Extra-Intestinal Manifestations of Celiac Disease: What Should We Know in 2022?
Abstract
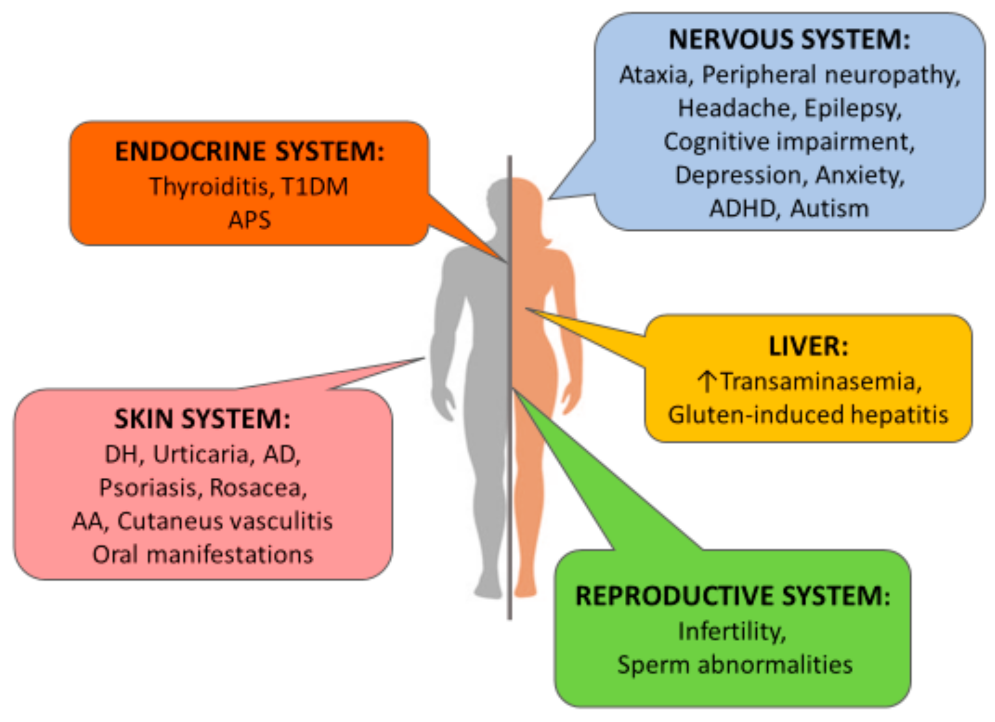
:1. Introduction
2. Cutaneous and Mucosal Manifestations
2.1. Dermatitis Herpetiformis
2.2. Urticaria
2.3. Atopic Dermatitis
2.4. Psoriasis
2.5. Rosacea
2.6. Oral Manifestations
2.7. Alopecia Areata
2.8. Cutaneous Vasculitis
2.9. Other Cutaneous Manifestations
3. Neurological Manifestations
3.1. Ataxia
3.2. Peripheral Neuropathy
3.3. Headache, Epilepsy, and Cognitive Impairment
4. Neuropsychiatric Manifestations
4.1. Depression
4.2. Anxiety, ADHD, and Autism
4.3. Other Psychiatric Disorders
5. Liver Manifestations
6. Reproductive Manifestations
7. Endocrinological-Associated Diseases
7.1. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Autoimmune Thyroiditis
7.2. Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome
7.3. Short Stature
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| T1DM | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| APS | Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome |
| DH | Dermatitis herpetiformis |
| AD | Atopic dermatitis |
| AA | Alopecia areata |
| ADHD | Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder |
References
- Pinto-Sánchez, M.I.; Bercik, P.; Verdu, E.F.; Bai, J.C. Extraintestinal Manifestations of Celiac Disease. Dig. Dis. 2015, 33, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Leffler, D.A.; Bai, J.C.; Biagi, F.; Fasano, A.; Green, P.H.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Kaukinen, K.; Kelly, C.P.; Leonard, J.N.; et al. The Oslo definitions for coeliac disease and related terms. Gut 2013, 62, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurikka, P.; Nurminen, S.; Kivelä, L.; Kurppa, K. Extraintestinal Manifestations of Celiac Disease: Early Detection for Better Long-Term Outcomes. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigo, L.; Beteta-Gorriti, V.; Alvarez, N.; Gómez de Castro, C.; de Dios, A.; Palacios, L.; Santos-Juanes, J. Cutaneous and Mucosal Manifestations Associated with Celiac Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villemur Moreau, L.; Dicky, O.; Mas, E.; Noirrit, E.; Marty, M.; Vaysse, F.; Olives, J.P. Oral manifestations of celiac disease in French children. Arch. Pédiatrie 2021, 28, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieri, M.; Tofani, E.; Defraia, E.; Giuntini, V.; Franchi, L. Enamel defects and aphthous stomatitis in celiac and healthy subjects: Systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled studies. J. Dent. 2017, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Dastoli, S.; Bennardo, L.; Boccuto, L.; Passante, M.; Silvestri, M.; Proietti, I.; Potenza, C.; Luzza, F.; Nisticò, S.P. The Skin in Celiac Disease Patients: The Other Side of the Coin. Medicina 2019, 55, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermeersch, P.; Geboes, K.; Mariën, G.; Hoffman, I.; Hiele, M.; Bossuyt, X. Diagnostic performance of IgG anti-deamidated gliadin peptide antibody assays is comparable to IgA anti-tTG in celiac disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, A.; Kelly, C.P.; Silvester, J.A. Celiac Disease: Extraintestinal Manifestations and Associated Conditions. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 54, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meresse, B.; Malamut, G.; Cerf-Bensussan, N. Celiac disease: An immunological jigsaw. Immunity 2012, 36, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reunala, T.; Salmi, T.; Hervonen, K.; Kaukinen, K.; Collin, P. Dermatitis Herpetiformis: A Common Extraintestinal Manifestation of Coeliac Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nardecchia, S.; Auricchio, R.; Discepolo, V.; Troncone, R. Extra-Intestinal Manifestations of Coeliac Disease in Children: Clinical Features and Mechanisms. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatia, B.K.; Millsop, J.W.; Debbaneh, M.; Koo, J.; Linos, E.; Liao, W. Diet and psoriasis, part II: Celiac disease and role of a gluten-free diet. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 71, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bramanti, E.; Cicciù, M.; Matacena, G.; Costa, S.; Magazzù, G. Clinical Evaluation of Specific Oral Manifestations in Pediatric Patients with Ascertained versus Potential Coeliac Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bıçak, D.A.; Urgancı, N.; Akyüz, S.; Usta, M.; Kızılkan, N.U.; Alev, B.; Yarat, A. Clinical evaluation of dental enamel defects and oral findings in coeliac children. Eur. Oral Res. 2019, 52, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macho, V.M.P.; Coelho, A.S.; E Silva, D.M.V.; de Andrade, D.J.C. Oral Manifestations in Pediatric Patients with Coeliac Disease—A Review Article. Open Dent. J. 2017, 11, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Gils, T.; Bouma, G.; Bontkes, H.J.; Mulder, C.J.J.; Brand, H.S. Self-reported oral health and xerostomia in adult patients with celiac disease versus a comparison group. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2017, 124, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallaji, Z.; Akhyani, M.; Ehsani, A.H.; Noormohammadpour, P.; Gholamali, F.; Bagheri, M.; Jahromi, J. Prevalence of anti-gliadin antibody in patients with alopecia areata: A case-control study. Tehran Univ. Med. J. 2011, 68, 738–742. [Google Scholar]
- Volta, U.; Bardazzi, F.; Zauli, D.; Franceschi, L.; Tosti, A.; Mounaro, N.; Ghetti, S.; Tetta, C.; Grassi, A.; Bianchi, F.B. Serological screening for coeliac disease in vitiligo and alopecia areata. Br. J. Dermatol. 1997, 136, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, W.T.; Smith, W.T. Neurological disorders associated with adult coeliac disease. Brain 1966, 89, 683–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mearns, E.S.; Taylor, A.; Thomas Craig, K.J.; Puglielli, S.; Cichewicz, A.B.; Leffler, D.A.; Sanders, D.S.; Lebwohl, B.; Hadjivassiliou, M. Neurological manifestations of neuropathy and ataxia in celiac disease: A systematic review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pennisi, M.; Bramanti, A.; Cantone, M.; Pennisi, G.; Bella, R.; Lanza, G. Neurophysiology of the “celiac brain”: Disentangling gut-brain connections. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjivassiliou, M.; Croall, I.D.; Zis, P.; Sarrigiannis, P.G.; Sanders, D.S.; Aeschlimann, P.; Grünewald, R.A.; Armitage, P.A.; Connolly, D.; Aeschlimann, D.; et al. Neurologic deficits in patients with newly diagnosed celiac disease are frequent and linked with autoimmunity to transglutaminase 6. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2678–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ford, R.P. The gluten syndrome: A neurological disease. Med. Hypotheses 2009, 73, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L. Brain hypoperfusion and neurological symptoms in celiac disease. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 799–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjivassiliou, M.; Gibson, A.; Davies-Jones, G.A.; Lobo, A.J.; Stephenson, T.J.; Milford-Ward, A. Does Cryptic Gluten Sensitivity play a part in Neurological Illness? Lancet 1996, 346, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjivassiliou, M.; Rao, D.G.; Grinewald, R.A.; Aeschlimann, D.P.; Sarrigiannis, P.G.; Hoggard, N.; Aeschlimann, P.; Mooney, P.D.; Sanders, D.S. Neurological Dysfunction in Coeliac Disease and Non-Coeliac Gluten Sensitivity. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rouvroye, M.D.; Zis, P.; Van Dam, A.M.; Rozemuller, A.J.M.; Bouma, G.; Hadjivassiliou, M. The Neuropathology of Gluten-Related Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luostarinen, L.; Hinamen, S.L.; Luostarinen, M.; Collin, P.; Pirttilä, T. Neuromuscular and sensory disturbances in patients with well-treated coeliac disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, G.; Bordo, B.M.; Schalling, R.; Villanacci, V.; Salemme, M.; Di Bella, C.; Baldini, V.; Bassotti, G. Neurological disorders and celiac disease. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2016, 62, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, T.C.; Lebwohl, B.; Verma, H.; Kumta, N.; Tennyson, C.; Lewis, S.; Scherl, E.; Swaminath, A.; Capiak, K.M.; DiGiacomo, D.; et al. Peripheral neuropathic symptoms in celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2012, 13, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicarelli, G.; Della Rocca, G.; Amboni, M.; Ciacci, C.; Mazzacca, G.; Filla, A.; Barone, P. Clinical and neurological abnormalities in adult celiac disease. Neurol. Sci. 2003, 24, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zis, P.; Julian, T.; Hadjivassiliou, M. Headache associated with coeliac disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ameghino, L.; Farez, M.F.; Wilken, M.; Goicochea, M.T. Headache in Patients with Celiac Disease and Its Response to the Gluten-Free Diet. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2019, 33, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaender, M.; D’Souza, W.J.; Trost, N.; Litewka, L.; Paine, M.; Cook, M. Visual disturbances representing occipital lobe epilepsy in patients with cerebral calcifications and coeliac disease: A case series. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 1623–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, G.; Bouquet, F.; Greco, L.; Lambertini, A.; Tassinari, C.A.; Ventura, A.; Tassinari, C.A. Coeliac disease, epilepsy, and cerebral calcifications. The Italian Working Group on Coeliac Disease and Epilepsy. Lancet 1992, 340, 439–443. [Google Scholar]
- Magaudda, A.; Dalla Bernardina, B.; De Marco, P.; Sfaello, Z.; Longo, M.; Colamaria, V.; Daniele, O.; Tortorella, G.; Tata, M.A.; Perri, R. Bilateral occipital calcification, epilepsy and coeliac disease: Clinical and neuroimaging features of a new syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1993, 56, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribaldone, D.G.; Astegiano, M.; Fagoonee, S.; Rizzetto, M.; Pellicano, R. Epilepsy and celiac disease: Review of literature. Panminerva Med. 2011, 53, 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Lea, M.E.; Harbord, M.; Sage, M.R. Bilateral occipital calcification associated with celiac disease, folate deficiency, and epilepsy. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1995, 16, 1498–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Zingone, F.; Tomson, T.; Ekbom, A.; Ciacci, C. Increased risk of epilepsy in biopsy-verified celiac disease: A population-based cohort study. Neurology 2012, 78, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, H.C.; Burger, P.C.; Hurwitz, B.J.; Hijmans, J.C.; Grant, J.P. Degeneration of the central nervous system associated with celiac disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 1982, 53, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, S.; Messelmani, M.; Zaouali, J.; Mrissa, R. Cognitive impairment in celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity: Review of literature on the main cognitive impairments, the imaging and the effect of gluten free diet. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2018, 118, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Di Silvio, B.; Fernstrom, M.H.; Fernstrom, J.D. Meal ingestion, amino acids and brain neurotransmitters: Effects of dietary protein source on serotonin and catecholamine synthesis rates. Physiol. Behav. 2009, 98, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.T.; Murray, J.A.; Greenaway, M.C.; Parisi, J.E.; Josephs, K.A. Cognitive impairment and celiac disease. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clappison, E.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Zis, P. Psychiatric manifestations of coeliac disease, a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campagna, G.; Pesce, M.; Tatangelo, R.; Rizzuto, A.; La Fratta, I.; Grilli, A. The progression of coeliac disease: Its neurological and psychiatric implications. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.F.; Gerdes, L.U. Meta-analysis on anxiety and depression in adult celiac disease. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2012, 125, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hees, N.J.; Van der Does, W.; Giltay, E.J. Coeliac disease, diet adherence and depressive symptoms. J. Psychosom. Res. 2013, 74, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Addolorato, G. Anxiety but not depression decreases in coeliac patients after one-year gluten-free diet: A longitudinal study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 36, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederhofer, H.; Pittschieler, K. A preliminary investigation of ADHD symptoms in persons with celiac disease. J. Atten. Disord. 2006, 10, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Underhill, J.; Liu, X.H.; Sham, P.C.; Donaldson, P.; Murray, R.M.; Wright, P.; Collier, D.A. Transmission disequilibrium analysis of HLA class II DRB1, DQA1, DQB1 and DPB1 polymorphisms in schizophrenia using family trios from a Han Chinese population. Schizophr. Res. 2001, 49, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicano, R.; Durazzo, M. Schizophrenia and celiac disease: Which is the role of the gluten-free diet? Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 806–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valvano, M.; Longo, S.; Stefanelli, G.; Frieri, G.; Viscido, A.; Latella, G. Celiac disease, gluten-free diet, and metabolic and liver disorders. Nutrients 2020, 12, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haggård, L.; Glimberg, I.; Lebwohl, B.; Sharma, R.; Verna, E.C.; Green, P.H.; Ludvigsson, J.F. High prevalence of celiac disease in autoimmune hepatitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2693–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukinen, K.; Halme, L.; Collin, P.; Färkkilä, M.; Mäki, M.; Vehmanen, P.; Partanen, J.; Höckerstedt, K. Celiac disease in patients with severe liver disease: Gluten-free diet may reverse hepatic failure. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zali, M.R.; Nejad, M.R.; Rostami, K.; Moayed, S. Liver complications in celiac disease. Hepat. Mon. 2011, 11, 333–341. [Google Scholar]
- Sainsbury, A.; Sanders, D.S.; Ford, A.C. Meta-analysis: Coeliac disease and hypertransaminasaemia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hussaini, A.; Basheer, A.; Czaja, A.J. Liver failure unmasks celiac disease in a child. Ann. Hepatol. 2013, 12, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Bai, J.C.; Biagi, F.; Card, T.R.; Ciacci, C.; Ciclitira, P.J.; Green, P.H.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Holdoway, A.; Van Heel, D.A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of adult coeliac disease: Guidelines from the British Society of Gastroenterology. Gut 2014, 63, 1210–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tersigni, C.; Castellani, R.; de Waure, C.; Fattorossi, A.; De Spirito, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Scambia, G.; Di Simone, N. Celiac disease and reproductive disorders: Meta-analysis of epidemiologic associations and potential pathogenic mechanisms. Hum. Reprod. Update 2014, 20, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tata, L.J.; Card, T.R.; Logan, R.F.A.; Hubbard, R.B.; Smith, C.J.P.; West, J. Fertility and pregnancy-related events in women with celiac disease: A population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moleski, S.M.; Lindenmeyer, C.C.; Veloski, J.J.; Miller, R.S.; Miller, C.L.; Kastenberg, D.; DiMarino, A.J. Increased rates of pregnancy complications in women with celiac disease. Ann. Gastroenterol. Q. Publ. Hell. Soc. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 236–240. [Google Scholar]
- Rujner, J. Age at menarche in girls with celiac disease. Ginekol. Pol. 1999, 70, 359–362. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, R.; Holmes, G.K.; Cooke, W.T. Coeliac disease, fertility, and pregnancy. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1982, 17, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, P.; Vilska, S.; Heinonen, P.K.; Hällström, O.; Pikkarainen, P. Infertility and coeliac disease. Gut 1996, 39, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitale, J. Recurrent miscarriage. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 783–784. [Google Scholar]
