Beyond Bronchiolitis Obliterans: In-Depth Histopathologic Characterization of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome after Lung Transplantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and BOS Diagnosis
2.2. Sample Collection and Histopathologic Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis and Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
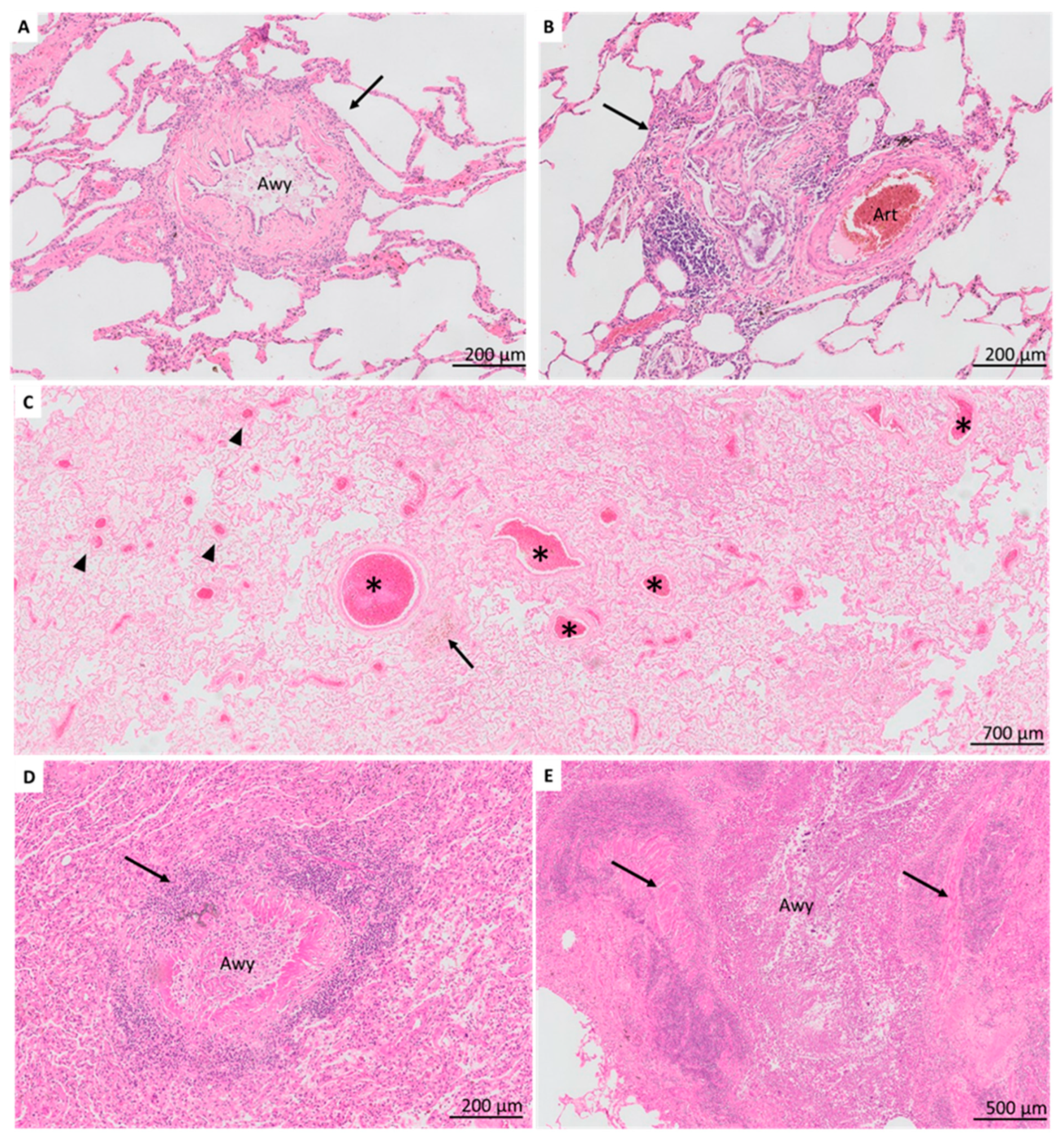
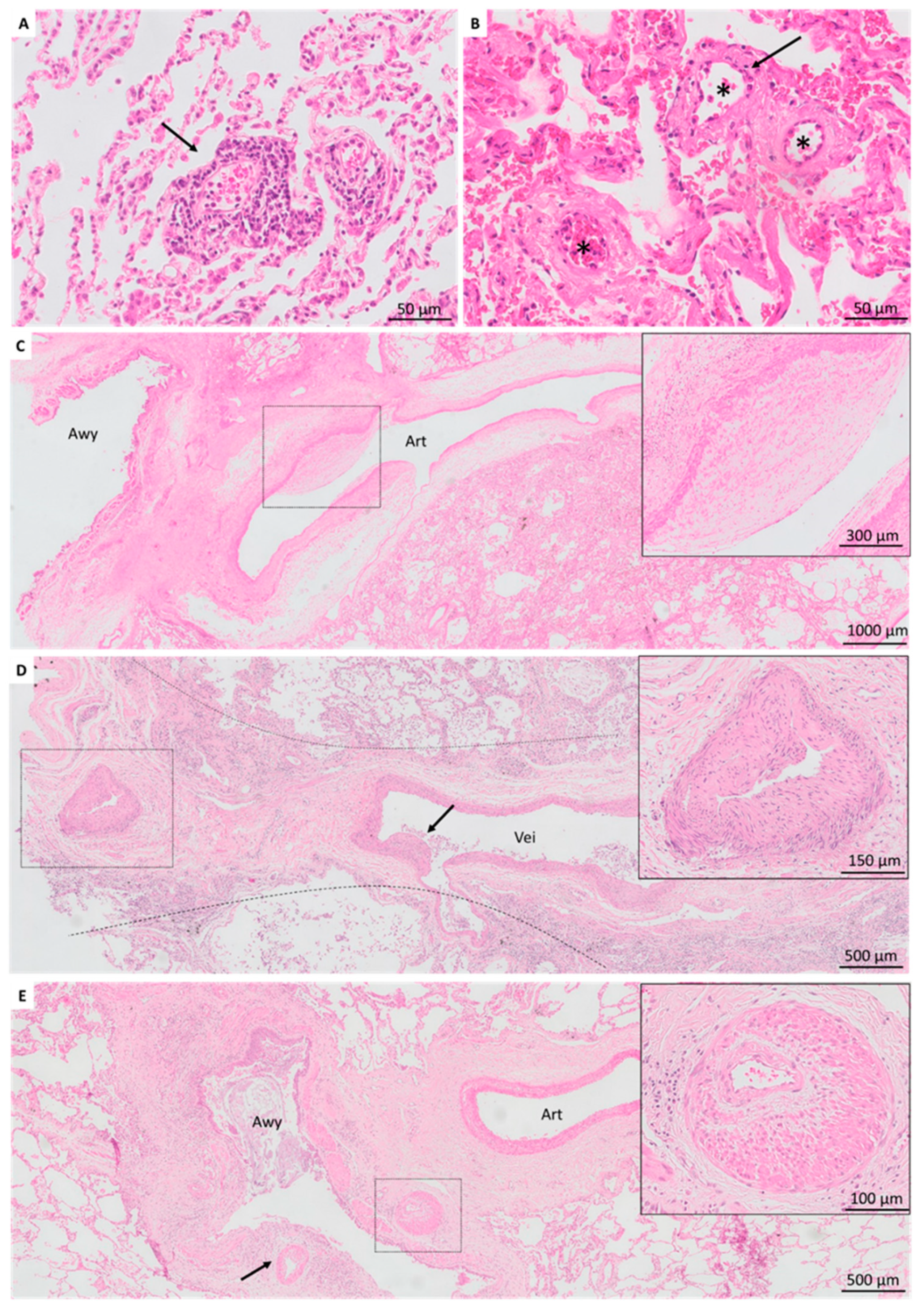
3.2. Airway-Centered Lesions
3.3. Vascular Lesions
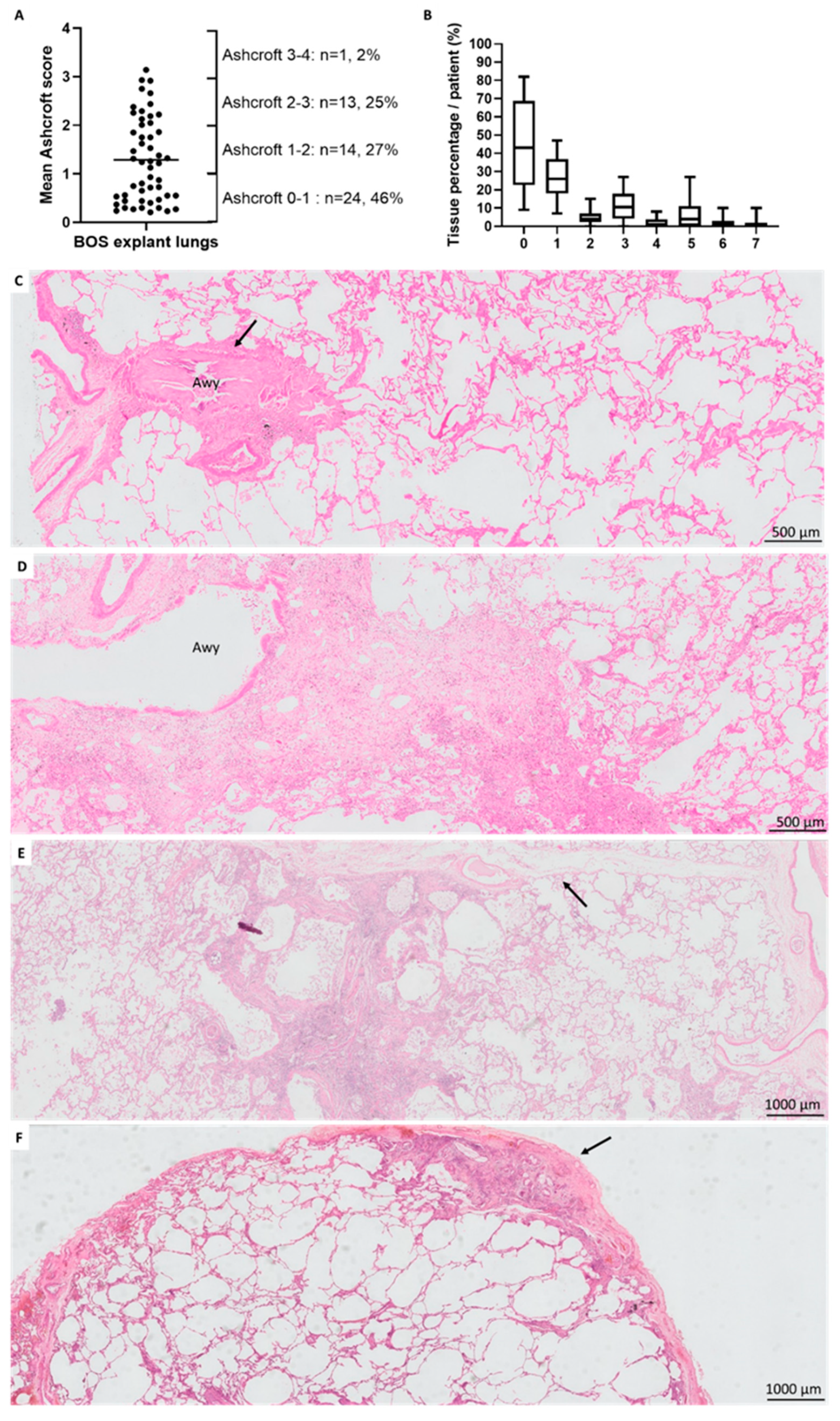
3.4. Fibrotic Changes
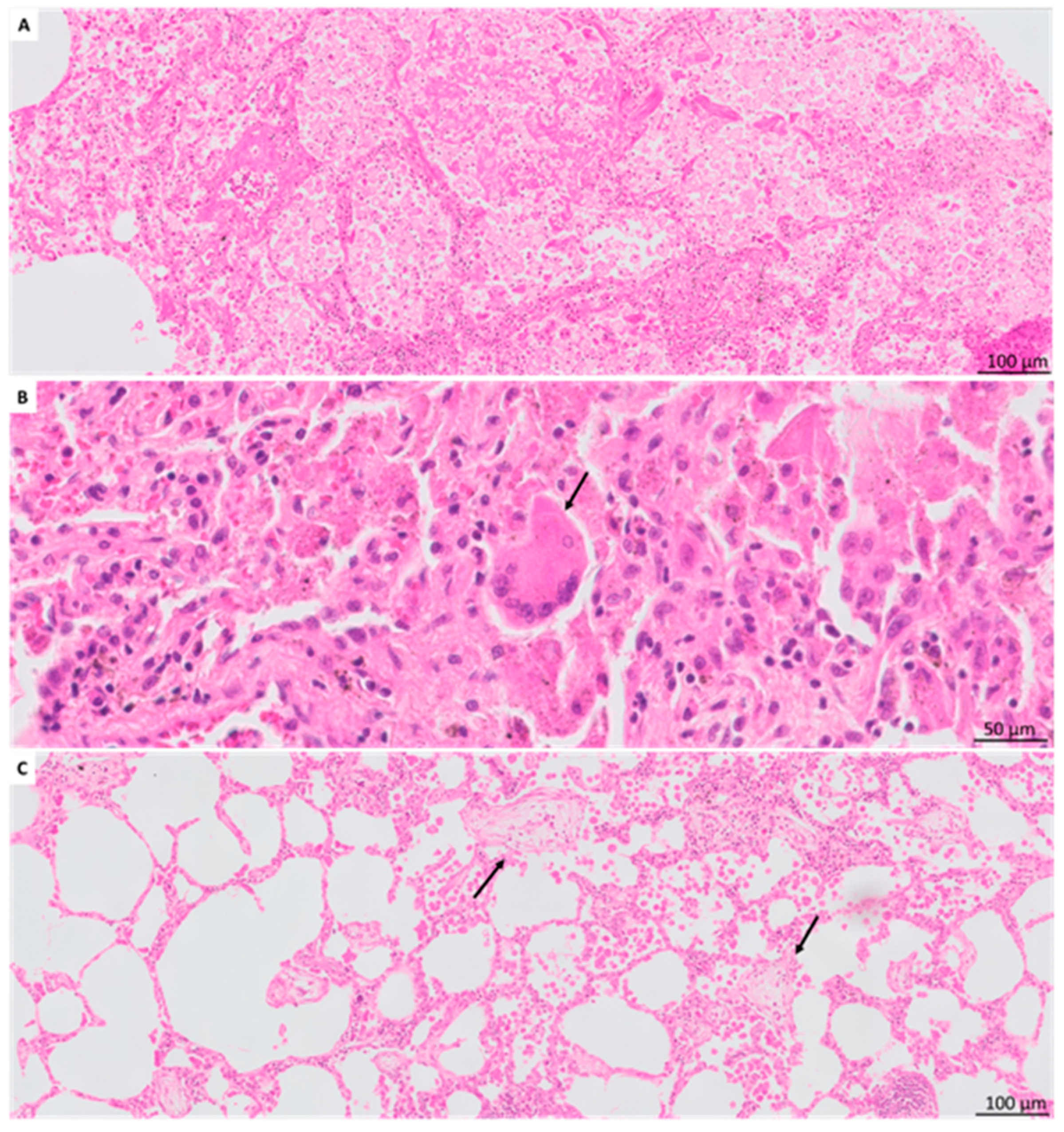
3.5. Other Histologic Findings
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chambers, D.C.; Yusen, R.D.; Cherikh, W.S.; Goldfarb, S.B.; Kucheryavaya, A.Y.; Khusch, K.; Levvey, B.J.; Lund, L.H.; Meiser, B.; Rossano, J.W.; et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-Fourth Adult Lung and Heart-Lung Transplantation Report—2017; Focus Theme: Allograft ischemic time. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2017, 36, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulkarni, H.S.; Cherikh, W.S.; Chambers, D.C.; Garcia, V.C.; Hachem, R.R.; Kreisel, D.E.; Puri, V.; Kozower, B.D.; Byers, D.E.; Witt, C.A.; et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome–free survival after lung transplantation: An International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation Thoracic Transplant Registry analysis. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2019, 38, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verleden, G.M.; Glanville, A.R.; Lease, E.D.; Fisher, A.J.; Calabrese, F.; Corris, P.A.; Ensor, C.R.; Gottlieb, J.; Hachem, R.R.; Lama, V.; et al. Chronic lung allograft dysfunction: Definition, diagnostic criteria, and approaches to treatment―A consensus report from the Pulmonary Council of the ISHLT. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2019, 38, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, M.; Waddell, T.K.; Wagnetz, U.; Roberts, H.C.; Hwang, D.M.; Haroon, A.; Wagnetz, D.; Chaparro, C.; Singer, L.G.; Hutcheon, M.A.; et al. Restrictive allograft syndrome (RAS): A novel form of chronic lung allograft dysfunction. