Evidence Map of Cupping Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Electronic Searches and Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
2.3.1. Design
2.3.2. Population
2.3.3. Intervention
2.3.4. Outcomes
2.3.5. Timing
2.3.6. Systematic Review Selection
2.4. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Extraction
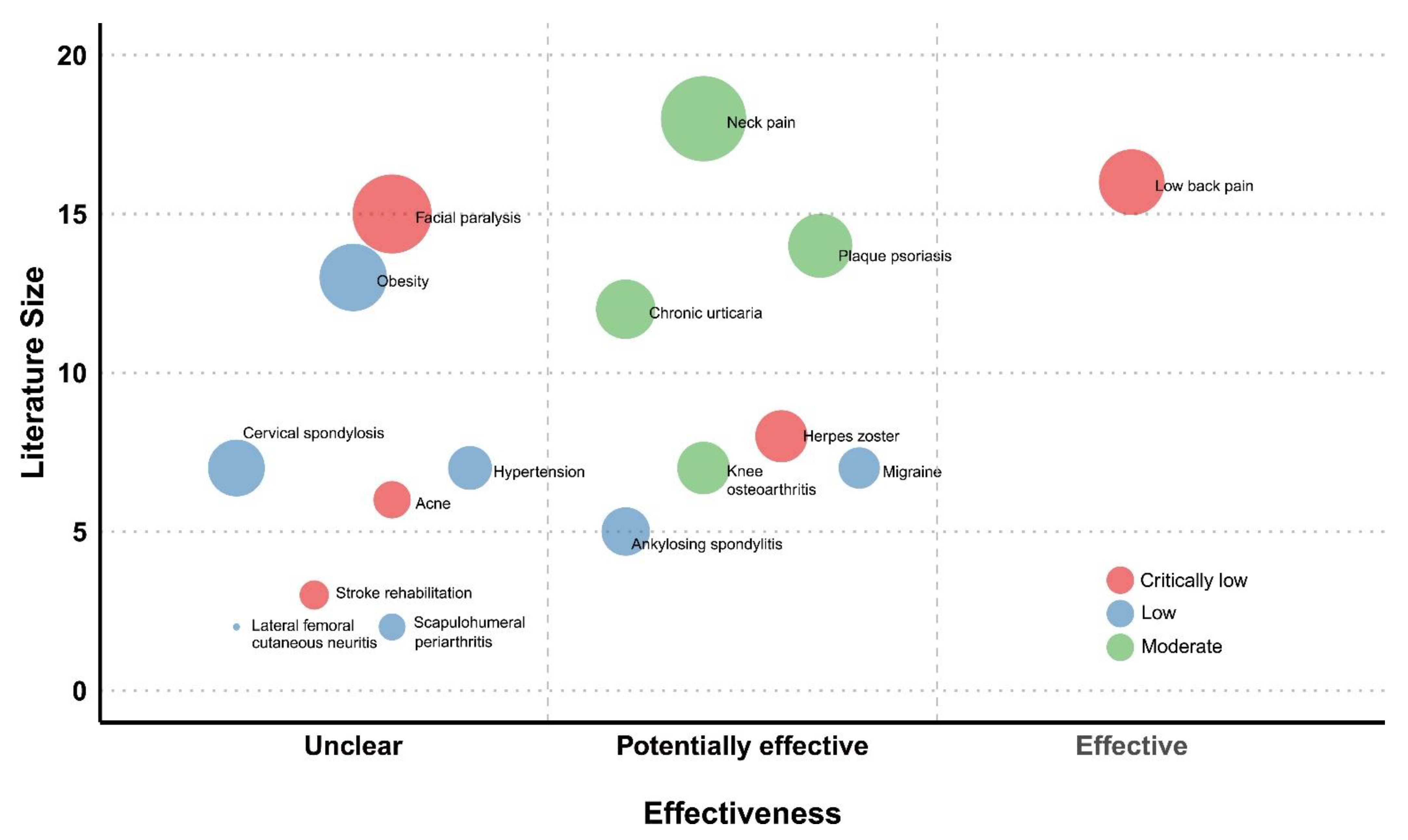
2.6. Evidence Map Presentation and Domains
- (1)
- X-axis: effect estimate
- (2)
- Y-axis: number of articles
- (3)
- Bubble size: number of participants in the total population
- (4)
- Color: strength of the findings
2.7. Narrative Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Description of Included SRs
3.1.1. Selection Diagram
3.1.2. Included Diseases
3.1.3. Intervention Components Described
3.2. Quality of the Included Systematic Reviews
3.3. Effectiveness
3.3.1. Evidence of a Positive Effect
3.3.2. Evidence of a Potentially Positive Effect
3.3.3. Evidence of Unclear
3.4. Evidence Map
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, K.C.; Chen, M.L.; Yeh, M.L.; Chen, Y.L.; Chou, P. Prevalence, pattern, and predictors of use of complementary and alternative medicine in Taiwan. Taiwan J. Public Health 2009, 28, 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Farhadi, K.; Schwebel, D.C.; Saeb, M.; Choubsaz, M.; Mohammadi, R.; Ahmadi, A. The effectiveness of wet-cupping for nonspecific low back pain in Iran: A randomized controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2009, 17, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboushanab, T.S.; AlSanad, S. Cupping Therapy: An Overview from a Modern Medicine Perspective. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2018, 11, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, M.K.; Reza, M.; Mohammad, A.; Keyvan, H.M. Wet-Cupping Is Effective on Persistent Nonspecific Low Back Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, F.J.; Schumann, S.; Cramer, H.; Hohmann, C.; Choi, K.E.; Rolke, R.; Langhorst, J.; Rampp, T.; Dobos, G.; Lauche, R. The Effects of Cupping Massage in Patients with Chronic Neck Pain—A Randomised Controlled Trial. Complement. Med. Res. 2017, 24, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teut, M.; Kaiser, S.; Ortiz, M.; Roll, S.; Binting, S.; Willich, S.N.; Brinkhaus, B. Pulsatile dry cupping in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee—A randomized controlled exploratory trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirali, I.Z. Cupping Therapy, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.S.; Kim, J.I.; Ernst, E. Is cupping an effective treatment? An overview of systematic reviews. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2011, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, C.C.; Chaves, E.C.L.; Cardoso, A.; Nogueira, D.A.; Correa, H.P.; Chianca, T.C.M. Cupping therapy and chronic back pain: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Revista Latino-Americana Enfermagem 2018, 26, e3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.R.; Kim, E.J.; Hwang, D.S.; Lee, J.; Shin, J.S.; Ha, I.H.; Lee, Y.J. Is cupping therapy effective in patients with neck pain? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e021070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Du, S.; Fish, A.; Tang, C.; Lou, Q.; Zhang, X. Wet cupping for hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2018, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.J.; Han, M.; Zhu, X.S.; Liu, J.P. An overview of systematic reviews of clinical evidence for cupping therapy. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Sci. 2015, 2, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D.; Shams-White, M.; Bright, O.J.; Parrott, J.S.; Chung, M. Creating a literature database of low-calorie sweeteners and health studies: Evidence mapping. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2016, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miake-Lye, I.M.; Hempel, S.; Shanman, R.; Shekelle, P.G. What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempel, S.; Taylor, S.L.; Solloway, M.R.; Miake-Lye, I.M.; Beroes, J.M.; Shanman, R.; Booth, M.J.; Siroka, A.M.; Shekelle, P.G. VA evidence-based synthesis program reports. In Evidence Map of Acupuncture; Department of Veterans Affairs: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, M.; Ding, X.; Zhang, J.; Kuai, L.; Ru, Y.; Sun, X.; Ma, T.; Miao, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Moving cupping therapy for plaque psoriasis: A PRISMA-compliant study of 16 randomized controlled trials. Medicine 2020, 99, e22539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.Q.; Zheng, L. Cupping therapy for treating ankylosing spondylitis: The evidence from systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2018, 32, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Q.; Guo, W.; Sun, Z.G.; Huang, Q.S.; Lee, E.Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, X.D. Cupping therapy for treating knee osteoarthritis: The evidence from systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2017, 28, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Cao, H.J.; Li, X.L.; Yang, X.Y.; Lai, B.Y.; Yang, G.Y.; Liu, J.P. Cupping therapy versus acupuncture for pain-related conditions: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials and trial sequential analysis. Chin. Med. 2017, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Zhu, C.; Liu, J. Wet cupping therapy for treatment of herpes zoster: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2010, 16, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Li, X.; Liu, J. An updated review of the efficacy of cupping therapy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Choi, T.Y.; Shin, B.C.; Han, C.H.; Ernst, E. Cupping for stroke rehabilitation: A systematic review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 294, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.H. Cupping Treatment for Migraine: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trial; Graduate School of Wonkwang University: Iksan, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.J.; Zhang, L.X.; Shi, Y.Z.; Yao, J.P.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zou, Z.H.; Zhou, S.Y.; Chen, M.L.; Li, C.X.; et al. Cupping therapy for patients with chronic urticaria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 18, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ren, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Gao, R. Efficacy and safety of acupuncture combined with cupping in the treatment of simple obesity: A meta-analysis. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Mater. World Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 3358–3366. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Bedah, A.M.N.; Elsubai, I.S.; Qureshi, N.A.; Aboushanab, T.S.; Ali, G.I.M.; El-Olemy, A.T.; Khalil, A.A.H.; Khalil, M.K.M.; Alqaed, M.S. The medical perspective of cupping therapy: Effects and mechanisms of action. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2019, 9, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolffe, T.A.M.; Whaley, P.; Halsall, C.; Rooney, A.A.; Walker, V.R. Systematic evidence maps as a novel tool to support evidence-based decision-making in chemicals policy and risk management. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| First Author (year) (Ref) Country | Condition Search Date No. of Primary Studies | Cupping Therapy | Comparator | Outcome | Overall Risk of Bias | Effect Estimates for Main Outcomes (Meta-Analysis) | Conclusion (Quoted from the Original Paper) | Overall Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moura (2018) [9] Brazil | Chronic back pain May 2018 16 RCTs | All types | -Sham -Waiting list -WM -None | Pain | High | MD −1.59 (−2.07, −1.10), p = 0.001 | …has shown positive results … | Effective |
| Kim (2018) [10] Korea | Neck pain Jan 2018 18 RCTs | All types | -Usual care -AT -Waiting list -No treatment | (1)Pain (2)Function | High | vs. no treatment (1) MD −2.42 (−3.98, −0.86), p < 0.00001 (2) MD −4.34 (−6.77, −1.19), p = 0.0005 vs. active control (1) MD −0.89 (−1.42, −0.37), p = 0.0009 (2) MD −4.36 (−8.67, −0.04), p = 0.05 | … reduce neck pain... | Potentially effective |
| Lu (2018) [11] China | Hypertension May 2018 7 RCTs | Wet cupping | -WM -AT | (1) SBP (2) DBP (3) Antihypertensive effect (4) Effective rate | High | (1) MD −2.24 (−9.13, 4.65), p = 0.52 (2) MD −2.11 (−8.85, 4.64), p = 0.54 (3) RR 1.09 (0.99, 1.20), p = 0.07 (4) RR 1.22 (1.05, 1.40), p = 0.007 | … no firm conclusions … | Unclear |
| Ma (2018) [18] China | Ankylosing spondylitis Dec 2017 5 RCTs | All types | -Sham/placebo -WM | (1) BASFI (2) BASDAI (3) ESR | High | (1) MD −16.63 (−17.75, −15.51), p < 0.00001 (2) MD −9.93 (−10.34, −9.52), p < 0.00001 (3) MD −3.96 (−4.69, −3.23), p < 0.00001 | …weak evidence … | Potentially effective |
| Li (2017) [19] China | Knee osteoarthritis Jan 2017 7 RCTs | All types | -Sham/placebo -WM | WOMAC (1) Pain (2) Stiffness (3) Physical function | High | vs. WM (1) MD −1.01 (−1.61, −0.41), p < 0.01 (2) MD −0.81 (−1.14, −0.48), p < 0.01 (3) MD −5.53 (−8.58, −2.47), p < 0.01 | …weak evidence … cupping therapy… | Potentially effective |
| Zhang (2017) [20] China | Several conditions Mar 2017 23 RCT (Cervical spondylosis, 7 RCTs; lateral femoral cutaneous neuritis, 2 RCTs; scapulohumeral periarthritis, 2 RCTs; Others, 12 RCTs) | All types | AT | Effective rate | High | Cervical spondylosis RR 1.13 (1.01, 1.26), p = 0.04 Lateral femoral cutaneous neuritis RR 1.10 (1.00, 1.22), p = 0.71 Scapulohumeral periarthritis RR 1.31 (1.15, 1.51), p = 0.84 | Cupping …safe… relieving pain. | Unclear |
| Cao (2010) [21] China | Herpes zoster Feb 2009 8 RCTs | Wet cupping | -No treatment -Placebo -WM | Effective rate | High | vs. WM RR 1.15 (1.91, 3.24), p = 0.0.005 | …appears to be effective… | Potentially effective |
| Cao (2012) [22] China | Several conditions Dec 2010 135 RCTs Herpes zoster (15 RCTs) Facial paralysis (15 RCTs) Acne (6 RCTs) Cervical spondylosis (6 RCTs) Other conditions (93 RCTs) | All types | -WM -AT | Effective rate | High | vs. WM Herpes zoster RR 2.07 (1.77, 2.43), p < 0.00001 Facial paralysis RR 1.49 (1.35, 1.65), p < 0.00001 Acne RR 2.14 (1.40, 2.65), p = 0.0003 Cervical spondylosis RR 2.07 (1.77, 2.43), p < 0.00001 | No confirm conclusion… | Unclear |
| Lee (2010a) [23] Korea | Stroke rehabilitation Mar 2010 5 studies (3 RCTs, 2 UOS) | All types | -AT | (1) Effective rate (2) VAS | High | (1) p < 0.05 (2) p = 0.004 | Insufficient… | Unclear |
