ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: An Update
Abstract
1. Epidemiology
2. Pathogenesis
3. Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis
4. Management of Kidney Involvement in AAV
4.1. Induction of Remission
4.1.1. Glucocorticoids
4.1.2. Cyclophosphamide
4.1.3. Rituximab
4.1.4. Combination CYC and RTX
4.1.5. Complement
4.1.6. Plasma Exchange
4.1.7. Supportive Management
4.2. Maintenance of Remission
4.3. Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease
4.4. Comorbidities and Unmet Needs
Future Therapies
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohammad, A.J.; Jacobsson, L.T.; Mahr, A.D.; Sturfelt, G.; Segelmark, M. Prevalence of Wegener’s granulomatosis, microscopic polyangiitis, polyarteritis nodosa and Churg-Strauss syndrome within a defined population in southern Sweden. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.A.; Mahr, A.; Mohammad, A.J.; Gatenby, P.; Basu, N.; Flores-Suárez, L.F. Classification, epidemiology and clinical subgrouping of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, i14–i22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, A.; Cornec, D.; Crowson, C.S.; Specks, U.; Matteson, E.L. The Epidemiology of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody-Associated Vasculitis in Olmsted County, Minnesota: A Twenty-Year US Population-Based Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 2338–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cui, Z.; Long, J.Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, J.W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.H. The frequency of ANCA-associated vasculitis in a national database of hospitalized patients in China. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, A.; Ekbom, A.; Brandt, L.; Askling, J. Increasing incidence of Wegener’s granulomatosis in Sweden, 1975–2001. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 2060–2063. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, F.A.; Lanyon, P.C.; Grainge, M.J.; Shaunak, R.; Mahr, A.; Hubbard, R.B.; Hubbard, R.B.; Watts, R.A. Incidence of ANCA-associated vasculitis in a UK mixed ethnicity population. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, A.J. An update on the epidemiology of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology 2020, 59 (Suppl. 3), 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iudici, M.; Quartier, P.; Terrier, B.; Mouthon, L.; Guillevin, L.; Puéchal, X. Childhood-onset granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2016, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.A.; Mooney, J.; Skinner, J.; Scott, D.G.; Macgregor, A.J. The contrasting epidemiology of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s) and microscopic polyangiitis. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, S.E.; Watts, R.A.; Bentham, G.; Innes, N.J.; Scott, D.G.I. Are environmental factors important in primary systemic vasculitis? A case–control study. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotch, M.F.; Hoffman, G.S.; Yerg, D.E.; Kaufman, G.I.; Targonski, P.; Kaslow, R.A. The epidemiology of Wegener’s granulomatosis. Estimates of the five-year period prevalence, annual mortality, and geographic disease distribution from population-based data sources. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatenby, P.A.; Lucas, R.M.; Engelsen, O.; Ponsonby, A.-L.; Clements, M. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitides: Could geographic patterns be explained by ambient ultraviolet radiation? Arthritis Care Res. 2009, 61, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, S.; Watts, R.A.; Kobayashi, S.; Suzuki, K.; Jayne, D.R.; Scott, D.G.; Hasimoto, H.; Nunoi, H. Comparison of the epidemiology of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis between Japan and the U.K. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 1916–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, M.; Bjørneklett, R.; Hruskova, Z.; MacKinnon, B.; Poulton, C.J.; Sindelar, L.; Mohammad, A.J.; Eriksson, P.; Gesualdo, L.; Geetha, D.; et al. Proteinase-3 and myeloperoxidase serotype in relation to demographic factors and geographic distribution in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated glomerulonephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 34, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.; Hartnett, J.; Mockler, D.; Little, M.A. Environmental risk factors associated with ANCA associated vasculitis: A systematic mapping review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahr, A.; Guillevin, L.; Poissonnet, M.; Aymé, S. Prevalences of polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, Wegener’s granulomatosis, and Churg-Strauss syndrome in a French urban multiethnic population in 2000: A capture-recapture estimate. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 51, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Schmitz, J.L.; Yang, J.; Hogan, S.L.; Bunch, D.; Hu, Y.; Jennette, C.E.; Berg, E.A.; Arnett, F.C.; Jennette, J.C.; et al. DRB1*15 Allele Is a Risk Factor for PR3-ANCA Disease in African Americans. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, P.A.; Rayner, T.F.; Trivedi, S.; Holle, J.U.; Watts, R.A.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Baslund, B.; Brenchley, P.; Bruchfeld, A.; Chaudhry, A.N.; et al. Genetically Distinct Subsets within ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkel, P.A.; Xie, G.; Monach, P.A.; Ji, X.; Ciavatta, D.J.; Byun, J.; Pinder, B.D.; Zhao, A.; Zhang, J.; Tadesse, Y.; et al. Identification of Functional and Expression Polymorphisms Associated with Risk for Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody-Associated Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmattulla, C.; Mooyaart, A.L.; Van Hooven, D.; Schoones, J.W.; Bruijn, J.A.; Dekkers, O.M.; Bajema, I.M. European Vasculitis Genetics Consortium Genetic variants in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 75, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, G.; Fu, X.; Stone, J.H.; Wallwork, R.; Zhang, Y.; Choi, H.K.; Wallace, Z.S. Association of Cigarette Smoking with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, S.L.; Satterly, K.K.; Dooley, M.A.; Nachman, P.H.