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2011, 30, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanville, A.R.; Verleden, G.M.; Todd, J.L.; Benden, C.; Calabrese, F.; Gottlieb, J.; Hachem, R.R.; Levine, D.; Meloni, F.; Palmer, S.M.; et al. Chronic lung allograft dysfunction: Definition and update of restrictive allograft syndrome―A consensus report from the Pulmonary Council of the ISHLT. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2019, 38, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epler, G.R.; Colby, T.V. The spectrum of bronchiolitis obliterans. Chest 1983, 83, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousem, S.A.; Burke, C.M.; Billingham, M.E. Pathologic pulmonary alterations in long-term human heart-lung transplantation. Hum. Pathol. 1985, 16, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazelaar, H.D.; Yousem, S.A. The pathology of combined heart-lung transplantation: An autopsy study. Hum. Pathol. 1988, 19, 1403–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanville, A.R.; Baldwin, J.C.; Burke, C.M.; Theodore, J.; Robin, E.D. Obliterative bronchiolitis after heart-lung transplantation: Apparent arrest by augmented immunosuppression. Ann. Intern. Med. 1987, 107, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, C.M.; Theodore, J.; Dawkins, K.D.; Yousem, S.A.; Blank, N.; Billingham, M.E.; Robin, E.D. Post-transplant obliterative bronchiolitis and other late lung sequelae in human heart-lung transplantation. Chest 1984, 86, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, C.M.; Theodore, J.; Dawkins, K.D.; Yousem, S.A.; Blank, N.; Billingham, M.E.; Van Kessel, A.; Jamieson, S.W.; Oyer, P.E.; Baldwin, J.C.; et al. Pathologic correlates of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome in pulmonary retransplant recipients. Chest 2006, 129, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Saggar, R.; Ross, D.J.; Saggar, R.; Zisman, D.A.; Gregson, A.; Lynch III, J.P.; Keane, M.P.; Weigt, S.S.; Ardehali, A.; Kubak, B.; et al. Pulmonary hypertension associated with lung transplantation obliterative bronchiolitis and vascular remodeling of the allograft. Am. J. Transpl. 2008, 8, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.C.; Raghu, G.; Verleden, G.M.; Corris, P.A.; Aurora, P.; Wilson, K.C.; Brozek, J.; Glanville, A.R. An international ISHLT/ATS/ERS clinical practice guideline: Diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome TASK FORCE REPORT ISHLT/ATS/ERS CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Executive summary. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2014, 44, 1479–1503. [Google Scholar]
