Update on New Aspects of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Hepatic Fibrosis and Portal Hypertension: Implications for Novel Therapeutic Options
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Renin Angiotensin System (RAS)
1.1.1. The Classical Arm of the Renin Angiotensin System
1.1.2. The Alternate Arm of the Renin Angiotensin System
1.2. The Role of Classical RAS in Liver Fibrosis
ACE Inhibitors (ACEi) and Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blockers (ARBs) in Liver Fibrosis
1.3. Role of the Alternate RAS in Hepatic Fibrogenesis
1.4. The Role of RAS in Portal Hypertension
1.5. The Role of RAS in Increasing Hepatic Resistance in the Cirrhotic Liver
1.6. The Role of RAS in Mesenteric Vasodilatation in Cirrhosis
1.7. Manipulation of the RAS in Portal Hypertension
1.8. Targeting the Classical RAS in Portal Hypertension
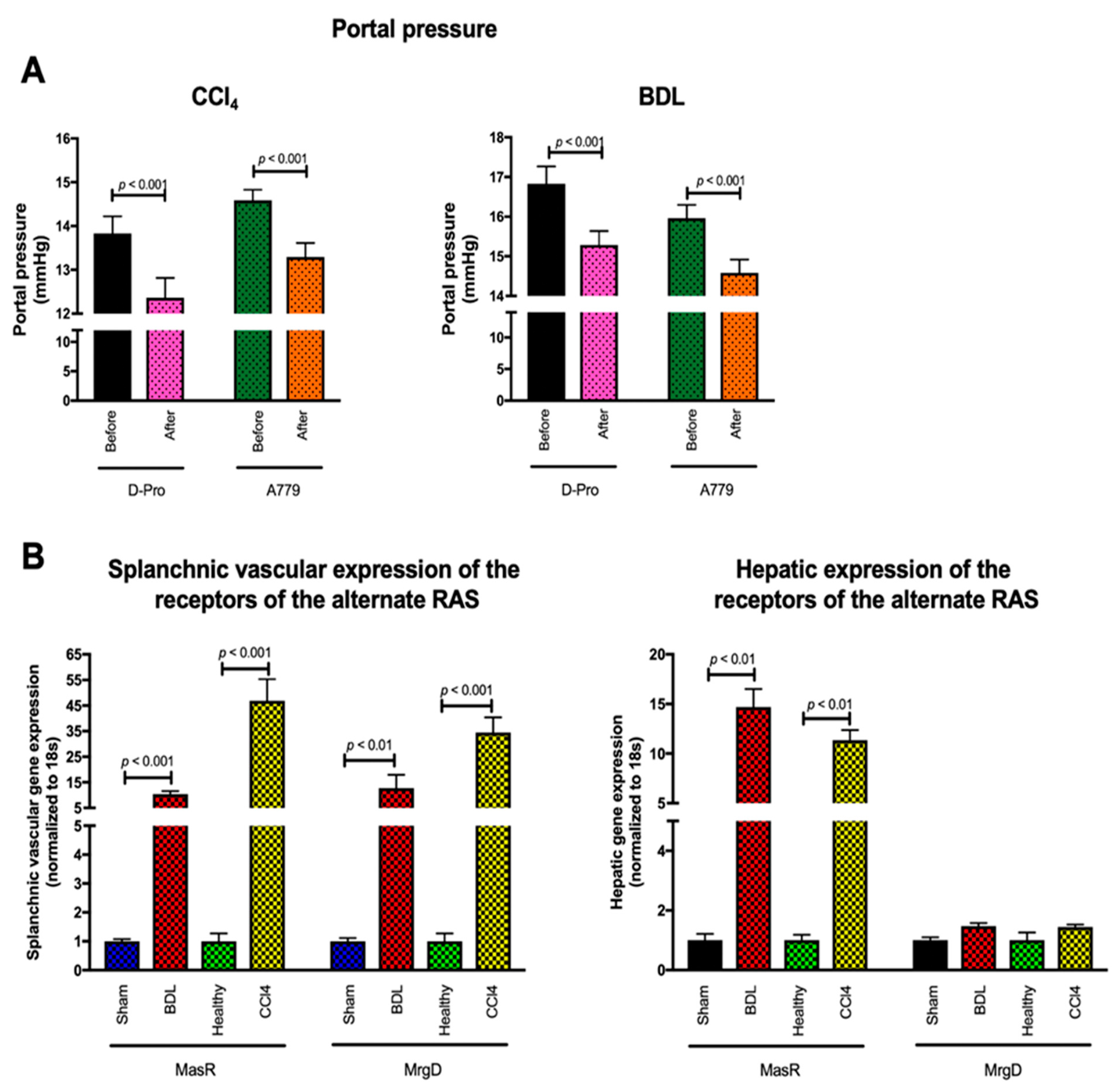
1.9. Targeting the Alternate RAS in Portal Hypertension
2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schuppan, D.; Afdhal, N.H. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2008, 371, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.A.; Herath, C.B.; Mak, K.Y.; Burrell, L.M.; Angus, P.W. Update on new aspects of the renin–angiotensin system in liver disease: Clinical implications and new therapeutic options. Clin. Sci. 2012, 123, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO. Summary Tables of Mortality Estimates by Cause, Age and Sex, Globally and by Region, 2000–2016; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.-C.; Zhang, Q.-B.; Qiao, L. Pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7312–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapaksha, I.G.; Angus, P.W.; Herath, C.B. Current therapies and novel approaches for biliary diseases. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzigotti, A. Advances and challenges in cirrhosis and portal hypertension. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warner, F.J.; Lubel, J.S.; McCaughan, G.W.; Angus, P.W. Liver fibrosis: A balance of ACEs? Clin. Sci. 2007, 113, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubel, J.S.; Herath, C.B.; Burrell, L.M.; Angus, J.A. Liver disease and the renin-angiotensin system: Recent discoveries and clinical implications. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansoè, G.; Aragno, M.; Mastrocola, R.; Mengozzi, G.; Novo, E.; Parola, M. Role of Chymase in the Development of Liver Cirrhosis and Its Complications: Experimental and Human Data. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komeda, K.; Takai, S.; Jin, D.; Tashiro, K.; Hayashi, M.; Tanigawa, N.; Miyazaki, M. Chymase inhibition attenuates tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in hamsters. Hepatol. Res. 2010, 40, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckelings, U.M.; Larhed, M.; Hallberg, A.; E Widdop, R.; Jones, E.S.; Wallinder, C.; Namsolleck, P.; Dahlöf, B.; Unger, T. Non-peptide AT2-receptor agonists. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2011, 11, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Macêdo, S.M.; Guimarães, T.A.; Feltenberger, J.D.; Santos, S.H.S. The role of renin-angiotensin system modulation on treatment and prevention of liver diseases. Peptides 2014, 62, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; A Quyyumi, A. Renin-Angiotensin System and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in the Metabolic Syndrome. Circulation 2004, 110, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, M.; Hsieh, F.; Baronas, E.; Godbout, K.; Gosselin, M.; Stagliano, N.; Donovan, M.; Woolf, B.; Robison, K.; Jeyaseelan, R.; et al. A Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme–Related Carboxypeptidase (ACE2) Converts Angiotensin I to Angiotensin 1-9. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipnis, S.R.; Hooper, N.M.; Hyde, R.; Karran, E.; Christie, G.; Turner, A.J. A Human Homolog of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme: Cloning and Functional Expression as a Captopril-Insensitive Carboxypeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33238–33243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schiavone, M.T.; Santos, R.A.