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J. Silica exposure in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated glomerulonephritis and lupus nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2001, 12, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Beaudreuil, S.; Lasfargues, G.; Lauériere, L.; El Ghoul, Z.; Fourquet, F.; Longuet, C.; Halimi, J.M.; Nivet, H.; Büchler, M. Occupational exposure in ANCA-positive patients: A case-control study. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Puerta, J.A.; Gedmintas, L.; Costenbader, K.H. The association between silica exposure and development of ANCA-associated vasculitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegeman, C.A.; Tervaert, J.W.C.; Sluiter, W.J.; Manson, W.L.; De Jong, P.E.; Kallenberg, C.G.M. Association of Chronic Nasal Carriage of Staphylococcus aureus and Higher Relapse Rates in Wegener Granulomatosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 120, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, J.D.; Jiang, J.-H.; Eggenhuizen, P.J.; Chua, L.L.; Van Timmeren, M.; Loh, K.L.; O’sullivan, K.M.; Gan, P.Y.; Zhong, Y.; Tsyganov, K.; et al. A plasmid-encoded peptide from Staphylococcus aureus induces anti-myeloperoxidase nephritogenic autoimmunity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, R.; Exner, M.; Brandes, R.; Ziebermayr, R.; Cunningham, D.; Alderson, C.; Davidovits, A.; Raab, I.; Jahn, R.; Ashour, O.; et al. Molecular mimicry in pauci-immune focal necrotizing glomerulonephritis. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkielman, J.D.; Lee, A.S.; Hummel, A.M.; Viss, M.A.; Jacob, G.L.; Homburger, H.A.; Peikert, T.; Hoffman, G.S.; Merkel, P.A.; Spiera, R.; et al. ANCA Are Detectable in Nearly All Patients with Active Severe Wegener’s Granulomatosis. Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, 643.e9–643.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoskar, A.A.; Suleiman, S.; Ayoub, I.; Hemminger, J.; Parikh, S.; Brodsky, S.V.; Bott, C.; Calomeni, E.; Nadasdy, G.M.; Rovin, B.; et al. Staphylococcus Infection–Associated GN—Spectrum of IgA Staining and Prevalence of ANCA in a Single-Center Cohort. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, T.; Gerken, G.; Büschenfelde, K.H.M.Z.; Mayet, W.J. Antineutrophil nuclear antibodies (ANNA) in primary biliary cirrhosis: Their prevalence and antigen specificity. Z. Gastroenterol. 1997, 35, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Afeltra, A.; Paggi, A.; De Rosa, F.G.; Manfredini, P.; Addessi, M.A.; Amoroso, A. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in autoimmune thyroid disorders. Endocr. Res. 1998, 24, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Heeringa, P.; Hu, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Aratani, Y.; Maeda, N.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies specific for myeloperoxidase cause glomerulonephritis and vasculitis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, A.; Xiao, H.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Bone marrow-derived cells are sufficient and necessary targets to mediate glomerulonephritis and vasculitis induced by anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 3355–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuligowski, M.P.; Kwan, R.Y.; Lo, C.; Wong, C.; James, W.G.; Bourges, D.; Ooi, J.D.; Abeynaike, L.D.; Hall, P.; Kitching, A.R.; et al. Antimyeloperoxidase antibodies rapidly induce alpha-4-integrin-dependent glomerular neutrophil adhesion. Blood 2009, 113, 6485–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, J.D.; Chang, J.; Hickey, M.J.; Borza, D.-B.; Fugger, L.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Kitching, A.R. The immunodominant myeloperoxidase T-cell epitope induces local cell-mediated injury in antimyeloperoxidase glomerulonephritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2615–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Krumbholz, M.; Schönermarck, U.; Back, W.; Gross, W.L.; Werb, Z.; Gröne, H.-J.; Brinkmann, V.; Jenne, D.E. Netting neutrophils in autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, R.J.; Terrell, R.S.; Charles, L.A.; Jennette, J.C. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies induce neutrophils to degranulate and produce oxygen radicals in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4115–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewert, B.H.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J. Anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies stimulate neutrophils to damage human endothelial cells. Kidney Int. 1992, 41, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajema, I.M.; Hagen, E.C.; De Heer, E.; Van Der Woude, F.J.; Bruijn, J.A. Colocalization of ANCA-antigens and fibrinoid necrosis in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 2025–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schlieben, D.J.; Korbet, S.M.; Kimura, R.E.; Schwartz, M.M.; Lewis, E.J. Pulmonary-renal syndrome in a newborn with placental transmission of ANCAs. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 45, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, L.; Cockwell, P.; Adu, D.; Savage, C.O. Neutrophil priming and apoptosis in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitis. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.R.; Witko-Sarsat, V. Proteinase 3: The odd one out that became an autoantigen. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millet, A.; Martin, K.R.; Bonnefoy, F.; Saas, P.; Mocek, J.; Alkan, M.; Terrier, B.; Kerstein, A.; Tamassia, N.; Satyanarayanan, S.K.; et al. Proteinase 3 on apoptotic cells disrupts immune silencing in autoimmune vasculitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 4107–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulahad, W.H.; Stegeman, C.A.; van der Geld, Y.M.; van der Meer, B.D.; Limburg, P.C.; Kallenberg, C.G. Functional defect of circulating regulatory CD4+ T cells in patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis in remission. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 2080–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Free, M.E.; Bunch, D.O.D.; McGregor, J.A.; Jones, B.E.; Berg, E.A.; Hogan, S.L.; Hu, Y.; Preston, G.A.