Clinical, Laboratory and Histological Features of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Related Noninflammatory Bullous Pemphigoid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. ELISA
2.3. Evaluation of Clinical Characteristics of BP
2.4. Peripheral Eosinophilia
2.5. Periblister Eosinophilic Infiltration
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data of the Study Patients
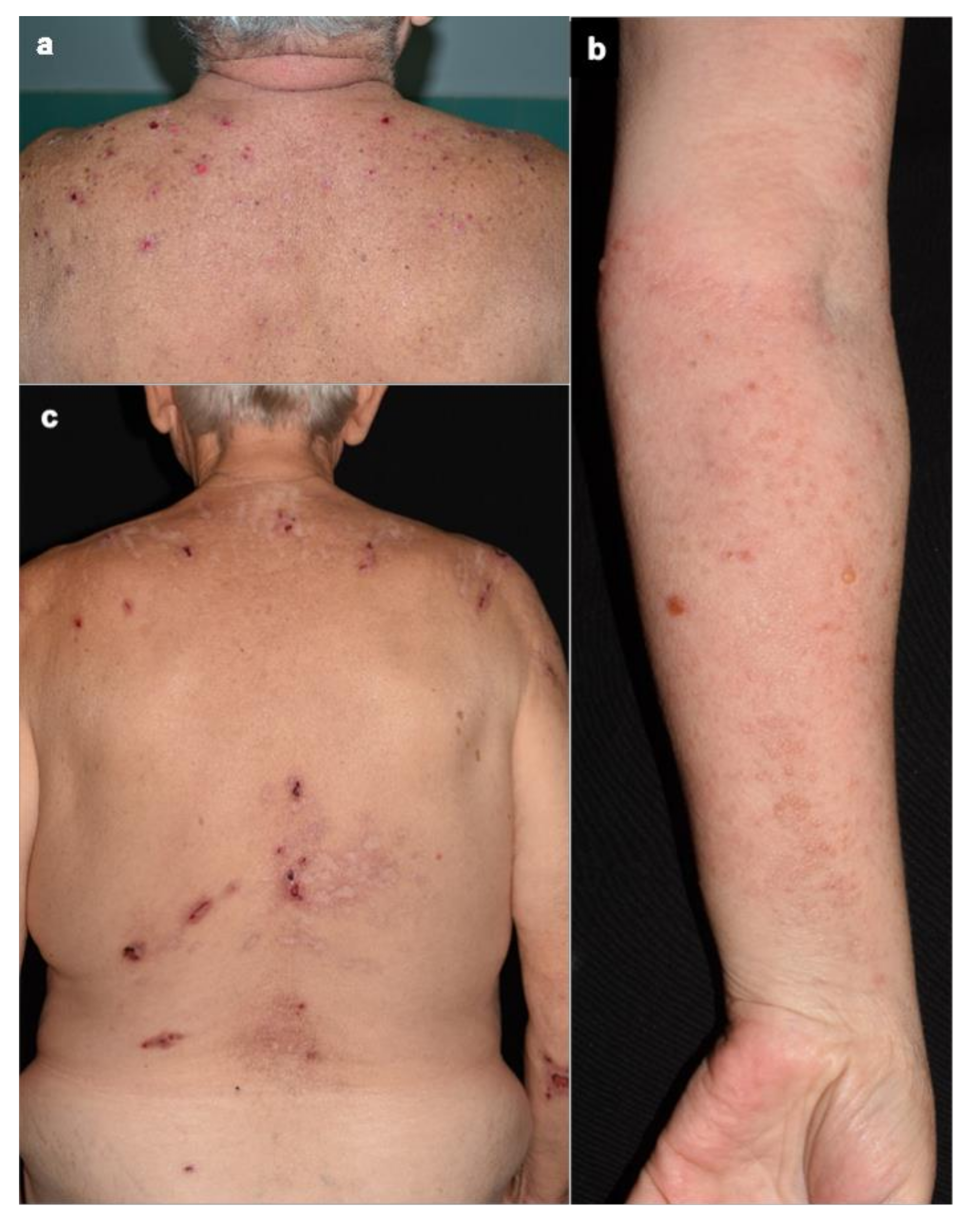
3.2. Clinical Characteristics
3.3. Eosinophilia in DPP4i and nonDPP4i-BP Patients
3.4. Periblister Tissue Eosinophilia
3.5. Immunopathological Findings
3.6. ELISA Results in nonDPP4i and DPP4i Patients
3.7. Patients’ Outcomes in DPP4i Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kridin, K.; Ludwig, R.J. The Growing Incidence of Bullous Pemphigoid: Overview and Potential Explanations. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, E.; Spindler, V.; Eming, R.; Amagai, M.; Antonicelli, F.; Baines, J.F.; Belheouane, M.; Bernard, P.; Borradori, L.; Caproni, M.; et al. Meeting Report of the Pathogenesis of Pemphigus and Pemphigoid Meeting in Munich, September 2016. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernard, P.; Antonicelli, F. Bullous pemphigoid: A review of its diagnosis, associations and treatment. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2017, 18, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, S.M.; Smeeth, L.; Hubbard, R.; Fleming, K.M.; Smith, C.J.P.; West, J. Bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus vulgaris—Incidence and mortality in the UK: Population based cohort study. BMJ 2008, 337, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hübner, F.; Recke, A.; Zillikens, D.; Linder, R.; Schmidt, E. Prevalence and age distribution of pemphigus and pemphigoid diseases in Germany. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 2495–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernard, P.; Vaillant, L.; Labeille, B.; Bedane, C.; Arbeille, B.; Denoeux, J.P.; Lorette, G.; Bonnetblanc, J.M.; Prost, C. Incidence and distribution of subepidermal autoimmune bullous skin diseases in three French regions. Bullous Diseases French Study Group. Arch. Dermatol. 1995, 131, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joly, P.; Baricault, S.; Sparsa, A.; Bernard, P.; Bédane, C.; Duvert-Lehembre, S.; Courville, P.; Bravard, P.; Rémond, B.; Doffoel-Hantz, V.; et al. Incidence and mortality of bullous pemphigoid in France. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Försti, A.K.; Jokelainen, J.; Timonen, M.; Tasanen, K. Increasing incidence of bullous pemphigoid in Northern Finland: A retrospective database study in Oulu University Hospital. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 1223–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravani, A.; Gaitanis, G.; Tsironi, T.; Tigas, S.; Bassukas, I.D. Changing prevalence of diabetes mellitus in bullous pemphigoid: It is the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, e438–e439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fania, L.; Di Zenzo, G.; Didona, B.; Pilla, M.A.; Sobrino, L.; Panebianco, A.; Mazzanti, C.; Abeni, D. Increased prevalence of diabetes mellitus in bullous pemphigoid patients during the last decade. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, e153–e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, Y.; Shimauchi, R.; Nishibori, N.; Kawashima, K.; Oshitani, S.; Fujiya, A.; Shibata, T.; Ohashi, N.; Izumi, K.; Nishie, W.; et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors-associated bullous pemphigoid: A retrospective study of 168 pemphigoid and 9304 diabetes mellitus patients. J. Diabetes. Investig. 2019, 10, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fania, L.; Di Zenzo, G.; Mazzanti, C.; Abeni, D. Commentary on ‘Changing prevalence of diabetes mellitus in bullous pemphigoid: It is the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors’. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, e439–e440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.; Aranburu, M.A.; Palacios-Zabalza, I.; Lertxundi, U.; Aguirre, C. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitors induced bullous pemphigoid: A case report and analysis of cases reported in the European pharmacovigilance database. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2016, 41, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, J.; Moulis, G.; Bennani, I.; Auffret, M.; Coupe, P.; Babai, S.; Hillaire-Buys, D.; Micallef, J.; Gautier, S. French Association of Regional PharmacoVigilance Centres. Bullous pemphigoid and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors: A case-noncase study in the French Pharmacovigilance Database. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Shirakawa, J.; Konishi, H.; Sagawa, N.; Terauchi, Y. Bullous Pemphigoid and Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors: A Disproportionality Analysis Based on the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report Database. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, e130–e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benzaquen, M.; Borradori, L.; Berbis, P.; Cazzaniga, S.; Valero, R.; Richard, M.A.; Feldmeyer, L. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors, a risk factor for bullous pemphigoid: Retrospective multicenter case-control study from France and Switzerland. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skandalis, K.; Spirova, M.; Gaitanis, G.; Tsartsarakis, A.; Bassukas, I.D. Drug-induced bullous pemphigoid in diabetes mellitus patients receiving dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitors plus metformin. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, C.; Buclin, T.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Cazzaniga, S.; Borradori, L.; Gilliet, M.; Feldmeyer, L. Use of Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitors and Bullous Pemphigoid. Dermatology 2017, 233, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kridin, K.; Cohen, A.D. Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitor-associated bullous pemphigoid: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, J.; Jacobsoone, A.; Coupe, P.; Auffret, M.; Babai, S.; Hillaire-Buys, D.; Jean-Pastor, M.J.; Vonarx, M.; Vermersch, A.; Tronquoy, A.F.; et al. Bullous pemphigoid induced by vildagliptin: A report of three cases. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 29, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsatsi, A.; Kyriakou, A.; Meltzanidou, P.; Trigoni, A.; Lamprou, F.; Kokolios, M.; Giannakou, A. Bullous pemphigoid in patients with DDP-4 inhibitors at the onset of disease: Does this differ from common bullous pemphigoid? Eur. J. Dermatol. 2018, 28, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.G.; Lee, H.J.; Yoon, M.S.; Kim, D.H. Association of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitor Use with Risk of Bullous Pemphigoid in Patients with Diabetes. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kridin, K.; Bergman, R. Association of Bullous Pemphigoid with Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Diabetes: Estimating the Risk of the New Agents and Characterizing the Patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaquevent, M.; Tétart, F.; Fardet LIngen-Housz-Oro, S.; Valeyrie-Allanore, L.; Bernard, P.; Hebert, V.; Roussel, A.; Avenel-Audran, M.; Chaby, G.; D’incan, M. Higher frequency of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor intake in bullous pemphigoid patients than in the French general population. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Izumi, K.; Nishie, W.; Mai, Y.; Wada, M.; Natsuga, K.; Ujiie, H.; Iwata, H.; Yamagami, J.; Shimizu, H. Autoantibody Profile Differentiates between Inflammatory and Noninflammatory Bullous Pemphigoid. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 2201–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horikawa, H.; Kurihara, Y.; Funakoshi, T.; Umegaki-Arao, N.; Takahashi, H.; Kubo, A.; Tanikawa, A.; Kodani, N.; Minami, Y.; Meguro, S.; et al. Unique clinical and serological features of bullous pemphigoid associated with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, 1462–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chijiwa, C.; Takeoka, S.; Kamata, M.; Tateishi, M.; Fukaya, S.; Hayashi, K.; Fukuyasu, A.; Tanaka, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Ohnishi, T.; et al. Decrease in eosinophils infiltrating into the skin of patients with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor-related bullous pemphigoid. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.; Nishie, W.; Izumi, K.; Yoshimoto, N.; Morita, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Toyonaga, E.; Ujiie, H.; Iwata, H.; Fujita, Y.; et al. Detection of anti-BP180 NC16A autoantibodies after the onset of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor-associated bullous pemphigoid: A report of three patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 790–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakama, K.; Koga, H.; Ishii, N.; Ohata, C.; Hashimoto, T.; Nakama, T. Clinical and Immunological Profiles of 14 Patients with Bullous Pemphigoid without IgG Autoantibodies to the BP180 NC16A Domain. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Díez, I.; Ivars-Lleó, M.; López-Aventín, D.; Ishii, N.; Hashimoto, T.; Iranzo, P.; Pujol, R.M.; España, A.; Herrero-Gonzalez, J.E. Bullous pemphigoid induced by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Eight cases with clinical and immunological characterization. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshiji, S.; Murakami, T.; Harashima, S.I.; Ko, R.; Kashima, R.; Yabe, D.; Ogura, M.; Doi, K.; Inagaki, N. Bullous pemphigoid associated with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: A report of five cases. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridin, K. Peripheral eosinophilia in bullous pemphigoid: Prevalence and influence on the clinical manifestation. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, D.F.; Daniel, B.S.; Joly, P.; Borradori, L.; Amagai, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Caux, F.; Marinovic, B.; Sinha, A.A.; Hertl, M.; et al. Definitions and outcome measures for bullous pemphigoid: Recommendations by an international panel of experts. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 66, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varpuluoma, O.; Försti, A.K.; Jokelainen, J.; Turpeinen, M.; Timonen, M.; Tasanen, K.; Huilaja, L. Oral diabetes medications other than dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors are not associated with bullous pemphigoid: A Finnish nationwide case-control study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 79, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varpuluoma, O.; Försti, A.K.; Jokelainen, J.; Turpeinen, M.; Timonen, M.; Huilaja, L.; Tasanen, K. Vildagliptin significantly increases the risk of bullous pemphigoid: A Finnish Nationwide Registry Study. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1659–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jha, A.; Misra, A.; Gupta, R.; Ghosh, A.; Tyagi, K.; Dutta, K.; Arora, B.; Durani, S. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors linked bullous pemphigoid in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A series of 13 cases. Diabetes Metab. Syndr 2020, 14, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magdaleno-Tapial, J.; Valenzuela-Oñate, C.; Esteban Hurtado, Á.; Ortiz-Salvador, J.M.; Subiabre-Ferrer, D.; Ferrer-Guillén, B.; von der Weth, M.G.; García-Legaz Martínez, M.; Martínez-Domenech, Á.; Hernández-Bel, P.; et al. Association between Bullous Pemphigoid and Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2020, 111, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, R.; Fayad, A.M.; Stephan, F.; Obeid, G.; Tomb, R. Bullous Pemphigoid Associated with Linagliptin Treatment. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sütő, G.; Molnár, G.A.; Rokszin, G.; Fábián, I.; Kiss, Z.; Szekanecz, Z.; Poór, G.; Jermendy, G.; Kempler, P.; Wittmann, I. Risk of morbidity and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor and/or dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor: A nationwide study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e001765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishie, W. