Mediators of Regional Kidney Perfusion during Surgical Pneumo-Peritoneum Creation and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury—A Review of Basic Physiology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Arterial Blood Supply and Renal Blood Flow
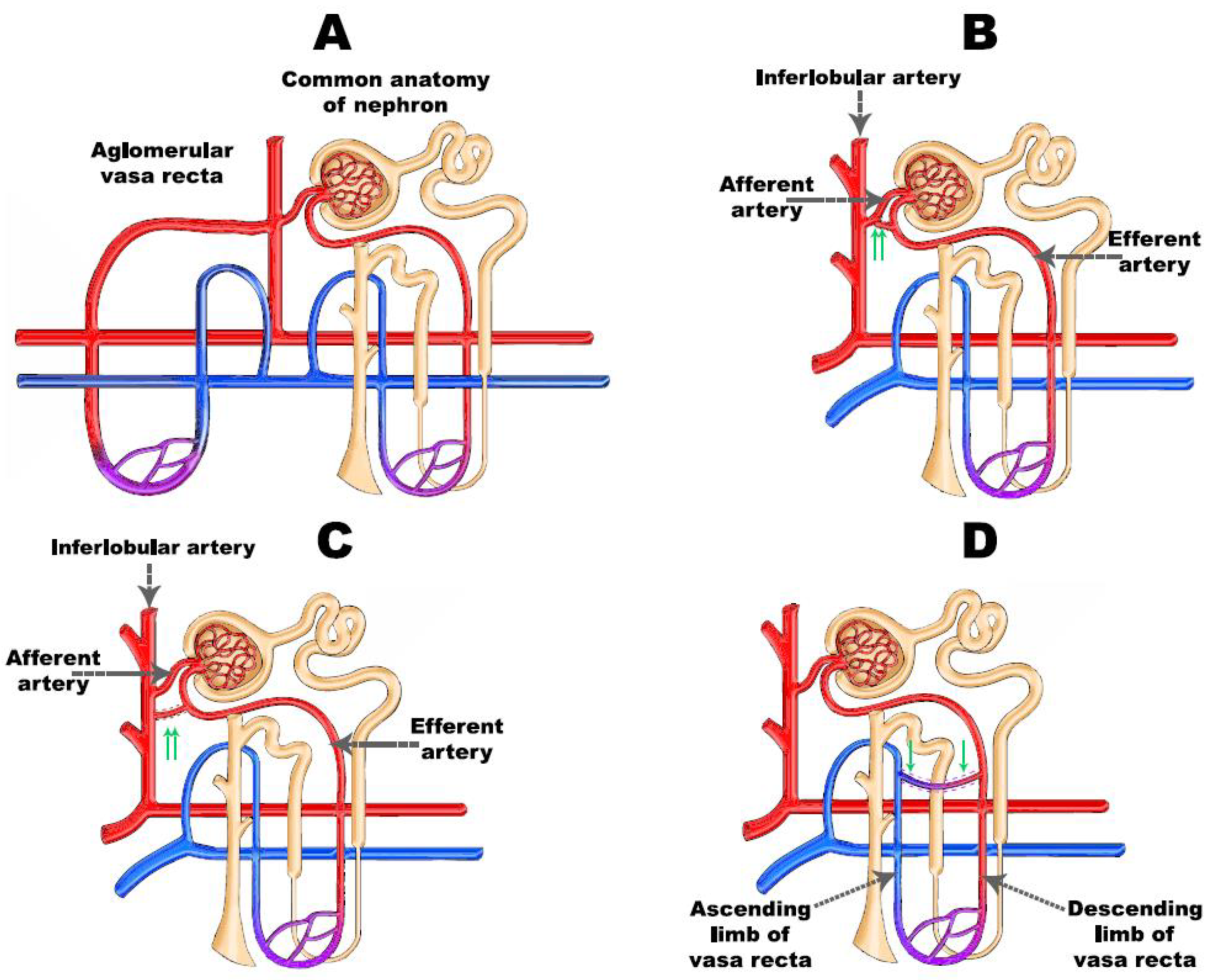
2.1. Renal Medullary Circulation
2.2. The Effects of Pneumoperitoneum on Renal Blood Flow
2.3. The Direct Effect of CO2 on Renal Vasculature
3. Venous Drainage and Congestion
3.1. The Effect of Pneumoperitoneum on the Blood Flow in the Inferior Vena Cava
3.2. The Backward Effect of Increased Renal Venous Pressure
3.3. The Role of the Renal Capsule
3.4. The Determinants of Renal Venous Pressure
4. Lymphatic Drainage of Renal Tissues
4.1. The Hilar and the Cortical Route
4.2. The Microanatomy of Lymphatic Capillaries
4.3. Lymph Moving Forces
4.4. The Turnover of Albumin, the Key Element of the Interstitium
5. Humoral Factors
5.1. The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
5.2. The Tubuloglomerular Feedback
5.3. Nitric Oxide
5.4. The Impact of Obstructive Jaundice
6. Ischemic-Reperfusion Injury
6.1. The No-Reflow Phenomenon
6.2. Protective Molecular Mechanisms
6.3. Protective Drugs
7. Inflammatory Response
7.1. Eicosanoids
7.2. Interleukin Family
7.3. Insulin-like Growth Factor 1
8. The Effects of Anesthesia
9. The Effects of Retroperitoneal Insufflation
10. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, Y.-S.; Jun, I.-G.; Go, Y.; Song, J.-G.; Hwang, G.-S. Comparison of acute kidney injury between open and laparoscopic pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy: Propensity score analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, L.S.; Eggers, P.W.; Star, R.A.; Kimmel, P.L. Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease as Interconnected Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, R.; Hsu, C.-Y. The Role of Acute Kidney Injury in Chronic Kidney Disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2016, 36, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferenbach, D.A.; Bonventre, J.V.; Division, B.E.; Hospital, W. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease: From the laboratory to the clinic. Nephrol. Ther. 2017, 12 (Suppl. S1), S41–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, A.; Lee, J.E.; Kwon, G.-Y.; Huh, W.; Lee, H.M.; Kim, Y.-G.; Kim, D.J.; Oh, H.Y.; Choi, H.Y. Post-operative acute kidney injury in patients with renal cell carcinoma is a potent risk factor for new-onset chronic kidney disease after radical nephrectomy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3496–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizota, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hamada, M.; Matsukawa, S.; Shimizu, S.; Kai, S. Intraoperative oliguria predicts acute kidney injury after major abdominal surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srisawat, N.; Kongwibulwut, M.; Laoveeravat, P.; Lumplertgul, N.; Chatkaew, P.; Saeyub, P.; Latthaprecha, K.; Peerapornratana, S.; Tiranathanagul, K.; Eiam-Ong, S.; et al. The role of intraoperative parameters on predicting laparoscopic abdominal surgery associated acute kidney injury. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalabi, A.; Nativ, O.; Sumri, M.; Bishara, B.; Khoury, W.; Awad, H.; Nativ, O.; Abassi, Z. Impact of Pneumoperitoneum on the Post-Operative Renal Function and Level of Acute Kidney Injury Markers: Comparison between Laparoscopic and Open Nephrectomy. Int. Arch. Urol. Complicat. 2017, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.K.; McCauley, J.; Cottam, D.; Mattar, S.G.; Holover, S.; Dallal, R.; Lord, J.; Danner, O.; Ramanathan, R.; Eid, G.; et al. Acute changes in renal function after laparoscopic gastric surgery for morbid obesity. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2006, 2, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbert, S.D.; Kork, F.; Jackson, M.L.; Vanga, N.; Ghebremichael, S.