Intrahematomal Ultrasound Enhances RtPA-Fibrinolysis in a Porcine Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Surgical Preparation
2.2. ICH Preparation
2.3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
2.4. ICH Treatment-Groups
2.5. Fixation and Sampling
2.6. Staining and Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
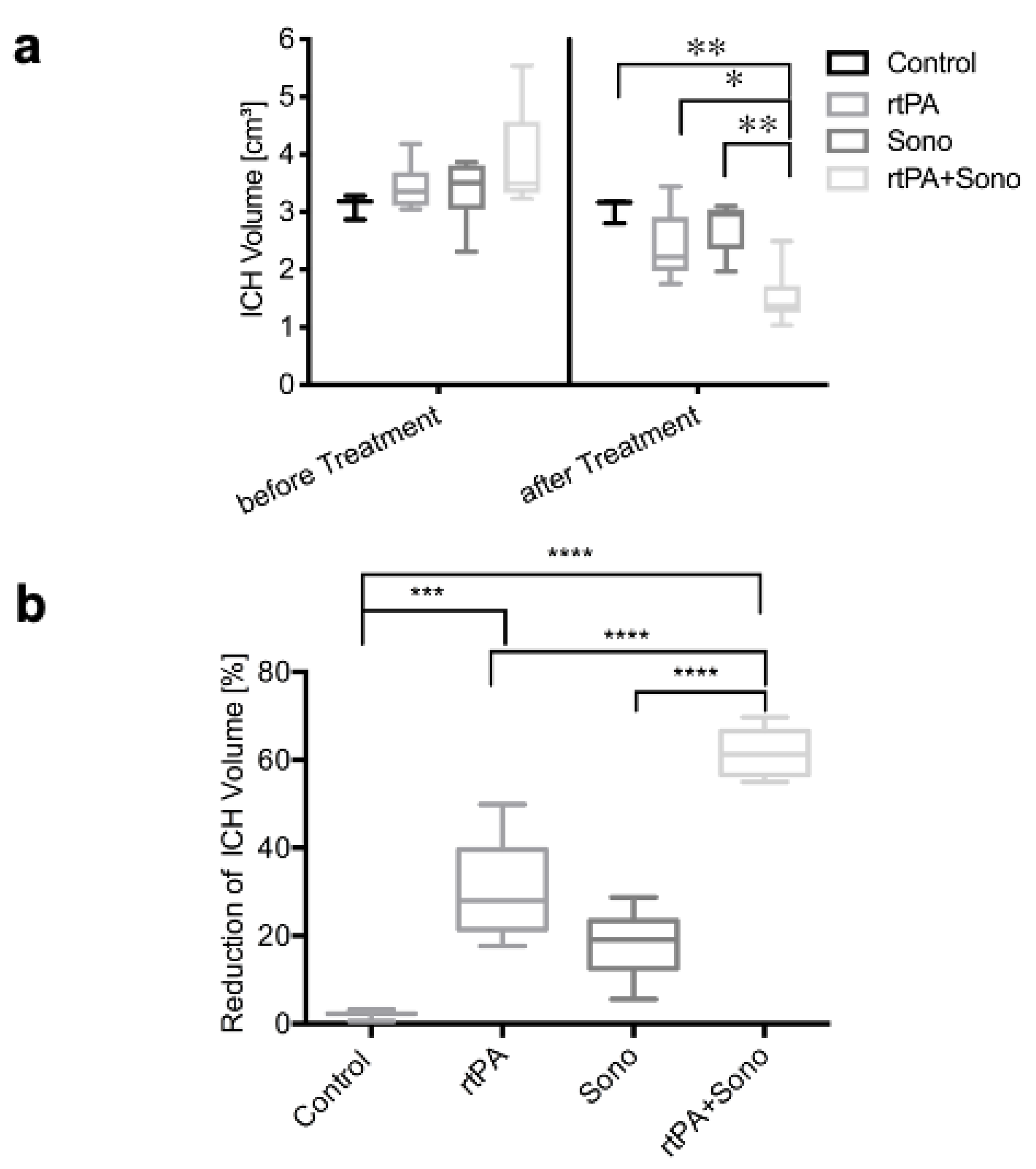
3.1. Hematoma Volume
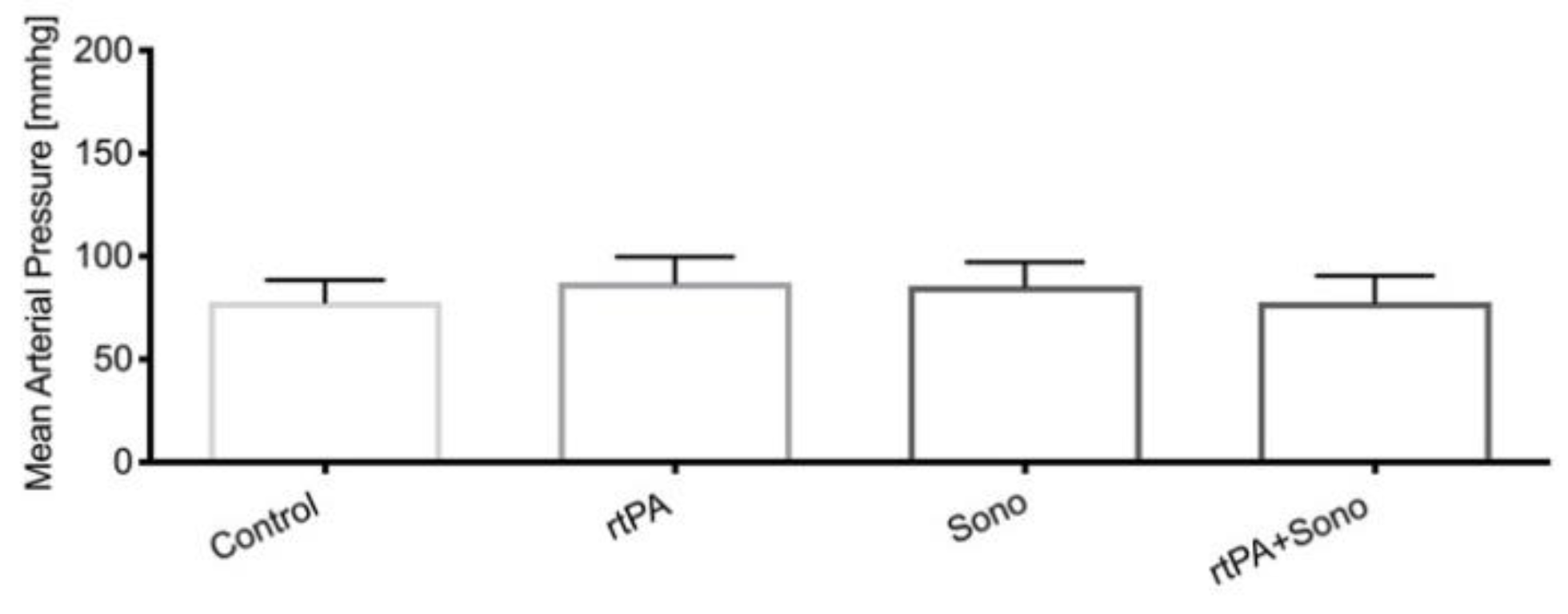
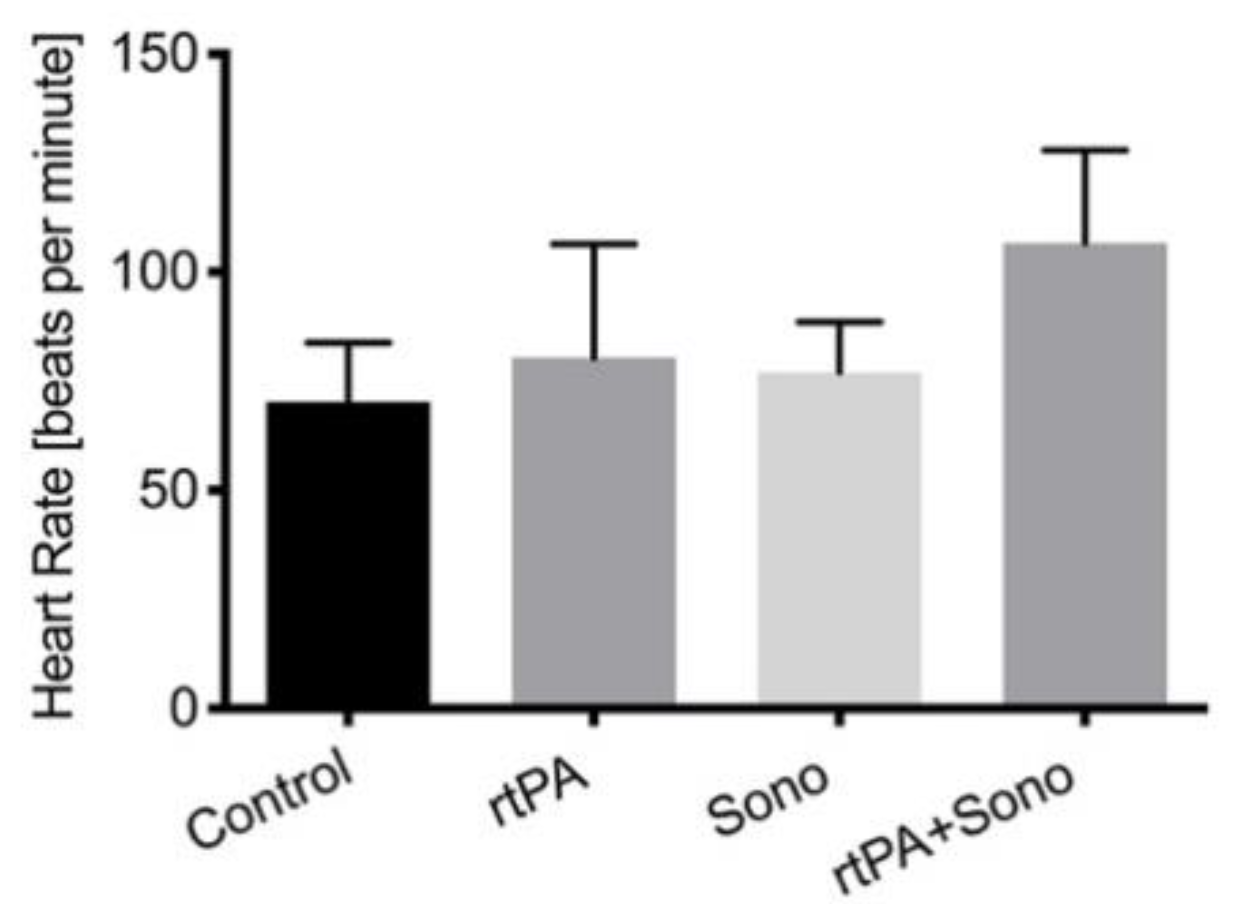
3.2. Vital Signs
3.3. Cranial MRI
3.4. HE-Staining: Microhemorrhages, Edema
3.5. Immunohistochemistry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Hachinski, V.; Donnan, G.A.; Gorelick, P.B.; Hacke, W.; Cramer, S.C.; Kaste, M.; Fisher, M.; Brainin, M.; Buchan, A.M.; Lo, E.H.; et al. Stroke: Working toward a Prioritized World Agenda. Int. J. Stroke 2010, 5, 238–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthi, R.V.; Feigin, V.L.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Mensah, G.A.; Connor, M.; Bennett, D.A.; Moran, A.E.; Sacco, R.L.; Anderson, L.M.; Truelsen, T.; et al. Global and Regional Burden of First-Ever Ischaemic and Haemorrhagic Stroke during 1990–2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e259–e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Asch, C.J.; Luitse, M.J.; Rinkel, G.J.; Van der Tweel, I.; Algra, A.; Klijn, C.J. Incidence, Case Fatality, and Functional Outcome of Intracerebral Haemorrhage over Time, According to Age, Sex, and Ethnic Origin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelow, A.D.; Gregson, B.A.; Fernandes, H.M.; Murray, G.D.; Teasdale, G.M.; Hope, D.T.; Karimi, A.; Shaw, M.D.M.; Barer, D.H. Early Surgery versus Initial Conservative Treatment in Patients with Spontaneous Supratentorial Intracerebral Haematomas in the International Surgical Trial in Intracerebral Haemorrhage (STICH): A Randomised Trial. Lancet 2005, 365, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelow, A.D.; Gregson, B.A.; Rowan, E.N.; Murray, G.D.; Gholkar, A.; Mitchell, P.M. STICH II Investigators Early Surgery versus Initial Conservative Treatment in Patients with Spontaneous Supratentorial Lobar Intracerebral Haematomas (STICH II): A Randomised Trial. Lancet 2013, 382, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregson, B.A.; Broderick, J.P.; Auer, L.M.; Batjer, H.; Chen, X.-C.; Juvela, S.; Morgenstern, L.B.; Pantazis, G.C.; Teernstra, O.P.M.; Wang, W.