- von der Thüsen, J.H.; Vandermeulen, E.; Vos, R.; Weynand, B.; Verbeken, E.K.; Verleden, S.E. The histomorphological spectrum of restrictive chronic lung allograft dysfunction and implications for prognosis. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.; De Soyza, A.; Fisher, A.J.; Pritchard, G.; Forrest, I.; Corris, P. A Descriptive Study of Small Airway Reticular Basement Membrane Thickening in Clinically Stable Lung Transplant Recipients. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2005, 24, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.; Snell, G.I.; Zheng, L.; Orsida, B.; Whitford, H.; Williams, T.J.; Haydn Walters, E. Endobronchial biopsy and bronchoalveolar lavage in stable lung transplant recipients and chronic rejection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.; Fishbein, M.C.; Snell, G.I.; Berry, G.J.; Boehler, A.; Burke, M.M.; Glanville, A.; Gould, F.K.; Magro, C.; Marboe, C.C.; et al. Revision of the 1996 Working Formulation for the Standardization of Nomenclature in the Diagnosis of Lung Rejection. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2007, 26, 1229–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenland, J.R.; Jones, K.D.; Hays, S.R.; Golden, J.A.; Urisman, A.; Jewell, N.P.; Caughey, G.H.; Trivedi, N.N. Association of large-airway lymphocytic bronchitis with bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashcroft, T.; Simpson, J.M.; Timbrell, V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J. Clin. Pathol. 1988, 41, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verleden, S.E.; Vasilescu, D.M.; Willems, S.; Ruttens, D.; Vos, R.; Vandermeulen, E.; Hostens, J.; McDonough, J.E.; Verbeken, E.K.; Verschakelen, J.; et al. The site and nature of airway obstruction after lung transplantation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombat, M.; Holifanjaniaina, S.; Hirschi, S.; Mal, H.; Stern, M. Histologic Reconstruction of Bronchiolar Lesions in Lung Transplant Patients with Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 