Glomerular Diseases in Diabetic Patients: Implications for Diagnosis and Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy and Secondary FSGS in Diabetics
3. IgA Nephropathy in Diabetics
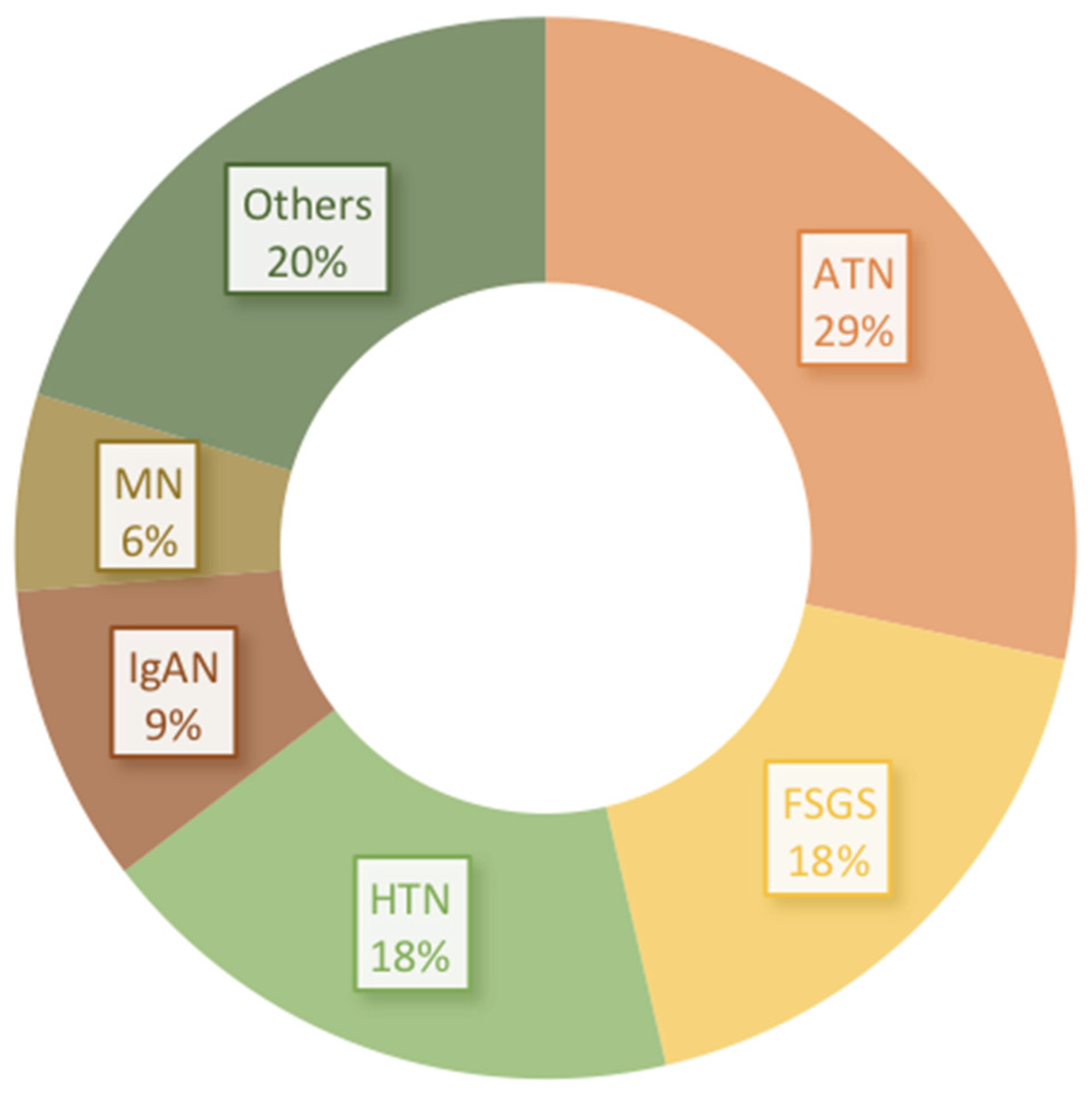
4. Other Glomerular Lesions
5. When Should We Suspect Nondiabetic Kidney Disease (NDKD) and Biopsy?
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2017; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017.