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Eltzschig, H.K. Perioperative Acute Kidney Injury. Anesthesiology 2020, 132, 180–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meersch, M.; Schmidt, C.; Zarbock, A. Perioperative Acute Kidney Injury. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 125, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalfino, L.; Tullo, L.; Donadio, I.; Malcangi, V.; Brienza, N. Intra-abdominal hypertension and acute renal failure in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 34, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, A.W.; The Pediatric Guidelines Sub-Committee for the World Society of the Abdominal Compartment Syndrome; Roberts, D.J.; De Waele, J.; Jaeschke, R.; Malbrain, M.L.N.G.; De Keulenaer, B.; Duchesne, J.; Bjorck, M.; Leppaniemi, A.; et al. Intra-abdominal hypertension and the abdominal compartment syndrome: Updated consensus definitions and clinical practice guidelines from the World Society of the Abdominal Compartment Syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1190–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliver, J.; Hall, J.E.; Hall, M.E.; Guyton, A.C. Guyton 14th edition. Hilos Tensados. 2019, 1, 1–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, D.A.; Deen, W.M.; Brenner, B.M. Handbook of Physiology. Renal Physiology; American Physiological Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1992; Volume I, pp. 545–638. [Google Scholar]
- Calzavacca, P.; Evans, R.; Bailey, M.; Lankadeva, Y.R.; Bellomo, R.; May, C.N. Long-term measurement of renal cortical and medullary tissue oxygenation and perfusion in unanesthetized sheep. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 308, R832–R839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrett, C.J.; Navakatikyan, M.A.; Malpas, S.C. Long-term control of renal blood flow: What is the role of the renal nerves? Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 280, R1534–R1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, D.L. Importance of the renal medullary circulation in the control of sodium excretion and blood pressure. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 284, R13–R27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabriel Navar, L. Regulation of renal hemodynamics. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275 Pt 2, 221–235. [Google Scholar]
- Lydon, T.K.; Crawford, C.; Peppiatt-Wildman, C.; Peppiatt-Wildman, C.M. Renal pericytes: Regulators of medullary blood flow. Acta Physiol. 2012, 207, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishara, B.; Karram, T.; Khatib, S.; Ramadan, R.; Schwartz, H.; Hoffman, A.; Abassi, Z. Impact of pneumoperitoneum on renal perfusion and excretory function: Beneficial effects of nitroglycerine. Surg. Endosc. 2008, 23, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, G.; Samoni, S.; De Rosa, S.; Ronco, C. The Pathophysiological Hypothesis of Kidney Damage during Intra-Abdominal Hypertension. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wever, K.E.; Bruintjes, M.H.D.; Warlé, M.C.; Hooijmans, C.R. Renal Perfusion and Function during Pneumoperitoneum: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Animal Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morya, R.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, P. Anatomical and Physiological Similarities of Kidney in Different Experimental Animals Used for Basic Studies. J. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2018, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casellas, D.; Mimran, A. Shunting in renal microvasculature of the rat: A scanning electron microscopic study of corrosion casts. Anat. Rec. 1981, 201, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, N.E.; Rapp, J.P. The distribution of valves in rat kidney arteries. Anat. Rec. 1969, 165, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, D.B.; Creasey, M. The fine structure of the intra-arterial cushions at the origins of the juxtamedullary afferent arterioles in the rat kidney. J. Anat. 1971, 110, 409–419. [Google Scholar]