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Khosla, M.C.; Ferrario, C.M. Release of vasopressin from the rat hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system by angiotensin-(1–7) heptapeptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 4095–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chappell, M.C. The Angiotensin-(1–7) Axis: Formation and Metabolism Pathways. Angiotensin-(1–7) 2019, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.A.; e Silva, A.C.S.; Maric, C.; Silva, D.M.; Machado, R.P.; de Buhr, I.; Heringer-Walther, S.; Pinheiro, S.V.B.; Lopes, M.T.; Bader, M.; et al. Angiotensin-(1–7) is an endogenous ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor Mas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8258–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santos, R.A.; Haibara, A.S.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J.; Simões e Silva, A.C.; Paula, R.D.; Pinheiro, S.V.; de Fátima Leite, M.; Lemos, V.S.; Silva, D.M.; Guerra, M.T.; et al. Characterization of a New Selective Antagonist for Angiotensin-(1–7), d-Pro7-Angiotensin-(1–7). Hypertension 2003, 41, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, D.; Vianna, H.; Cortes, S.; Campagnole-Santos, M.; Santos, R.; Lemos, V.S. Evidence for a new angiotensin-(1–7) receptor subtype in the aorta of Sprague–Dawley rats. Peptides 2007, 28, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gembardt, F.; Grajewski, S.; Vahl, M.; Schultheiss, H.-P.; Walther, T. Angiotensin metabolites can stimulate receptors of the Mas-related genes family. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 319, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautner, R.Q.; Villela, D.C.; Fraga-Silva, R.A.; Silva, N.; Verano-Braga, T.; Costa-Fraga, F.; Jankowski, J.; Jankowski, V.; Sousa, F.; Alzamora, A.; et al. Discovery and characterization of alamandine: A novel component of the renin-angiotensin system. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herath, C.B.; Mak, K.; Burrell, L.M.; Angus, P.W. Angiotensin-(1–7) reduces the perfusion pressure response to angiotensin II and methoxamine via an endothelial nitric oxide-mediated pathway in cirrhotic rat liver. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2013, 304, G99–G108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetzner, A.; Gebolys, K.; Meinert, C.; Klein, S.; Uhlich, A.; Trebicka, J.; Villacañas, Ó.; Walther, T. G-Protein–Coupled Receptor MrgD Is a Receptor for Angiotensin-(1–7) Involving Adenylyl Cyclase, cAMP, and Phosphokinase. Hypertension 2016, 68, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bader, M. Tissue Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Systems: Targets for Pharmacological Therapy. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 439–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehme, A.; Zouein, F.A.; Zayeri, Z.D.; Zibara, K. An Update on the Tissue Renin Angiotensin System and Its Role in Physiology and Pathology. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2019, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bataller, R.; Sancho-Bru, P.; Gines, P.; Lora, J.M.; Al-Garawi, A.; Solé, M.; Colmenero, J.; Nicolás, J.M.; Jiménez, W.; Weich, N.; et al. Activated human hepatic stellate cells express the renin-angiotensin system and synthesize angiotensin II. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.C.; Struthers, A.D. Targeting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2013, 10, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nistala, R.; Wei, Y.; Sowers, J.R.; Whaley-Connell, A. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system-mediated redox effects in chronic kidney disease. Transl. Res. 2009, 153, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bataller, R.; Schwabe, R.F.; Choi, Y.H.; Yang, L.; Paik, Y.H.; Lindquist, J.; Qian, T.; Schoonhoven, R.; Hagedorn, C.H.; Lemasters, J.J.; et al. NADPH oxidase signal transduces angiotensin II in hepatic stellate cells and is critical in hepatic fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubel, J.S.; Herath, C.B.; Tchongue, J.; Grace, J.; Jia, Z.; Spencer, K.; Casley, D.; Crowley, P.; Sievert, W.; Burrell, L.M.; et al. Angiotensin-(1–7), an alternative metabolite of the renin–angiotensin system, is up-regulated in human liver disease and has antifibrotic activity in the bile-duct-ligated rat. Clin. Sci. 2009, 117, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paizis, G.; Cooper, M.E.; Schembri, J.M.; Tikellis, C.; Burrell, L.M.; Angus, P.W. Up-regulation of components of the renin-angiotensin system in the bile duct–ligated rat liver. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Mehr, A.P.; Kreutz, R. Physiology of Local Renin-Angiotensin Systems. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 747–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, C.B.; Warner, F.J.; Lubel, J.S.; Dean, R.G.; Jia, Z.; Lew, R.A.; Smith, A.I.; Burrell, L.M.; Angus, J.A. Upregulation of hepatic angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and angiotensin-(1–7) levels in experimental biliary fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, K.Y.; Chin, R.; Cunningham, S.C.; Habib, M.R.; Torresi, J.; Sharland, A.F.; E Alexander, I.; Angus, J.A.; Herath, C.B. ACE2 Therapy Using Adeno-associated Viral Vector Inhibits Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajapaksha, I.G.; Mak, K.Y.; Huang, P.; Burrell, L.M.; Angus, J.A.; Herath, C.B. The small molecule drug diminazene aceturate inhibits liver injury and biliary fibrosis in mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L. Hepatic Stellate Cells: Protean, Multifunctional, and Enigmatic Cells of the Liver. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 125–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataller, R.; Gäbele, E.; Parsons, C.J.; Morris, T.; Yang, L.; Schoonhoven, R.; A Brenner, D.; Rippe, R.A. Systemic infusion of angiotensin II exacerbates liver fibrosis in bile duct-ligated rats. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, C.B.; Mak, K.Y.; Angus, P.W. Role of the Alternate RAS in Liver Disease and the GI Tract. In The Protective Arm of the Renin Angiotensin System (RAS); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Bataller, R.; Ginès, P.; Nicolás, J.M.; Görbig, M.; Garcia–Ramallo, E.; Gasull, X.; Bosch, J.; Arroyo, V.; Rodés, J. Angiotensin II induces contraction and proliferation of human hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleve, L.D. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maretti-Mira, A.C.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; DeLeve, L.D. Role of incomplete stem cell maturation in hepatic fibrosis. In HEPATOLOGY; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jarnagin, W.R.; Rockey, D.C.; E Koteliansky, V.; Wang, S.S.; Bissell, D.M. Expression of variant fibronectins in wound healing: Cellular source and biological activity of the EIIIA segment in rat hepatic fibrogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 127, 2037–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, G.; Shah, V.H.; Gracia-Sancho, J. Sinusoidal communication in liver fibrosis and regeneration. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonsson, J.R.; Clouston, A.D.; Ando, Y.; Kelemen, L.I.; Horn, M.J.; Adamson, M.D.; Purdie, D.M.; Powell, E.E. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition Attenuates the Progression of Rat Hepatic Fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkay, C.; Yönem, Ö.; Arıcı, S.; Koyuncu, A.; Kanbay, M.; Arici, S. Effect of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme Inhibition on Experimental Hepatic Fibrogenesis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 53, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paizis, G.; Gilbert, R.E.; Cooper, M.E.; Murthi, P.; Schembri, J.M.; Wu, L.L.; Rumble, J.R.; Kelly, D.J.; Tikellis, C.; Cox, A.; et al. Effect of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade on experimental hepatic fibrogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2001, 35, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, E.-T.; Liu, R.-X.; Wen, Y.; Yin, C.-H. Telmisartan attenuates hepatic fibrosis in bile duct-ligated rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, H.-S.; Li, D.-G.; Lu, H.-M.; Zhan, Y.-T.; Wang, Z.-R.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J.-L.; Xu, Q.-F. Effects of AT1 receptor antagonist, losartan, on rat hepatic fibrosis induced by CCl4. World J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 6, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, A.; Ono, M.; Saibara, T.; Nozaki, Y.; Masuda, K.; Yoshioka, A.; Takahashi, M.; Akisawa, N.; Iwasaki, S.; Oben, J.A.; et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker inhibits fibrosis in rat nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2007, 45, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corey, K.E.; Shah, N.; Misdraji, J.