- Fortunato, F.; Martinelli, D.; Prato, R.; Pedalino, B. Results from Ad Hoc and Routinely Collected Data among Celiac Women with Infertility or Pregnancy Related Disorders: Italy, 2001–2011. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, e614269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadir, M.; Iranikhah, A.; Jandaghi, M.; Joukar, F.; Sedigh-Rahimabadi, M.; Mansour-Ghanaei, F. Unexplained infertility as primary presentation of celiac disease, a case report and literature review. Iran. J. Reprod. Med. 2011, 9, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Castaño, M.; Gómez-Gordo, R.; Cuevas, D.; Núñez, C. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prevalence of Coeliac Disease in Women with Infertility. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Arora, S.; Lal, S.; Strand, T.A.; Makharia, G.K. Celiac Disease in Women With Infertility: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 50, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glimberg, I.; Haggård, L.; Lebwohl, B.; Green, P.H.R.; Ludvigsson, J.F. The prevalence of celiac disease in women with infertility—A systematic review with meta-analysis. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2021, 20, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, K.S.; Jayanthi, V.; Probert, C.S.J.; Stewart, C.R.; Mayberry, J.F. Infertility, Obstetric and Gynaecological Problems in Coeliac Sprue. Dig. Dis. 1994, 12, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farthing, M.J.; Rees, L.H.; Edwards, C.R.; Dawson, A.M. Male gonadal function in coeliac disease: 2. Sex hormones. Gut 1983, 24, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakker, S.F.; Tushuizen, M.E.; von Blomberg, B.M.; Bontkes, H.J.; Mulder, C.J.; Simsek, S. Screening for coeliac disease in adult patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: Myths, facts and controversy. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2016, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freeman, H.J. Endocrine manifestations in celiac disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 8472–8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, D. Endocrinopathies in celiac disease: When the endocrinologist sees what is invisible to the gastroenterologist. Acta Biomed. 2018, 89, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Walker-Smith, J.A. Diabetes and coeliac disease. Lancet 1969, 2, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfström, P.; Sundström, J.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Associations between coeliac disease and type 1 diabetes. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, B.T.; Holmes, G.K.; Cooke, W.T. Coeliac disease and immunological disorders. Br. Med. J. 1978, 1, 537539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Midhagen, G.; Järnerot, G.; Kraaz, W. Adult coeliac disease within a defined geographic area in Sweden. A study of prevalence and associated diseases. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1988, 23, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Driessche, A.; Eenkhoorn, V.; Van Gaal, L.; De Block, C. Type 1 diabetes and autoimmune polyglandular syndrome: A clinical review. Neth. J. Med. 2009, 67, 376–387. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhotia, M.; Pahadia, H.R.; Kumar, H.; Singh, J.; Tak, S. A Case of Autoimmune Polyglandular Syndrome (APS) Type II with Hypothyroidism, Hypoadrenalism, and Celiac Disease. A Rare Combination. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, OD01–OD03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsueda, K.; Rosenberg, I.H. Malabsorption with idiopathic hypoparathyroidism responding to treatment for coincident celiac sprue. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1982, 27, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Saini, S.; Makharia, G.K.; Datta Gupta, S.; Goswami, R. Prevalence of coeliac disease in idiopathic hypoparathyroidism and effect of glutenfree diet on calcaemic control. Clin. Endocrinol. 