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; et al. Patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis have defective Treg cell function exacerbated by the presence of a suppression-resistant effector cell population. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunch, D.O.; McGregor, J.G.; Khandoobhai, N.B.; Aybar, L.T.; Burkart, M.E.; Hu, Y.; Hogan, S.L.; Poulton, C.J.; Berg, E.A.; Falk, R.J.; et al. Decreased CD5+ B Cells in Active ANCA Vasculitis and Relapse after Rituximab. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilde, B.; Thewissen, M.; Damoiseaux, J.; Knippenberg, S.; Hilhorst, M.; Van Paassen, P.; Witzke, O.; Tervaert, J.C. Regulatory B cells in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1416–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, D.; Shida, H.; Tomaru, U.; Yoshida, M.; Nishio, S.; Atsumi, T.; Ishizu, A. Enhanced Formation and Disordered Regulation of NETs in Myeloperoxidase-ANCA–Associated Microscopic Polyangiitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, M.; Hirayama, K.; Ebihara, I.; Shimohata, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Koyama, A. Serum levels of BAFF and APRIL in myeloperoxidase anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated renal vasculitis: Association with disease activity. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2011, 118, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, N.J.; Williams, J.M.; Morgan, M.D.; Challa, A.; Gordon, J.; Pepper, R.J.; Salama, A.D.; Harper, L.; Savage, C.O.S. ANCA-stimulated neutrophils release BLyS and promote B cell survival: A clinically relevant cellular process. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 2229–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venhoff, N.; Niessen, L.; Kreuzaler, M.; Rolink, A.G.; Hässler, F.; Rizzi, M.; Voll, R.E.; Thiel, J. Reconstitution of the peripheral B lymphocyte compartment in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitides treated with rituximab for relapsing or refractory disease. Autoimmunity 2014, 47, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, G.; Chen, M.; Su, Y.; Xu, L.X.; Zhao, M.H.; Li, K.S. Serum B-cell activating factor in myeloperoxiase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies-associated vasculitis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 348, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siminovitch, K.A. PTPN22 and autoimmune disease. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 1248–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tizaoui, K.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, G.H.; Kronbichler, A.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, K.H.; Shin, J.I. Association of PTPN22 1858C/T Polymorphism with Autoimmune Diseases: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Approach. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagiello, P.; Aries, P.; Arning, L.; Wagenleiter, S.E.; Csernok, E.; Hellmich, B.; Gross, W.L.; Epplen, J.T. The PTPN22 620W allele is a risk factor for Wegener’s granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 4039–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, E.J.; Niederer, H.A.; Williams, J.; Harper, L.; Watts, R.A.; Lyons, P.A.; Smith, K.G.C. Confirmation of the genetic association of CTLA4 and PTPN22 with ANCA-associated vasculitis. BMC Med. Genet. 2009, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, P.Y.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Kitching, A.R.; Ooi, J.D. Myeloperoxidase (MPO)-specific CD4+ T cells contribute to MPO-anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) associated glomerulonephritis. Cell. Immunol. 2013, 282, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruth, A.-J.; Kitching, A.R.; Kwan, R.Y.Q.; Odobasic, D.; Ooi, J.D.K.; Timoshanko, J.R.; Hickey, M.J.; Holdsworth, S.R. Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies and Effector CD4+ Cells Play Nonredundant Roles in Anti-Myeloperoxidase Crescentic Glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Eggenhuizen, P.; O’sullivan, K.M.; Alikhan, M.A.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Ooi, J.D.; Kitching, A.R. CD8+T Cells Effect Glomerular Injury in Experimental Anti-Myeloperoxidase GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 28, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.S.; Gan, P.Y.; O’sullivan, K.M.; Hammett, M.V.; Summers, S.A.; Ooi, J.D.; Lundgren, B.A.; Boyd, R.L.; Scott, H.S.; Kitching, A.R.; et al. Thymic Deletion and Regulatory T Cells Prevent Antimyeloperoxidase GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odobasic, D.; Gan, P.-Y.; Summers, S.A.; Semple, T.J.; Muljadi, R.C.; Iwakura, Y.; Kitching, A.R.; Holdsworth, S.R. Interleukin-17A Promotes Early but Attenuates Established Disease in Crescentic Glomerulonephritis in Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, E.F.; Lyons, P.A.; Carr, E.J.; Hollis, J.L.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Willcocks, L.C.; Koukoulaki, M.; Brazma, A.; Jovanovic, V.; Kemeny, D.M.; et al. A CD8+ T cell transcription signature predicts prognosis in autoimmune disease. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulahad, W.H.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; Limburg, P.C.; Stegeman, C.A. Urinary CD4+ effector memory T cells reflect renal disease activity in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2830–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattar, K.; Bickenbach, A.; Csernok, E.; Rosseau, S.; Grandel, U.; Seeger, W.; Grimminger, F.; Sibelius, U. Wegener’s granulomatosis: Antiproteinase 3 antibodies induce monocyte cytokine and prostanoid release-role of autocrine cell activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 71, 996–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Weidner, S.; Neupert, W.; Goppelt-Struebe, M.; Rupprecht, H.D. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies induce human monocytes to produce oxygen radicals in vitro. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’sullivan, K.M.; Lo, C.Y.; Summers, S.A.; Elgass, K.D.; McMillan, P.J.; Longano, A.; Ford, S.L.; Gan, P.