- Pallone, T.L.; Silldorff, E.P.; Turner, M.R. Intrarenal blood flow: Microvascular anatomy and the regulation of medullary perfusion. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1998, 25, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzavacca, P.; May, C.N.; Bellomo, R. Glomerular haemodynamics, the renal sympathetic nervous system and sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 2178–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sgouralis, I.; Evans, R.G.; Layton, A.T. Renal medullary and urinary oxygen tension during cardiopulmonary bypass in the rat. Math. Med. Biol. A J. IMA 2016, 34, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pannabecker, T.L.; Layton, A.T. Targeted delivery of solutes and oxygen in the renal medulla: Role of microvessel architecture. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2014, 307, F649–F655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roman, R.J.; Cowley, A.W.; Garcia-Estañ, J.; Lombard, J.H. Pressure-diuresis in volume-expanded rats. Cortical and medullary hemodynamics. Hypertension 1988, 12, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crawford, C.; Kennedy-Lydon, T.; Sprott, C.; Desai, T.; Sawbridge, L.; Munday, J.; Unwin, R.; Wildman, S.; Peppiatt-Wildman, C. An intact kidney slice model to investigate vasa recta properties and function in situ. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 2012, 120, p17–p31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, A.W. Role of the renal medulla in volume and arterial pressure regulation. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1997, 273, R1–R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, P.M. Renal oxygen delivery: Matching delivery to metabolic demand. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 33, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallone, T.L. Vasoconstriction of outer medullary vasa recta by angiotensin II is modulated by prostaglandin E2. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1994, 266, F850–F857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, C.; Kennedy-Lydon, T.M.; Callaghan, H.; Sprott, C.; Simmons, R.L.; Sawbridge, L.; Syme, H.M.; Unwin, R.J.; Wildman, S.S.P.; Peppiatt-Wildman, C.M. Extracellular nucleotides affect pericyte-mediated regulation of rat in situ vasa recta diameter. Acta Physiol. 2011, 202, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmeda, A.F.; Johns, E.J. The regulation of blood perfusion in the renal cortex and medulla by reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide in the anaesthetised rat. Acta Physiol. 2011, 204, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, N.W.; Mattson, D.L. Role of l-arginine uptake mechanisms in renal blood flow responses to angiotensin II in rats. Acta Physiol. 2011, 203, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzavacca, P.; Bailey, M.; Velkoska, E.; Burrell, L.M.; Ramchandra, R.; Bellomo, R.; May, C.N. Effects of Renal Denervation on Regional Hemodynamics and Kidney Function in Experimental Hyperdynamic Sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, e401–e409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, P.B.; Ehmke, H.; Nafz, B.; Kirchheim, H.R. Sympathetic modulation of renal autoregulation by carotid occlusion in conscious dogs. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1990, 258, F364–F370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, Y.; Head, G.; Denton, K.; May, C.N.; Schlaich, M.P. Role of the Sympathetic Nervous System and Its Modulation in Renal Hypertension. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pontes, R.B.; Girardi, A.C.C.; Nishi, E.E.; Campos, R.R.; Bergamaschi, C.T. Crosstalk between the renal sympathetic nerve and intrarenal angiotensin II modulates proximal tubular sodium reabsorption. Exp. Physiol. 