| Seo (2018) [24] Korea | Migraine Sep 2016 7 RCTs | All types | -WM -AT | (1) Effective rate (2) VAS | High | vs. WM (1) RR 1.22 (1.08, 1.37), p = 0.001 (2) MD −3.29 (−8.22, 1.64), p = 0.19 Cupping + AT vs. AT (1) RR 1.05 (0.99, 1.12), p = 0.13 | …improves…effect of migraine … | Potentially effective |
| Xing (2020) [17] China | Plaque psoriasis Mar 2020 16 RCTs | Moving cupping | -Oral Chinese medicine -Placebo -WM | (1) Recovery rate (2) Recurrence rate (3) VAS | High | (1) SMD −1.22 (−1.58, −0.85), p < 0.00001 (2) RR 0.33 (0.16, 0.68), p = 0.003 (3) WMD −0.27 (–0.71, 0.17), p = 0.22 | …could be an effective… | Potentially effective |
| Xiao (2020) [25] China | Chronic urticaria May 2019 12 RCTs | All types | -AT -WM | (1) Effective rate (2) Recurrence rate | High | Wet cupping vs. WM (1) RR 1.10 (0.97, 1.25), p = 0.14 (2) RR 0.56 (0.23, 1.36), p = 0.20 Cupping + WM vs. WM (1) RR 1.18(1.01, 1.39), p = 0.03 (2) RR 0.52(0.32, 0.84), p = 0.007 | … it may enhance the efficacy | Potentially effective |
| Yang (2020) [26] China | Obesity June 2019 13 RCTs | All types | -AT -Cupping | (1) Effective rate (2) Weight (3) BMI (4) Waist circumference | High | AT + cupping vs. AT (1) OR 2.28 (1.56, 3.32), p < 0.0001 (2) SMD −0.21 (−0.36, −0.06), p = 0.007 (3) SMD −0.69 (−0.85, −0.54), p < 0.00001 (4) SMD −0.46 (−0.75, −0.17), p = 0.002 AT + cupping vs. cupping (1) OR 8.79 (4.20, 18.40), p < 0.0001 (2) SMD −0.54 (−0.79, −0.29), p < 0.001 (3) SMD −0.42 (−0.67, −0.17), p = 0.001 (4) SMD −0.46 (−0.75, −0.17), p = 0.002 | Insufficient… | Unclear |
| Study ID | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | Rating Overall Confidence * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moura (2018) [9] | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Critically low |
| Kim (2018) [10] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Moderate |
| Lu (2018) [11] | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Low |
| Ma (2018) [18] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Low |
| Li (2017) [19] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Moderate |
| Zhang (2017) [20] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Low |
| Cao (2010) [21] | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Critically low |
| Cao (2012) [22] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Critically low |
| Lee (2010a) [23] | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No-MA | No-MA | Yes | No-MA | No-MA | Yes | Critically low |
| Seo (2018) [24] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Low |
| Xing (2020) [17] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Moderate |
| Xiao (2020) [25] | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Moderate |
| Yang (2020) [26] | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Low |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, T.Y.; Ang, L.; Ku, B.; Jun, J.H.; Lee, M.S. Evidence Map of Cupping Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081750
Choi TY, Ang L, Ku B, Jun JH, Lee MS. Evidence Map of Cupping Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(8):1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081750
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Tae Young, Lin Ang, Boncho Ku, Ji Hee Jun, and Myeong Soo Lee. 2021. "Evidence Map of Cupping Therapy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 8: 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081750
APA StyleChoi, T. Y., Ang, L., Ku, B., Jun, J. H., & Lee, M. S. (2021). Evidence Map of Cupping Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(8), 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081750







