The Complement System, T Cell Response, and Cytokine Shift in Normotensive versus Pre-Eclamptic and Lupus Pregnancy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Immune Mechanisms in Normotensive Pregnancy
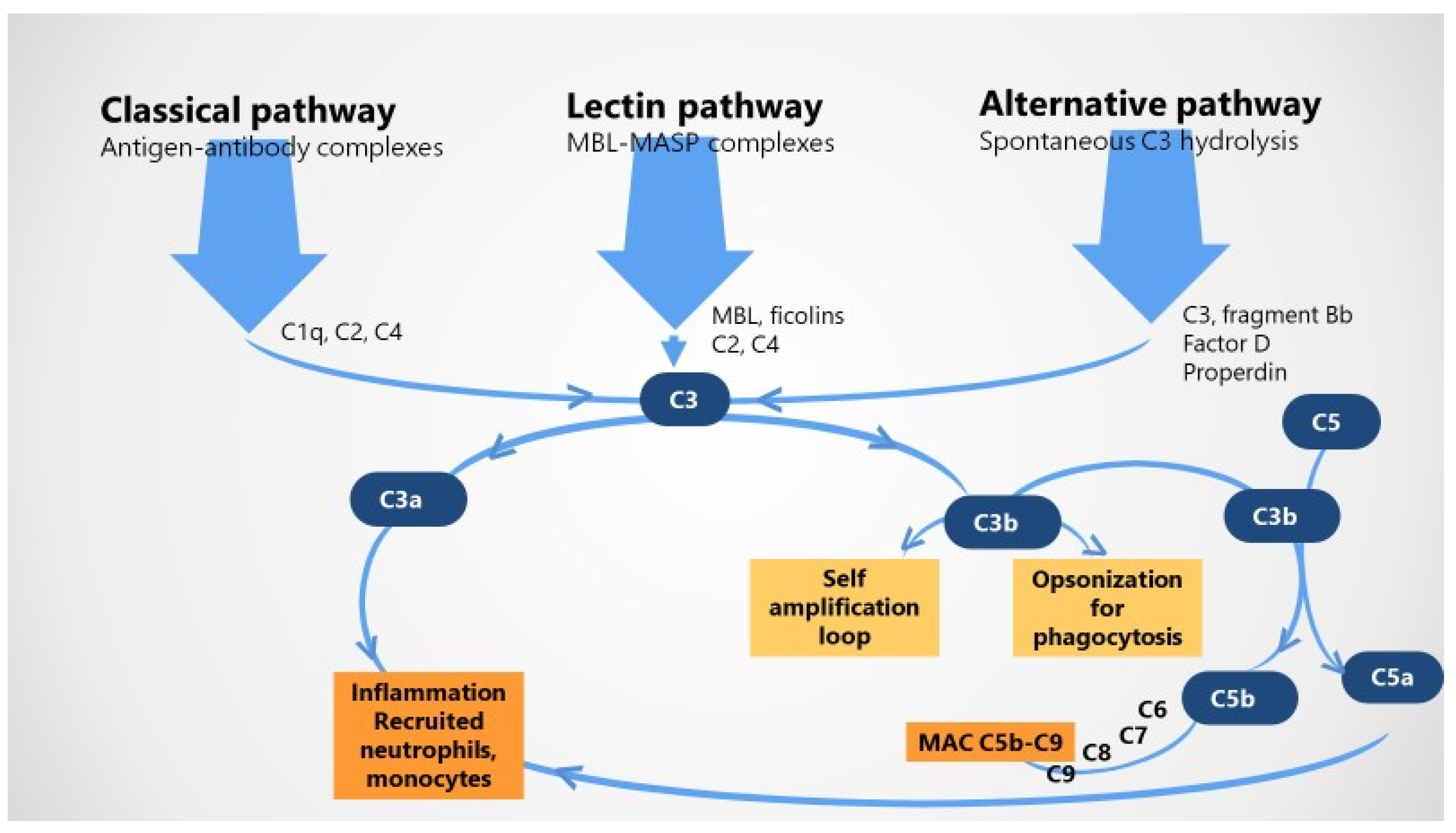
2.1. The Complement System in Healthy Pregnancy
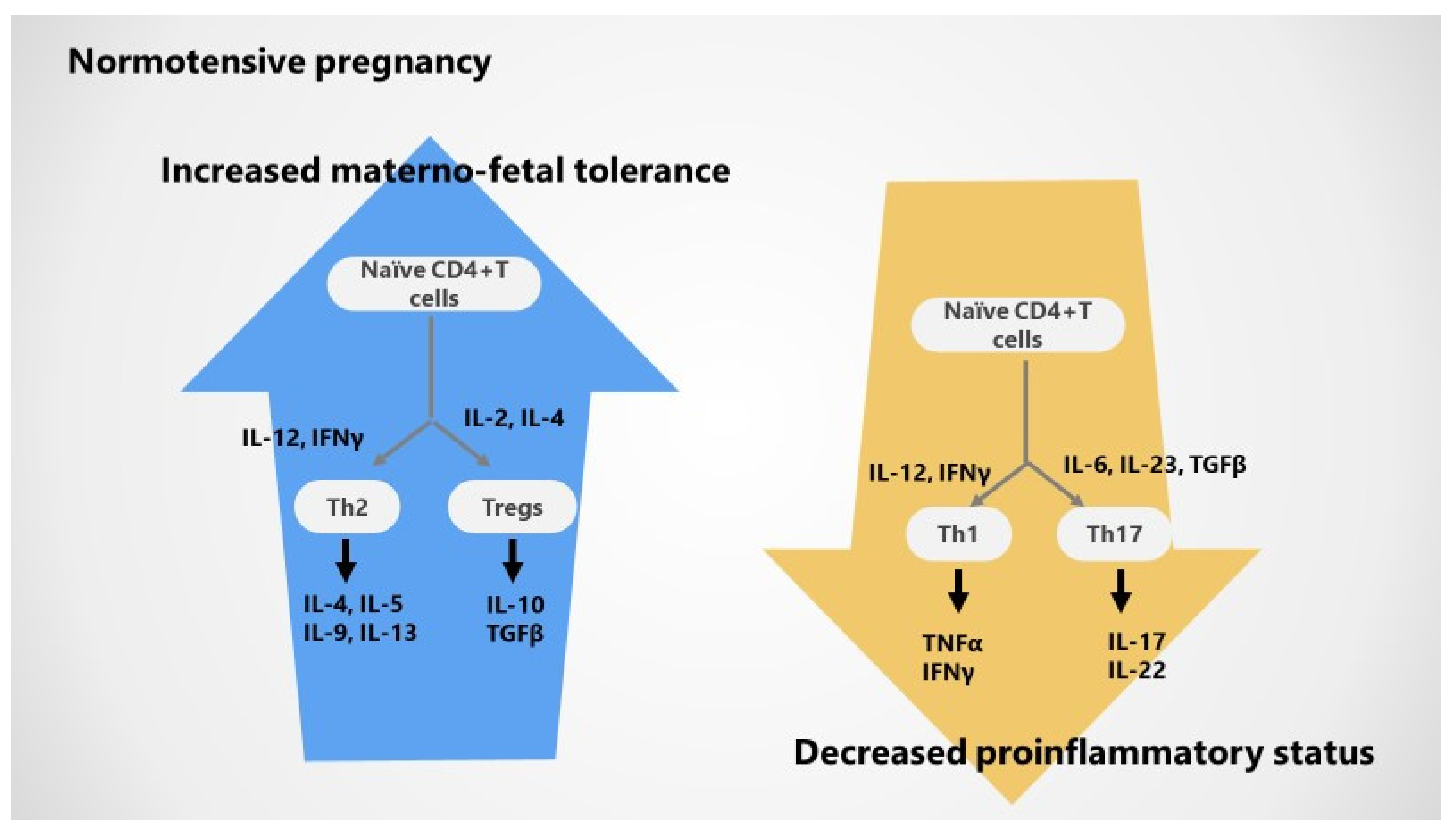
2.2. Adaptive T Cell Tolerance in Healthy Pregnancy
2.3. Cytokines in Normotensive Pregnancy
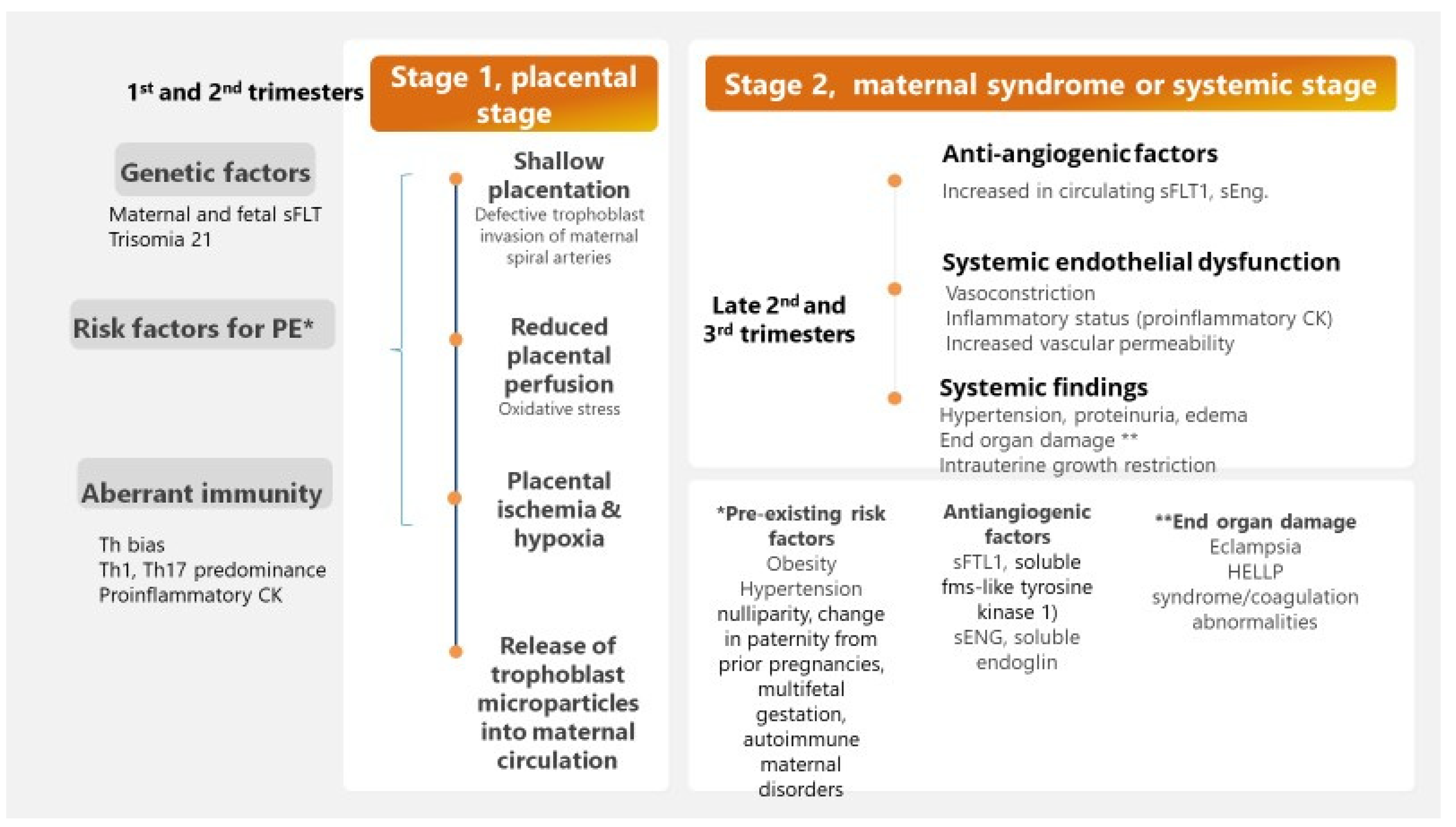
3. Immune Mechanisms in Pre-Eclamptic Pregnancy
3.1. The Complement System and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes
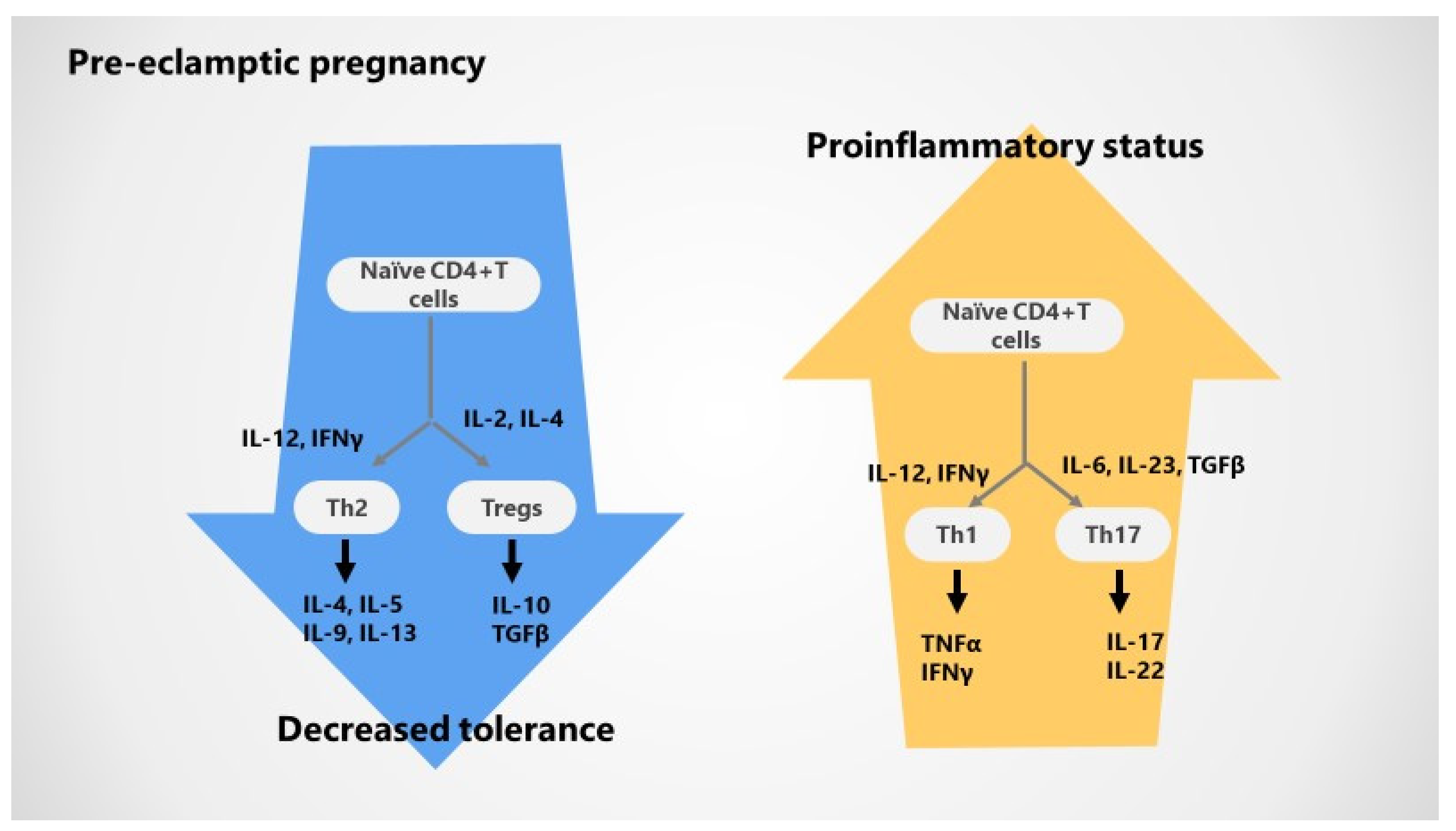
3.2. Impaired T Cell Tolerance in Pre-Eclampsia
3.3. Cytokines Variations during Pre-Eclampsia
4. Immune Alterations in Lupus Pregnancy with and without Pre-Eclampsia
4.1. Complement during Lupus Pregnancy
4.2. T Cell Responses and Cytokines Variations during Lupus Pregnancy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collier, A.Y.; Smith, L.A.; Karumanchi, S.A. Review of the immune mechanisms of pre-eclampsia and the potential of immune modulating therapy. Hum. Immunol. 2021, 82, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.; Lemoine, E.; Granger, J.P.; Karumanchi, S.A. Pre-eclampsia Pathophysiology, Challenges, and Perspectives. Compendium on the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1094–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Sengupta, P. Defining pregnancy phases with cytokine shift. J. Pregnancy Reprod. 2017, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yockey, J.L.; Iwasaki, A. Immunity Review Interferons and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Pregnancy and Fetal Development. Immunity 2018, 49, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prabhudas, M.; Bonney, E.; Caron, K.; Dey, S.; Erlebacher, A.; Fazleabas, A.; Fisher, S.; Golos, T.; Matzuk, M.; McCune, J.M.; et al. Immune mechanisms at the maternal-fetal interface: Perspectives and challenges. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaMarca, B.; Cornelius, D.C.; Harmon, A.C.; Amaral, L.M.; Cunningham, M.W.; Faulkner, J.L.; Wallace, K. Identifying immune mechanisms mediating the hypertension during pre-eclampsia. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 311, R1–R9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LaMarca, B.; Cornelius, D.; Wallace, K. Elucidating immune mechanisms causing hypertension during pregnancy. Phisiology 2013, 28, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, S.A.; Care, A.S.; Moldenhauerm, L.M. Regulatory T cells in embryo implantation and the immune response to pregnancy. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4224–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, X.; Ghaemi, M.S.; Ando, K.; Peterson, L.S.; Ganio, E.A.; Tsai, A.S.; Gaudilliere, D.K.; Stelzer, I.A.; Einhaus, J.; Bertrand, B.; et al. Differential dynamics of the maternal immune system in healthy pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todros, T.; Paulesu, L.; Cardaropoli, S.; Rolfo, A.; Masturzo, B.; Ermini, L.; Romagnoli, R.; Ietta, F. Role of the Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor in the Pathophysiology of Pre-Eclampsia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, E.A.; Thadhani, R.; Benzing, T.; Karumanchi, S.A. Pre-eclampsia: Pathogenesis, novel diagnostics and therapies. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alwis, N.; Binder, N.; Hannan, N. Pre-eclampsia: Challenges for nanomedicine development in pregnancy. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 824–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; Task Force on Hypertension in Pregnancy. Hypertension in pregnancy. Report of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Task Force on Hypertension in Pregnancy. Obs. Gynecol. 2013, 122, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar]
- ACOG. Practice bulletin no. 202 Summary: Gestational hypertension and pre-eclampsia. Obs. Gynecol. 2019, 133, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, R.; Chaiworapongsa, T. Pre-eclampsia: A link between trophoblast dysregulation and an antiangiogenic state. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2775–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Tziolos, N.; Bertsias, G.; Boumpas, D.T. Update οn the diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simionescu, A.A.; Daia-Iliescu, S. Pregnancy, systemic lupus erythematosus and a short communication on labor complications as new onset of the disease. Rom. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 30, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Andreoli, L.; Bertsias, G.K.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Brown, S.; Cervera, R.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Doria, A.; Fischer-Betz, R.; Forger, F.; Moraes-Fontes, M.F.; et al. EULAR recommendations for women’s health and the management of family planning, assisted reproduction, pregnancy and menopause in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and/or antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, M.; Bernardino, V.; Taulaigo, A.; Fernandes, J.; Lladó, A.; Serrano, F. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Pregnancy; InTech Open: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chighizola, C.B.; Lonati, P.A.; Trespidi, L.; Meroni, P.L.; Tedesco, F. The Complement System in the Pathophysiology of Pregnancy and in Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases during Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.Y.; Guerra, M.M.; Kaplowitz, E.; A Laskin, C.; Petri, M.; Branch, D.W.; Lockshin, M.D.; Sammaritano, L.R.; Merrill, J.T.; Porter, T.F.; et al. Complement activation predicts adverse pregnancy outcome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and/or antiphospholipid antibodies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannu, N.; Singh, R.; Sharma, S.; Chopra, S.; Bhatnagar, A. Altered Tregs and oxidative stress in pregnancy associated lupus. Adv. Rheumatol. 2019, 59, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teirilä, L.; Heikkinen-Eloranta, J.; Kotimaa, J.; Meri, S.; Lokki, A.I. Regulation of the complement system and immunological tolerance in pregnancy. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 45, 101337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, G.; Lingo, J.J.; Fleming, S.D.; Regal, J.F. Essential Role of Complement in Pregnancy: From Implantation to Parturition and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardi, G.; Yarilin, D.; Thurman, J.M.; Holers, V.M.; Salmon, J.E. Complement activation induces dysregulation of angiogenic factors and causes fetal rejection and growth restriction. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2165–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Regal, J.F.; Gilbert, J.S.; Burwick, R.M. The complement system and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denny, K.J.; Woodruff, T.M.; Taylor, S.M.; Callaway, L.K. Complement in Pregnancy: A Delicate Balance. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2013, 69, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvany-Celades, M.; Van Der Zwan, A.; Benner, M.; Setrajcic-Dragos, V.; Gomes, H.A.B.; Iyer, V.; Norwitz, E.R.; Strominger, J.L.; Tilburgs, T. Three Types of Functional Regulatory T Cells Control T Cell Responses at the Human Maternal-Fetal Interface. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2537–2547.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinborn, A.; Schmitt, E.; Kisielewicz, A.; Rechenberg, S.; Seissler, N.; Mahnke, K.; Schaier, M.; Zeier, M.; Sohn, C. Pregnancy-associated diseases are characterized by the composition of the systemic regulatory T cell (T reg) pool with distinct subsets of T regs. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 167, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerset, D.A.; Zheng, Y.; Kilby, M.D.; Sansom, D.M.; Drayson, M.T. Normal human pregnancy is associated with an elevation in the immune suppressive CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T-cell subset. Immunology 2004, 112, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, S.; Zhang, X.; Hamana, H.; Shima, T.; Ushijima, A.; Tsuda, K.; Muraguchi, A.; Kishi, H.; Saito, S. Clonally Expanded Decidual Effector Regulatory T Cells Increase in Late Gestation of Normal Pregnancy, but Not in Preeclampsia, in Humans. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redman, C.W.; Sargent, I.L. Latest advances in understanding pre-eclampsia. Science 2005, 308, 1592–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneman, I.; Pienaar, D.; Suvakov, S.; Simic, T.P.; Garovic, V.D.; McClements, L. Mechanisms of key innate immune cells in early-and late-onset pre-eclampsia. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palei, A.C.; Spradley, F.T.; Warrington, J.P.; George, E.M.; Granger, J.P. Pathophysiology of hypertension in pre-eclampsia: A lesson in integrative physiology. Acta Physiol. 2013, 208, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, J.R.; O’Brien, J.M.; Bergauer, N.K.; Jacques, D.L.; Sibai, B.M. Mild gestational hypertension remote from term: Progression and outcome. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2001, 184, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maric-Bilkan, C.; Abrahams, V.M.; Arteaga, S.S.; Bourjeily, G.; Conrad, K.P.; Catov, J.M.; Costantine, M.M.; Cox, B.; Garovic, V.; George, E.; et al. Research Recommendations from the National Institutes of Health Workshop on Predicting, Preventing, and Treating Preeclampsia. Hypertension 2019, 73, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, E.; Medcalf, K.E.; Park, A.L.; Ray, J.G. High Risk of Pre-eclampsia Identification Group. Clinical risk factors for pre-eclampsia determined in early pregnancy: Systematic review and meta-analysis of large cohort studies. BMJ 2016, 353, i1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yonekura Collier, A.R.; Zsengeller, Z.; Pernicone, E.; Salahuddin, S.; Khankin, E.V.; Karumanchi, S.A. Placental sFLT1 is associated with complement activation and syncytiotrophoblast damage in pre-eclampsia, Hypertens. Pregnancy 2019, 38, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierik, E.; Prins, J.R.; Van Goor, H.; Dekker, G.A.; Daha, M.R.; Seelen, M.A.; Scherjon, S.A. Dysregulation of Complement Activation and Placental Dysfunction: A Potential Target to Treat Pre-eclampsia? Front. Immunol. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lokki, A.I.; Heikkinen-Eloranta, J.; Jarva, H.; Saisto, T.; Lokki, M.L.; Laivuori, H.; Meri, S. Complement Activation and Regulation in Pre-eclamptic Placenta. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buurma, A.; Cohen, D.; Veraar, K.; Schonkeren, D.; Claas, F.H.; Bruijn, J.A.; Bloemenkamp, K.W.; Baelde, H.J. Pre-eclampsia is characterized by placental complement dysregulation. Hypertension 2012, 60, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burwick, R.M.; Feinberg, B.B. Complement activation and regulation in pre-eclampsia and hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count syndrome. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burwick, R.M.; Velásquez, J.A.; Valencia, C.M.; Gutiérrez-Marín, J.; Edna-Estrada, F.; Silva, J.L.; Trujillo-Otálvaro, J.; Vargas-Rodríguez, J.; Bernal, Y.; Quintero, A.; et al. Terminal Complement Activation in Pre-eclampsia. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 132, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lynch, A.M.; Wagner, B.D.; Giclas, P.C.; West, N.A.; Gibbs, R.S.; Holers, V.M. The Relationship of Longitudinal Levels of Complement Bb during Pregnancy with Pre-eclampsia. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2016, 75, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banadakoppa, M.; Balakrishnan, M.; Yallampalli, C. Upregulation and release of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase receptor 1 mediated by complement activation in human syncytiotrophoblast cells. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2018, 80, e13033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, M.C.; Cubro, H.; McCormick, D.J.; Milic, N.M.; Garovic, V.D. Pre-eclamptic Women Have Decreased Circulating IL-10 (Interleukin-10) Values at the Time of Pre-eclampsia Diagnosis—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hypertension 2020, 76, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, T.E.C.; Scherjon, S.A.; Faas, M.M.; Prins, J.R. Lower activation of CD4+ memory T cells in pre-eclampsia compared to healthy pregnancies persists postpartum. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2019, 136, 102613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Eviston, D.; Hsu, P.; Mariño, E.; Chidgey, A.; Santner-Nanan, B.; Wong, K.; Richards, J.L.; Yap, Y.A.; Collier, F.; et al. Decreased maternal serum acetate and impaired fetal thymic and regulatory T cell development in pre-eclampsia. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, A.; Cornelius, D.; Amaral, L.; Paige, A.; Herse, F.; Ibrahim, T.; Wallukat, G.; Faulkner, J.; Moseley, J.; Dechend, R.; et al. IL-10 supplementation increases Tregs and decreases hypertension in the RUPP rat model of pre-eclampsia. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2015, 34, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.C.; Sung, N.; Gilman-Sachs, A.; Kwak-Kim, J.T. T Helper (Th) Cell Profiles in Pregnancy and Recurrent Pregnancy Losses: Th1/Th2/Th9/Th17/Th22/Tfh Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmochwal-Kolarz, D.; Kludka-Sternik, M.; Tabarkiewicz, J.; Kolarz, B.; Rolinski, J.; Leszczynska-Gorzelak, B.; Oleszczuk, J. The predominance of Th17 lymphocytes and decreased number and function of Treg cells in pre-eclampsia. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2012, 93, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldi, G.; Rigó, J.; Stenczer, B.; Vásárhelyi, B.; Molvarec, A. Increased Prevalence of IL-17-Producing Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes in Pre-eclampsia. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2011, 66, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, J.E.; Heuser, C.; Triebwasser, M.; Liszewski, M.K.; Kavanagh, D.; Roumenina, L.; Branch, D.W.; Goodship, T.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Atkinson, J.P. Mutations in complement regulatory proteins predispose to pre-eclampsia: A genetic analysis of the PROMISSE cohort. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1001013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Immune Pathway | Local/Maternal–Fetal Changes | Systemic Changes/Peripheral Blood |
|---|---|---|
| T helper bias | ||
| Th1 | Increased TNFα | Increased TNFα |
| Th2 | Decreased IL-4 | Reduced IL-4 |
| Tregs | Reduced FoxP3 and IL-10 expression in first trimester and at delivery | Decreased Treg proportion and suppressive capacity |