-Z.; et al. Individual Patient Data Subgroup Meta-Analysis of Surgery for Spontaneous Supratentorial Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2012, 43, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scaggiante, J.; Zhang, X.; Mocco, J.; Kellner, C.P. Minimally Invasive Surgery for Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2018, 49, 2612–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, D.F.; Thompson, R.E.; Rosenblum, M.; Yenokyan, G.; Lane, K.; McBee, N.; Mayo, S.W.; Bistran-Hall, A.J.; Gandhi, D.; Mould, W.A.; et al. Minimally Invasive Surgery with Thrombolysis in Intracerebral Haemorrhage Evacuation (MISTIE III): A Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label Phase 3 Trial with Blinded Endpoint. Lancet 2019, 393, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lippitz, B.E.; Mayfrank, L.; Spetzger, U.; Warnke, J.P.; Bertalanffy, H.; Gilsbach, J.M. Lysis of Basal Ganglia Haematoma with Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator (RtPA) after Stereotactic Aspiration: Initial Results. Acta Neurochir. 1994, 127, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, E.; Hanley, D.F.; Newell, D.W. Minimally Invasive Treatment for Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neurosurg. Focus 2012, 32, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, D.W.; Shah, M.M.; Wilcox, R.; Hansmann, D.R.; Melnychuk, E.; Muschelli, J.; Hanley, D.F. Minimally Invasive Evacuation of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage Using Sonothrombolysis. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggers, J.; Seidel, G.; Koch, B.; König, I.R. Sonothrombolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke for Patients Ineligible for Rt-PA. Neurology 2005, 64, 1052–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggers, J.; Koch, B.; Meyer, K.; König, I.; Seidel, G. Effect of Ultrasound on Thrombolysis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 53, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffenberger, S.; Devcic-Kuhar, B.; Kollmann, C.; Kastl, S.P.; Kaun, C.; Speidl, W.S.; Weiss, T.W.; Demyanets, S.; Ullrich, R.; Sochor, H.; et al. Can a Commercial Diagnostic Ultrasound Device Accelerate Thrombolysis? An in Vitro Skull Model. Stroke 2005, 36, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfaffenberger, S.; Wojta, J.; Gottsauner-Wolf, M. High-Frequency Transtemporal Sonothrombolysis. Stroke 2005, 36, 1356–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barlinn, K.; Barreto, A.D.; Sisson, A.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Schafer, M.E.; Alleman, J.; Zhao, L.; Shen, L.; Cava, L.F.; Rahbar, M.H.; et al. CLOTBUST-Hands Free. Stroke 2013, 44, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barlinn, K.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Molina, C.A.; Alexandrov, D.A.; Schafer, M.E.; Alleman, J.; Alexandrov, A.V. TUCSON Investigators Exploratory Analysis of Estimated Acoustic Peak Rarefaction Pressure, Recanalization, and Outcome in the Transcranial Ultrasound in Clinical Sonothrombolysis Trial. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2013, 41, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffertshofer, M.; Gass, A.; Ringleb, P.; Sitzer, M.; Sliwka, U.; Els, T.; Sedlaczek, O.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Hennerici, M.G. Transcranial Low-Frequency Ultrasound-Mediated Thrombolysis in Brain Ischemia: Increased Risk of Hemorrhage with Combined Ultrasound and Tissue Plasminogen Activator: Results of a Phase II Clinical Trial. Stroke 2005, 36, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behrens, S.; Spengos, K.; Daffertshofer, M.; Schroeck, H.; Dempfle, C.E.; Hennerici, M. Transcranial Ultrasound-Improved Thrombolysis: Diagnostic vs. Therapeutic Ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2001, 27, 1683–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, A.V.; Demchuk, A.M.; Felberg, R.A.; Christou, I.; Barber, P.A.; Burgin, W.S.; Malkoff, M.; Wojner, A.W.; Grotta, J.C. High Rate of Complete Recanalization and Dramatic Clinical Recovery During TPA Infusion When Continuously Monitored With 2-MHz Transcranial Doppler Monitoring. Stroke 2000, 31, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexandrov, A.V.; Molina, C.A.; Grotta, J.C.; Garami, Z.; Ford, S.R.; Alvarez-Sabin, J.; Montaner, J.; Saqqur, M.; Demchuk, A.M.; Moyé, L.A.; et al. Ultrasound-Enhanced Systemic Thrombolysis for Acute Ischemic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2170–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cintas, P.; Traon, A.P.L.; Larrue, V. High Rate of Recanalization of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion During 2-MHz Transcranial Color-Coded Doppler Continuous Monitoring Without Thrombolytic Drug. Stroke 2002, 33, 626–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rohde, V.; Rohde, I.; Thiex, R.; Ince, A.; Jung, A.; Dückers, G.; Gröschel, K.; Röttger, C.; Küker, W.; Müller, H.D.; et al. Fibrinolysis Therapy Achieved with Tissue Plasminogen Activator and Aspiration of the Liquefied Clot after Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Rapid Reduction in Hematoma Volume but Intensification of Delayed Edema Formation. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiex, R.; Tsirka, S.E. Brain Edema after Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Mechanisms, Treatment Options, Management Strategies, and Operative Indications. Neurosurg. Focus 2007, 22, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keric, N.; Maier, G.S.; Samadani, U.; Kallenberg, K.; Dechent, P.; Brueck, W.; Heuer, J.; Rohde, V. Tissue Plasminogen Activator Induced Delayed Edema in Experimental Porcine Intracranial Hemorrhage: Reduction with Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Administration. Transl. Stroke Res. 2012, 3, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pieters, M.; Hekkenberg, R.T.; Barrett-Bergshoeff, M.; Rijken, D.C. The Effect of 40 KHz Ultrasound on Tissue Plasminogen Activator-Induced Clot Lysis in Three in Vitro Models. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2004, 30, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keric, N.; Masomi-Bornwasser, J.; Müller-Werkmeister, H.; Kantelhardt, S.R.; König, J.; Kempski, O.; Giese, A. Optimization of Catheter Based RtPA Thrombolysis in a Novel In Vitro Clot Model for Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Bio. Med. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, e5472936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masomi-Bornwasser, J.; Winter, P.; Müller-Werkmeister, H.; Strand, S.; König, J.; Kempski, O.; Ringel, F.; Kantelhardt, S.R.; Keric, N.; Giese, A. Correction: Combination of Ultrasound and RtPA Enhances Fibrinolysis in an In Vitro Clot System. PLoS ONE 2018, 12, e0200456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.R.; Xi, G.; Hua, Y.; Kleinholz, M.; Courten-Myers, G.M.; De Myers, R.E.; Broderick, J.P.; Brott, T.G. Lobar Intracerebral Hemorrhage Model in Pigs. Stroke 1996, 27, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, C.; Rohde, V.; Meyer, B.; Hassler, W. Stereotactic Puncture and Lysis of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage Using Recombinant Tissue-Plasminogen Activator. Neurosurgery 1995, 36, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, A.D.; Alexandrov, A.V.; Shen, L.; Sisson, A.; Bursaw, A.W.; Sahota, P.; Peng, H.; Ardjomand-Hessabi, M.; Pandurengan, R.; Rahbar, M.H.; et al. CLOTBUST-Hands Free: Pilot Safety Study of a Novel Operator-Independent Ultrasound Device in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 3376–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexandrov, A.V.; Köhrmann, M.; Soinne, L.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Barreto, A.D.; Demchuk, A.M.; Sharma, V.K.; Mikulik, R.; Muir, K.W.; Brandt, G.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Sonothrombolysis for Acute Ischaemic Stroke: A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Phase 3, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mhoedema Anesthesia: Swine. Available online: https://www.researchservices.umn.edu/services-name/research-animal-resources/research-support/guidelines/anesthesia-swine (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Braaten, J.V.; Goss, R.A.; Francis, C.W. Ultrasound Reversibly Disaggregates Fibrin Fibers. Thromb. Haemost. 1997, 78, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.W.; Blinc, A.; Lee, S.; Cox, C. Ultrasound Accelerates Transport of Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator into Clots. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1995, 21, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keric, N.; Kantelhardt, S.R.; Neulen, A.; Dechent, P.; Henning, A.; Vollmer, F.C.; Thiemann, I.; Giese, A. Image-Guided Intracranial Endosonography. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2013, 25, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orakcioglu, B.; Kentar, M.M.; Schiebel, P.; Uozumi, Y.; Unterberg, A.; Sakowitz, O.W. Perihemorrhagic Ischemia Occurs in a Volume-Dependent Manner as Assessed by Multimodal Cerebral Monitoring in a Porcine Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2015, 22, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herweh, C.; Jüttler, E.; Schellinger, P.D.; Klotz, E.; Jenetzky, E.; Orakcioglu, B.; Sartor, K.; Schramm, P. Evidence against a Perihemorrhagic Penumbra Provided by Perfusion Computed Tomography. Stroke 2007, 38, 2941–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orakcioglu, B.; Fiebach, J.B.; Steiner, T.; Kollmar, R.; Jüttler, E.; Becker, K.; Schwab, S.; Heiland, S.; Meyding-Lamadé, U.K.; Schellinger, P.D. Evolution of Early Perihemorrhagic Changes—Ischemia vs. Edema: An MRI Study in Rats. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 193, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, A.M.; López-Mut, J.V.; Benlloch, V.; Chamarro, R.; Soler, J.; Láinez, M.J.A. Perfusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage at Baseline and during the 1st and 2nd Week: A Longitudinal Study. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2007, 23, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidwell, C.S.; Saver, J.L.; Mattiello, J.; Warach, S.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Starkman, S.; Vespa, P.M.; Villablanca, J.P.; Martin, N.A.; Frazee, J.; et al. Diffusion-Perfusion MR Evaluation of Perihematomal Injury in Hyperacute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neurology 2001, 57, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orakcioglu, B.; Kentar, M.; Uozumi, Y.; Santos, E.; Schiebel, P.; Unterberg, A.; Sakowitz, O.W. Multiparametric Characterisation of the Perihemorrhagic Zone in a Porcine Model of Lobar ICH. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2011, 111, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keep, R.F.; Hua, Y.; Xi, G. Intracerebral Haemorrhage: Mechanisms of Injury and Therapeutic Targets. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, G.; Reiser, G.; Keep, R.F. The Role of Thrombin and Thrombin Receptors in Ischemic, Hemorrhagic and Traumatic Brain Injury: Deleterious or Protective? J. Neurochem. 