1157–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meignin, V.; Thivolet-Bejui, F.; Kambouchner, M.; Hussenet, C.; Bondeelle, L.; Mitchell, A.; Chagnon, K.; Begueret, H.; Segers, V.; Cottin, V. Lung histopathology of non-infectious pulmonary complications after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Histopathology 2018, 73, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, D.; Maurer, J.; Chaparro, C.; Idolor, L. Evaluation of transbronchial lung biopsy specimens in the diagnosis of bronchiolitis obliterans after lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 1994, 13, 963–971. [Google Scholar]
- Yousem, S.A.; Berry, G.J.; Cagle, P.T.; Chamberlain, D.; Husain, A.N.; Hruban, R.H.; Marchevsky, A.; Ohori, N.P.; Ritter, J.; Stewart, S.; et al. Revision of the 1990 working formulation for the classification of pulmonary allograft rejection: Lung Rejection Study Group. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 1996, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kotoulas, C.; Melachrinou, M.; Konstantinou, G.N.; Alexopoulos, D.; Dougenis, D. Bronchial arteries: An arteriosclerosis-resistant circulation. Respiration 2010, 79, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofek, E.; Sato, M.; Saito, T.; Wagnetz, U.; Roberts, H.C.; Chaparro, C.; Waddell, T.K.; Singer, L.G.; Hutcheon, M.A.; Keshavjee, S.; et al. Restrictive allograft syndrome post lung transplantation is characterized by pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis. Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, A.V.; Eapen, M.S.; McAlinden, K.D.; Chia, C.; Larby, J.; Myers, S.; Dey, S.; Haug, G.; Markos, J.; Glanville, A.R.; et al. Endothelial to mesenchymal transition (EndMT) and vascular remodeling in pulmonary hypertension and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2020, 14, 1027–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghigna, M.R.; Mooi, W.J.; Grünberg, K. Pulmonary hypertensive vasculopathy in parenchymal lung diseases and/or hypoxia: Number 1 in the Series “Pathology for the clinician” Edited by Peter Dorfmüller and Alberto Cavazza. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dotan, Y.; Stewart, J.; Gangemi, A.; Wang, H.; Aneja, A.; Chakraborty, B.; Dass, C.; Zhao, H.; Marchetti, N.; D’Alonzo, G.; et al. Pulmonary vasculopathy in explanted lungs from patients with interstitial lung disease undergoing lung transplantation. