Influence of Overhanging Bleb on Corneal Higher-Order Aberrations after Trabeculectomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
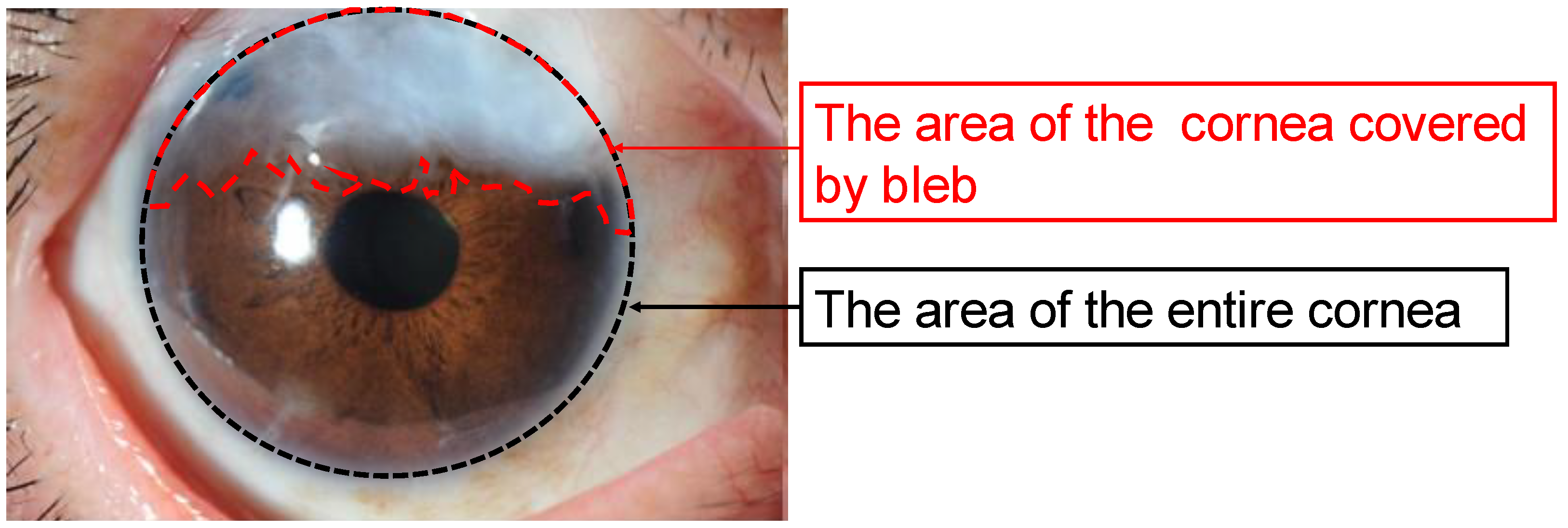
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quigley, H.A.; Addicks, E.M.; Green, W.R.; Maumenee, A.E. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1981, 99, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, J.E. Trabeculectomy. Preliminary report of a new method. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1968, 66, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, P.J.; Fechtner, R.D. Antifibrotics and wound healing in glaucoma surgery. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2003, 48, 314–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou-Yang, P.B.; Qi, X.; Duan, X.C. Histopathology and treatment of a huge overhanging filtering bleb. BMC Ophthalmol. 2016, 16, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, K.; Krishna, R. Surgical management of a dysfunctional filtering bleb. Ophthal. Surg. Lasers 2002, 33, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzl, I.M.; Katz, L.J.; Shindler, R.L.; Spaeth, G.L. Surgical management of overhanging blebs after filtering procedures. J. Glaucoma 1999, 8, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claridge, K.G.; Galbraith, J.K.; Karmel, V.; Bates, A.K. The effect of trabeculectomy on refraction, keratometry and corneal topography. Eye 1995, 9, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, S.; Amano, S.; Honda, N.; Mimura, T.; Usui, T.; Araie, M. Effect of trabeculectomy on ocular and corneal higher-order aberrations. JPN J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 55, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesudovs, K.; Coster, D.J. Penetrating keratoplasty for keratoconus: The nexus between corneal wavefront aberrations and visual performance. J. Refract. Surg. 2006, 22, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesudovs, K.; Figueiredo, F.C. Corneal first surface wavefront aberrations before and after pterygium surgery. J. Refract. Surg. 2006, 22, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, K.; Erkilic, K.; Topaktas, D.; Colin, J. Effect of pterygia on refractive indices, corneal topography, and ocular aberrations. Cornea 2011, 30, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, K.; Tokunaga, T.; Okamoto, K.; Miyata, K.; Oshika, T. Influence of pterygium size on corneal higher-order aberration evaluated using anterior-segment optical coherence tomography. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018, 18, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, K.; Minami, K.; Otani, A.; Tokunaga, T.; Tokuda, S.; Amano, S. Proposal for a novel severity grading system for Pterygia based on corneal topographic data. Cornea 2017, 36, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheie, H.G.; Guehl, J.J. Surgical management of overhanging blebs after filtering procedures. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1979, 97, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, G.G.; Proia, A.D.; Shields, M.B. Clinicopathologic features and surgical management of dissecting glaucoma filtering blebs. Ophthalmic. Surg. Lasers 1997, 28, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.R.; Kotas-Neumann, R. Free conjunctival patch for repair of persistent late bleb leak. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1994, 117, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, O. Management of large, leaking, and inadvertent filtering blebs with the neodymium: YAG laser. Ophthalmology 1998, 105, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.S.C.; Ching, R.H.Y.; Yam, J.C.S.; Chan, C.W.N. Safe excision of a large overhanging cystic bleb following autologous blood injection and compression suture. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 27, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Ge, J.; Zhuo, Y. Dry eye disease in patients with functioning filtering blebs after trabeculectomy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojzis, P.; Majerova, K.; Plaza-Puche, A.B.; Hrckova, L.; Alio, J.L. Visual outcomes of a new toric trifocal diffractive intraocular lens. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2015, 41, 2695–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.S.; Park, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Yoon, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Tchah, H. Corneal coma and trefoil changes associated with incision location in cataract surgery. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2015, 41, 2145–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshika, T.; Sugita, G.; Miyata, K.; Tokunaga, T.; Samejima, T.; Okamoto, C.; Ishii, Y. Influence of tilt and decentration of scleral-sutured intraocular lens on ocular higher-order wavefront aberration. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okamoto, F.; Yamane, N.; Okamoto, C.; Hiraoka, T.; Oshika, T. Changes in higher-order aberrations after scleral buckling surgery for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dietze, P.J.; Oram, O.; Kohnen, T.; Feldman, R.M.; Koch, D.D.; Gross, R.L. Visual function following trabeculectomy, effect on corneal topography and contrast sensitivity. J. Glaucoma 1997, 6, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, A.M.; Sorkhabi, R.D.; Nasiri, K.; Tajlil, A. Effect of trabeculectomy on ocular higher-order aberrations in patients with open angle glaucoma. North. Clin. Istanb. 2018, 5, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weale, R.A. Pterygium. In Epidemiology of Eye Disease, 2nd ed.; Johnson, G.J., Minassian, D.C., Weale, R.A., West, S.K., Eds.; Arnold Publishers: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Grostern, R.J.; Torczynski, E.; Brown, S.V. Surgical repair and histopathologic features of a dissecting glaucoma filtration bleb. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1999, 117, 1566–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, Y.; Hirota, A.; Hirooka, K.; Kiuchi, Y. Improvements in optical characteristics after excision of an overhanging bleb developed following trabeculectomy. Case Rep. Ophthalmol. Med. 2021, 4, 7433987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhang, K.; Yang, J.; Lu, Y. Changes of corneal higher-order aberrations after cataract surgery. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2014, 91, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, E.A.; Alcón, E.; Rubio, E.; Marín, J.M.; Artal, P. One-year follow-up of changes in refraction and aberrations induced by corneal incision. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montés-Micó, R.; Cáliz, A.; Alió, J.L. Wavefront analysis of higher-order aberrations in dry eye patients. J. Refract. Surg. 2004, 20, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.C. Theoretical model of the contributions of corneal asphericity and anterior chamber depth to peripheral wavefront aberrations. Ophthalmic. Physiol. Opt. 2014, 34, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.H.; Seo, J.H. Short-term change in higher-order aberrations after mitomycin-C-augmented trabeculectomy. Int. Ophthalmol. 2019, 39, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Sun, X.; Chu, R.; Zhuang, H.; He, J.C. Dynamic wavefront aberrations and visual acuity in control and dry eyes. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2009, 92, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, S.; Maeda, N.; Hori, Y.; Inoue, T.; Watanabe, H.; Hirohara, Y.; Mihashi, T.; Fujikado, T.; Tano, Y. Effects of suppression of blinking on quality of vision in borderline cases of evaporative dry eye. Cornea 2008, 27, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denoyer, A.; Rabut, G.; Baudouin, C. Tear film aberration dynamics and vision-related quality of life in patients with dry eye disease. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 1811–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Control (n = 65) | OHB (n = 61) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 66.23 ± 19.32 | 67.47 ± 11.11 | 0.66 |
| Gender (Male/Female) | 42/23 | 34/27 | 0.31 |