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Diabetes Work Group. KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, S1–S115. [Google Scholar]
- Umanath, K.; Lewis, J.B. Update on diabetic nephropathy: Core curriculum 2018. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, N.S.; Canetta, P.A.; Bomback, A.S. Glomerular diseases in patients with diabetes mellitus: An underappreciated epidemic. Kidney360 2020, 1, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.G.; Bomback, A.S.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Herlitz, L.C.; Stokes, M.B.; Markowitz, G.S.; D’Agati, V.D. The modern spectrum of renal biopsy findings in patients with diabetes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pham, T.T.; Sim, J.J.; Kujubu, D.A.; Liu, I.-L.A.; Kumar, V.A. Prevalence of nondiabetic renal disease in diabetic patients. Am. J. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, S.; González, E.; López-Revuelta, K.; Ibernon, M.; López, D.; Martín-Gómez, A.; Garcia-Osuna, R.; Linares, T.; Díaz, M.; Martín, N.; et al. Risk factors for non-diabetic renal disease in diabetic patients. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Huang, T.; Chen, N.; Xu, G.; Zhang, P.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, T.; Wang, L.; Xiong, M.; et al. The modern spectrum of biopsy-proven renal disease in Chinese diabetic patients-a retrospective descriptive study. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mak, S.K.; Gwi, E.; Chan, K.W.; Wong, P.N.; Lo, K.Y.; Lee, K.F.; Wong, A.K. Clinical predictors of non-diabetic renal disease in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1997, 12, 2588–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzucco, G.; Bertani, T.; Fortunato, M.; Bernardi, M.; Leutner, M.; Boldorini, R.; Monga, G. Different patterns of renal damage in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A multicentric study on 393 biopsies. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 39, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, G.; Friedman, D.J.; Ross, M.D.; Lecordier, L.; Uzureau, P.; Freedman, B.I.; Bowden, D.W.; Langefeld, C.D.; Oleksyk, T.K.; Knob, A.L.U.; et al. Association of trypanolytic ApoL1 variants with kidney disease in African Americans. Science 2010, 329, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gharavi, A.G.; Kiryluk, K.; Choi, M.; Li, Y.; Hou, P.; Xie, J.; Sanna-Cherchi, S.; Men, C.J.; Julian, B.A.; Wyatt, R.J.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentino, M.; Bolignano, D.; Tesar, V.; Pisano, A.; Van Biesen, W.; Tripepi, G.; D’Arrigo, G.; Gesualdo, L. Renal biopsy in patients with diabetes: A pooled meta-analysis of 48 studies. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caramori, M.L. Should all patients with diabetes have a kidney biopsy? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Shaughnessy, M.M.; Hogan, S.L.; Poulton, C.J.; Falk, R.J.; Singh, H.K.; Nickeleit, V.; Jennette, J.C. Temporal and demographic trends in glomerular disease epidemiology in the Southeastern United States, 1986–2015. CJASN 2017, 12, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menke, A.; Casagrande, S.S.; Geiss, L.S.; Cowie, C.C. Prevalence of and trends in diabetes among adults in the united states, 1988–2012. JAMA 2015, 314, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Non-Communicable Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Whaley-Connell, A.; Sowers, J.R. Obesity and kidney disease: From population to basic science and the search for new therapeutic targets. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, A.; Yang, P.; Cao, X.; Li, X.; Goswami, R.; Wang, Y.; Luo, T.; Liao, K.; et al. Abdominal obesity is more closely associated with diabetic kidney disease than general obesity. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, e179–e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taal, M.W. Risk factors and chronic kidney disease. In Brenner and Rector’s the Kidney, 10th ed.; Skorecki, K., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 669–692.e7. [Google Scholar]