-Y.; Kerr, P.G.; Kitching, A.R.; et al. Renal participation of myeloperoxidase in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 1030–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilhorst, M.; Shirai, T.; Berry, G.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. T Cell–Macrophage Interactions and Granuloma Formation in Vasculitis. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.D.; Ley, K. M1 and M2 macrophages: The chicken and the egg of immunity. J. Innate Immun. 2014, 6, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; David, M.Z.; Hyjek, E.; Chang, A.; Meehan, S.M. M2 Macrophage Infiltrates in the Early Stages of ANCA-Associated Pauci-Immune Necrotizing GN. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, A.; Xiao, H.; Jennette, J.C.; Schneider, W.; Luft, F.C.; Kettritz, R. C5a receptor mediates neutrophil activation and ANCA-induced glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Dairaghi, D.J.; Powers, J.P.; Ertl, L.S.; Baumgart, T.; Wang, Y.; Seitz, L.C.; Penfold, M.E.; Gan, L.; Hu, P.; et al. C5a Receptor (CD88) Blockade Protects against MPO-ANCA GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 25, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, P.A.; Niles, J.; Jimenez, R.; Spiera, R.F.; Rovin, B.H.; Bomback, A.; Pagnoux, C.; Potarca, A.; Schall, T.J.; Bekker, P.; et al. Adjunctive Treatment with Avacopan, an Oral C5a Receptor Inhibitor, in Patients with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020, 2, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayne, D.R.; Merkel, P.A.; Schall, T.J.; Bekker, P. Avacopan for the Treatment of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, S.L.; Falk, R.J.; Chin, H.; Cai, J.; Jennette, C.E.; Jennette, J.C.; Nachman, P.H. Predictors of Relapse and Treatment Resistance in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Small-Vessel Vasculitis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 143, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, G.S.; Kerr, G.S.; Leavitt, R.Y.; Hallahan, C.W.; Lebovics, R.S.; Travis, W.D.; Rottem, M.; Fauci, A.S. Wegener Granulomatosis: An Analysis of 158 Patients. Ann. Intern. Med. 1992, 116, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinico, R.A.; Di Toma, L.; Radice, A. Renal involvement in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody associated vasculitis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berden, A.E.; Ferrario, F.; Hagen, E.C.; Jayne, D.R.; Jennette, J.C.; Joh, K.; Neumann, I.; Noël, L.-H.; Pusey, C.D.; Waldherr, R.; et al. Histopathologic Classification of ANCA-Associated Glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Daalen, E.E.; Wester Trejo, M.A.C.; Göçeroğlu, A.; Ferrario, F.; Joh, K.; Noël, L.H.; Ogawa, Y.; Wilhelmus, S.; Ball, M.J.; Hansova, E.; et al. Developments in the Histopathological Classification of ANCA-Associated Glomerulonephritis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, S.R.; Noriega, M.; Tennstedt, P.; Vettorazzi, E.; Busch, M.; Nitschke, M.; Jabs, W.J.; Özcan, F.; Wendt, R.; Hausberg, M.; et al. Development and validation of a renal risk score in ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer, H.A.; Bajema, I.M.; Van Houwelingen, H.C.; Ferrario, F.; Noël, L.-H.; Waldherr, R.; Jayne, D.R.; Rasmussen, N.; Bruijn, J.A.; Hagen, E.C. Renal histology in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Differences between diagnostic and serologic subgroups. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, X.; Tervaert, J.-W.C.; Arimura, Y.; Blockmans, D.; Flores-Suárez, L.F.; Guillevin, L.; Hellmich, B.; Jayne, D.; Jennette, J.C.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; et al. Position paper: Revised 2017 international consensus on testing of ANCAs in granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitching, A.R.; Anders, H.-J.; Basu, N.; Brouwer, E.; Gordon, J.; Jayne, D.R.; Kullman, J.; Lyons, P.A.; Merkel, P.A.; Savage, C.O.S.; et al. ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damoiseaux, J.; Csernok, E.; Rasmussen, N.; Moosig, F.; van Paassen, P.; Baslund, B.; Vermeersch, P.; Blockmans, D.; Cohen Tervaert, J.W.; Bossuyt, X. Detection of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs): A multicentre European Vasculitis Study Group (EUVAS) evaluation of the value of indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) versus antigen-specific immunoassays. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachman, P.H.; Hogan, S.L.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J. Treatment response and relapse in antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated microscopic polyangiitis and glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1996, 7, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slot, M.C.; Tervaert, J.W.; Franssen, C.F.; Stegeman, C.A. Renal survival and prognostic factors in patients with PR3-ANCA associated vasculitis with renal involvement. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhail, T.M.; Hoffman, G.S. Longterm outcome of Wegener’s granulomatosis in patients with renal disease requiring dialysis. J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, E.; Cattran, D.; Magil, A.; Greenwood, C.; Churchill, D.; Sutton, D.; Clark, W.; Morrin, P.; Posen, G.; Bernstein, K.; et al. A Prospective Randomized Trial of Plasma Exchange as Additive Therapy in Idiopathic Crescentic Glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1992, 20, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Gasim, A.; Derebail, V.K.; Chung, Y.; McGregor, J.G.; Lionaki, S.; Poulton, C.J.; Hogan, S.L.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; et al. Predictors of Treatment Outcomes in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis with Severe Kidney Failure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, D.; Manning, R.T. The use of alkylating agents in the treatment of Wegener’s granulomatosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1967, 67, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, M.; Watts, R.A.; Bajema, I.M.; Cid, M.C.; Crestani, B.; Hauser, T.; Hellmich, B.; Holle, J.U.; Laudien, M.; Little, M.A.; et al. EULAR/ERA-EDTA recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.; Merkel, P.A.; Peh, C.