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2020, 7, e000532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collum, S.D.; Amione-Guerra, J.; Cruz-Solbes, A.S.; DiFrancesco, A.; Hernandez, A.M.; Hanmandlu, A.; Youker, K.; Guha, A.; Karmouty-Quintana, H. Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Current and Future Perspectives. Can. Respir. J. 2017, 2017, 1430350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, C.M.; Calomeni, E.P.; Nadasdy, T.; Shusterman, B.D.; Pope-Harman, A.L.; Ross, P., Jr. Ultrastructure as a diagnostic adjunct in the evaluation of lung allograft biopsies. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2005, 29, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro, C.M.; Abbas, A.E.; Seilstad, K.; Pope-Harman, A.L.; Nadasdy, T.; Ross, P., Jr. C3d and the septal microvasculature as a predictor of chronic lung allograft dysfunction. Hum. Immunol. 2006, 67, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eapen, M.S.; Lu, W.; Gaikwad, A.V.; Bhattarai, P.; Chia, C.; Hardikar, A.; Haug, G.; Sohal, S.S. Endothelial to mesenchymal transition: A precursor to post-COVID-19 interstitial pulmonary fibrosis and vascular obliteration? Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2003167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez-Giménez, B.; Clofent, D.; Meseguer, M.L.; Masgoret, C.B.; Monforte, V.; Berastegui, C.; Revilla-Lopez, E.; Barrecheguren, M.; Arjona-Peris, M.; Ruiz, V.; et al. Is there a procoagulant state long-term after lung transplantation? A prospective study. Respir. Med. 2021, 188, 106584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Total | Autopsy | Redo-LTx | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, N | 52 | 23 | 29 | |
| Age at transplant (y) | 43 (27–57) | 56 (39–60) | 30 (25–47) | 0.0077 |
| Male, N (%) | 21 (40) | 7 (30) | 14 (48) | 0.43 |
| Underlying disease, N (%) | ||||
| Emphysema | 17 (33) | 14 (61) | 3 (10) | 0.0002 |
| ILD | 10 (19) | 4 (17) | 6 (21) | >0.99 |
| CF + BRECT | 19 (37) | 2 (9) | 17 (59) | 0.0003 |
| PHT + Eisenmenger | 4 (8) | 3 (13) | 1 (3) | 0.31 |
| Other | 2 (4) | 0 | 2 (7) | 0.50 |
| Type of transplant, N (%) | ||||
| BLTx | 37 (71) | 11 (48) | 26 (90) | 0.016 |
| HLTx | 4 (8) | 3 (13) | 1 (3) | 0.31 |
| SLTx | 11 (21) | 9 (39) | 2 (7) | 0.0066 |