- Grabias, B.M.; Konstantopoulos, K. The physical basis of renal fibrosis: Effects of altered hydrodynamic forces on kidney homeostasis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2014, 306, F473–F485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Rooney, M.T.; Tuttle, K.R. Diabetic kidney disease: Challenges, progress, and possibilities. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 2032–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agati, V.D.; Chagnac, A.; De Vries, A.P.; Levi, M.; Porrini, E.; Herman-Edelstein, M.; Praga, M. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: Clinical and pathologic characteristics and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choung, H.-Y.G.; Bomback, A.S.; Stokes, M.B.; Santoriello, D.; Campenot, E.S.; Batal, I.; Markowitz, G.S.; D’Agati, V.D. The spectrum of kidney biopsy findings in patients with morbid obesity. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayliss, G.; Weinrauch, L.A.; D’Elia, J.A. Pathophysiology of obesity-related renal dysfunction contributes to diabetic nephropathy. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2012, 12, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostetter, T.H. Hyperfiltration and glomerulosclerosis. Semin. Nephrol. 2003, 23, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strippoli, G.F.; Bonifati, C.; Craig, M.E.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Craig, J.C. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists for preventing the progression of diabetic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 2006, CD006257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praga, M.; Borstein, B.; Andres, A.; Arenas, J.; Oliet, A.; Montoyo, C.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rodicio, J.L. Nephrotic proteinuria without hypoalbuminemia: Clinical characteristics and response to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1991, 17, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.F.; Green, D.; Jamerson, K.; Ruilope, L.M.; Kuranoff, S.J.; Littke, T.; Viberti, G.; ASCEND Study Group. Avosentan for overt diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2010, 21, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohan, D.E.; Pritchett, Y.; Molitch, M.; Wen, S.; Garimella, T.; Audhya, P.; Andress, D.L. Addition of atrasentan to renin-angiotensin system blockade reduces albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trachtman, H.; Nelson, P.; Adler, S.; Campbell, K.N.; Chaudhuri, A.; Derebail, V.K.; Gambaro, G.; Gesualdo, L.; Gipson, D.S.; Hogan, J.; et al. Duet: A phase 2 study evaluating the efficacy and safety of sparsentan in patients with fsgs. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 2745–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komers, R.; Diva, U.; Inrig, J.K.; Loewen, A.; Trachtman, H.; Rote, W.E. Study design of the phase 3 sparsentan versus irbesartan (Duplex) study in patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavit, L.; Lifschitz, M.D.; Epstein, M. Aldosterone blockade and the mineralocorticoid receptor in the management of chronic kidney disease: Current concepts and emerging treatment paradigms. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bomback, A.; Muskala, P.; Bald, E.; Chwatko, G.; Nowicki, M. Low-dose spironolactone, added to long-term ACE inhibitor therapy, reduces blood pressure and urinary albumin excretion in obese patients with hypertensive target organ damage. Clin. Nephrol. 2009, 72, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; et al. Effect of finerenone on chronic kidney disease outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomback, A.S.; Kshirsagar, A.V.; Amamoo, M.A.; Klemmer, P.J. Change in proteinuria after adding aldosterone blockers to ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers in CKD: A systematic review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 51, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaneethan, S.D.; Nigwekar, S.U.; Sehgal, A.R.; Strippoli, G.F.M. Aldosterone antagonists for preventing the progression of chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.-F.; Mann, J.F.; McMurray, J.J.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, H.-J.; Peired, A.J.; Romagnani, P. SGLT2 inhibition requires reconsideration of fundamental paradigms in chronic kidney disease, “diabetic nephropathy”, IgA nephropathy and podocytopathies with FSGS lesions. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.C.; Stefansson, B.V.; Batiushin, M.; Bilchenko, O.; Cherney, D.Z.; Chertow, G.M.; Douthat, W.; Dwyer, J.P.; Escudero, E.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; et al. The dapagliflozin and prevention of adverse outcomes in chronic kidney disease (Dapa-ckd) trial: Baseline characteristics. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 1700–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; Dekkers, C.C.J.; Barbour, S.J.; Cattran, D.; Gafor, A.H.A.; Greasley, P.J.; Laverman, G.D.; Lim, S.K.; Di Tanna, G.L.; Reich, H.N.; et al. Effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on proteinuria in non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease (Diamond): A randomised, double-blind, crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekeran, H.; Reich, H.N.; Hladunewich, M.A.; Cattran, D.; Lovshin, J.A.; Lytvyn, Y.; Bjornstad, P.; Lai, V.; Tse, J.; Cham, L.; et al. Dapagliflozin in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: A combined human-rodent pilot study. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2018, 314, F412–F422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bays, H.E.; Weinstein, R.; Law, G.; Canovatchel, W. Canagliflozin: Effects in overweight and obese subjects without diabetes mellitus. Obesity 2014, 22, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nehus, E.J.; Khoury, J.C.; Inge, T.H.; Xiao, N.; Jenkins, T.M.; Moxey-Mims, M.M.; Mitsnefes, M.M. Kidney outcomes three years after bariatric surgery in severely obese adolescents. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.C.; Toto, R.D.; Stefansson, B.V.; Jongs, N.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; McMurray, J.J.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Correa-Rotter, R.; et al. A pre-specified analysis of the DAPA-CKD trial indicates effects of dapagliflozin on major adverse kidney events in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, H.N.; Troyanov, S.; Scholey, J.W.; Cattran, D.C. Remission of proteinuria improves prognosis in IgA nephropathy. JASN 2007, 18, 3177–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauen, T.; Eitner, F.; Fitzner, C.; Sommerer, C.; Zeier, M.; Otte, B.; Panzer, U.; Peters, H.; Benck, U.; Mertens, P.R.; et al. Intensive supportive care plus immunosuppression in IgA nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Wong, M.G.; Jardine, M.J.; Hladunewich, M.; Jha, V.; Monaghan, H.; Zhao, M.; Barbour, S.; Reich, H.; et al. Effect of oral methylprednisolone on clinical outcomes in patients with IgA nephropathy: The testing randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fervenza, F.C.; Appel, G.B.; Barbour, S.J.; Rovin, B.H.; Lafayette, R.A.; Aslam, N.; Jefferson, J.A.; Gipson, P.E.; Rizk, D.V.; Sedor, J.R.; et al. Rituximab or cyclosporine in the treatment of membranous nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J. Non-diabetic renal disease (Ndrd) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (Type 2 dm). J. Assoc. Physicians India 2013, 61, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.I.; Park, J.T.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, S.J.; Oh, H.J.; Yoo, D.E.; Han, S.H.; Yoo, T.-H.; Kang, S.-W. Renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes with or without coexisting non-diabetic renal disease. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 92, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Xia, X.; Wu, X.F.; Yu, X.Q.; Huang, F.X. Diabetic retinopathy in predicting diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal disease: A meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghavi, S.F.; Roark, T.; Zelnick, L.R.; Najafian, B.; Andeen, N.K.; Alpers, C.E.; Pichler, R.; Ayers, E.; de Boer, I.H. Histopathologic and clinical features in patients with diabetes and kidney disease. Kidney360 2020, 1, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, A.; Shikata, K.; Matsuda, M.; Usui, H.; Okada, S.; Ogawa, D.; Wada, J.; Makino, H. Clinical features of non-diabetic renal diseases in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2005, 69, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Looker, H.C.; Mauer, M.; Nelson, R.G. Role of kidney biopsies for biomarker discovery in diabetic kidney disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, J.J.; Owen, J.G.; Blady, S.J.; Almaani, S.; Avasare, R.S.; Bansal, S.; Lenz, O.; Luciano, R.L.; Parikh, S.V.; Ross, M.J.; et al. The feasibility and safety of obtaining research kidney biopsy cores in patients with diabetes: An interim analysis of the trident study. CJASN 2020, 15, 1024–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliva-Damaso, N.; Mora-Gutiérrez, J.M.; Bomback, A.S. Glomerular Diseases in Diabetic Patients: Implications for Diagnosis and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091855
Oliva-Damaso N, Mora-Gutiérrez JM, Bomback AS. Glomerular Diseases in Diabetic Patients: Implications for Diagnosis and Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(9):1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091855
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliva-Damaso, Nestor, José María Mora-Gutiérrez, and Andrew S. Bomback. 2021. "Glomerular Diseases in Diabetic Patients: Implications for Diagnosis and Management" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 9: 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091855
APA StyleOliva-Damaso, N., Mora-Gutiérrez, J. M., & Bomback, A. S. (2021). Glomerular Diseases in Diabetic Patients: Implications for Diagnosis and Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(9), 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091855