-A.; Szpirt, W.M.; Puéchal, X.; Fujimoto, S.; Hawley, C.M.; Khalidi, N.; Floßmann, O.; Wald, R.; et al. Plasma Exchange and Glucocorticoids in Severe ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanouzas, D.; McGregor, J.A.G.; Nightingale, P.; Salama, A.D.; Szpirt, W.M.; Basu, N.; Morgan, M.D.; Poulton, C.J.; Draibe, J.B.; Krarup, E.; et al. Intravenous pulse methylprednisolone for induction of remission in severe ANCA associated Vasculitis: A multi-center retrospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlier, C.; Henegar, C.; Launay, O.; Pagnoux, C.; Berezne, A.; Bienvenu, B.; Cohen, P.; Mouthon, L.; Guillevin, L. Risk factors for major infections in Wegener granulomatosis: Analysis of 113 patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 68, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Sada, K.E.; Otsuka, F.; Takano, M.; Toyota, N.; Sugiyama, K.; Wakabayashi, H.; Kawabata, T.; Kawabata, T. Evaluation of weekly-reduction regimen of glucocorticoids in combination with cyclophosphamide for anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis in Japanese patients. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 2999–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, J.; Harper, L. Adverse effects of therapy for ANCA-associated vasculitis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 23, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauci, A.S.; Wolff, S.M. Wegener’s granulomatosis: Studies in eighteen patients and a review of the literature. Medicine 1973, 52, 535–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauci, A.S.; Haynes, B.F.; Katz, P.; Wolff, S.M. Wegener’s granulomatosis: Prospective clinical and therapeutic experience with 85 patients for 21 years. Ann. Intern. Med. 1983, 98, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, K.; Harper, L.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Flores Suarez, L.F.; Gregorini, G.; Gross, W.L.; Luqmani, R.; Pusey, C.D.; Rasmussen, N.; Sinico, R.A.; et al. Pulse Versus Daily Oral Cyclophosphamide for Induction of Remission in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody—Associated Vasculitis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, L.; Morgan, M.D.; Walsh, M.; Hoglund, P.; Westman, K.; Flossmann, O.; Tesar, V.; Vanhille, P.; De Groot, K.; Luqmani, R.; et al. Pulse versus daily oral cyclophosphamide for induction of remission in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Long-term follow-up. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Merkel, P.A.; Spiera, R.; Seo, P.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; Clair, E.W.S.; Turkiewicz, A.; Tchao, N.K.; et al. Rituximab versus Cyclophosphamide for ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, D.; Specks, U.; Stone, J.H.; Merkel, P.A.; Seo, P.; Spiera, R.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; Clair, E.W.S.; et al. Rituximab Versus Cyclophosphamide for ANCA-Associated Vasculitis with Renal Involvement. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casal Moura, M.; Irazabal, M.V.; Eirin, A.; Zand, L.; Sethi, S.; Borah, B.J.; Winters, J.L.; Moriarty, J.P.; Cartin-Ceba, R.; Berti, A.; et al. Efficacy of Rituximab and Plasma Exchange in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis with Severe Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 2688–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.B.; Tervaert, J.W.C.; Hauser, T.; Luqmani, R.; Morgan, M.D.; Peh, C.A.; Savage, C.O.; Segelmark, M.; Tesar, V.; Van Paassen, P.; et al. Rituximab versus Cyclophosphamide in ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdoo, S.P.; Medjeral-Thomas, N.; Gopaluni, S.; Tanna, A.; Mansfield, N.; Galliford, J.; Griffith, M.; Levy, J.; Cairns, T.D.; Jayne, D.; et al. Long-term follow-up of a combined rituximab and cyclophosphamide regimen in renal anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 34, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortazar, F.B.; Muhsin, S.A.; Pendergraft, W.F., III; Wallace, Z.S.; Dunbar, C.; Laliberte, K.; Niles, J.L. Combination Therapy with Rituximab and Cyclophosphamide for Remission Induction in ANCA Vasculitis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, R.J.; McAdoo, S.P.; Moran, S.M.; Kelly, D.; Scott, J.; Hamour, S.; Burns, A.; Griffith, M.; Galliford, J.; Levy, J.B.; et al. A novel glucocorticoid-free maintenance regimen for anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Jayne, D.R.; Bruchfeld, A.N.; Harper, L.; Schaier, M.; Venning, M.C.; Hamilton, P.; Burst, V.; Grundmann, F.; Jadoul, M.; Szombati, I.; et al. Randomized Trial of C5a Receptor Inhibitor Avacopan in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2756–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, D.R.; Gaskin, G.; Rasmussen, N.; Abramowicz, D.; Ferrario, F.; Guillevin, L.; Mirapeix, E.; Savage, C.O.; Sinico, R.A.; Stegeman, C.A.; et al. Randomized Trial of Plasma Exchange or High-Dosage Methylprednisolone as Adjunctive Therapy for Severe Renal Vasculitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2180–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.; Casian, A.; Flossmann, O.; Westman, K.; Höglund, P.; Pusey, C.; Jayne, D.R. Long-term follow-up of patients with severe ANCA-associated vasculitis comparing plasma exchange to intravenous methylprednisolone treatment is unclear. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellos, I.; Michelakis, I.; Nikolopoulos, D. The role of plasma exchange in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: A meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronbichler, A.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Mayer, G. Frequency, risk factors and prophylaxis of infection in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 346–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronbichler, A.; Kerschbaum, J.; Gopaluni, S.; Tieu, J.; Alberici, F.; Jones, R.B.; Smith, R.M.; Jayne, D.R.W. Trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis prevents severe/life-threatening infections following rituximab in antineutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, D.; Rasmussen, N.; Andrassy, K.; Bacon, P.; Tervaert, J.W.C.; Dadoniené, J.; Ekstrand, A.; Gaskin, G.; Gregorini, G.; De Groot, K.