| Time to CLAD (y) | 2.2 (1.0–5.0) | 3.5 (1.1–6.0) | 1.5 (1.0–3.7) | 0.34 |
| Time to graft loss (y) | 5.4 (2.3–8.2) | 5.5 (2.4–8.6) | 4.8 (2.2–7.7) | 0.97 |
| Graft survival after CLAD onset (y) | 1.4 (0.6–3.7) | 1.1 (0.3–2.3) | 2.1 (0.7–4.4) | 0.29 |
| Time BOS1 to BOS3 (y) * | 0.4 (0.1–1.5) | 0.8 (0.2–1.7) | 0.3 (0.1–1.4) | 0.43 |
| Time BOS3 to graft loss (y) | 0.9 (0.5–2.3) | 0.6 (0.1–2.2) | 1.1 (0.5–2.5) | 0.23 |
| Post-LTx best FEV1 (L) | 2.4 (1.9–3.1) | 2.1 (1.5–2.8) | 2.8 (2.3–3.6) | 0.0012 |
| Post-LTx best FVC (L) | 3.3 (2.6–4.0) | 2.9 (2.4–3.8) | 3.4 (2.9–4.2) | 0.035 |
| FEV1 before graft loss (L) | 0.6 (0.5–0.9) | 0.8 (0.6–1.3) | 0.6 (0.5–0.8) | 0.12 |
| FEV1 decline (%) | 72.1 (60.8–79.8) | 60.8 (40.3–67.2) | 77.4 (72.8–80.8) | <0.0001 |
| Time last FEV1 to graft loss (d) | 29 (10–47) | 44 (24–59) | 18 (8–39) | 0.015 |
| CLAD (BOS) stage before graft loss | ||||
| Stage 1 | 5 (10) | 4 (17) | 1 (3) | 0.16 |
| Stage 2 | 4 (8) | 4 (17) | 0 | 0.033 |
| Stage 3 | 6 (12) | 6 (26) | 0 | 0.0050 |
| Stage 4 | 37 (71) | 9 (39) | 28 (97) | <0.0001 |
| Ever AR, N(%) | 30 (58) | 12 (52) | 18 (62) | 0.58 |
| Ever severe AR (≥A2), N(%) | 16 (31) | 6 (26) | 10 (34) | 0.56 |
| Ever LB, N(%) | 17 (33) | 7 (30) | 10 (34) | >0.99 |
| Ever severe LB (=B2R), N(%) | 9 (17) | 4 (17) | 5 (17) | >0.99 |
| History of DSAs, N(%) | 6 (12) | 3 (13) | 3 (10) | >0.99 |
| BAL at BOS1 diagnosis ** | ||||
| Total cell count (10³/mL) | 151.0 (69.0–280.0) | 151.0 (80.0–697.5) | 155.5 ( 55.25–247.0) | 0.77 |
| Macrophages % | 70.4 (49.2–90.6) | 61.8 (34.3–90.8) | 75.7 (54.9–89.6) | 0.80 |
| Lymphocytes % | 6.0 (2.2–12.4) | 5.5 (0.9–18.4) | 6.3 (3.2–11.4) | 0.88 |
| Neutrophils % | 8.0 (3.0 -39.0) | 18.0 (2.5–60.2) | 7.2 (3.4–35.7) | 0.89 |
| Eosinophils % | 0.2 (0.0–1.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.4) | 0.2 (0.0–2.0) | 0.16 |
| BOS: Autopsy vs. Redo-LTx | BOS vs. Non-CLAD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOS Autopsy | BOS Redo-LTx | Adjusted p Value | BOS Total | Non-CLAD | Adjusted p Value | |
| Patients, N | 23 | 29 | 52 | 26 | ||
| Airway lesions | ||||||
| Small-airway lymphocytic bronchiolitis | 3 (13) | 17 (59) | 0.051 | 20 (38) | 1 (4) | 0.034 |
| Large-airway lymphocytic bronchitis | 13 (57) | 16 (55) | 1.00 | 29 (56) | 1 (4) | 0.0038 |
