Biomarkers in Fabry Disease. Implications for Clinical Diagnosis and Follow-up
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Pathogenesis
3. Markers of Fabry Disease
3.1. Clinical Markers
3.2. New Markers. Candidate Severity and Predictive Biomarkers in Fabry Disease
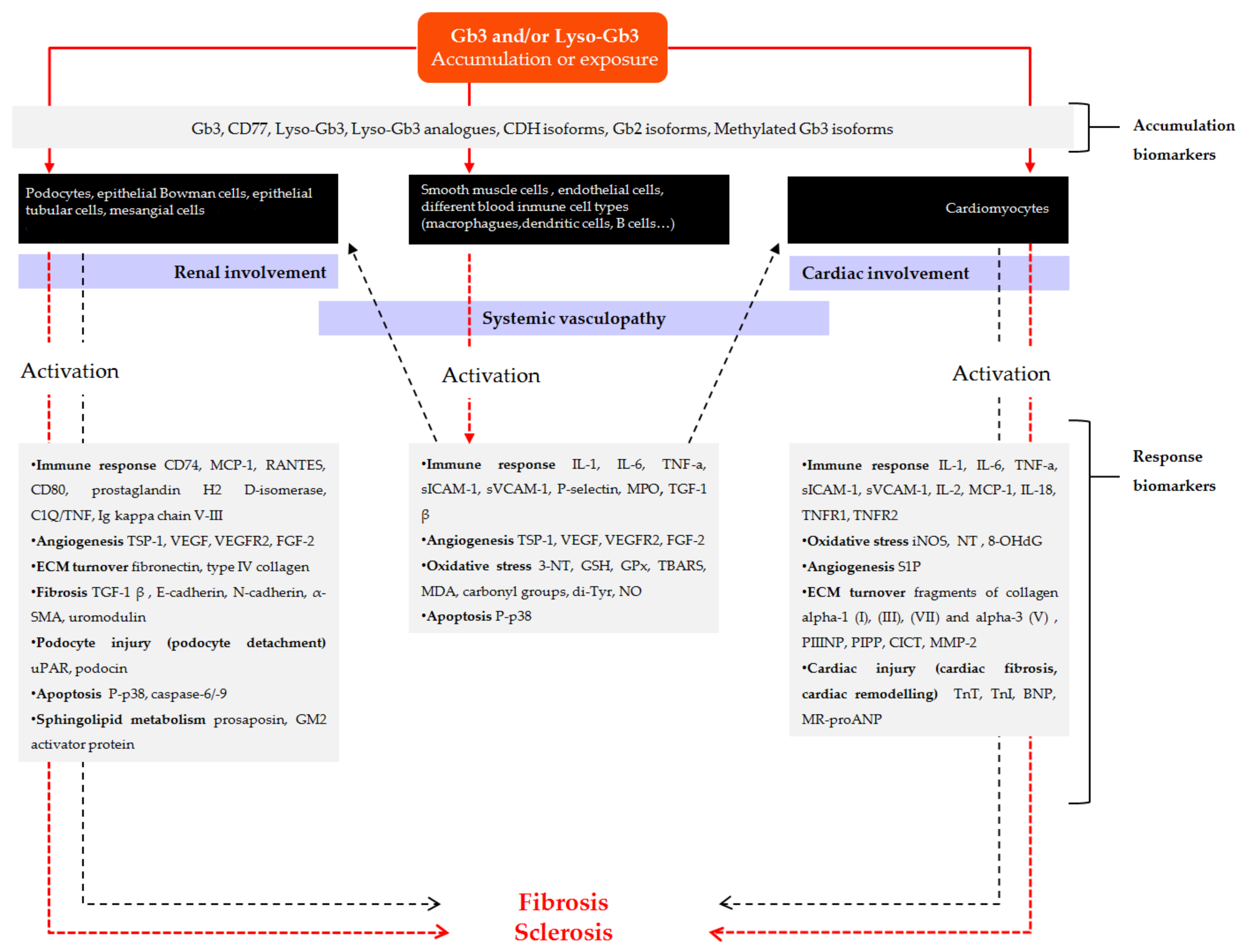
3.2.1. Accumulation Biomarkers
3.2.2. Response Biomarkers
New Biomarkers Related to Systemic Vasculopathy
New Biomarkers Related to Nephropathy
New Biomarkers Related to Cardiomyopathy
4. Future Lines of Work
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehta, A.; Hughes, D.A. Fabry Disease. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; 5 August 2002; [Updated 5 January 2017]; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993–2021. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera-González, S.; Josa-Laorden, C.; Torralba-Cabeza, M.A. Fisiopatología de la enfermedad de Fabry. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2018, 218, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidemann, F.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Politei, J.; Oliveira, J.P.; Wanner, C.; Warnock, D.G.; Ortiz, A. Fibrosis: A key feature of Fabry disease with potential therapeutic implications. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meikle, P.J.; Hopwood, J.J.; Clague, A.E.; Carey, W.F. Prevalence of lysosomal storage disorders. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1999, 281, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.; Meikle, P.J.; Hopwood, J.J. Epidemiology of lysosomal storage diseases: An overview. In Fabry Disease: Perspectives from 5 Years of FOS [Internet]; Metha, A., Beck, M., Sunder-Plassmaann, G., Eds.; Oxford PharmaGenesis: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Spada, M.; Pagliardini, S.; Yasuda, M.; Tukel, T.; Thiagarajan, G.; Sakuraba, H.; Ponzone, A.; Desnick, R.J. High incidence of later-onset Fabry disease revealed by newborn screening. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 79, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, H.C.; Chiang, C.C.; Niu, D.M.; Wang, C.H.; Kao, S.M.; Tsai, F.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Liu, H.C.; Huang, C.K.; Gao, H.J.; et al. Detecting multiple lysosomal storage diseases by tandem mass spectrometry—A national newborn screening program in Taiwan. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 431, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.Y.; Chong, K.W.; Hsu, J.H.; Yu, H.C.; Shih, C.C.; Huang, C.H.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, C.H.; Chiang, C.C.; Ho, H.J.; et al. High incidence of the cardiac variant of fabry disease revealed by newborn screening in the Taiwan Chinese population. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2009, 2, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chien, Y.H.; Lee, N.C.; Chiang, S.C.; Desnick, R.J.; Hwu, W.L. Fabry disease: Incidence of the common later-onset α-galactosidase A IVS4 + 919G→A mutation in Taiwanese newborns—Superiority of DNA-based to enzyme-based newborn screening for common mutations. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Y.; Lelis, A.; Mirocha, J.; Wilcox, W.R. Heterozygous Fabry women are not just carriers, but have a significant burden of disease and impaired quality of life. Genet. Med. 2007, 9, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowak, A.; Mechtler, T.P.; Desnick, R.J.; Kasper, D.C. Plasma LysoGb3: A useful biomarker for the diagnosis and treatment of Fabry disease heterozygotes. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 120, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, Y.; Chen, B.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.; Ren, H.; Xu, Y.; Ni, L.; Yu, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, N. Clinical significance of plasma globotriaosylsphingosine levels in chinese patients with fabry disease. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 3733–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruyama, H.; Miyata, K.; Mikame, M.; Taguchi, A.; Guili, C.; Shimura, M.; Murayama, K.; Inoue, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Sugimura, K.; et al. Effectiveness of plasma lyso-Gb3 as a biomarker for selecting high-risk patients with Fabry disease from multispecialty clinics for genetic analysis. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurberg, B.L.; Byers, H.R.; Granter, S.R.; Phelps, R.G.; Gordon, R.E.; O’Callaghan, M. Monitoring the 3-year efficacy of enzyme replacement therapy in fabry disease by repeated skin biopsies. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, W.R.; Banikazemi, M.; Guffon, N.; Waldek, S.; Lee, P.; Linthorst, G.E.; Desnick, R.J.; Germain, D.P. Long-term safety and efficacy of enzyme replacement therapy for Fabry disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 75, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eng, C.M.; Guffon, N.; Wilcox, W.R.; Germain, D.P.; Lee, P.; Waldek, S.; Caplan, L.; Linthorst, G.E.; Desnick, R.J. Safety and Efficacy of Recombinant Human α-Galactosidase A Replacement Therapy in Fabry’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thurberg, B.L.; Rennke, H.; Colvin, R.B.; Dikman, S.; Gordon, R.E.; Collins, A.B.; Desnick, R.J.; O’Callaghan, M. Globotriaosylceramide accumulation in the fabry kidney is cleared from multiple cell types after enzyme replacement therapy. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Najafian, B.; Tøndel, C.; Svarstad, E.; Sokolovkiy, A.; Smith, K.; Mauer, M. One year of enzyme replacement therapy reduces globotriaosylceramide inclusions in podocytes in Male adult patients with Fabry disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirrs, S.M.; Bichet, D.G.; Casey, R.; Clarke, J.T.R.; Lemoine, K.; Doucette, S.; West, M.L. Outcomes of patients treated through the Canadian Fabry disease initiative. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014, 111, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidemann, F.; Niemann, M.; Breunig, F.; Herrmann, S.; Beer, M.; Störk, S.; Voelker, W.; Ertl, G.; Wanner, C.; Strotmann, J. Long-term effects of enzyme replacement therapy on fabry cardiomyopathy. Evidence for a better outcome with early treatment. Circulation 2009, 119, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rombach, S.M.; Van Den Bogaard, B.; De Groot, E.; Groener, J.E.M.; Poorthuis, B.J.; Linthorst, G.E.; Van Den Born, B.J.H.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Aerts, J.M.F.G. Vascular aspects of fabry disease in relation to clinical manifestations and elevations in plasma globotriaosylsphingosine. Hypertension 2012, 60, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbey, F.; Brakch, N.; Linhart, A.; Jeanrenaud, X.; Palecek, T.; Bultas, J.; Burnier, M.; Hayoz, D. Increased carotid intima-media thickness in the absence of atherosclerotic plaques in an adult population with Fabry disease. Acta Paediatr. Int. J. Paediatr. 2006, 95, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, J.M.; Groener, J.E.; Kuiper, S.; Donker-Koopman, W.E.; Strijland, A.; Ottenhoff, R.; Van Roomen, C.; Mirzaian, M.; Wijburg, F.A.; Linthorst, G.E.; et al. Elevated globotriaosylsphingosine is a hallmark of Fabry disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2812–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rombach, S.M.; Twickler, T.B.; Aerts, J.M.F.G.; Linthorst, G.E.; Wijburg, F.A.; Hollak, C.E.M. Vasculopathy in patients with Fabry disease: Current controversies and research directions. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2010, 99, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGraba, T.; Azhar, S.; Dignat-George, F.; Brown, E.; Boutière, B.; Altarescu, G.; McCarron, R.; Schiffmann, R. Profile of endothelial and leukocyte activation in fabry patients. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 47, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.S.; Meng, X.L.; Moore, D.F.; Quirk, J.M.; Shayman, J.A.; Schiffmann, R.; Kaneski, C.R. Globotriaosylceramide induces oxidative stress and up-regulates cell adhesion molecule expression in Fabry disease endothelial cells. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2008, 95, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shu, L.; Vivekanandan-Giri, A.; Pennathur, S.; Smid, B.E.; Aerts, J.M.F.G.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Shayman, J.A. Establishing 3-nitrotyrosine as a biomarker for the vasculopathy of Fabry disease. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalliokoski, R.J.; Kalliokoski, K.K.; Penttinen, M.; Kantola, I.; Leino, A.; Viikari, J.S.; Simell, O.; Nuutila, P.; Raitakari, O.T. Structural and functional changes in peripheral vasculature of Fabry patients. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puccio, D.; Coppola, G.; Corrado, E.; Muratori, I.; Pistone, G.; Buongiorno, M.R.; Aricò, M.; Novo, S. Non invasive evaluation of endothelial function in patients with Anderson-Fabry disease. Int. Angiol. 2005, 24, 295–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kalliokoski, R.J.; Kalliokoski, K.K.; Sundell, J.; Engblom, E.; Penttinen, M.; Kantola, I.; Raitakari, O.T.; Knuuti, J.; Nuutila, P. Impaired myocardial perfusion reserve but preserved peripheral endothelial function in patients with Fabry disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2005, 28, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrow, P.P.; Krzanowski, M.; Undas, A. Reduced coronary flow reserve in Anderson-Fabry disease measured by transthoracic Doppler echocardiography. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2005, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.J.; Kaissarian, N.M.; Desch, K.C.; Kelly, R.J.; Shu, L.; Bodary, P.F.; Shayman, J.A. α-galactosidase A deficiency promotes von Willebrand factor secretion in models of Fabry disease. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tseng, W.L.; Chou, S.J.; Chiang, H.C.; Wang, M.L.; Chien, C.S.; Chen, K.H.; Leu, H.B.; Wang, C.Y.; Chang, Y.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; et al. Imbalanced production of reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial antioxidant SOD2 in fabry disease-specific human induced pluripotent stem cell-differentiated vascular endothelial cells. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, H.S.; Park, S.W.; Im, I.; Seo, D.; Yoo, H.W.; Go, H.; Kim, Y.H.; Koh, G.Y.; Lee, B.H.; Han, Y.M. Enhanced thrombospondin-1 causes dysfunction of vascular endothelial cells derived from Fabry disease-induced pluripotent stem cells. EBioMedicine 2020, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Kim, J.A.; Na, H.Y.; Cho, S.E.; Park, S.; Jung, S.C.; Suh, S.H. Globotriaosylceramide induces lysosomal degradation of endothelial K Ca3.1 in fabry disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.A.; Joo, K.Y.; Choi, S.; Choi, E.N.; Shin, J.A.; Han, K.H.; Jung, S.C.; Suh, S.H. Globotriaosylceramide leads to KCa3.1 channel dysfunction: A new insight into endothelial dysfunction in Fabry disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozenfeld, P.; Feriozzi, S. Contribution of inflammatory pathways to Fabry disease pathogenesis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 122, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauhin, W.; Lidove, O.; Masat, E.; Mingozzi, F.; Mariampillai, K.; Ziza, J.M.; Benveniste, O. Innate and adaptive immune response in fabry disease. JIMD Rep. 2015, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanova, M.M.; Changsila, E.; Iaonou, C.; Goker-Alpan, O. Impaired autophagic and mitochondrial functions are partially restored by ERT in Gaucher and Fabry diseases. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Najafian, B.; Svarstad, E.; Bostad, L.; Gubler, M.C.; Tøndel, C.; Whitley, C.; Mauer, M. Progressive podocyte injury and globotriaosylceramide (GL-3) accumulation in young patients with Fabry disease. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schermer, B.; Benzing, T. Lipid-protein interactions along the slit diaphragm of podocytes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Sanz, A.B.; Carrasco, S.; Saleem, M.A.; Mathieson, P.W.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A. Globotriaosylsphingosine actions on human glomerular podocytes: Implications for Fabry nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebau, M.C.; Braun, F.; Höpker, K.; Weitbrecht, C.; Bartels, V.; Müller, R.U.; Brodesser, S.; Saleem, M.A.; Benzing, T.; Schermer, B.; et al. Dysregulated Autophagy Contributes to Podocyte Damage in Fabry’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Najafian, B.; Tøndel, C.; Svarstad, E.; Gubler, M.C.; Oliveira, J.P.; Mauer, M. Accumulation of globotriaosylceramide in podocytes in fabry nephropathy is associated with progressive podocyte loss. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alroy, J.; Sabnis, S.; Kopp, J.B. Renal pathology in Fabry disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, S134–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenfeld, P.A.; de los Angeles Bolla, M.; Quieto, P.; Pisani, A.; Feriozzi, S.; Neuman, P.; Bondar, C. Pathogenesis of Fabry nephropathy: The pathways leading to fibrosis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2020, 129, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsley, P.S.; Ledbetter, J.A. The role of the CD28 receptor during T cell responses to antigen. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1993, 11, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorina, P.; Vergani, A.; Bassi, R.; Niewczas, M.A.; Altintas, M.M.; Pezzolesi, M.G.; D’Addio, F.; Chin, M.; Tezza, S.; Nasr, M.B.; et al. Role of podocyte B7-1 in diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1415–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Jinde, K.; Endoh, M.; Sakai, H. Clinical significance of costimulatory molecules CD80/CD86 expression in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trimarchi, H. Abatacept and Glomerular Diseases: The Open Road for the Second Signal as a New Target is Settled Down. Recent Pat. Endocr. Metab. Immune Drug Discov. 2015, 9, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goumenos, D.S.; Tsamandas, A.C.; Oldroyd, S.; Sotsiou, F.; Tsakas, S.; Petropoulou, C.; Bonikos, D.; El Nahas, A.M.; Vlachojannis, J.G. Transforming growth factor-β1 and myofibroblasts: A potential pathway towards renal scarring in human glomerular disease. Nephron 2001, 87, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; Chung, A.C.K.; Lan, H.Y. Role of the TGF-β/BMP-7/Smad pathways in renal diseases. Clin. Sci. 2013, 124, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeisberg, M.; Neilson, E.G. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.H.; Choi, E.N.; Jeon, Y.J.; Jung, S.C. Possible role of transforming growth factor-β1 and vascular endothelial growth factor in Fabry disease nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeon, Y.J.; Jung, N.; Park, J.W.; Park, H.Y.; Jung, S.C. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney tubular epithelial cells induced by globotriaosylsphingosine and globotriaosylceramide. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.M.; Labilloy, A.; Eshbach, M.L.; Roy, A.; Subramanya, A.R.; Monte, S.; Labilloy, G.; Weisz, O.A. Characterization and phosphoproteomic analysis of a human immortalized podocyte model of fabry disease generated using CRISPR/CAS9 technology. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2016, 311, F1015–F1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancini, G.B.; Morás, A.M.; Reinhardt, L.S.; Busatto, F.F.; de Moura Sperotto, N.D.; Saffi, J.; Moura, D.J.; Giugliani, R.; Vargas, C.R. Globotriaosylsphingosine induces oxidative DNA damage in cultured kidney cells. Nephrology 2017, 22, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remuzzi, G. Nephropathic nature of proteinuria. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 1999, 8, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, M.N.; Cane, P.; Florio, R.; Kavantzas, N.; Close, L.; Shah, J.; Lee, P.; Elliott, P. A detailed pathologic examination of heart tissue from three older patients with Anderson—Fabry disease on enzyme replacement therapy. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2010, 19, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.; Chien, C.S.; Chiang, H.C.; Huang, W.L.; Chou, S.J.; Chang, W.C.; Chang, Y.L.; Leu, H.B.; Chen, K.H.; Wang, K.L.; et al. Interleukin-18 deteriorates Fabry cardiomyopathy and contributes to the development of left ventricular hypertrophy in Fabry patients with GLA IVS4 + 919 G > A mutation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 87161–87179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Hanawa, H.; Jiao, S.; Hasegawa, G.; Ohno, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Suzuki, T.; Kashimura, T.; Obata, H.; Tanaka, K.; et al. Elevated Endomyocardial Biopsy Macrophage-Related Markers in Intractable Myocardial Diseases. Inflammation 2015, 38, 2288–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimenti, C.; Scopelliti, F.; Vulpis, E.; Tafani, M.; Villanova, L.; Verardo, R.; De Paulis, R.; Russo, M.A.; Frustaci, A. Increased oxidative stress contributes to cardiomyocyte dysfunction and death in patients with Fabry disease cardiomyopathy. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidemann, F.; Beer, M.; Kralewski, M.; Siwy, J.; Kampmann, C. Early detection of organ involvement in Fabry disease by biomarker assessment in conjunction with LGE cardiac MRI: Results from the SOPHIA study. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 126, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakch, N.; Dormond, O.; Bekri, S.; Golshayan, D.; Correvon, M.; Mazzolai, L.; Steinmann, B.; Barbey, F. Evidence for a role of sphingosine-1 phosphate in cardiovascular remodelling in Fabry disease. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, H.Y.; Chien, C.S.; Yarmishyn, A.A.; Chou, S.J.; Yang, Y.P.; Wang, M.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Leu, H.B.; Yu, W.C.; Chang, Y.L.; et al. Generation of GLA-Knockout Human Embryonic Stem Cell Lines to Model Autophagic Dysfunction and Exosome Secretion in Fabry Disease-Associated Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Cells 2019, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.H.; Chien, Y.; Wang, K.L.; Leu, H.B.; Hsiao, C.Y.; Lai, Y.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Chang, Y.L.; Lin, S.J.; Niu, D.M.; et al. Evaluation of Proinflammatory Prognostic Biomarkers for Fabry Cardiomyopathy With Enzyme Replacement Therapy. Can. J. Cardiol. 2016, 32, 1221.e1–1221.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.; Germain, D.P.; Desnick, R.J.; Politei, J.; Mauer, M.; Burlina, A.; Eng, C.; Hopkin, R.J.; Laney, D.; Linhart, A.; et al. Fabry disease revisited: Management and treatment recommendations for adult patients. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 123, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporeale, A.; Pieroni, M.; Pieruzzi, F.; Lusardi, P.; Pica, S.; Spada, M.; Mignani, R.; Burlina, A.; Bandera, F.; Guazzi, M.; et al. Predictors of Clinical Evolution in Prehypertrophic Fabry Disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, e008424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, P.D.; Calvin, J.; Hogg, S.; O’Driscoll, E.; Halsall, D.; Burling, K.; Maguire, G.; Wright, N.; Cox, T.M.; Meikle, P.J.; et al. Monitoring enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease—Role of urine globotriaosylceramide. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2005, 28, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffmann, R.; Waldek, S.; Benigni, A.; Auray-Blais, C. Biomarkers of Fabry disease nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombach, S.M.; Dekker, N.; Bouwman, M.G.; Linthorst, G.E.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Wijburg, F.A.; Kuiper, S.; vd Bergh Weerman, M.A.; Groener, J.E.M.; Poorthuis, B.J.; et al. Plasma globotriaosylsphingosine: Diagnostic value and relation to clinical manifestations of Fabry disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2010, 1802, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, E.; Mills, K.; Morris, P.; Vellodi, A.; Lee, P.; Waldek, S.; Winchester, B. Is globotriaosylceramide a useful biomarker in Fabry disease? Acta Paediatr. 2007, 94, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, G.; Burlina, A.P.; Kolamunnage, T.B.; Zampieri, M.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Strisciuglio, P.; Zaninotto, M.; Plebani, M.; Burlina, A.B. Diagnosis of sphingolipidoses: A new simultaneous measurement of lysosphingolipids by LC-MS/MS. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettazzoni, M.; Froissart, R.; Pagan, C.; Vanier, M.T.; Ruet, S.; Latour, P.; Guffon, N.; Fouilhoux, A.; Germain, D.P.; Levade, T.; et al. LC-MS/MS multiplex analysis of lysosphingolipids in plasma and amniotic fluid: A novel tool for the screening of sphingolipidoses and Niemann-Pick type C disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, M.; Rolfs, A.; Störk, S.; Bijnens, B.; Breunig, F.; Beer, M.; Ertl, G.; Wanner, C.; Weidemann, F. Gene mutations versus clinically relevant phenotypes lyso-gb3 defines fabry disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auray-Blais, C.; Ntwari, A.; Clarke, J.T.R.; Warnock, D.G.; Oliveira, J.P.; Young, S.P.; Millington, D.S.; Bichet, D.G.; Sirrs, S.; West, M.L.; et al. How well does urinary lyso-Gb3 function as a biomarker in Fabry disease? Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 1906–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duro, G.; Zizzo, C.; Cammarata, G.; Burlina, A.; Burlina, A.; Polo, G.; Scalia, S.; Oliveri, R.; Sciarrino, S.; Francofonte, D.; et al. Mutations in the GLA gene and LysoGb3: Is it really Anderson-Fabry disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yogasundaram, H.; Nikhanj, A.; Putko, B.N.; Boutin, M.; Jain-Ghai, S.; Khan, A.; Auray-Blais, C.; West, M.L.; Oudit, G.Y. Elevated inflammatory plasma biomarkers in patients with fabry disease: A critical link to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smid, B.E.; Van der Tol, L.; Biegstraaten, M.; Linthorst, G.E.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Poorthuis, B.J.H.M. Plasma globotriaosylsphingosine in relation to phenotypes of fabry disease. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 52, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baydakova, G.V.; Ilyushkina, A.A.; Moiseev, S.; Bychkov, I.O.; Nikitina, N.V.; Buruleva, T.A.; Zakharova, E.Y. α-Galactosidase A/lysoGb3 ratio as a potential marker for Fabry disease in females. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 501, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, A.; Mechtler, T.P.; Hornemann, T.; Gawinecka, J.; Theswet, E.; Hilz, M.J.; Kasper, D.C. Genotype, phenotype and disease severity reflected by serum LysoGb3 levels in patients with Fabry disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 123, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Breemen, M.J.; Rombach, S.M.; Dekker, N.; Poorthuis, B.J.; Linthorst, G.E.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Breunig, F.; Wanner, C.; Aerts, J.M.; Hollak, C.E. Reduction of elevated plasma globotriaosylsphingosine in patients with classic Fabry disease following enzyme replacement therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2011, 1812, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rombach, S.M.; Aerts, J.M.F.G.; Poorthuis, B.J.H.M.; Groener, J.E.M.; Donker-Koopman, W.; Hendriks, E.; Mirzaian, M.; Kuiper, S.; Wijburg, F.A.; Hollak, C.E.M.; et al. Long-Term Effect of Antibodies against Infused Alpha-Galactosidase A in Fabry Disease on Plasma and Urinary (lyso)Gb3 Reduction and Treatment Outcome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auray-Blais, C.; Boutin, M.; Gagnon, R.; Dupont, F.O.; Lavoie, P.; Clarke, J.T.R. Urinary globotriaosylsphingosine-related biomarkers for Fabry disease targeted by metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2745–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, F.O.; Gagnon, R.; Boutin, M.; Auray-Blais, C. A Metabolomic Study Reveals Novel Plasma Lyso-Gb3 Analogs As Fabry Disease Biomarkers. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manwaring, V.; Boutin, M.; Auray-Blais, C. A metabolomic study to identify new globotriaosylceramide-related biomarkers in the plasma of fabry disease patients. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9039–9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutin, M.; Auray-Blais, C. Metabolomic discovery of novel urinary galabiosylceramide∈analogs as Fabry disease biomarkers. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boutin, M.; Auray-Blais, C. Multiplex tandem mass spectrometry analysis of novel plasma lyso-Gb 3-related analogues in fabry disease. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 3476–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, P.; Boutin, M.; Auray-Blais, C. Multiplex analysis of novel urinary lyso-Gb3-related biomarkers for fabry disease by tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, S.; Auray-Blais, C.; Boutin, M.; Lavoie, P.; Nunes, J.P.; Martins, E.; Garman, S.; Oliveira, J.P. Variations in the GLA gene correlate with globotriaosylceramide and globotriaosylsphingosine analog levels in urine and plasma. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 447, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Auray-Blais, C.; Blais, C.M.; Ramaswami, U.; Boutin, M.; Germain, D.P.; Dyack, S.; Bodamer, O.; Pintos-Morell, G.; Clarke, J.T.R.; Bichet, D.G.; et al. Urinary biomarker investigation in children with Fabry disease using tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 438, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, F.J.; Baig, S.; Rambhatla, S.B.; Vijapurapu, R.; Auray-Blais, C.; Boutin, M.; Steeds, R.; Wheeldon, N.; Dawson, C.; Geberhiwot, T. The clinical utility of total concentration of urinary globotriaosylsphingosine plus its analogues in the diagnosis of Fabry disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 500, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auray-Blais, C.; Lavoie, P.; Boutin, M.; Ntwari, A.; Hsu, T.R.; Huang, C.K.; Niu, D.M. Biomarkers associated with clinical manifestations in Fabry disease patients with a late-onset cardiac variant mutation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 466, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heywood, W.E.; Doykov, I.; Spiewak, J.; Hallqvist, J.; Mills, K.; Nowak, A. Global glycosphingolipid analysis in urine and plasma of female Fabry disease patients. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 2726–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutin, M.; Menkovic, I.; Martineau, T.; Vaillancourt-Lavigueur, V.; Toupin, A.; Auray-Blais, C. Separation and Analysis of Lactosylceramide, Galabiosylceramide, and Globotriaosylceramide by LC-MS/MS in Urine of Fabry Disease Patients. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 13382–13390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abaoui, M.; Boutin, M.; Lavoie, P.; Auray-Blais, C. Tandem mass spectrometry multiplex analysis of methylated and non-methylated urinary Gb3 isoforms in Fabry disease patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 452, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaidis, T.; Relle, M.; Golbas, M.; Brochhausen, C.; Galle, P.R.; Beck, M.; Schwarting, A. Downregulation of α-galactosidase A upregulates CD77: Functional impact for Fabry nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Üçeyler, N.; Böttger, J.; Henkel, L.; Langjahr, M.; Mayer, C.; Nordbeck, P.; Wanner, C.; Sommer, C. Detection of blood Gb3 deposits as a new tool for diagnosis and therapy monitoring in patients with classic Fabry disease. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.M.; Silva, A.S.D.; Silva, R.N.D.; Monte Neto, J.T.; Nascimento, F.F.D.; Sousa, J.L.; Costa Filho, H.C.S.D.A.L.; Sales Filho, H.L.A.; Labilloy, A.; Monte, S.J.H.D. CD77 levels over enzyme replacement treatment in Fabry Disease Family (V269M). J. Bras. Nefrol. 2018, 40, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Francesco, P.N.; Mucci, J.M.; Ceci, R.; Fossati, C.A.; Rozenfeld, P.A. Fabry disease peripheral blood immune cells release inflammatory cytokines: Role of globotriaosylceramide. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2013, 109, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancini, G.B.; Vanzin, C.S.; Rodrigues, D.B.; Deon, M.; Ribas, G.S.; Barschak, A.G.; Manfredini, V.; Netto, C.B.O.; Jardim, L.B.; Giugliani, R.; et al. Globotriaosylceramide is correlated with oxidative stress and inflammation in Fabry patients treated with enzyme replacement therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaneski, C.R.; Moore, D.F.; Ries, M.; Zirzow, G.C.; Schiffmann, R. Myeloperoxidase predicts risk of vasculopathic events in hemizgygous males with Fabry disease. Neurology 2006, 67, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biancini, G.B.; Jacques, C.E.; Hammerschmidt, T.; de Souza, H.M.; Donida, B.; Deon, M.; Vairo, F.P.; Lourenço, C.M.; Giugliani, R.; Vargas, C.R. Biomolecules damage and redox status abnormalities in Fabry patients before and during enzyme replacement therapy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 461, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Carpio, D.; Sanz, A.B.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Mezzano, S.; Ortiz, A. Lyso-Gb3 activates Notch1 in human podocytes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5720–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trimarchi, H.; Canzonieri, R.; Schiel, A.; Costales-Collaguazo, C.; Politei, J.; Stern, A.; Paulero, M.; Rengel, T.; Andrews, J.; Forrester, M.; et al. Increased urinary CD80 excretion and podocyturia in Fabry disease. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trimarchi, H.; Canzonieri, R.; Schiel, A.; Politei, J.; Costales-Collaguazo, C.; Stern, A.; Paulero, M.; Rengel, T.; Valiño-Rivas, L.; Forrester, M.; et al. Expression of uPAR in Urinary Podocytes of Patients with Fabry Disease. Int. J. Nephrol. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Möller, C.C.; Altintas, M.M.; Li, J.; Schwarz, K.; Zacchigna, S.; Xie, L.; Henger, A.; Schmid, H.; Rastaldi, M.P.; et al. Modification of kidney barrier function by the urokinase receptor. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.; El Hindi, S.; Li, J.; Fornoni, A.; Goes, N.; Sageshima, J.; Maiguel, D.; Karumanchi, S.A.; Yap, H.K.; Saleem, M.; et al. Circulating urokinase receptor as a cause of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trimarchi, H.; Canzonieri, R.; Muryan, A.; Schiel, A.; Araoz, A.; Forrester, M.; Karl, A.; Lombi, F.; Andrews, J.; Pomeranz, V.; et al. Copious Podocyturia without Proteinuria and with Normal Renal Function in a Young Adult with Fabry Disease. Case Rep. Nephrol. 