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor-associated bullous pemphigoid: A recently recognized autoimmune blistering disease with unique clinical, immunological and genetic characteristics. Immunol. Med. 2019, 42, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridin, K.; Bergman, R. Assessment of the Prevalence of Mucosal Involvement in Bullous Pemphigoid. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukvić Mokos, Z.; Petković, M.; Balić, A.; Marinović, B. The association between clinical and laboratory findings of bullous pemphigoid and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in the elderly: A retrospective study. Croat. Med. J. 2020, 61, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridin, K. Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors (DPP4i)-associated bullous pemphigoid: Estimating the clinical profile and exploring intraclass differences. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, P.; Venot, J.; Constant, F.; Bonnetblanc, J.M. Blood eosinophilia as a severity marker for bullous pemphigoid. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1987, 16, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messingham, K.N.; Holahan, H.M.; Frydman, A.S.; Fullenkamp, C.; Srikantha, R.; Fairley, J.A. Human eosinophils express the high affinity IgE receptor, FcεRI, in bullous pemphigoid. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fania, L.; Salemme, A.; Provini, A.; Pagnanelli, G.; Collina, M.C.; Abeni, D.; Didona, B.; Di Zenzo, G.; Mazzanti, C. Detection and characterization of IgG, IgE, and IgA autoantibodies in patients with bullous pemphigoid associated with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takama, H.; Yoshida, M.; Izumi, K.; Yanagishita, T.; Muto, J.; Ohshima, Y.; Nishie, W.; Shimizu, H.; Akiyama, M.; Watanabe, D. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor-associated Bullous Pemphigoid: Recurrence with Epitope Spreading. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2018, 98, 983–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Díez, I.; España, A.; Iranzo, P. Epitope spreading phenomena in dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor-associated bullous pemphigoid. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 1267–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ständer, S.; Schmidt, E.; Zillikens, D.; Ludwig, R.J.; Kridin, K. More Severe Erosive Phenotype Despite Lower Circulating Autoantibody Levels in Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor (DPP4i)-Associated Bullous Pemphigoid: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 22, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujiie, H.; Muramatsu, K.; Mushiroda, T.; Ozeki, T.; Miyoshi, H.; Iwata, H.; Nakamura, A.; Nomoto, H.; Cho, K.Y.; Sato, N.; et al. HLA-DQB1*03:01 as a Biomarker for Genetic Susceptibility to Bullous Pemphigoid Induced by DPP-4 Inhibitors. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindgren, O.; Varpuluoma, O.; Tuusa, J.; Ilonen, J.; Huilaja, L.; Kokkonen, N.; Tasanen, K. Gliptin-associated Bullous Pemphigoid and the Expression of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4/CD26 in Bullous Pemphigoid. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attaway, A.; Mersfelder, T.L.; Vaishnav, S.; Baker, J.K. Bullous pemphigoid associated with dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors. A case report and review of literature. J. Dermatol. Case Rep. 2014, 8, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiie, H.; Sasaoka, T.; Izumi, K.; Nishie, W.; Shinkuma, S.; Natsuga, K.; Nakamura, H.; Shibaki, A.; Shimizu, H. Bullous pemphigoid autoantibodies directly induce blister formation without complement activation. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 4415–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Büdinger, L.; Borradori, L.; Yee, C.; Eming, R.; Ferencik, S.; Grosse-Wilde, H.; Merk, H.F.; Yancey, K.; Hertl, M. Identification and characterization of autoreactive T cell responses to bullous pemphigoid antigen 2 in patients and healthy controls. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Gronow, M.; Kaczowka, S.; Gawdi, G.; Pizzo, S.V. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV/CD26) is a cell-surface plasminogen receptor. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhrborn, D.; Wronkowitz, N.; Eckel, J. DPP4 in Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klemann, C.; Wagner, L.; Stephan, M.; von Hörsten, S. Cut to the chase: A review of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase-4’s (DPP4) entanglement in the immune system. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 185, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forssmann, U.; Stoetzer, C.; Stephan, M.; Kruschinski, C.; Skripuletz, T.; Schade, J.; Schmiedl, A.; Pabst, R.; Wagner, L.; Hoffmann, T.; et al. Inhibition of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV enhances CCL11/eotaxin-mediated recruitment of eosinophils in vivo. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofmann, S.C.; Voith, U.; Schönau, V.; Sorokin, L.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Franzke, C.W. Plasmin Plays a Role in the In Vitro. Generation of the Linear IgA Dermatosis Antigen LADB97. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1730–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, E.; Wehr, B.; Tabengwa, E.M.; Reimer, S.; Bröcker, E.B.; Zillikens, D. Elevated expression and release of tissue-type, but not urokinase-type, plasminogen activator after binding of autoantibodies to bullous pemphigoid antigen 180 in cultured human keratinocytes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 135, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishie, W.; Lamer, S.; Schlosser, A.; Licarete, E.; Franzke, C.W.; Hofmann, S.C.; Jackow, J.; Sitaru, C.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L. Ectodomain shedding generates Neoepitopes on collagen XVII, the major autoantigen for bullous pemphigoid. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 4938–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| nonDPP4i | DPP4i | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y, mean) | 75.4 | 71.1 | NS | |
| Sex Female | 70/113 (61.9%) | 9/14 (64.2%) | NS | |
| Atypical form of BP | 15/46 (32.6%) | 10/14 (71.4%) | 0.014 | |
| BPDAI(mean) | E/B | 24.8 | 22.9 | 0.66 |
| U/E | 16.5 | 6.8 | 0.012 | |
| Damage | 0.9 | 2.5 | 0.027 | |
| Mucosa | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.6 | |
| Mucosal involvement | 24/113 (21.2%) | 3/14 (21.4%) | NS | |
| Serum eosinophil count(cells/μL, mean) | 0.894 (n = 101) | 0.317 (n = 14) | <0.0001 | |
| Periblister eosinophil count(mean) | 19.09 (n = 32) | 6.75 (n = 13) | 0.0012 | |
| DIF | C3 | 106/110 (96.4%) | 11/14 (78.6%) | 0.031 |
| IgG | 101/110 (91.8%) | 13/14 (92.9%) | NS | |
| IgA | 10/110 (9.2%) | 1/14 (7.1%) | NS | |
| IgM | 2/110 (1.8%) | 0/14 (0%) | NS | |
| ELISA(mean) | BP180 | 3.47 | 1.19 | 0.005 |
| BP230 | 1.47 | 0.35 | 0.018 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kinyó, Á.; Hanyecz, A.; Lengyel, Z.; Várszegi, D.; Oláh, P.; Gyömörei, C.; Kálmán, E.; Berki, T.; Gyulai, R. Clinical, Laboratory and Histological Features of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Related Noninflammatory Bullous Pemphigoid. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091916
Kinyó Á, Hanyecz A, Lengyel Z, Várszegi D, Oláh P, Gyömörei C, Kálmán E, Berki T, Gyulai R. Clinical, Laboratory and Histological Features of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Related Noninflammatory Bullous Pemphigoid. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(9):1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091916
Chicago/Turabian StyleKinyó, Ágnes, Anita Hanyecz, Zsuzsanna Lengyel, Dalma Várszegi, Péter Oláh, Csaba Gyömörei, Endre Kálmán, Tímea Berki, and Rolland Gyulai. 2021. "Clinical, Laboratory and Histological Features of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Related Noninflammatory Bullous Pemphigoid" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 9: 1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091916
APA StyleKinyó, Á., Hanyecz, A., Lengyel, Z., Várszegi, D., Oláh, P., Gyömörei, C., Kálmán, E., Berki, T., & Gyulai, R. (2021). Clinical, Laboratory and Histological Features of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Related Noninflammatory Bullous Pemphigoid. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(9), 1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091916