| Bronchiolitis obliterans | 9 (39) | 29 (100) | 0.0039 | 38 (73) | 0 | 0.0038 |
| Vanishing airways | 12 (52) | 1 (3) | 0.0039 | 13 (25) | 0 | 0.13 |
| Bronchiectasis | 1 (4) | 9 (31) | 1.00 | 10 (19) | 0 | 0.98 |
| Follicular bronchiolitis | 0 | 1 (3) | 1.00 | 1 (2) | 0 | 1.00 |
| Mucus plugs | 6 (26) | 13 (45) | 1.00 | 19 (37) | 16 (62) | 1.00 |
| Squamous metaplasia | 4 (17) | 5 (17) | 1.00 | 9 (17) | 3 (12) | 1.00 |
| Respiratory bronchiolitis | 0 | 2 (7) | 1.00 | 2 (4) | 1 (4) | 1.00 |
| Vascular lesions | ||||||
| Acute rejection | 6 (26) | 2 (7) | 1.00 | 8 (15) | 1 (4) | 1.00 |
| Pulmonary arteriopathy | 7 (30) | 10 (34) | 1.00 | 17 (33) | 1 (4) | 0.15 |
| Media hypertrophy | 2 (9) | 8 (28) | 1.00 | 10 (19) | 0 | 0.98 |
| Intima hyperplasia | 7 (30) | 10 (34) | 1.00 | 17 (33) | 1 (4) | |
| Pulmonary venopathy | 4 (17) | 10 (34) | 1.00 | 14 (27) | 0 | 0.13 |
| Intima hyperplasia | 4 (17) | 10 (34) | 1.00 | 14 (27) | 0 | 0.13 |
| Venous occlusion | 2 (9) | 3 (10) | 1.00 | 5 (10) | 0 | 1.00 |
| Bronchial arteriopathy | 2 (9) | 9 (31) | 1.00 | 11 (21) | 0 | 0.49 |
| Media hypertrophy | 2 (9) | 9 (31) | 1.00 | 11 (21) | 0 | 0.49 |
| Intima hyperplasia | 2 (9) | 9 (31) | 1.00 | 11 (21) | 0 | 0.49 |
| Microvascular injury | 0 | 2 (7) | 1.00 | 2 (4) | 1 (4) | 1.00 |
| Thrombi | 1 (4) | 2 (7) | 1.00 | 3 (6) | 5 (19) | 1.00 |
| Alveolar compartment | ||||||
| Pneumocyte hyperplasia | 3 (13) | 12 (41) | 1.00 | 15 (29) | 9 (35) | 1.00 |
| Emphysema | 11 (48) | 18 (62) | 1.00 | 29 (56) | 4 (15) | 0.027 |
| Hemosiderophages | 6 (26) | 9 (31) | 1.00 | 15 (29) | 3 (12) | 1.00 |
| Neutrophils in alveoli | 5 (22) | 2 (7) | 1.00 | 7 (13) | 15 (58) | 0.0038 |
| Eosinophils in alveoli | 0 | 1 (3) | 1.00 | 1 (2) | 0 | 1.00 |
| Organizing pneumonia | 6 (26) | 5 (17) | 1.00 | 11 (21) | 10 (38) | 1.00 |
| AFOP | 3 (13) | 1 (3) | 1.00 | 4 (8) | 1 (4) | 1.00 |
| Hyaline membranes | 5 (22) | 0 | 0.55 | 5 (10) | 9 (35) | 0.18 |
| Cholesterol clefts | 2 (9) | 6 (21) | 1.00 | 8 (15) | 0 | 1.00 |
| Giant cells | 2 (9) | 11 (38) | 0.90 | 13 (25) | 1 (4) | 0.94 |
| RBCs intra-alveolar | 13 (57) | 14 (48) | 1.00 | 27 (52) | 16 (62) | 1.00 |
| Fibrin intra-alveolar | 9 (39) | 4 (14) | 1.00 | 13 (25) | 12 (46) | 1.00 |
| Foamy macrophages intra-alveolar | 1 (4) | 9 (31) | 1.00 | 10 (19) | 0 | 0.98 |
| Fibrotic lesions | ||||||