2003, 84, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zazulia, A.R.; Diringer, M.N.; Videen, T.O.; Adams, R.E.; Yundt, K.; Aiyagari, V.; Grubb, R.L.; Powers, W.J. Hypoperfusion without Ischemia Surrounding Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2001, 21, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garg, R.K.; Khan, J.; Dawe, R.J.; Conners, J.; John, S.; Prabhakaran, S.; Kocak, M.; Bhabad, S.; Simpson, S.L.; Ouyang, B.; et al. The Influence of Diffusion Weighted Imaging Lesions on Outcomes in Patients with Acute Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enzmann, D.R.; Britt, R.H.; Lyons, B.E.; Buxton, J.L.; Wilson, D.A. Natural History of Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Sonography, Computed Tomography and Neuropathology. Am. J. Neuroradiol 1981, 2, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.R.; Xi, G.; Hua, Y.; Zuccarello, M.; De Courten-Myers, G.M.; Broderick, J.P.; Brott, T.G. Ultra-Early Clot Aspiration after Lysis with Tissue Plasminogen Activator in a Porcine Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Edema Reduction and Blood-Brain Barrier Protection. J. Neurosurg. 1999, 90, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragunow, M.; Faull, R. The Use of C-Fos as a Metabolic Marker in Neuronal Pathway Tracing. J. Neurosci. Methods 1989, 29, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, Q.-W.; Wang, J. Modulators of Microglial Activation and Polarization after Intracerebral Haemorrhage. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Misra, S.; Yadav, A.K.; Sagar, R.; Verma, B.; Grover, A.; Prasad, K. Role of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein as a Biomarker in Differentiating Intracerebral Haemorrhage from Ischaemic Stroke and Stroke Mimics: A Meta-Analysis. Biomarkers 2020, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luger, S.; Jæger, H.S.; Dixon, J.; Bohmann, F.O.; Schaefer, J.; Richieri, S.P.; Larsen, K.; Hov, M.R.; Bache, K.G.; Foerch, C.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein and Ubiquitin Carboxy-Terminal Hydrolase-L1 Serum Concentrations for Differentiating Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage from Ischemic Stroke. Neurocrit. Care 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, I.; Algin, A.; Poyraz, M.K.; Yumrutas, O. Diagnostic Value of Serum Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein and S100B Serum Levels in Emergency Medicine Patients with Traumatic versus Nontraumatic Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2018, 21, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerch, C.; Curdt, I.; Yan, B.; Dvorak, F.; Hermans, M.; Berkefeld, J.; Raabe, A.; Neumann-Haefelin, T.; Steinmetz, H.; Sitzer, M. Serum Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein as a Biomarker for Intracerebral Haemorrhage in Patients with Acute Stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Control | rtPA | Ultrasound | rtPA + Ultrasound | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Area 1) | (Area 1) | (Area 1) | (Area 1) | |
