Alpha Smooth Muscle Actin (αSMA) Immunohistochemistry Use in the Differentiation of Pancreatic Cancer from Chronic Pancreatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
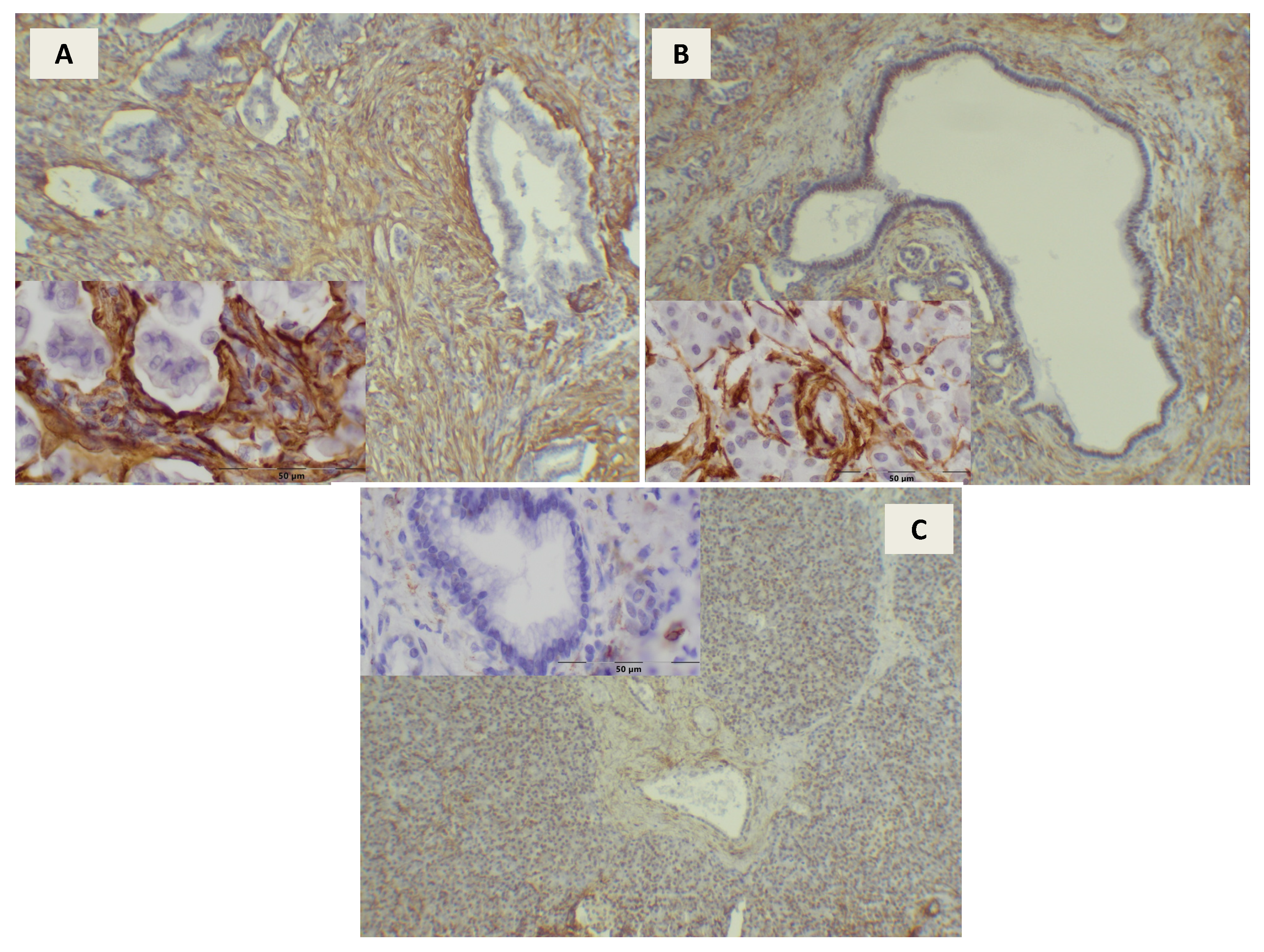
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braganza, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; McCloy, R.F.; McMahon, M.J. Chronic pancreatitis. Lancet 2011, 377, 1184–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, H.; Apte, M.V.; Keim, V.; Wilson, J.S. Chronic pancreatitis: Challenges and advances in pathogenesis, genetics, diagnosis, and therapy. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1557–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etrnad, B.; Whitcomb, D.C. Chronic pancreatitis: Diagnosis, classification, and new genetic developments. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 682–707. [Google Scholar]
- Manohar, M.; Verma, A.K.; Venkateshaiah, S.U.; Sanders, N.L.; Mishra, A. Pathogenic mechanisms of pancreatitis. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 8, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, M.V.; Park, S.; Phillips, P.A.; Santucci, N.; Goldstein, D.; Kumar, R.K.; Ramm, G.A.; Buchler, M.; Friess, H.; McCarroll, J.A.; et al. Desmoplastic reaction in pancreatic cancer: Role of pancreatic stellate cells. Pancreas 2004, 29, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, M.V.; Pirola, R.C.; Wilson, J.S. Pancreatic stellate cells: A starring role in normal and diseased pancreas. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandol, S.; Edderkaoui, M.; Gukovsky, I.; Lugea, A.; Gukovskaya, A. Desmoplasia of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachem, M.G.; Zhou, S.; Buck, K.; Schneiderhan, W.; Siech, M. Pancreatic stellate cells—Role in pancreas cancer. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2008, 393, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, S.; Lowenfels, A.B.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Maisonneuve, P.; Pezzilli, R. Pancreatic cancer in chronic pancreatitis; aetiology, incidence, and early detection. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 24, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenfels, A.B.; Maisonneuve, P.; Cavallini, G. Pancreatitis and the risk of pancreatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, B.; Sugiyama, Y.; Chen, A.; Uffort, E.; Nealon, W.; Mark Evers, B. Inflammatory mechanisms contributing to pancreatic cancer development. Ann. Surg. 2004, 239, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcea, G.; Dennison, A.R.; Steward, W.P.; Berry, D.P. Role of inflammation in pancreatic carcinogenesis and the implications for future therapy. Pancreatology 2005, 5, 514–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonlaufen, A.; Joshi, S.; Qu, C.; Phillips, P.A.; Xu, Z.; Parker, N.R.; Toi, C.S.; Pirola, R.C.; Wilson, J.S.; Goldstein, D.; et al. Pancreatic stellate cells: Partners in crime with pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Vonlaufen, A.; Phillips, P.A.; Fiala-Beer, E.