Asbun, H.J.; Ball, C.G.; Bassi, C.; Beane, J.; Behrman, S.W.; Berger, A.C.; Bloomston, M.; Callery, M.P.; et al. Incorporation of Procedure-specific Risk Into the ACS-NSQIP Surgical Risk Calculator Improves the Prediction of Morbidity and Mortality After Pancreatoduodenectomy. Ann. Surg. 2017, 265, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cohen, M.E.; Hall, B.L.; Ko, C.Y.; Bilimoria, K.Y. Evaluation and Enhancement of Calibration in the American College of Surgeons NSQIP Surgical Risk Calculator. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2016, 223, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.E.; Liu, Y.; Ko, C.Y.; Hall, B.L. An Examination of American College of Surgeons NSQIP Surgical Risk Calculator Accuracy. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2017, 224, 787–795e781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajitsaria, P.; Eissa, S.Z.; Kerridge, R.K. Risk Assessment. Curr. Anesthesiol. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boyd, O.; Jackson, N. How is risk defined in high-risk surgical patient management? Crit. Care 2005, 9, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hacohen Solovitz, A.; Ivry, S.; Ronen, O. Man against the machine—Differences in surgical risk evaluation. A cohort prospective study. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 60, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, S.; Wilson, J.; Abbatematteo, J.; Kubilis, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Kshitij, K.; Hoh, D.J. Predictive performance of the American College of Surgeons universal risk calculator in neurosurgical patients. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.Y.; Kohtakangas, E.L.; Asai, K.; Shum, J.B. Predictive Power of the NSQIP Risk Calculator for Early Post-Operative Outcomes After Whipple: Experience from a Regional Center in Northern Ontario. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2018, 49, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyle, B.; Landercasper, J.; Johnson, J.M.; Al-Hamadani, M.; Vang, C.A.; Groshek, J.; Hennessy, J.L.; Theede, L.M.; Zutavern, K.; Linebarger, J.H. Is the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program surgical risk calculator applicable for breast cancer patients undergoing breast-conserving surgery? Am. J. Surg. 2016, 211, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, V.; Levites, H.; Peskoe, S.; Hein, R.; Avashia, Y.; Erdmann, D. Validation of the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Risk Model for Patients Undergoing Panniculectomy. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2019, 83, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vosler, P.S.; Orsini, M.; Enepekides, D.J.; Higgins, K.M. Predicting complications of major head and neck oncological surgery: An evaluation of the ACS NSQIP surgical risk calculator. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 47, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samson, P.; Robinson, C.; Bradley, J.; Lee, A.; Broderick, S.; Kreisel, D.; Krupnick, A.S.; Patterson, G.A.; Puri, V.; Meyers, B.F.; et al. The National Surgical Quality Improvement Program risk calculator does not adequately stratify risk for patients with clinical stage I non–small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 151, 697–705.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teoh, D.; Halloway, R.N.; Heim, J.; Vogel, R.I.; Rivard, C. Evaluation of the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Surgical Risk Calculator in Gynecologic Oncology Patients Undergoing Minimally Invasive Surgery. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2016, 24, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbel, R.; Aboyans, V.; Boileau, C.; Bossone, E.; di Bartolomeo, R.; Eggebrecht, H.; Evangelista, A.; Falk, V.; Frank, H.; Gaemperli, O.; et al. 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: Document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 2873–2926. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Creager, M.; Beckman, J.; Loscalzo, J. Vascular Medicine A Companion to Braunwald’s Heart Disease, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2020 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e139–e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero, A.; Illig, K.A. Overview of aortic aneurysm management in the endovascular era. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 29, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, T.S.; Schneider, D.B. Fenestrated and Branched Stent Grafts for Repair of Complex Aortic Aneurysms. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 22, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanhainen, A.; Verzini, F.; Van Herzeele, I.; Allaire, E.; Bown, M.; Cohnert, T.; Dick, F.; van Herwaarden, J.; Karkos, C.; Koelemay, M.; et al. Editor’s Choice—European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Abdominal Aorto-iliac Artery Aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2019, 57, 8–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steyerberg, E.W.; Vickers, A.J.; Cook, N.R.; Gerds, T.; Gonen, M.; Obuchowski, N.; Pencina, M.J.; Kattan, M.W. Assessing the performance of prediction models: A framework for traditional and novel measures. Epidemiology 2010, 21, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Calster, B.; McLernon, D.J.; Van Smeden, M.; Wynants, L.; Steyerberg, E.W. Calibration: The Achilles heel of predictive analytics. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vergouwe, Y.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Eijkemans, M.J.; Habbema, J.D. Validity of prognostic models: When is a model clinically useful? Semin. Urol. Oncol. 2002, 20, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattan, M.W.; Gerds, T.A. The index of prediction accuracy: An intuitive measure useful for evaluating risk prediction models. Diagn. Progn. Res. 2018, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.H.; Chen, H.H.; Lee, K.C.; Liu, L.; Eisenstein, S.; Parry, L.; Cosman, B.; Ramamoorthy, S. Assessment of the Addition of Hypoalbuminemia to ACS-NSQIP Surgical Risk Calculator in Colorectal Cancer. Medicine 2016, 95, e2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, G.S.; Ogundimu, E.O.; Altman, D.G. Sample size considerations for the external validation of a multivariable prognostic model: A resampling study. Stat. Med. 2016, 35, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirracchio, R.; Ranzani, O.T. Recalibrating our prediction models in the ICU: Time to move from the abacus to the computer. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Value (n = 234) | |
|---|---|
| Age, n (%) | |
| Under 65 years | 44 (18.8) |
| 65–74 years | 104 (44.4) |
| 75–84 years | 77 (32.9) |
| 85 years or older | 9 (3.8) |
| Gender: Male, n (%) | 201 (85.9) |
| Procedure, n (%) | |
| Open tube | 35 (15.0) |
| Open bifurcation | 44 (18.8) |
| EVAR 1 | 77 (32.9) |
| (F/B)EVAR 2 | 56 (23.9) |
| TEVAR 3 | 22 (9.4) |
| Height, mean (SD), m | 1.76 (0.09) |
| Weight, mean (SD), kg | 81.22 (14.73) |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 26.09 (4.10) |
| Functional status, n (%) | |
| Independent | 229 (97.9) |
| Partially dependent | 5 (2.1) |
| Dependent | 0 (0) |
| ASA, n (%) | |
| I | 1 (0.4) |
| II | 112 (47.9) |
| III | 113 (48.3) |
| IV | 8 (3.4) |
| Steroid use for chronic condition: Yes, n (%) | 12 (5.1) |
| Ascites within 30 days prior to surgery: Yes, n (%) | 1 (0.4) |
| Systemic sepsis within 48 hours prior to surgery: Yes, n (%) | 0 (0) |
| Ventilator dependent: Yes, n (%) | 0 (0) |
| Disseminated Cancer: Yes, n (%) | 5 (2.1) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | |
| No | 195 (83.3) |
| Oral Medication | 32 (13.7) |
| Insulin | 7 (3.0) |
| Hypertension requiring medication: Yes, n (%) | 163 (69.7) |
| Congestive heart failure in 30 days prior to surgery: Yes, n (%) | 9 (3.8) |
| Dyspnea, n (%) | |
| None | 194 (82.9) |
| With moderate exertion | 39 (16.7) |
| At rest | 1 (0.4) |
| Current smoker (within 1 year): Yes, n (%) | 87 (37.2) |
| History of severe COPD: Yes, n (%) | 31 (13.2) |
| Dialysis: Yes, n (%) | 4 (1.7) |
| Acute renal failure: Yes, n (%) | 9 (3.8) |
| Complications | Observed Outcomes, % | Predicted Risks, Mean % | AUC | Brier Score | Nullmodel Brier Score | IPA Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serious complication | 29.5 | 13.6 | 0.680 | 0.225 | 0.208 | −0.084 |
| Any complication | 40.6 | 14.1 | 0.661 | 0.301 | 0.241 | −0.249 |
| Pneumonia | 8.5 | 2.5 | 0.621 | 0.081 | 0.078 | −0.039 |
| Cardiac complication | 2.1 | 2.0 | 0.562 | 0.021 | 0.021 | 0.000 |
| Surgical site infection | 3.8 | 1.6 | 0.560 | 0.038 | 0.037 | −0.027 |
| Urinary tract infection | 8.5 | 1.3 | 0.757 | 0.082 | 0.078 | −0.051 |
| Venoust hromboembolism | 1.3 | 0.9 | 0.797 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.000 |
| Renal failure * | 9.5 | 7.4 | 0.657 | 0.089 | 0.086 | 0.018 |
| Readmission | 6.0 | 6.8 | 0.737 | 0.055 | 0.056 | 0.000 |
| Return to operation room | 6.8 | 5.4 | 0.535 | 0.064 | 0.064 | −0.035 |
| Death | 3.1 | 1.3 | 0.554 | 0.030 | 0.029 | 0.118 |
| Discharge to nursing or rehab facility | 9.4 | 7.1 | 0.806 | 0.075 | 0.085 | 0.000 |
| Sepsis | 1.7 | 2.6 | 0.700 | 0.017 | 0.017 | −0.035 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hers, T.M.; Van Schaik, J.; Keekstra, N.; Putter, H.; Hamming, J.F.; Van Der Vorst, J.R. Inaccurate Risk Assessment by the ACS NSQIP Risk Calculator in Aortic Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225426
Hers TM, Van Schaik J, Keekstra N, Putter H, Hamming JF, Van Der Vorst JR. Inaccurate Risk Assessment by the ACS NSQIP Risk Calculator in Aortic Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(22):5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225426
Chicago/Turabian StyleHers, Tessa M., Jan Van Schaik, Niels Keekstra, Hein Putter, Jaap F. Hamming, and Joost R. Van Der Vorst. 2021. "Inaccurate Risk Assessment by the ACS NSQIP Risk Calculator in Aortic Surgery" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 22: 5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225426
APA StyleHers, T. M., Van Schaik, J., Keekstra, N., Putter, H., Hamming, J. F., & Van Der Vorst, J. R. (2021). Inaccurate Risk Assessment by the ACS NSQIP Risk Calculator in Aortic Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(22), 5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225426