| BCVA (logMAR) | −0.0086 ± 0.14 | 0.16 ± 0.30 | <0.0001 |
| IOP (mmHg) | 14.00 ± 3.66 | 11.60 ± 4.43 | 0.0012 |
| Lens status (phakic/IOL) | 43/22 | 27/34 | 0.013 |
| Spherical equivalents | −2.25 ± 3.65 | −2.98 ± 2.87 | 0.22 |
| Control (n = 65) | OHB (n = 61) | |
|---|---|---|
| Type of glaucoma | ||
| PACG (%) | 3 (4.6) | 4 (6.6) |
| POAG (%) | 37 (56.9) | 46 (75.4) |
| Exfoliation G (%) | 4 (6.2) | 5 (8.2) |
| Uveitic G (%) | 0 (0) | 3 (4.9) |
| Rubeotic G (%) | 1 (0) | 1 (1.6) |
| Childhood G (%) | 2 (3.1) | 2 (3.3) |
| Steroid-induced G (%) | 3 (3.1) | 0 (0) |
| PPG (%) | 16 (24.6) | 0 (0) |
| PAC (%) | 1 (1.5) | 0 (0) |
| Operation (First time) | ||
| TLE (%) | - | 53 (86.89) |
| TLE + PEA + IOL (%) | - | 6 (9.84) |
| Ex-PRESS (%) | - | 2 (3.28) |
| Average number of TLE surgeries | - | 1.33 ± 0.85 |
| 1st time (%) | - | 51 (83.61) |
| 2nd time (%) | - | 4 (6.56) |
| 3rd time or more (%) | - | 6 (9.84) |
| Period after the last surgery (year) | - | 3.18 ± 3.81 |
| Control (n = 65) | OHB (n = 61) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corneal total higher-order aberrations (μm, RMS) | 0.26 ± 0.14 | 0.36 ± 0.40 | 0.47 |
| Corneal coma aberrations (μm, RMS) | 0.10 ± 0.05 | 0.16 ± 0.13 | 0.042 |
| Corneal spherical aberrations (μm, RMS) | 0.04 ± 0.62 | 0.04 ± 0.07 | 0.72 |
| Corneal coma-like aberrations (μm, RMS) | 0.16 ± 0.09 | 0.31 ± 0.32 | 0.022 |
| Corneal spherical-like aberrations (μm, RMS) | 0.09 ± 0.71 | 0.16 ± 0.21 | 0.11 |
| Corneal Total Higher-Order Aberrations (μm, RMS) | Corneal Coma Aberrations (μm, RMS) | Corneal Spherical Aberrations (μm, RMS) | Corneal Coma-Like Aberrations (μm, RMS) | Corneal Spherical-Like Aberrations (μm, RMS) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | p | β | p | β | p | β | p | β | p | |
| Ratio of cornea covered by bleb | 0.38 | 0.0026 | 0.39 | 0.0018 | 0.34 | 0.0071 | 0.10 | 0.43 | 0.30 | 0.021 |
| Number of TLE ≥ 2 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.061 | 0.099 | 0.45 | 0.077 | 0.56 | 0.13 | 0.31 |
| IOP < 8 | −0.54 | 0.17 | −0.31 | 0.45 | −0.16 | 0.71 | −0.48 | 0.23 | −0.03 | 0.94 |
| Age | v0.03 | 0.84 | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.0067 | 0.96 | −0.046 | 0.73 | −0.12 | 0.36 |
| Corneal Total Higher-Order Aberrations (μm, RMS) | Corneal Coma Aberrations (μm, RMS) | Corneal Spherical Aberrations (μm, RMS) | Corneal Coma-Like Aberrations (μm, RMS) | Corneal Spherical-Like Aberrations (μm, RMS) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | p | VIF | β | p | VIF | β | p | VIF | β | p | VIF | β | p | VIF | |
| Ratio of cornea covered by bleb | 0.37 | 0.0034 | 1.01 | 0.40 | 0.0013 | 1.01 | 0.34 | 0.0084 | 1.01 | 0.093 | 0.48 | 1.01 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 1.01 |
| Number of TLE ≥ 2 | 0.038 | 0.78 | 1.29 | 0.048 | 0.72 | 1.29 | −0.085 | 0.55 | 1.29 | 0.038 | 0.80 | 1.29 | 0.0035 | 0.98 | 1.29 |
| IOP < 8 | −0.51 | 0.12 | 1.25 | −0.45 | 0.43 | 1.25 | −0.18 | 0.69 | 1.25 | −0.33 | 0.52 | 1.25 | −0.0031 | 0.99 | 1.25 |
| Age | −0.025 | 0.84 | 1.02 | 0.20 | 0.11 | 1.02 | 0.0056 | 0.65 | 1.02 | −0.024 | 0.86 | 1.02 | −0.072 | 0.57 | 1.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mizuno, Y.; Hirooka, K.; Kiuchi, Y. Influence of Overhanging Bleb on Corneal Higher-Order Aberrations after Trabeculectomy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010177
Mizuno Y, Hirooka K, Kiuchi Y. Influence of Overhanging Bleb on Corneal Higher-Order Aberrations after Trabeculectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(1):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010177
Chicago/Turabian StyleMizuno, Yu, Kazuyuki Hirooka, and Yoshiaki Kiuchi. 2022. "Influence of Overhanging Bleb on Corneal Higher-Order Aberrations after Trabeculectomy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 1: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010177
APA StyleMizuno, Y., Hirooka, K., & Kiuchi, Y. (2022). Influence of Overhanging Bleb on Corneal Higher-Order Aberrations after Trabeculectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(1), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010177