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Biankin, A.V.; Goldstein, D.; Pirola, R.C.; Wilson, J.S.; et al. Role of pancreatic stellate cells in pancreatic cancer metastasis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunѐr, S.; Lindman, J.L.; Ansari, D.; Gundewar, C.; Andersson, R. Pancreatic cancer: The role of pancreatic stellate cells in tumor progression. Pancreatology 2010, 10, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, R.F.; Moore, T.; Arumugam Ramachandran, V.; Amos, K.D.; Rivera, A.; Ji, B.; Evans, D.B.; Logsdon, C.D. Cancer-associated stromal fibroblasts promote pancreatic tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinemann, V.; Reni, M.; Ychou, M.; Richel, D.J.; Macarulla, T.; Ducreux, M. Tumour-stroma interactions in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Rationale and current evidence for new therapeutic strategies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolske, K.M.; Ponnatapura, J.; Kolokythas, O.; Burke, L.M.B.; Tappouni, R.; Lalwani, N. Chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic tumor? A problem-solving approach. Radiographics 2019, 39, 1965–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.C.N.; Tang, R.S.Y.; Wong, J.C.T.; Chan, A.W.H.; Teoh, A.Y.B. Endoscopic ultrasound of pancreatic lesions. J. Vis. Surg. 2016, 2, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Irie, H.; Takagi, T.; Suzuki, R.; Konno, N.; Asama, H.; Sato, Y.; Nakamura, J.; Takasumi, M.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Efficacy of EUS-guided FNB using a Franseen needle for tissue acquisition and microsatellite instability evaluation in unresectable pancreatic lesions. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiriac, H.; Bucobo, J.C.; Tzimas, D.; Grewel, S.; Lacomb, J.F.; Rowehl, L.M.; Nagula, S.; Wu, M.; Kim, J.; Sasson, A.; et al. Successful creation of pancreatic cancer organoids by means of EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy sampling for personalized cancer treatment. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukswai, N.; Khoury, J.D. Immunohistochemistry innovations for diagnosis and tissue-based biomarker detection. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2019, 14, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Guidelines Version 1.2020 Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Available online: http://www.nccn.org (accessed on 17 March 2020).