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Zheng, H.; Bhan, A.K.; Chung, R.T. The effect of angiotensin-blocking agents on liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C. Liver Int. 2009, 29, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stokkeland, K.; Lageborn, C.T.; Höijer, J.; Bottai, M.; Stål, P.; Söderberg-Löfdal, K.; Ekbom, A. Statins and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors are Associated with Reduced Mortality and Morbidity in Chronic Liver Disease. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.Y.; Cho, M.Y.; Baik, S.K.; Jeong, P.H.; Suk, K.T.; Jang, Y.O.; Yea, C.J.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.S.; Kwon, S.O.; et al. Beneficial effects of candesartan, an angiotensin-blocking agent, on compensated alcoholic liver fibrosis—A randomized open-label controlled study. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Shibuya, A.; Minamino, T.; Takada, J.; Tanaka, Y.; Okuwaki, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Koizumi, W. Effects of 1-year administration of olmesartan on portal pressure and TGF-beta1 in selected patients with cirrhosis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debernardi-Venon, W.; Martini, S.; Biasi, F.; Vizio, B.; Termine, A.; Poli, G.; Brunello, F.; Alessandria, C.; Bonardi, R.; Saracco, G.; et al. AT1 receptor antagonist Candesartan in selected cirrhotic patients: Effect on portal pressure and liver fibrosis markers. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiji, H.; Noguchi, R.; Ikenaka, Y.; Kaji, K.; Douhara, A.; Yamao, J.; Toyohara, M.; Mitoro, A.; Sawai, M.; Yoshida, M.; et al. Combination of branched-chain amino acid and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor improves liver fibrosis progression in patients with cirrhosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2011, 5, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terui, Y.; Saito, T.; Watanabe, H.; Togashi, H.; Kawata, S.; Kamada, Y.; Sakuta, S. Effect of angiotensin receptor antagonist on liver fibrosis in early stages of chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2002, 36, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, S.; Wilkinson, N.; Tiniakos, D.; Wilkinson, J.; Burt, A.D.; McColl, E.; Stocken, D.D.; Steen, N.; Barnes, J.; Goudie, N.; et al. A randomised controlled trial of losartan as an anti-fibrotic agent in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, N.; Li, F.; Zhou, Z.; Han, Q.; Lv, Y.; Sang, J.; Liu, Z. Therapeutic effect of renin angiotensin system inhibitors on liver fibrosis. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Runyon, B.A. Introduction to the revised American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guideline management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis 2012. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1651–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EASL. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 406–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paizis, G.; Tikellis, C.; E Cooper, M.; Schembri, J.M.; A Lew, R.; I Smith, A.; Shaw, T.; Warner, F.J.; Zuilli, A.; Burrell, L.M.; et al. Chronic liver injury in rats and humans upregulates the novel enzyme angiotensin converting enzyme 2. Gut 2005, 54, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajapaksha, I.G.; Gunarathne, L.S.; Asadi, K.; Cunningham, S.C.; Sharland, A.; Alexander, I.E.; Angus, P.W.; Herath, C.B. Liver-Targeted Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 Therapy Inhibits Chronic Biliary Fibrosis in Multiple Drug-Resistant Gene 2-Knockout Mice. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 1656–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, F.D.; Ferreira, A.J.; Sinisterra, R.D.; Jacoby, B.A.; Sousa, F.B.; Caliari, M.V.; Silva, G.A.; Melo, M.B.; Nadu, A.P.; Souza, L.E.; et al. An Oral Formulation of Angiotensin-(1–7) Produces Cardioprotective Effects in Infarcted and Isoproterenol-Treated Rats. Hypertension 2011, 57, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastos, A.C.; Magalhães, G.S.; Gregório, J.F.; Matos, N.A.; Motta-Santos, D.; Bezerra, F.S.; Santos, R.A.S.; Santos, M.J.C.; Rodrigues-Machado, M.G. Oral formulation angiotensin-(1–7) therapy attenuates pulmonary and systemic damage in mice with emphysema induced by elastase. Immunobiology 2020, 225, 151893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, V.P.; Barbosa, M.A.; De Castro, U.G.M.; Zacarias, A.C.; Bezerra, F.S.; De Sá, R.G.; De Lima, W.G.; Dos Santos, R.A.S.; Alzamora, A.C. Antioxidant Effects of Oral Ang-(1–7) Restore Insulin Pathway and RAS Components Ameliorating Cardiometabolic Disturbances in Rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wysocki, J.; Ye, M.; Rodriguez, E.; González-Pacheco, F.R.; Barrios, C.; Evora, K.; Schuster, M.; Loibner, H.