| Mean Ashcroft score | 1.26 (SD 1.04) | 1.306 (SD 0.72) | 1.00 | 1.29 (SD 0.87) | 0.48 (SD 0.49) | 0.0038 |
| Ashcroft score ≥5 | 10 (43) | 18 (62) | 1.00 | 28 (54) | 4 (15) | 0.053 |
| Bronchocentric fibrosis | 5 (22) | 16 (55) | 0.090 | 21 (40) | 0 | 0.0038 |
| Paraseptal fibrosis | 8 (35) | 9 (31) | 1.00 | 17 (33) | 2 (8) | 0.89 |
| Subpleural fibrosis | 6 (26) | 9 (31) | 1.00 | 15 (29) | 3 (12) | 1.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vanstapel, A.; Verleden, S.E.; Verbeken, E.K.; Braubach, P.; Goos, T.; De Sadeleer, L.; Kaes, J.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Jonigk, D.; Ackermann, M.; et al. Beyond Bronchiolitis Obliterans: In-Depth Histopathologic Characterization of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome after Lung Transplantation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010111
Vanstapel A, Verleden SE, Verbeken EK, Braubach P, Goos T, De Sadeleer L, Kaes J, Vanaudenaerde BM, Jonigk D, Ackermann M, et al. Beyond Bronchiolitis Obliterans: In-Depth Histopathologic Characterization of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome after Lung Transplantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(1):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010111
Chicago/Turabian StyleVanstapel, Arno, Stijn E. Verleden, Eric K. Verbeken, Peter Braubach, Tinne Goos, Laurens De Sadeleer, Janne Kaes, Bart M. Vanaudenaerde, Danny Jonigk, Maximilian Ackermann, and et al. 2022. "Beyond Bronchiolitis Obliterans: In-Depth Histopathologic Characterization of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome after Lung Transplantation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 1: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010111
APA StyleVanstapel, A., Verleden, S. E., Verbeken, E. K., Braubach, P., Goos, T., De Sadeleer, L., Kaes, J., Vanaudenaerde, B. M., Jonigk, D., Ackermann, M., Ceulemans, L. J., Van Raemdonck, D. E., Neyrinck, A. P., Vos, R., Verleden, G. M., Weynand, B., & on behalf of the Leuven Lung Transplant Group. (2022). Beyond Bronchiolitis Obliterans: In-Depth Histopathologic Characterization of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome after Lung Transplantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(1), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010111