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cyriac, J.; Mahadevan, P.; Augustine, P.; Ramesh, H.; Koshy, A. Stellate cell activation in tropical calcific pancreatitis compared to alcoholic pancreatitis, adenocarcinoma of pancreas and normal pancreas. JOP 2012, 13, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sinn, M.; Denkert, C.; Striefler, J.K.; Pelzer, U.; Stieler, J.M.; Bahra, M.; Lohneis, P.; Dörken, B.; Oettle, H.; Riess, H.; et al. α-Smooth muscle actin expression and desmoplastic stromal reaction in pancreatic cancer: Results from the CONKO-001 study. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1917–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.M.; Silva, M.A.; D’Costa, Z.; Bockelmann, R.; Soonawalla, Z.; Liu, S.; O’Neill, E.; Mukherjee, S.; McKenna, W.G.; Muschel, R.; et al. The prognostic role of desmoplastic stroma in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 4183–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drifka, C.R.; Tod, J.; Loeffler, A.G.; Liu, Y.; Thomas, G.J.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Kao, W.J. Periductal stromal collagen topology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma differs from that of normal and chronic pancreatitis. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkan, M.; Michalski, C.W.; Rieder, S.; Reiser-Erkan, C.; Abiatari, I.; Kolb, A.; Giese, N.A.; Esposito, I.; Friess, H.; Kleeff, J. The activated stroma index is a novel and independent prognostic marker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, I.; Hasebe, T.; Sasaki, S.; Konishi, M.; Inoue, K.; Nakagohri, T.; Oda, T.; Mukai, K.; Kinoshita, T. Advanced pancreatic ductal cancer: Fibrotic focus and beta-catenin expression correlate with outcome. Pancreas 2003, 26, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H.; Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Nakata, K.; Yu, J.; Kayashima, T.; Cui, L.; Manabe, T.; Ohtsuka, T.; Tanaka, M. α-Smooth muscle actin expressing stroma promotes an aggressive tumor biology in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2010, 8, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maréchal, R.; Bachet, J.B.; Calomme, A.; Demetter, P.; Delpero, J.R.; Svrcek, M.; Cros, J.; Bardier-Dupas, A.; Puleo, F.; Monges, G.; et al. Sonic hedgehog and Gli1 expression predict outcome in resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froeling, F.E.; Feig, C.; Chelala, C.; Dobson, R.; Mein, C.E.; Tuveson, D.A.; Clevers, H.; Hart, I.R.; Kocher, H.M. Retinoic acid-induced pancreatic stellate cell quiescence reduces paracrine Wnt-beta-catenin signaling to slow tumor progression. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1486–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, R.; Musteanu, M.; Garcia-Garcia, E.; Lopez-Casas, P.P.; Megias, D.; Guerra, C.; Muñoz, M.; Quijano, Y.; Cubillo, A.; Rodriguez-Pascual, J.; et al. Stromal disrupting effects of nab-paclitaxel in pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Borad, M.J.; Laheru, D.A.; Smith, L.S.; Wood, T.E.; Muñoz, M.; Quijano, Y.; Cubillo, A.; Rodriguez-Pascual, J.; et al. Gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel is an active regimen in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A phase I/II trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4548–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, T.; Tajima, H.; Makino, I.; Okazaki, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ohbatake, Y.; Nakanuma, S.; Hayashi, H.; Takamura, H.; Ninomiya, I.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel reduces the number of cancer-associated fibroblasts through depletion of pancreatic stroma. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Torlakovic, E.E.; Nielsen, S.; Vyberg, M.; Taylor, C.R. Getting controls under control: The time is now for immunohistochemistry. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 68, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitano, M.; Yoshida, T.; Itonaga, M.; Tamura, T.; Hatamaru, K.; Yamashita, Y. Impact of endoscopic ultrasonography on diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Pinto, E.; Grimm, I.S.; Baron, T.H. Endoscopic ultrasound fine-needle aspiration vs. fine-needle biopsy: Tissue is always the issue. Endosc. Int. Open 2016, 4, E506–E507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]






| Baseline Characteristics of the Study Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients | PDAC Patients | CP Patients | |
| 83 | 31 | ||
| Age | 59.6 ± 8.74 (34–76) | 49.7 ± 9.65 (23–64) | |
| Sex | Female | 37 (45%) | 9 (29%) |
| Male | 46 (55%) | 22 (71%) | |
| Symptoms | Jaundice | 37 (45%) | 5 (16%) |
| BMI | 25.15 ± 3.73 | 22.84 ± 4.72 | |
| Blood tests | Fasting glucose | 118.44 ± 34.02 | 103.26 ± 20.05 |
| CA 19-9 serum level | 217.3 ± 348.7 | 68.3 ± 135.8 | |
| Comorbidities | DM | 29 (47%) | 11 (35.5%) |
| DM newly diagnosed | 12 (14.5%) | 3 (9.6%) | |
| TNM Classification | IA | 5 (6%) | n/a |
| IB | 21 (25%) | n/a | |
| IIA | 19 (23%) | n/a | |
| IIB | 32 (38.5%) | n/a | |
| III | 3 (3.6%) | n/a | |
| IV | 3 (3.6%) | n/a | |
| Tumor Grading | G-1 | 16 (19.3%) | n/a |
| G-2 | 60 (72.3%) | n/a | |
| G-3 | 7 (8.4%) | n/a | |
| Localization | Head of the pancreas | 68 (82%) | 27 (87%) |
| Body of the pancreas | 8 (9.6%) | 0 | |
| Tail of the pancreas | 7 (8.4%) | 4 (13%) | |
| Tumor Dimension [cm] | 3.45 (0.5–6.0) | n/a | |
| Type of operations | Whipple’s operation | 63 (76%) | 25 (81%) |
| Resection of the body and tail of pancreas | 8 (9.6%) | 0 | |
| Resection of the tail of the pancreas | 3 (3.6%) | 4 (13%) | |
| Beger operation | 0 | 2 (6%) | |
| Total pancreatectomy | 9 (10.8%) | 0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Winter, K.; Dzieniecka, M.; Strzelczyk, J.; Wągrowska-Danilewicz, M.; Danilewicz, M.; Małecka-Wojciesko, E. Alpha Smooth Muscle Actin (αSMA) Immunohistochemistry Use in the Differentiation of Pancreatic Cancer from Chronic Pancreatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5804. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245804
Winter K, Dzieniecka M, Strzelczyk J, Wągrowska-Danilewicz M, Danilewicz M, Małecka-Wojciesko E. Alpha Smooth Muscle Actin (αSMA) Immunohistochemistry Use in the Differentiation of Pancreatic Cancer from Chronic Pancreatitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(24):5804. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245804
Chicago/Turabian StyleWinter, Katarzyna, Monika Dzieniecka, Janusz Strzelczyk, Małgorzata Wągrowska-Danilewicz, Marian Danilewicz, and Ewa Małecka-Wojciesko. 2021. "Alpha Smooth Muscle Actin (αSMA) Immunohistochemistry Use in the Differentiation of Pancreatic Cancer from Chronic Pancreatitis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 24: 5804. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245804
APA StyleWinter, K., Dzieniecka, M., Strzelczyk, J., Wągrowska-Danilewicz, M., Danilewicz, M., & Małecka-Wojciesko, E. (2021). Alpha Smooth Muscle Actin (αSMA) Immunohistochemistry Use in the Differentiation of Pancreatic Cancer from Chronic Pancreatitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(24), 5804. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245804