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Maintenance Therapy for Vasculitis Associated with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibodies. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagnoux, C.; Mahr, A.; Hamidou, M.A.; Boffa, J.-J.; Ruivard, M.; Ducroix, J.-P.; Kyndt, X.; Lifermann, F.; Papo, T.; Lambert, M.; et al. Azathioprine or Methotrexate Maintenance for ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2790–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puéchal, X.; Pagnoux, C.; Perrodeau, É.; Hamidou, M.; Boffa, J.J.; Kyndt, X.; Papo, T.; Merrien, D.; Smail, A.; Delaval, P.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes Among Participants in the WEGENT Trial of Remission-Maintenance Therapy for Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener’s) or Microscopic Polyangiitis. Arthriti Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemstra, T.F.; Walsh, M.; Mahr, A.; Savage, C.O.; de Groot, K.; Harper, L.; Hauser, T.; Neumann, I.; Tesar, V.; Wissing, K.-M.; et al. Mycophenolate mofetil vs azathioprine for remission maintenance in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2010, 304, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillevin, L.; Pagnoux, C.; Karras, A.; Khouatra, C.; Aumaître, O.; Cohen, P.; Maurier, F.; Decaux, O.; Ninet, J.; Gobert, P.; et al. Rituximab versus Azathioprine for Maintenance in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Jayne, D.; Merkel, P.A.A. Randomized, Controlled Trial of Rituximab versus Azathioprine After Induction of Remission with Rituximab for Patients with ANCA-associated Vasculitis and Relapsing Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.M.; Jones, R.B.; Specks, U.; Bond, S.; Nodale, M.; Aljayyousi, R.; Andrews, J.; Bruchfeld, A.; Camilleri, B.; Carette, S.; et al. Rituximab as therapy to induce remission after relapse in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, P.; Terrier, B.; Perrodeau, É.; Cohen, P.; Faguer, S.; Huart, A.; Hamidou, M.; Agard, C.; Bonnotte, B.; Samson, M.; et al. Comparison of individually tailored versus fixed-schedule rituximab regimen to maintain ANCA-associated vasculitis remission: Results of a multicentre, randomised controlled, phase III trial (MAINRITSAN2). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, P.; Perrodeau, É.; Samson, M.; Bonnotte, B.; Néel, A.; Agard, C.; Huart, A.; Karras, A.; Lifermann, F.; Godmer, P.; et al. Long-Term Rituximab Use to Maintain Remission of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: A Randomized Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayne, D.; Blockmans, D.; Luqmani, R.; Moiseev, S.; Ji, B.; Green, Y.; Hall, L.; Roth, D.; Henderson, R.B.; Merkel, P.A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab and Azathioprine for Maintenance of Remission in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, J.; Doll, H.; Suppiah, R.; Flossmann, O.; Harper, L.; Höglund, P.; Jayne, D.; Mahr, A.; Westman, K.; Luqmani, R. Damage in the anca-associated vasculitides: Long-term data from the European Vasculitis Study group (EUVAS) therapeutic trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiseev, S.; Novikov, P.; Jayne, D.; Mukhin, N. End-stage renal disease in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 32, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, A.J.; Segelmark, M. A population-based study showing better renal prognosis for proteinase 3 antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated nephritis versus myeloperoxidase ANCA-associated nephritis. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionaki, S.; Hogan, S.L.; Jennette, C.E.; Hu, Y.; Hamra, J.B.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Nachman, P.H. The clinical course of ANCA small-vessel vasculitis on chronic dialysis. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, M.A.; Hassan, B.; Jacques, S.; Game, D.; Salisbury, E.; Courtney, A.E.; Brown, C.; Salama, A.D.; Harper, L. Renal transplantation in systemic vasculitis: When is it safe? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 3219–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Yu, H.J.; Zhang, W.; Ren, H.; Chen, X.N.; Shen, P.Y.; Xu, Y.-W.; Li, X.; Pan, X.-X.; Ni, L.-Y.; et al. Analyzing fatal cases of Chinese patients with primary antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies-associated renal vasculitis: A 10-year retrospective study. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2008, 31, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itabashi, M.; Takei, T.; Yabuki, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Ando, M.; Akamatsu, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Mitobe, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Mochizuki, T.; et al. Clinical outcome and prognosis of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis in Japan. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2010, 115, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseev, S.; Kronbichler, A.; Makarov, E.; Bulanov, N.; Crnogorac, M.; Direskeneli, H.; Galesic, K.; Gazel, U.; Geetha, D.; Guillevin, L.; et al. Association of venous thromboembolic events with skin, pulmonary and kidney involvement in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A multinational study. Rheumatology 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronbichler, A.; Leierer, J.; Gauckler, P.; Shin, J.I. Comorbidities in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, iii79–iii83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Fu, X.; Liao, K.