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Ferrario, C.M.; et al. Targeting the Degradation of Angiotensin II With Recombinant Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2. Hypertension 2010, 55, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudit, G.Y.; Liu, G.C.; Zhong, J.; Basu, R.; Chow, F.L.; Zhou, J.; Loibner, H.; Janzek, E.; Schuster, M.; Penninger, J.M.; et al. Human Recombinant ACE2 Reduces the Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes 2009, 59, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haschke, M.; Schuster, M.; Poglitsch, M.; Loibner, H.; Salzberg, M.; Bruggisser, M.; Penninger, J.; Krähenbühl, S. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Recombinant Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 in Healthy Human Subjects. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Österreicher, C.H.; Taura, K.; De Minicis, S.; Seki, E.; Penz-Österreicher, M.; Kodama, Y.; Kluwe, J.; Schuster, M.; Oudit, G.Y.; Penninger, J.M.; et al. Angiotensin-converting-enzyme 2 inhibits liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 2009, 50, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naso, M.F.; Tomkowicz, B.; Perry, W.L.; Strohl, W.R. Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) as a Vector for Gene Therapy. BioDrugs 2017, 31, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexander, I.E.; Cunningham, S.C.; Logan, G.J.; Christodoulou, J. Potential of AAV vectors in the treatment of metabolic disease. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prada, J.A.H.; Ferreira, A.J.; Katovich, M.J.; Shenoy, V.; Qi, Y.; Santos, R.A.S.; Castellano, R.K.; Lampkins, A.J.; Gubala, V.; Ostrov, D.A.; et al. Structure-Based Identification of Small-Molecule Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Activators as Novel Antihypertensive Agents. Hypertension 2008, 51, 1312–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraga-Silva, R.A.; Sorg, B.S.; Wankhede, M.; DeDeugd, C.; Jun, J.Y.; Baker, M.B.; Li, Y.; Castellano, R.K.; Katovich, M.J.; Raizada, M.K.; et al. ACE2 Activation Promotes Antithrombotic Activity. Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.S.; Froemming, G.R.A.; Omar, E.; Singh, H.J. ACE2 activation by xanthenone prevents leptin-induced increases in blood pressure and proteinuria during pregnancy in Sprague-Dawley rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2014, 49, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.J.; Shenoy, V.; Qi, Y.; Fraga-Silva, R.A.; Santos, R.A.; Katovich, M.J.; Raizada, M.K. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activation protects against hypertension-induced cardiac fibrosis involving extracellular signal-regulated kinases. Exp. Physiol. 2011, 96, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.M.; Messiha, B.A.S.; Mansour, A.M. Modulation of brain ACE and ACE2 may be a promising protective strategy against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: An experimental trial in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2018, 391, 1003–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cole-Jeffrey, C.T.; Shenoy, V.; Espejo, A.; Hanna, M.; Song, C.; Pepine, C.J.; Katovich, M.J.; Raizada, M.K. Diminazene Aceturate Enhances Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Activity and Attenuates Ischemia-Induced Cardiac Pathophysiology. Hypertension 2013, 62, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, V.; Gjymishka, A.; Jarajapu, Y.P.; Qi, Y.; Afzal, A.; Rigatto, K.; Ferreira, A.J.; Fraga-Silva, R.A.; Kearns, P.; Douglas, J.Y.; et al. Diminazene Attenuates Pulmonary Hypertension and Improves Angiogenic Progenitor Cell Functions in Experimental Models. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peregrine, A.; Mamman, M. Pharmacology of diminazene: A review. Acta Trop. 1993, 54, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaru, D.E.; Liwo, D.A.; Isakina, D.; Okori, E.E. Retrospective long-term study of effects of berenil by follow-up of patients treated since 1965. Tropenmedizin und Parasitol. 1984, 35, 148–150. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Shil, P.K.; Zhu, P.; Yang, H.; Verma, A.; Lei, B.; Li, Q. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Activator Diminazene Aceturate Ameliorates Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis in Mice. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 3809–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foureaux, G.; Nogueira, J.C.; Nogueira, B.S.; Fulgêncio, G.O.; Menezes, G.B.; Fernandes, S.O.A.; Cardoso, V.N.; Fernandes, R.S.; Oliveira, G.P.; Franca, J.R.; et al. Antiglaucomatous Effects of the Activation of Intrinsic Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 4296–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Qiu, Y.; Fu, X.; Lin, R.; Lei, C.; Wang, J.; Lei, B. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activator diminazene aceturate prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by inhibiting MAPK and NF-ΚB pathways in human retinal pigment epithelium. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosch, J.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C. Complications of cirrhosis. I. Portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32 (Suppl. 1), 141–156. [Google Scholar]
- Tandon, P.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Portal Hypertension and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Prognosis and Beyond. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 1318–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraldes, J.G.; Bosch, J.; Abraldeṣ, J.G. Clinical Features and Natural History of Variceal Hemorrhage. In Clinical Gastroenterology; Springer Nature: London, UK, 2007; pp. 167–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ripoll, C.; Groszmann, R.; Garcia–Tsao, G.; Grace, N.; Burroughs, A.; Planas, R.; Escorsell, A.; Garcia–Pagan, J.C.; Makuch, R.; Patch, D.; et al. Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient Predicts Clinical Decompensation in Patients With Compensated Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martell, M.; Coll, M.; Ezkurdia, N.; Raurell, I.; Genescà, J. Physiopathology of splanchnic vasodilation in portal hypertension. World J. Hepatol. 2010, 2, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groszmann, R.J.; Abraldes, J.G. Portal hypertension: From bedside to bench. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2005, 39 (Suppl. 2), S125–S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pagán, J.C.; Villanueva, C.; Vila, M.C.; Albillos, A.; Genescà, J.; Ruiz-Del-Arbol, L.; Rodriguez, M.; Calleja, J.L.; González, A.; Solà, R.; et al. Isosorbide Mononitrate in the Prevention of First Variceal Bleed in Patients Who Cannot Receive β-blockers. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 908–914. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, P.S.; Runyon, B.A. The changing role of beta-blocker therapy in patients with cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Amico, G.; Pagliaro, L.; Bosch, J. The treatment of portal hypertension: A meta-analytic review. Hepatology 1995, 22, 332–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.; Abraldes, J.G.; Berzigotti, A.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Bosch, J. Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone inhibitors in the reduction of portal pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennenberg, M.; Trebicka, J.; Sauerbruch, T.; Heller, J. Mechanisms of extrahepatic vasodilation in portal hypertension. Gut 2008, 57, 1300–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo-Baruqui, A.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Armendáriz-Borunda, J. Role of angiotensin II in liver fibrosis-induced portal hypertension and therapeutic implications. Hepatol. Res. 2010, 40, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.S.E.; Miranda, A.S.; Rocha, N.P.; Teixeira, A.L. Renin angiotensin system in liver diseases: Friend or foe? World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3396–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.A.; Klein, S.; Herath, C.B.; Granzow, M.; Schierwagen, R.; Masing, N.; Walther, T.; Sauerbruch, T.; Burrell, L.M.; Angus, J.A.; et al. Activation of the Mas Receptor by Angiotensin-(1–7) in the Renin–Angiotensin System Mediates Mesenteric Vasodilatation in Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 874–884.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunarathne, L.S.; Angus, P.W.; Herath, C.B. Blockade of Mas Receptor or Mas-Related G-Protein Coupled Receptor Type D Reduces Portal Pressure in Cirrhotic but Not in Non-cirrhotic Portal Hypertensive Rats. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herath, C.B.; Lubel, J.S.; Jia, Z.; Velkoska, E.; Casley, D.; Brown, L.; Tikellis, C.; Burrell, L.M.; Angus, P.W. Portal pressure responses and angiotensin peptide production in rat liver are determined by relative activity of ACE and ACE2. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, G98–G106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gunarathne, L.S.; Rajapaksha, H.; Shackel, N.; Angus, P.W.; Herath, C.B. Cirrhotic portal hypertension: From pathophysiology to novel therapeutics. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 6111–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiji, H.; Yoshii, J.; Ikenaka, Y.; Noguchi, R.; Tsujinoue, H.; Nakatani, T.; Imazu, H.; Yanase, K.; Kuriyama, S.; Fukui, H. Inhibition of renin-angiotensin system attenuates liver enzyme-altered preneoplastic lesions and fibrosis development in rats. J. Hepatol. 2002, 37, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.S.; Lu, H.M.; Li, D.G.; Zhan, Y.T.; Wang, Z.R.; Huang, X.; Cheng, J.L.; Xu, Q.F. The regulatory role of AT1 receptor on activated HSCs in hepatic fibrogenesis: Effects of RAS inhibitors on hepatic fibrosis induced by CCl4. World J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 6, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macgilchrist, A.J.; Howes, L.G.; Hawksby, C.; Reid, J.L. Plasma noradrenaline in cirrhosis: A study of kinetics and temporal relationship to ascites formation. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 21, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlitsch, A.; Pleiner, J.; Mittermayer, F.; Schaller, G.; Homoncik, M.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Wolzt, M. Vasoconstrictor hyporeactivity can be reversed by antioxidants in patients with advanced alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver and ascites. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 2028–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angus, P.W. Role of endothelin in systemic and portal resistance in cirrhosis. Gut 2006, 55, 1230–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miñano, C.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Clinical Pharmacology of Portal Hypertension. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 2010, 39, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sieber, C.C.; Groszmann, R.J. In vitro hyporeactivity to methoxamine in portal hypertensive rats: Reversal by nitric oxide blockade. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 1992, 262, G996–G1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newby, D.E.; Jalan, R.; Masumori, S.; Hayes, P.C.; Boon, N.A.; Webb, D.J. Peripheral vascular tone in patients with cirrhosis: Role of the renin–angiotensin and sympathetic nervous systems. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998, 38, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hennenberg, M.; Trebicka, J.; Biecker, E.; Schepke, M.; Sauerbruch, T.; Heller, J. Vascular dysfunction in human and rat cirrhosis: Role of receptor-desensitizing and calcium-sensitizing proteins. Hepatology 2007, 45, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neef, M.; Biecker, E.; Heller, J.; Schepke, M.; Nischalke, H.D.; Wolff, M.; Spengler, U.; Reichen, J.; Sauerbruch, T. Portal hypertension is associated with increased mRNA levels of vasopressor G-protein-coupled receptors in human hepatic arteries. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 33, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennenberg, M.; Biecker, E.; Trebicka, J.; Jochem, K.; Zhou, Q.; Schmidt, M.; Jakobs, K.H.; Sauerbruch, T.; Heller, J. Defective RhoA/Rho-kinase signaling contributes to vascular hypocontractility and vasodilation in cirrhotic rats. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 838–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennenberg, M.; Trebicka, J.; Kohistani, A.Z.; Heller, J.; Sauerbruch, T. Vascular hyporesponsiveness to angiotensin II in rats with CCl4-induced liver cirrhosis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 39, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Boas, W.W.; Ribeiro-Oliveira, A., Jr.; Pereira, R.M.; da Cunha Ribeiro, R.; Almeida, J.; Nadu, A.P.; e Silva, A.C.S.; dos Santos, R.A.S. Relationship between angiotensin-(1–7) and angiotensin II correlates with hemodynamic changes in human liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2512–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quilley, J.; Fulton, D.; McGiff, J.C. Hyperpolarizing Factors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997, 54, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacerdoti, D.; Gatta, A.; McGiff, J.C. Role of cytochrome P450-dependent arachidonic acid metabolites in liver physiology and pathophysiology. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2003, 72, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tox, U.; Steffen, H.M. Impact of inhibitors of the Renin-Angiotensin-aldosterone system on liver fibrosis and portal hypertension. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 3649–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.S.; Kågedal, B.; Wahren, J. Effects of captopril on hepatic venous pressure and blood flow in patients with liver cirrhosis. Am. J. Med. 1984, 76, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.K.; Park, D.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.K.; Kwon, S.O.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, J.W.; Chang, S.J. Captopril reduces portal pressure effectively in portal hypertensive patients with low portal venous velocity. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 38, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.T.; Cheng, J.S.; Lin, M.; tseng, W.S.; Chang, J.M.; Lai, K.H. Haemodynamic effects of enalaprilat on portal hypertension in patients with HBsAg-positive cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1995, 10, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, P.; Ochmann, J.; Kantorová, I. Effect of enalapril treatment and sclerotherapy of esophageal varices on hepatic hemodynamics in portal hypertension. Hepatogastroenterology 1992, 39, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Gracia-Sancho, J.; Laviña, B.; Rodríguez-Vilarrupla, A.; García-Calderó, H.; Bosch, J.; García-Pagán, J.C. Enhanced vasoconstrictor prostanoid production by sinusoidal endothelial cells increases portal perfusion pressure in cirrhotic rat livers. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepke, M.; Wiest, R.; Flacke, S.; Heller, J.; Stoffel-Wagner, B.; Herold, T.; Ghauri, M.; Sauerbruch, T. Irbesartan Plus Low-Dose Propranolol Versus Low-Dose Propranolol Alone in Cirrhosis: A Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepke, M.; Werner, E.; Biecker, E.; Schiedermaier, P.; Heller, J.; Neef, M.; Caselmann, W.H.; Sauerbruch, T.; Stoffel-Wagner, B.; Hofer, U. Hemodynamic effects of the angiotensin II receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Herath, C.B.; Schierwagen, R.; Grace, J.; Haltenhof, T.; Uschner, F.E.; Strassburg, C.P.; Sauerbruch, T.; Walther, T.; Angus, P.W.; et al. Hemodynamic Effects of the Non-Peptidic Angiotensin-(1–7) Agonist AVE0991 in Liver Cirrhosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansoè, G.; Aragno, M.; Mastrocola, R.; Restivo, F.; Mengozzi, G.; Smedile, A.; Rosina, F.; Danni, O.; Parola, M.; Rizzetto, M. Neutral endopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.11) in cirrhotic liver: A new target to treat portal hypertension? J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajapaksha, I.G.; Gunarathne, L.S.; Angus, P.W.; Herath, C.B. Update on New Aspects of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Hepatic Fibrosis and Portal Hypertension: Implications for Novel Therapeutic Options. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040702
Rajapaksha IG, Gunarathne LS, Angus PW, Herath CB. Update on New Aspects of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Hepatic Fibrosis and Portal Hypertension: Implications for Novel Therapeutic Options. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(4):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040702
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajapaksha, Indu G., Lakmie S. Gunarathne, Peter W. Angus, and Chandana B. Herath. 2021. "Update on New Aspects of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Hepatic Fibrosis and Portal Hypertension: Implications for Novel Therapeutic Options" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 4: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040702
APA StyleRajapaksha, I. G., Gunarathne, L. S., Angus, P. W., & Herath, C. B. (2021). Update on New Aspects of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Hepatic Fibrosis and Portal Hypertension: Implications for Novel Therapeutic Options. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(4), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040702