| GFAP | 2.67 ± 0.58 | 2.33 ± 0.52 | 2.5 ± 0.55 | 2.33 ± 0.52 |
| cFos | 1.33 ± 0.58 | 1.17 ± 0.41 | 1.67 ± 0.82 | 1.83 ± 0.75 |
| Iba1 | 2 ± 1.00 | 2.5 ± 0.55 | 2.5 ± 0.84 | 2.5 ± 0.84 |
| Control contralaterally | rtPA contralaterally | Ultrasound contralaterally | rtPA + Ultrasound contralaterally | |
| (area 2) | (area 2) | (area 2) | (area 2) | |
| GFAP | 2 ± 1 | 1.33 ± 0.52 | 1.33 ± 0.52 | 1 ± 0 |
| cFos | 1.67 ± 0.58 | 1.33 ± 0.82 | 1.67 ± 1.03 | 2 ± 0.89 |
| Iba1 | 1.67 ± 0.58 | 2 ± 0.63 | 2 ± 0.63 | 2 ± 0.63 |
| rtPA (area 1) vs. Sono contralaterally (area 2) | 0.0444 | Sono (area 1) vs. rtPA + Sono contralaterally (area 2) | 0.0005 |
| rtPA (area 1) vs. rtPA + Sono contralaterally (area 2) | 0.0025 | rtPA + Sono (area 1) vs. rtPA contralaterally (area 2) | 0.0444 |
| Sono (area 1) vs. rtPA contralaterally (area 2) | 0.0112 | rtPA + Sono (area 1) vs. Sono contralaterally (area 2) | 0.0444 |
| Sono (area 1) vs. Sono contralaterally (area 2) | 0.0112 | rtPA + Sono (area 1) vs. rtPA + Sono contralaterally (area 2) | 0.0025 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masomi-Bornwasser, J.; Heimann, A.; Schneider, C.; Klodt, T.; Elmehdawi, H.; Kronfeld, A.; Krenzlin, H.; Tanyildizi, Y.; Kreitner, K.-F.; Kempski, O.; et al. Intrahematomal Ultrasound Enhances RtPA-Fibrinolysis in a Porcine Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040563
Masomi-Bornwasser J, Heimann A, Schneider C, Klodt T, Elmehdawi H, Kronfeld A, Krenzlin H, Tanyildizi Y, Kreitner K-F, Kempski O, et al. Intrahematomal Ultrasound Enhances RtPA-Fibrinolysis in a Porcine Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(4):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040563
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasomi-Bornwasser, Julia, Axel Heimann, Christian Schneider, Tristan Klodt, Hammoud Elmehdawi, Andrea Kronfeld, Harald Krenzlin, Yasemin Tanyildizi, Karl-Friedrich Kreitner, Oliver Kempski, and et al. 2021. "Intrahematomal Ultrasound Enhances RtPA-Fibrinolysis in a Porcine Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 4: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040563
APA StyleMasomi-Bornwasser, J., Heimann, A., Schneider, C., Klodt, T., Elmehdawi, H., Kronfeld, A., Krenzlin, H., Tanyildizi, Y., Kreitner, K.-F., Kempski, O., Sommer, C., Ringel, F., & Keric, N. (2021). Intrahematomal Ultrasound Enhances RtPA-Fibrinolysis in a Porcine Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(4), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040563






