A Follow-Up Study of a European IgG4-Related Disease Cohort Treated with Rituximab
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Clinical and Morphologic Data
2.3. Responder Index (RI)
2.4. Treatment Protocols
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
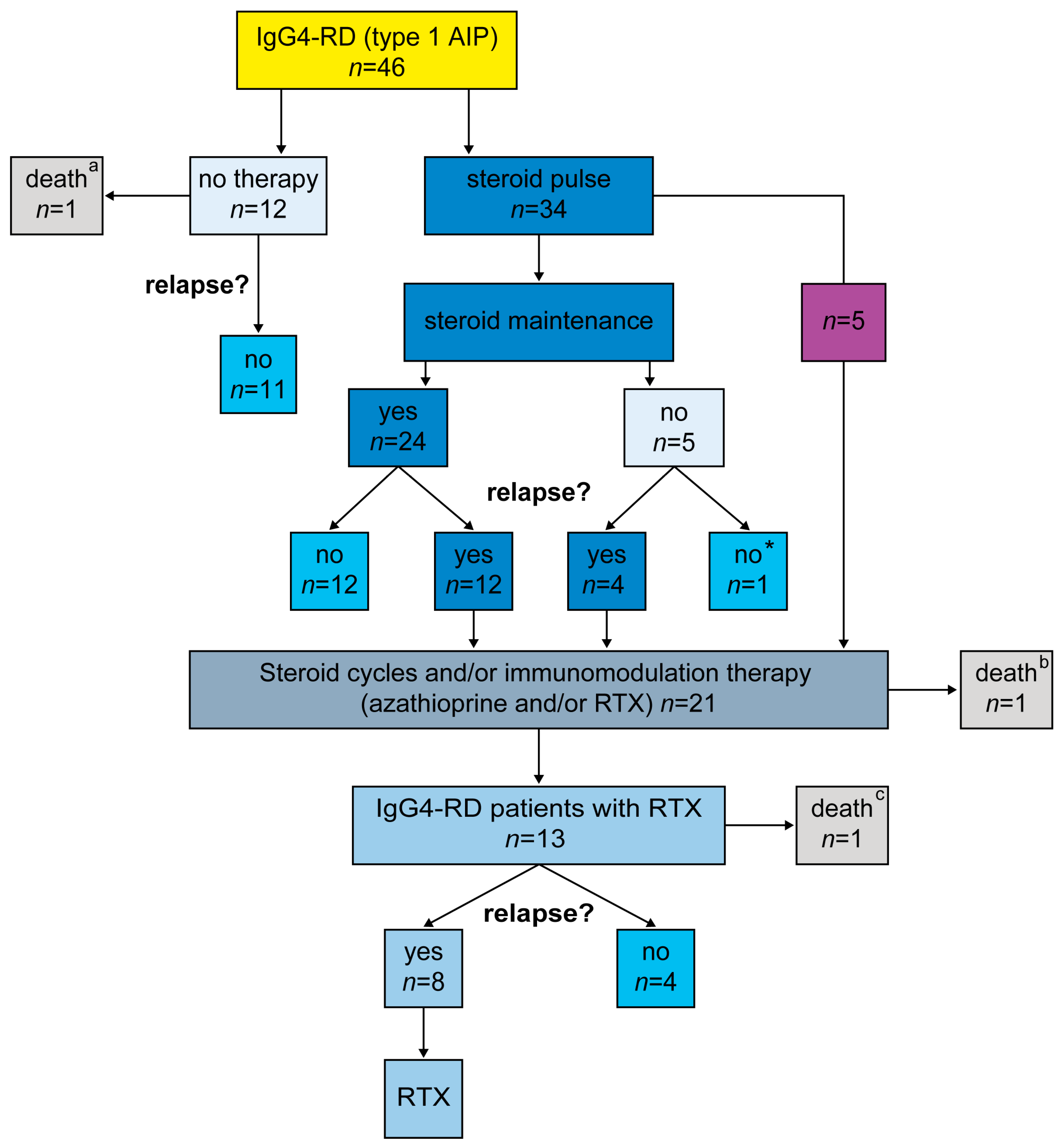
3.2. Treatment Response and Relapse Rates
3.3. Treating IgG4-RD Patients with Rituximab
3.4. Assessing Treatment Response According to the Responder Index
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarles, H.; Sarles, J.C.; Muratore, R.; Guien, C. Chronic inflammatory sclerosis of the pancreas—An autonomous pancreatic disease? Am. J. Dig. Dis. 1961, 6, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimosegawa, T.; Chari, S.T.; Frulloni, L.; Kamisawa, T.; Kawa, S.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Kim, M.H.; Kloppel, G.; Lerch, M.M.; Lohr, M.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: Guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology. Pancreas 2011, 40, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Michaely, H.; Ruckert, F.; Weiss, C.; Strobel, P.; Belle, S.; Hirth, M.; Wilhelm, T.J.; Haas, S.L.; Jesenofsky, R.; et al. Diagnosing autoimmune pancreatitis with the Unifying-Autoimmune-Pancreatitis-Criteria. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Naden, R.P.; Chari, S.; Choi, H.K.; Della-Torre, E.; Dicaire, J.F.; Hart, P.A.; Inoue, D.; Kawano, M.; Khosroshahi, A.; et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Naden, R.P.; Chari, S.; Choi, H.; Della-Torre, E.; Dicaire, J.F.; Hart, P.A.; Inoue, D.; Kawano, M.; Khosroshahi, A.; et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol 2020, 72, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloppel, G.; Luttges, J.; Lohr, M.; Zamboni, G.; Longnecker, D. Autoimmune pancreatitis: Pathological, clinical, and immunological features. Pancreas 2003, 27, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaccarino, L.; Talarico, R.; Scire, C.A.; Amoura, Z.; Burmester, G.; Doria, A.; Faiz, K.; Frank, C.; Hachulla, E.; Hie, M.; et al. IgG4-related diseases: State of the art on clinical practice guidelines. RMD Open 2018, 4 (Suppl. S1), e000787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohr, J.M.; Beuers, U.; Vujasinovic, M.; Alvaro, D.; Frokjaer, J.B.; Buttgereit, F.; Capurso, G.; Culver, E.L.; de-Madaria, E.; Della-Torre, E.; et al. European Guideline on IgG4-related digestive disease—UEG and SGF evidence-based recommendations. United Eur. Gastroenterol J. 2020, 8, 637–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masamune, A.; Nishimori, I.; Kikuta, K.; Tsuji, I.; Mizuno, N.; Iiyama, T.; Kanno, A.; Tachibana, Y.; Ito, T.; Kamisawa, T.; et al. Randomised controlled trial of long-term maintenance corticosteroid therapy in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 2017, 66, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, P.A.; Kamisawa, T.; Brugge, W.R.; Chung, J.B.; Culver, E.L.; Czako, L.; Frulloni, L.; Go, V.L.; Gress, T.M.; Kim, M.H.; et al. Long-term outcomes of autoimmune pancreatitis: A multicentre, international analysis. Gut 2013, 62, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosroshahi, A.; Stone, J.H. Treatment approaches to IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, H.; Vullierme, M.P.; Maire, F.; Hentic, O.; Ruszniewski, P.; Levy, P.; Rebours, V. Risk factors and treatment of relapses in autoimmune pancreatitis: Rituximab is safe and effective. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, C.; Della-Torre, E.; Lanzillotta, M.; Bozzolo, E.; Baldissera, E.; Milani, R.