2016, 84, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfström, P.; Montgomery, S.M.; Kämpe, O.; Ekbom, A.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Risk of primary adrenal insufficiency in patients with celiac disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3595–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, A.G.; Aarsetøy, H.; Undlien, D.E.; Hovdenak, N.; Aksnes, L.; Husebye, E.S. High frequency of coeliac disease among patients with autoimmune adrenocortical failure. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 38, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrubisková, K.; Jackuliak, P.; Vanuga, P.; Pura, M.; Payer, J. Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 2 associated with autoimmune hypophysitis and coeliac disease. Vnitr. Lek. 2010, 56, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Delvecchio, M.; De Bellis, A.; Francavilla, R.; Rutigliano, V.; Predieri, B.; Indrio, F.; De Venuto, D.; Sinisi, A.A.; Bizzarro, A.; Bellastella, A.; et al. Antipituitary antibodies in children with newly diagnosed celiac disease: A novel finding contributing to lineargrowth impairment. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meazza, C.; Pagani, S.; Laarej, K.; Cantoni, F.; Civallero, P.; Boncimino, A.; Bozzola, M. Short stature in children with coeliac disease. Pediatric Endocrinol. Rev. 2009, 6, 457–463. [Google Scholar]
- Delvecchio, M.; Faienza, M.F.; Lonero, A.; Rutigliano, V.; Francavilla, R.; Cavallo, L. Prolactin may be increased in newly diagnosed celiac children and adolescents and decreases after 6 months of gluten free diet. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2014, 81, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saari, A.; Harju, S.; Mäkitie, O.; Saha, M.T.; Dunkel, L.; Sankilampi, U. Systematic growth monitoring for the early detection of celiac disease in children. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, e1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonti, R.; Lebwohl, B.; Lewis, S.K.; Daya, H.A.; Klavan, H.; Aguilar, K.; Green, P.H. Men with celiac disease are shorter than their peers in the general population. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, J.C.W.; Grote, F.K.; Oostdijk, W.; Wit, J.M. Short stature and the probability of coeliac disease, in the absence of gastrointestinal symptoms. Arch. Dis. Child. 2004, 89, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.D.; Singh, P.; Farooqui, N.; Strand, T.; Ahuja, V.; Makharia, G.K. Prevalence of celiac disease in patients with short stature: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Grade 0 | Grade I | Grade II | Grade III | Grade IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No defects. | Defect in enamel color (yellow or brown marks) | Slight structural enamel defects (rough surface, groves) | Evident structural defects (deep groves, large opacities) | Severe structural defects (lesions) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Durazzo, M.; Ferro, A.; Brascugli, I.; Mattivi, S.; Fagoonee, S.; Pellicano, R. Extra-Intestinal Manifestations of Celiac Disease: What Should We Know in 2022? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010258
Durazzo M, Ferro A, Brascugli I, Mattivi S, Fagoonee S, Pellicano R. Extra-Intestinal Manifestations of Celiac Disease: What Should We Know in 2022? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(1):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010258
Chicago/Turabian StyleDurazzo, Marilena, Arianna Ferro, Isabella Brascugli, Simone Mattivi, Sharmila Fagoonee, and Rinaldo Pellicano. 2022. "Extra-Intestinal Manifestations of Celiac Disease: What Should We Know in 2022?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 1: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010258
APA StyleDurazzo, M., Ferro, A., Brascugli, I., Mattivi, S., Fagoonee, S., & Pellicano, R. (2022). Extra-Intestinal Manifestations of Celiac Disease: What Should We Know in 2022? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(1), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010258