| Decreased Treg clonal expansion | Lower activation of memory T reg | |
| Th17 | Increased TCD4 | Upregulated Th17 cells |
| Aberrant complement activation | ||
| Classical pathway | C1q deposition in chorionic villi, placental blood vessels, endothelia | Low or relative stable C1q |
| Lectin pathway | Higher C4d, ficolins, H, L deposition in syncytiotrophoblast | Low levels of C4, Ficolins, H |
| Alternative pathway | C3 deposition in decidua, villous endothelial cells | Higher levels of Bb |
| Anaphylatoxins (C3a, C5a) | Lower C3a receptor and conflicting results of higher and lower C5a expression | Higher C3aHigher or normal C5a |
| Terminal MAC (C5b-C9) | Increased MAC deposition in stroma and syncytiotrophoblast | Higher MAC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ancuța, E.; Zamfir, R.; Martinescu, G.; Crauciuc, D.V.; Ancuța, C. The Complement System, T Cell Response, and Cytokine Shift in Normotensive versus Pre-Eclamptic and Lupus Pregnancy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5722. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245722
Ancuța E, Zamfir R, Martinescu G, Crauciuc DV, Ancuța C. The Complement System, T Cell Response, and Cytokine Shift in Normotensive versus Pre-Eclamptic and Lupus Pregnancy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(24):5722. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245722
Chicago/Turabian StyleAncuța, Eugen, Radu Zamfir, Gabriel Martinescu, Dragoș Valentin Crauciuc, and Codrina Ancuța. 2021. "The Complement System, T Cell Response, and Cytokine Shift in Normotensive versus Pre-Eclamptic and Lupus Pregnancy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 24: 5722. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245722
APA StyleAncuța, E., Zamfir, R., Martinescu, G., Crauciuc, D. V., & Ancuța, C. (2021). The Complement System, T Cell Response, and Cytokine Shift in Normotensive versus Pre-Eclamptic and Lupus Pregnancy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(24), 5722. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245722