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; Langford, C.A.; Merkel, P.A.; Monach, P.; Seo, P.; Specks, U.; Spiera, R.; et al. Disease Activity, Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody Type, and Lipid Levels in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Fu, X.; Harkness, T.; Stone, J.H.; Zhang, Y.; Choi, H. All-cause and cause-specific mortality in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Overall and according to ANCA type. Rheumatology 2019, 59, 2308–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortazar, F.B.; Pendergraft, W.F., III; Wenger, J.; Owens, C.T.; Laliberte, K.; Niles, J.L. Effect of Continuous B Cell Depletion with Rituximab on Pathogenic Autoantibodies and Total IgG Levels in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besada, E.; Koldingsnes, W.; Nossent, J.C. Serum immunoglobulin levels and risk factors for hypogammaglobulinaemia during long-term maintenance therapy with rituximab in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.J.; Robson, J.C.; Goodman, S.M.; Hoon, E.; Lai, L.Y.; Simon, L.S.; Harrison, E.; Neill, L.; Richards, P.; Nelsen, L.M.; et al. A Patient-reported Outcome Measure for Effect of Glucocorticoid Therapy in Adults with Inflammatory Diseases Is Needed: Report from the OMERACT 2016 Special Interest Group. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 1754–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.; Doll, H.; Suppiah, R.; Flossmann, O.; Harper, L.; Höglund, P.; Jayne, D.; Mahr, A.; Westman, K.; Luqmani, R. Glucocorticoid treatment and damage in the anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitides: Long-term data from the European Vasculitis Study Group trials. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, N.; McClean, A.; Harper, L.; Amft, E.N.; Dhaun, N.; Luqmani, R.A.; A Little, M.; Jayne, D.R.; Flossmann, O.; McLaren, J.; et al. The characterisation and determinants of quality of life in ANCA associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 73, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milman, N.; McConville, E.; Robson, J.C.; Boonen, A.; Tugwell, P.; Wells, G.A.; Chaudhuri, D.; Dawson, J.; Tomasson, G.; Ashdown, S.; et al. Updating OMERACT Core Set of Domains for ANCA-associated Vasculitis: Patient Perspective Using the International Classification of Function, Disability, and Health. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.C.; Tomasson, G.; Milman, N.; Ashdown, S.; Boonen, A.; Casey, G.C.; Cronholm, P.F.; Cuthbertson, D.; Dawson, J.; Direskeneli, H.; et al. OMERACT Endorsement of Patient-reported Outcome Instruments in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–associated Vasculitis. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, J.C.; Dawson, J.; Doll, H.; Cronholm, P.F.; Milman, N.; Kellom, K.; Ashdown, S.; Easley, E.; Gebhart, D.; Lanier, G.; et al. Validation of the ANCA-associated vasculitis patient-reported outcomes (AAV-PRO) questionnaire. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mössner, E.; Brünker, P.; Moser, S.; Püntener, U.; Schmidt, C.; Herter, S.; Grau, R.; Gerdes, C.; Nopora, A.; Van Puijenbroek, E.; et al. Increasing the efficacy of CD20 antibody therapy through the engineering of a new type II anti-CD20 antibody with enhanced direct and immune effector cell–mediated B-cell cytotoxicity. Blood 2010, 115, 4393–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.; Aroca, G.; Alvarez, A.; Fragoso-Loyo, H.; Zuta Santillan, E.; Rovin, B.; Brunetta, P.; Schindler, T.; Hassan, I.; Cascino, M.; et al. Two-Year Results from a Randomized, Controlled Study of Obinutuzumab for Proliferative Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- McClure, M.; Gopaluni, S.; Jayne, D.; Jones, R. B cell therapy in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Current and emerging treatment options. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atisha-Fregoso, Y.; Malkiel, S.; Harris, K.M.; Byron, M.; Ding, L.; Kanaparthi, S.; Barry, W.T.; Gao, W.; Ryker, K.; Tosta, P.; et al. Phase II Randomized Trial of Rituximab Plus Cyclophosphamide Followed by Belimumab for the Treatment of Lupus Nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa, E.R.; Stegeman, C.A.; Bos, N.A. Kallenberg CGM, Tervaert JWC. Differential B- and T-cell activation in Wegener’s granulomatosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 103, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Borstel, A.; Land, J.; Abdulahad, W.H.; Rutgers, A.; Stegeman, C.A.; Diepstra, A.; Heeringa, P.; Sanders, J.S. CD27+CD38hi B Cell Frequency During Remission Predicts Relapsing Disease in Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Patients. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, D.; Brink, R. The germinal center reaction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, C.A.; Monach, P.A.; Specks, U.; Seo, P.; Cuthbertson, D.; McAlear, C.A.; Ytterberg, S.R.; Hoffman, G.S.; Krischer, J.P.; Merkel, P.A.; et al. An open-label trial of abatacept (CTLA4-IG) in non-severe relapsing granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1376–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnell, J.L.; Rieder, S.A.; Ettinger, R.; Kolbeck, R. Targeting the CD40-CD40L pathway in autoimmune diseases: Humoral immunity and beyond. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 141, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corneth, O.B.J.; Wolterink, R.G.J.K.; Hendriks, R.W. BTK Signaling in B Cell Differentiation and Autoimmunity. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 393, 67–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Borstel, A.; Abdulahad, W.H.; Sanders, J.S.; Rip, J.; Neys, S.F.H.; Hendriks, R.W.; Stegeman, C.A.; Heeringa, P.; Rutgers, A.; Corneth, O.B.J. Evidence for enhanced Bruton’s tyrosine kinase activity in transitional and naïve B cells of patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 2230–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mócsai, A.; Ruland, J.; Tybulewicz, V.L.J. The SYK tyrosine kinase: A crucial player in diverse biological functions. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAdoo, S.P.; Prendecki, M.; Tanna, A.; Bhatt, T.; Bhangal, G.; McDaid, J.; Masuda, E.S.; Cook, H.T.; Tam, F.W.; Pusey, C.D. Spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition is an effective treatment for established vasculitis in a pre-clinical model. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusunoki, Y.; Nakazawa, D.; Shida, H.; Hattanda, F.; Miyoshi, A.; Masuda, S.; Nishio, S.; Tomaru, U.; Atsumi, T.; Ishizu, A. Peptidylarginine Deiminase Inhibitor Suppresses Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation and MPO-ANCA Production. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Disease | Incidence * [7] | ANCA-Positivity | PR3-ANCA | MPO-ANCA | Predominant Organ Involvement | Rate of Renal Involvement [77] | RPGN [77] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPA | 1.9–13 | ~90% | ~75% | ~20% | Nose and sinuses, lungs, kidneys, joints, eyes | ~70% | ~50% |