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Crippa, S.; Falconi, M.; Dagna, L. Long-term efficacy of maintenance therapy with Rituximab for IgG4-related disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 74, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carruthers, M.N.; Stone, J.H.; Deshpande, V.; Khosroshahi, A. Development of an IgG4-RD Responder Index. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 2012, 259408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Khosroshahi, A.; Carruthers, M.D.; Perugino, C.A.; Choi, H.; Campochiaro, C.; Culver, E.L.; Cortazar, F.; Della-Torre, E.; Ebbo, M.; et al. An International Multispecialty Validation Study of the IgG4-Related Disease Responder Index. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2018, 70, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, M.N.; Khosroshahi, A.; Augustin, T.; Deshpande, V.; Stone, J.H. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Mattoo, H.; Carruthers, M.; Mahajan, V.S.; Della Torre, E.; Lee, H.; Kulikova, M.; Deshpande, V.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngwa, T.N.; Law, R.; Murray, D.; Chari, S.T. Serum immunoglobulin G4 level is a poor predictor of immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Pancreas 2014, 43, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, M.N.; Topazian, M.D.; Khosroshahi, A.; Witzig, T.E.; Wallace, Z.S.; Hart, P.A.; Deshpande, V.; Smyrk, T.C.; Chari, S.; Stone, J.H. Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: A prospective, open-label trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Della-Torre, E.; Sekigami, Y.; Carruthers, M.; Wallace, Z.S.; Deshpande, V.; Stone, J.H.; Pillai, S. De novo oligoclonal expansions of circulating plasmablasts in active and relapsing IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, K.; Chari, S.T.; Frulloni, L.; Lerch, M.M.; Kamisawa, T.; Kawa, S.; Kim, M.H.; Levy, P.; Masamune, A.; Webster, G.; et al. International consensus for the treatment of autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, P.A.; Topazian, M.D.; Witzig, T.E.; Clain, J.E.; Gleeson, F.C.; Klebig, R.R.; Levy, M.J.; Pearson, R.K.; Petersen, B.T.; Smyrk, T.C.; et al. Treatment of relapsing autoimmune pancreatitis with immunomodulators and rituximab: The Mayo Clinic experience. Gut 2013, 62, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, L.A.; Arnold, F.; Siegel, F.; Backhus, J.; Beyer, G.; Weiss, F.U.; Perkhofer, L.; Beutel, A.; Seufferlein, T.; Muller, M.; et al. Serum IgG4 levels outperform IgG4/IgG RNA ratio in differential diagnosis of IgG4-related disease. JHEP Rep 2020, 2, 100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhus, J.; Seufferlein, T.; Perkhofer, L.; Hermann, P.C.; Kleger, A. IgG4-Related Diseases in the Gastrointestinal Tract: Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis and Treatment Challenges. Digestion 2019, 100, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbo, M.; Grados, A.; Samson, M.; Groh, M.; Loundou, A.; Rigolet, A.; Terrier, B.; Guillaud, C.; Carra-Dalliere, C.; Renou, F.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of rituximab in IgG4-related disease: Data from a French nationwide study of thirty-three patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillette de Buy Wenniger, L.J.; Doorenspleet, M.E.; Klarenbeek, P.L.; Verheij, J.; Baas, F.; Elferink, R.P.; Tak, P.P.; de Vries, N.; Beuers, U. Immunoglobulin G4+ clones identified by next-generation sequencing dominate the B cell receptor repertoire in immunoglobulin G4 associated cholangitis. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2390–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Maehara, T.; Deshpande, V.; Della-Torre, E.; Wallace, Z.S.; Kulikova, M.; Drijvers, J.M.; Daccache, J.; Carruthers, M.N.; et al. Clonal expansion of CD4(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, M.H.; Cho, D.H.; Jun, J.H.; Nam, K.; Song, T.J.; Park, D.H.; Lee, S.S.; Seo, D.W.; et al. Relapse rate and predictors of relapse in a large single center cohort of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis: Long-term follow-up results after steroid therapy with short-duration maintenance treatment. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detlefsen, S.; Zamboni, G.; Frulloni, L.; Feyerabend, B.; Braun, F.; Gerke, O.; Schlitter, A.M.; Esposito, I.; Kloppel, G. Clinical features and relapse rates after surgery in type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis differ from type 2: A study of 114 surgically treated European patients. Pancreatology 2012, 12, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.H.; Kim, M.H.; Park, D.H.; Hwang, C.Y.; Park, S.J.; Lee, S.S.; Seo, D.W.; Lee, S.K. Is a 2-week steroid trial after initial negative investigation for malignancy useful in differentiating autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer? A prospective outcome study. Gut 2008, 57, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Codina, A.; Pinilla, B.; Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Lopez, C.; Fraile-Rodriguez, G.; Fonseca-Aizpuru, E.; Carballo, I.; Brito-Zeron, P.; Feijoo-Masso, C.; Lopez-Dupla, M.; et al. Treatment and outcomes in patients with IgG4-related disease using the IgG4 responder index. Joint Bone Spine 2018, 85, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Mohapatra, S.; Lennon, R.J.; Piovezani Ramos, G.; Postier, N.; Gleeson, F.C.; Levy, M.J.; Pearson, R.K.; Petersen, B.T.; Vege, S.S.; et al. Rituximab Maintenance Therapy Reduces Rate of Relapse of Pancreaticobiliary Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleger, A.; Seufferlein, T.; Wagner, M.; Tannapfel, A.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Mayerle, J. IgG4-related autoimmune diseases: Polymorphous presentation complicates diagnosis and treatment. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2015, 112, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Pretis, N.; Amodio, A.; Bernardoni, L.; Campagnola, P.; Capuano, F.; Chari, S.T.; Crino, S.; Gabbrielli, A.; Massella, A.; Topazian, M.; et al. Azathioprine Maintenance Therapy to Prevent Relapses in Autoimmune Pancreatitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggett, M.T.; Culver, E.L.; Kumar, M.; Hurst, J.M.; Rodriguez-Justo, M.; Chapman, M.H.; Johnson, G.J.; Pereira, S.P.; Chapman, R.W.; Webster, G.J.M.; et al. Type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis is associated with extrapancreatic organ failure, malignancy, and mortality in a prospective UK cohort. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugino, C.A.; Stone, J.H. IgG4-related disease: An update on pathophysiology and implications for clinical care. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbo, M.; Grados, A.; Guedj, E.; Gobert, D.; Colavolpe, C.; Zaidan, M.; Masseau, A.; Bernard, F.; Berthelot, J.M.; Morel, N.; et al. Usefulness of 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography for staging and evaluation of treatment response in IgG4-related disease: A retrospective multicenter study. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2014, 66, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berti, A.; Della-Torre, E.; Gallivanone, F.; Canevari, C.; Milani, R.; Lanzillotta, M.; Campochiaro, C.; Ramirez, G.A.; Bozzalla Cassione, E.; Bozzolo, E.; et al. Quantitative measurement of 18F-FDG PET/CT uptake reflects the expansion of circulating plasmablasts in IgG4-related disease. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2017, 56, 2084–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brito-Zeron, P.; Bosch, X.; Ramos-Casals, M.; Stone, J.H. IgG4-related disease: Advances in the diagnosis and treatment. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 30, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire, F.; Le Baleur, Y.; Rebours, V.; Vullierme, M.P.; Couvelard, A.; Voitot, H.; Sauvanet, A.; Hentic, O.; Levy, P.; Ruszniewski, P.; et al. Outcome of patients with type 1 or 2 autoimmune pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujasinovic, M.; Valente, R.; Maier, P.; von Beckerath, V.; Haas, S.L.; Arnelo, U.; Del Chiaro, M.; Kartalis, N.; Pozzi-Mucelli, R.M.; Fernandez-Moro, C.; et al. Diagnosis, treatment and long-term outcome of autoimmune pancreatitis in Sweden. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzillotta, M.; Vinge-Holmquist, O.; Overbeek, K.A.; Poulsen, J.L.; Demirci, A.F.; Macinga, P.; Lohr, M.; Rosendahl, J. PrescrAIP: A Pan-European Study on Current Treatment Regimens of Auto-Immune Pancreatitis. Front Med (Lausanne) 2020, 7, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Characteristic | IgG4-RD (n = 46) |
|---|---|
| Mean age—years | 54.2 |
| Sex—number (%) | |
| male | 31 (67.4) |
| female | 15 (32.6) |
| Smoking status—number (%) | |
| active | 13 (28.3) |
| never | 20 (43.5) |
| former | 13 (28.3) |
| Exocrine insufficiency—number (%) * | |
| yes | 11 (26.8) |
| no | 27 (65.8) |
| unclear | 3 (7.3) |
| Endocrine insufficiency—number (%) * | |
| yes | 12 (29.3) |
| no | 28 (68.3) |
| unclear | 1 (2.4) |
| Characteristic | IgG4-RD (n = 46) | |
|---|---|---|
| Extrapancreatic manifestation—number (%) | ||
| yes | 30 (65.2) | |
| no | 16 (34.8) | |
| Number of affected organs—mean (min; max) | 2 (1; 5) | |
| Steroid pulse—number (%) | ||
| yes | 34 (73.9) | |
| no | 12 (26.1) | |
| Steroid maintenance therapy—number (%) | ||
| yes | 24 (82.8) | |
| no | 5 (17.2) | |
| Relapse therapy | IgG4-RD (n = 20) | |
| Steroids + immunomodulatory therapy—number (%) | ||
| azathioprine mono | 3 (15) | |
| azathioprine followed by rituximab | 5 (25) | |
| rituximab mono | 7 (35) | |
| Steroid cycle therapy—number (%) | 5 (25) | |
| Surgery—number (%) | IgG4-RD (n = 11) | Relapse (n = 9) |
| pancreatectomy | 1 (9.1) | 0 |
| partial pancreatic resection | 6 (54.5) * | 5 (55.6) |
| partial nephrectomy | 1 (9.1) | 1 (11.1) |
| submandibulectomy | 2 (18.2) | 2 (22.2) |
| tumor resection at the pulmonary artery | 1 (9.1) | 1 (11.1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Backhus, J.; Neumann, C.; Perkhofer, L.; Schulte, L.A.; Mayer, B.; Seufferlein, T.; Müller, M.; Kleger, A. A Follow-Up Study of a European IgG4-Related Disease Cohort Treated with Rituximab. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061329
Backhus J, Neumann C, Perkhofer L, Schulte LA, Mayer B, Seufferlein T, Müller M, Kleger A. A Follow-Up Study of a European IgG4-Related Disease Cohort Treated with Rituximab. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(6):1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061329
Chicago/Turabian StyleBackhus, Johanna, Christian Neumann, Lukas Perkhofer, Lucas A Schulte, Benjamin Mayer, Thomas Seufferlein, Martin Müller, and Alexander Kleger. 2021. "A Follow-Up Study of a European IgG4-Related Disease Cohort Treated with Rituximab" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 6: 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061329
APA StyleBackhus, J., Neumann, C., Perkhofer, L., Schulte, L. A., Mayer, B., Seufferlein, T., Müller, M., & Kleger, A. (2021). A Follow-Up Study of a European IgG4-Related Disease Cohort Treated with Rituximab. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(6), 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061329