2015, 2015, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, B.; Scott, C.R.; Mauer, M.; Shankland, S.; Pippin, J.; Jefferson, J.A.; Wallace, E.; Warnock, D.; Najafian, B. Urinary podocyte loss is increased in patients with fabry disease and correlates with clinical severity of fabry nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trimarchi, H.; Canzonieri, R.; Schiel, A.; Politei, J.; Stern, A.; Andrews, J.; Paulero, M.; Rengel, T.; Aráoz, A.; Forrester, M.; et al. Podocyturia is significantly elevated in untreated vs. treated Fabry adult patients. J. Nephrol. 2016, 29, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimarchi, H. Podocyturia: Potential applications and current limitations. World J. Nephrol. 2017, 6, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puelles, V.G.; Bertram, J.F.; Moeller, M.J. Quantifying podocyte depletion: Theoretical and practical considerations. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 369, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuford, C.M.; Walters, J.J.; Holland, P.M.; Sreenivasan, U.; Askari, N.; Ray, K.; Grant, R.P. Absolute Protein Quantification by Mass Spectrometry: Not as Simple as Advertised. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7406–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau, T.; Boutin, M.; Côté, A.M.; Maranda, B.; Bichet, D.G.; Auray-Blais, C. Tandem mass spectrometry analysis of urinary podocalyxin and podocin in the investigation of podocyturia in women with preeclampsia and Fabry disease patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 495, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, F.; L’Imperio, V.; Marti, H.P.; Svarstad, E.; Smith, A.; Bolognesi, M.M.; Magni, F.; Pagni, F.; Pieruzzi, F. Proteomics for the study of new biomarkers in Fabry disease: State of the art. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2021, 132, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manwaring, V.; Heywood, W.E.; Clayton, R.; Lachmann, R.H.; Keutzer, J.; Hindmarsh, P.; Winchester, B.; Heales, S.; Mills, K. The identification of new biomarkers for identifying and monitoring kidney disease and their translation into a rapid mass spectrometry-based test: Evidence of presymptomatic kidney disease in pediatric fabry and type-I diabetic patients. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 2013–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtová, L.; Zima, T.; Tesař, V.; Michalová, J.; Přikryl, P.; Dostálová, G.; Linhart, A. Study of urinary proteomes in Anderson-Fabry disease. Ren. Fail. 2010, 32, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matafora, V.; Cuccurullo, M.; Beneduci, A.; Petrazzuolo, O.; Simeone, A.; Anastasio, P.; Mignani, R.; Feriozzi, S.; Pisani, A.; Comotti, C.; et al. Early markers of Fabry disease revealed by proteomics. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vylet’al, P.; Hålková, H.; Živná, M.; Berná, L.; Novák, P.; Elleder, M.; Kmoch, S. Abnormal expression and processing of uromodulin in Fabry disease reflects tubular cell storage alteration and is reversible by enzyme replacement therapy. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2008, 31, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doykov, I.D.; Heywood, W.E.; Nikolaenko, V.; Piewak, J.Å.; Hällqvist, J.; Clayton, P.T.; Mills, P.; Warnock, D.G.; Nowak, A.; Mills, K. Rapid, proteomic urine assay for monitoring progressive organ disease in Fabry disease. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 57, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, P.; Tsui, P.; Laville, M.P.; Livi, G.P.; Sarau, H.M.; Bril, A.; Berrebi-Bertrand, I. EDG1 receptor stimulation leads to cardiac hypertrophy in rat neonatal myocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 1589–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, L.C.; Mezzaroma, E.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Marchetti, C.; Carbone, S.; Abbate, A.; Toldo, S. Interleukin-18 as a therapeutic target in acute myocardial infarction and heart failure. Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.H.; Chou, Y.C.; Hsiao, C.Y.; Chien, Y.; Wang, K.L.; Lai, Y.H.; Chang, Y.L.; Niu, D.M.; Yu, W.C. Amelioration of serum 8-OHdG level by enzyme replacement therapy in patients with Fabry cardiomyopathy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, J.S.; Hughes, D.A.; Tayebjee, M.H.; MacFadyen, R.J.; Mehta, A.B.; Elliott, P.M. Extracellular matrix turnover and disease severity in Anderson-Fabry disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loso, J.; Lund, N.; Avanesov, M.; Muschol, N.; Lezius, S.; Cordts, K.; Schwedhelm, E.; Patten, M. Serum Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Fabry Associated Cardiomyopathy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, J.; Niemann, M.; Störk, S.; Frantz, S.; Beer, M.; Ertl, G.; Wanner, C.; Weidemann, F. Relation of burden of myocardial fibrosis to malignant ventricular arrhythmias and outcomes in fabry disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguiar, P.; Azevedo, O.; Pinto, R.; Marino, J.; Cardoso, C.; Sousa, N.; Cunha, D.; Hughes, D.; Soares, J.L.D. Biomarkers of myocardial fibrosis: Revealing the natural history of fibrogenesis in Fabry disease cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dass, S.; Suttie, J.J.; Piechnik, S.K.; Ferreira, V.M.; Holloway, C.J.; Banerjee, R.; Mahmod, M.; Cochlin, L.; Karamitsos, T.D.; Robson, M.D.; et al. Myocardial tissue characterization using magnetic resonance noncontrast T1 mapping in hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 5, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sado, D.M.; Maestrini, V.; Piechnik, S.K.; Banypersad, S.M.; White, S.K.; Flett, A.S.; Robson, M.D.; Neubauer, S.; Ariti, C.; Arai, A.; et al. Noncontrast myocardial T1 mapping using cardiovascular magnetic resonance for iron overload. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.M.; Piechnik, S.K.; Dall’Armellina, E.; Karamitsos, T.D.; Francis, J.M.; Ntusi, N.; Holloway, C.; Choudhury, R.P.; Kardos, A.; Robson, M.D.; et al. T1 Mapping for the diagnosis of acute myocarditis using CMR: Comparison to T2-Weighted and late gadolinium enhanced imaging. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bönner, F.; Spieker, M.; Haberkorn, S.; Jacoby, C.; Flögel, U.; Schnackenburg, B.; Horn, P.; Reinecke, P.; Neizel-Wittke, M.; Kelm, M.; et al. Myocardial T2 Mapping Increases Noninvasive Diagnostic Accuracy for Biopsy-Proven Myocarditis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 1467–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurz, P.; Luecke, C.; Eitel, I.; Föhrenbach, F.; Frank, C.; Grothoff, M.; De Waha, S.; Rommel, K.P.; Lurz, J.A.; Klingel, K.; et al. Comprehensive Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Suspected Myocarditis the MyoRacer-Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 1800–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnen, S.; Radunski, U.K.; Lund, G.K.; Kandolf, R.; Stehning, C.; Schnackenburg, B.; Adam, G.; Blankenberg, S.; Muellerleile, K. Performance of T1 and T2 Mapping Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance to Detect Active Myocarditis in Patients with Recent-Onset Heart Failure. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spieker, M.; Katsianos, E.; Gastl, M.; Behm, P.; Horn, P.; Jacoby, C.; Schnackenburg, B.; Reinecke, P.; Kelm, M.; Westenfeld, R.; et al. T2 mapping cardiovascular magnetic resonance identifies the presence of myocardial inflammation in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy as compared to endomyocardial biopsy. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 19, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roller, F.C.; Fuest, S.; Meyer, M.; Harth, S.; Gündüz, D.; Bauer, P.; Schneider, C.; Rolfs, A.; Krombach, G.A.; Tanislav, C. Assessment of Cardiac Involvement in Fabry Disease (FD) with Native T1 Mapping. RoFo 2019, 191, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nordin, S.; Kozor, R.; Bulluck, H.; Castelletti, S.; Rosmini, S.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Baig, S.; Mehta, A.; Hughes, D.; Moon, J.C. Cardiac Fabry Disease With Late Gadolinium Enhancement Is a Chronic Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1707–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappi, C.; Altiero, M.; Imbriaco, M.; Nicolai, E.; Giudice, C.A.; Aiello, M.; Diomiaiuti, C.T.; Pisani, A.; Spinelli, L.; Cuocolo, A. First experience of simultaneous PET/MRI for the early detection of cardiac involvement in patients with Anderson-Fabry disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carnicer-Cáceres, C.; Arranz-Amo, J.A.; Cea-Arestin, C.; Camprodon-Gomez, M.; Moreno-Martinez, D.; Lucas-Del-Pozo, S.; Moltó-Abad, M.; Tigri-Santiña, A.; Agraz-Pamplona, I.; Rodriguez-Palomares, J.F.; et al. Biomarkers in Fabry Disease. Implications for Clinical Diagnosis and Follow-up. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081664
Carnicer-Cáceres C, Arranz-Amo JA, Cea-Arestin C, Camprodon-Gomez M, Moreno-Martinez D, Lucas-Del-Pozo S, Moltó-Abad M, Tigri-Santiña A, Agraz-Pamplona I, Rodriguez-Palomares JF, et al. Biomarkers in Fabry Disease. Implications for Clinical Diagnosis and Follow-up. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(8):1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081664
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarnicer-Cáceres, Clara, Jose Antonio Arranz-Amo, Cristina Cea-Arestin, Maria Camprodon-Gomez, David Moreno-Martinez, Sara Lucas-Del-Pozo, Marc Moltó-Abad, Ariadna Tigri-Santiña, Irene Agraz-Pamplona, Jose F Rodriguez-Palomares, and et al. 2021. "Biomarkers in Fabry Disease. Implications for Clinical Diagnosis and Follow-up" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 8: 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081664
APA StyleCarnicer-Cáceres, C., Arranz-Amo, J. A., Cea-Arestin, C., Camprodon-Gomez, M., Moreno-Martinez, D., Lucas-Del-Pozo, S., Moltó-Abad, M., Tigri-Santiña, A., Agraz-Pamplona, I., Rodriguez-Palomares, J. F., Hernández-Vara, J., Armengol-Bellapart, M., del-Toro-Riera, M., & Pintos-Morell, G. (2021). Biomarkers in Fabry Disease. Implications for Clinical Diagnosis and Follow-up. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(8), 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081664