| EGPA | 0.8–4 | ~40% | <10% | 30–40% | Lungs, upper airways, peripheral nerves, heart, skin | ~25% | <15% |
| MPA | 1.5–16 | ~90% | ~25% | ~60% | Kidneys | >90% | ~65% |
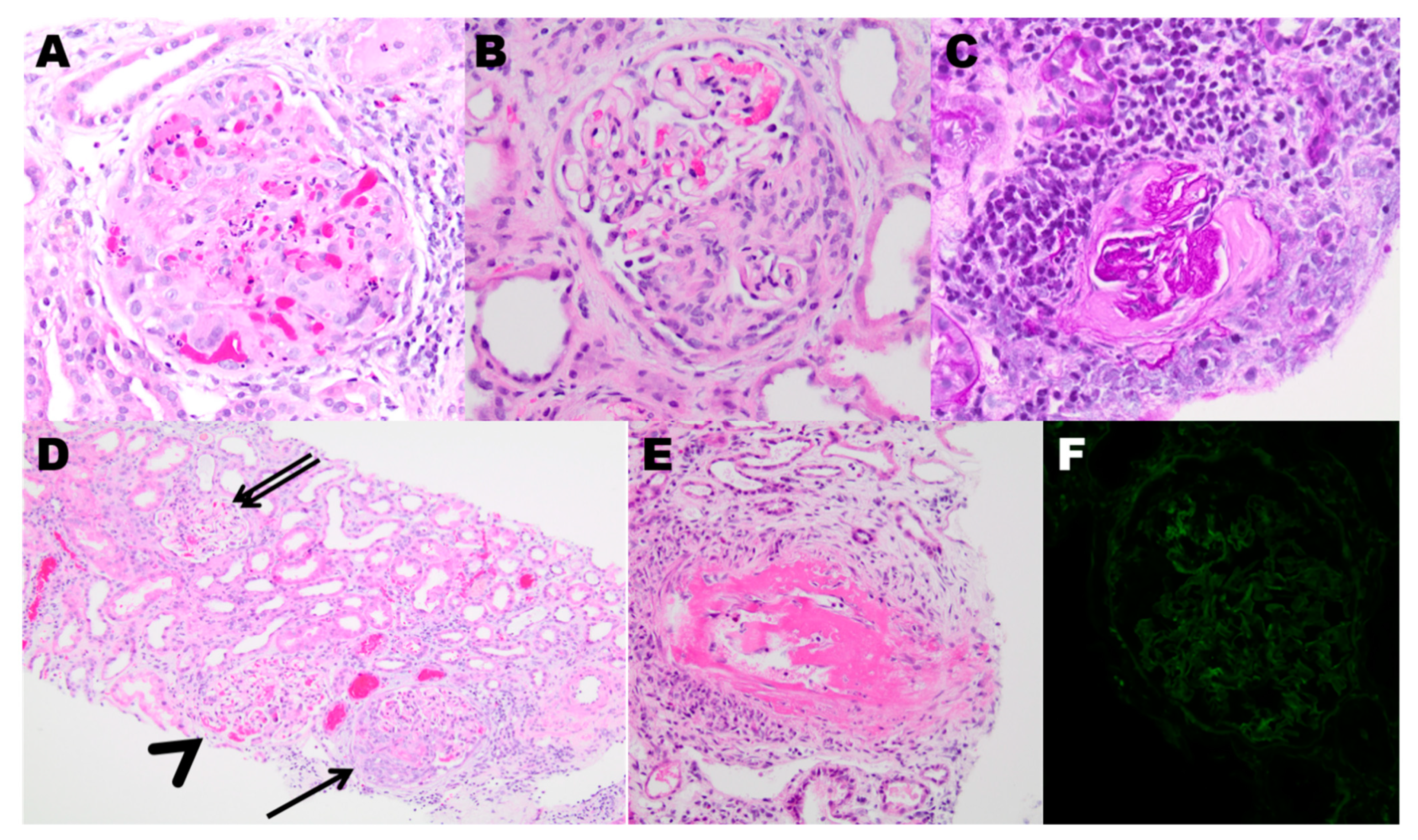
| Class | Criteria |
|---|---|
| Focal | ≥50% of glomeruli are normal |
| Crescentic | ≥50% of glomeruli have cellular crescents |
| Sclerotic | ≥50% of glomeruli are globally sclerosed |
| Mixed | Not fulfilling any of the above criteria |
| Week | Standard-Dose Arm | Reduced-Dose Arm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <50 kg | 50–75 kg | >75 kg | <50 kg | 50–75 kg | >75 kg | |
| pulse | pulse | pulse | pulse | pulse | pulse | |
| 1 | 50 | 60 | 75 | 50 | 60 | 75 |
| 2 | 50 | 60 | 75 | 25 | 30 | 40 |
| 3–4 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| 5–6 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| 7–8 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 12.5 | 15 | 20 |
| 9–10 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 10 | 12.5 | 15 |
| 11–12 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 7.5 | 10 | 12.5 |
| 13–14 | 12.5 | 15 | 20 | 6 | 7.5 | 10 |
| 15–16 | 10 | 10 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 7.5 |
| 17–18 | 10 | 10 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 7.5 |
| 19–20 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 21–22 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 23–52 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| >52 | Investigators’ local practice | |||||
| Trial Name | N, Population | Kidney Involvement | Intervention | Control | Primary Endpoint and Conclusion | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYCLOPS [99] | 149, new AAV | 100% (excluded patients with sCr > 5.7 mg/dL) | Pulse CYC (15 mg/kg) every 2–3 weeks | DO CYC (2 mg/kg/d) | No difference in time to remission | Higher risk of relapse in the pulse CYC group on long-term follow up [100] |
| MEPEX [109] | 137, AAGN and sCr > 5.7 mg/dL | 100% | PLEX | IV MP | Renal recovery at 3 months. PLEX superior | No difference in long-term outcomes [110] |
| PEXIVAS [92] | 704, new or relapsing | 98% (29% with sCr > 5.7 mg/dL) | (1) PLEX * (2) low-dose GC * | (1) no PLEX * (2) standard-dose GC * | (1) Death or ESRD at 12 months. No difference (2) No difference in efficacy | No difference in subgroup analysis for ESRD, death, alveolar hemorrhage |
| RAVE [101] | 197, new or relapsing | 52%, (excluded patients with sCr > 4 mg/dL) | RTX (375 mg/m2) for 4 weekly doses | PO CYC (2 mg/kg/d) followed by AZA | Remission (BVAS = 0) and completion of steroid taper at 6 months. No difference | RTX better for relapsing disease |
| RITUXVAS [104] | 44, new AAGN | 100% | RTX (375 mg/m2) for 4 weekly doses + IV CYC (15 mg/kg) for 2 doses | IV CYC (15 mg/kg/d) for 6–10 doses followed by AZA | Sustained remission (BVAS = 0 for 6 months). No difference | |
| ADVOCATE [73] | 331, new or relapsing | 81% | Avacopan with RTX or CYC | Prednisone with RTX or CYC | (1) Clinical remission (BVAS = 0 and no steroids # at week 26). No difference (2) Sustained remission (BVAS = 0 at weeks 26 and 52 and no steorids # at week 52). Avacopan superior |
| Trial Name | N, Population | Kidney Involvement | Induction Agent | Intervention | Control | Primary Endpoint and Conclusion | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYCAZAREM [114] | 155, new AAV | 94% (excluded those with sCr > 5.7 mg/dL) | DO CYC | AZA (2 mg/kg/d) | DO CYC (1.5 mg/kg/d) | Relapse at 18 months. No difference | MPA relapses less frequently than GPA |
| MAINRITSAN [118] | 115, new or relapsing | 70% | Pulse CYC | RTX (500 mg) days 0, 14 then every 6 months | AZA (2 mg/kg/d) for 1 year followed by a taper | Major organ relapse at 28 months. RTX superior. | Most relapses occurred after B-cell return |
| MAINRITSAN 2 [121] | 162, new or relapsing | 72% | CYC or RTX or MTX ** | Tailored * RTX (500 mg) | Scheduled RTX (500 mg) every 6 months | Relapse at 28 months. No difference | No difference in adverse events. Fewer RTX doses in tailored arm |
| MAINRITSAN 3 [122] | 97 patients from MAINRITSAN 2 | 63% | CYC or RTX or MTX ** | RTX (500 mg) every 6 months for 18 months | Placebo | Relapse-free survival at 28 months. Less relapses with extended treatment | Most relapses occurred in GPA patients |
| RITAZAREM [120] | 170, relapsed AAV | N/A | RTX | RTX (1 g) every 4 months for 20 months | AZA (2 mg/kg/d) | Time to relapse. RTX superior. | |
| IMPROVE [117] | 156, new AAV | N/A | CYC | AZA (2 mg/kg/d) for 1 year followed by a taper | MMF (2 g/d) for 1 year followed by a taper | Relapse-free survival. Relapses more common with MMF | |
| BREVAS [123] | 105, new or relapsing | N/A | CYC or RTX | Belimumab (10 mg/kg) + AZA | Placebo + AZA | Time to protocol-specified event ‡. No difference. | No relapses in patients induced with RTX and receiving belimumab |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almaani, S.; Fussner, L.A.; Brodsky, S.; Meara, A.S.; Jayne, D. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: An Update. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071446
Almaani S, Fussner LA, Brodsky S, Meara AS, Jayne D. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: An Update. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(7):1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071446
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmaani, Salem, Lynn A. Fussner, Sergey Brodsky, Alexa S. Meara, and David Jayne. 2021. "ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: An Update" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 7: 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071446
APA StyleAlmaani, S., Fussner, L. A., Brodsky, S., Meara, A. S., & Jayne, D. (2021). ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: An Update. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(7), 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071446