2015, 100, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, D.L.; Lu, S.; Roman, R.J.; Cowley, A.W. Relationship between renal perfusion pressure and blood flow in different regions of the kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1993, 264, R578–R583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demyttenaere, S.V.; Taqi, A.; Polyhronopoulos, G.N.; Bergman, S.; Stanbridge, D.D.; Unikowsky, B.; Carli, F.; Fried, G.M.; Feldman, L.S. Targeting individual hemodynamics to maintain renal perfusion during pneumoperitoneum in a porcine model. Surgery 2007, 142, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotkoff, L.M.; Lilienfield, L.S. Extravascular renal albumin. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1967, 212, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veress, J. Neues Instrument zur Ausführung von Brust- oder Bauchpunktionen und Pneumothoraxbehandlung. DMW Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 1938, 64, 1480–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neudecker, J.; Sauerland, S.; Neugebauer, E.; Bergamaschi, R.; Bonjer, H.J.; Cuschieri, A.; Fuchs, K.-H.; Jacobi, C.; Jansen, F.W.; Koivusalo, A.-M.; et al. The European Association for Endoscopic Surgery clinical practice guideline on the pneumoperitoneum for laparoscopic surgery. Surg. Endosc. 2002, 16, 1121–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, M.; Sägesser, H.; Reichen, J.; Krähenbühl, L. Alterations in hemodynamics and hepatic and splanchnic circulation during laparoscopy in rats. Surg. Endosc. 2001, 15, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.M.; Troy, J.L.; Daugharty, T.M. The dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. J. Clin. Investig. 1971, 50, 1776–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, M.; Lopes, R.I.; Borba, M.; Omokawa, M.; Naufal, R.; Miyaji, K.; Matsumura, N.; Vieira, N.; Pereira, P.R.B. Comparison of the Effects of Carbon Dioxide and Helium Pneumoperitoneum on Renal Function. J. Endourol. 2008, 22, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundell, S.M.; Tsopelas, C.; Chatterton, B.; Touloumtzoglou, J.; Hewett, P.J. Experimental study of peritoneal blood flow and insufflation pressure during laparoscopy. Br. J. Surg. 2002, 89, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, C.; Boccara, G.; Pouzeratte, Y.; Eliet, J.; Gal, C.S.-L.; Vergnes, C.; Bichet, D.G.; Guillon, G.; Fabre, J.M.; Colson, P. The Relationship among Carbon Dioxide Pneumoperitoneum, Vasopressin Release, and Hemodynamic Changes. Anesth. Analg. 1999, 89, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, T.S.O.; Ladeira, R.T.; Bafi, A.T.; de Azevedo, L.C.P.; Machado, F.R.; Freitas, F.G.R. Duration of hemodynamic effects of crystalloids in patients with circulatory shock after initial resuscitation. Ann. Intensive Care 2014, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Freitas, P.F.S.; Durães, L.C.; De Carvalho, F.A.N.O.; Duarte, S.A.C.; Carneiro, F.P.; De Sousa, J.B. Effects of pneumoperitoneum with carbon dioxide and helium on renal function and morphology in rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2013, 28, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, A.W.; Azadzoi, K.M.; Hatzichristou, D.G.; Siroky, M.B.; Krane, R.J.; Babayan, R.K. Effects of Intra-Abdominal Pressure on Renal Tissue Perfusion During Laparoscopy*. J. Endourol. 1994, 8, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.; MacIntyre, J.; Shearer; Craigen, I.; Smith, G. Effect of carbon dioxide on renal blood flow. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1970, 219, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beguin, F.; Dunnihoo, D.; Quilligan, E. Effect of carbon dioxide elevation on renal blood flow in the fetal lamb in utero. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1974, 119, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C.L.; Schlader, Z.J.; Reed, E.L.; Worley, M.L.; Johnson, B.D. Renal and segmental artery hemodynamic response to acute, mild hypercapnia. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2020, 318, R822–R827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuto, K.; Kitano, S.; Yoshida, T.; Bandoh, T.; Mitarai, Y.; Kobayashi, M. Hemodynamic and arterial blood gas changes during carbon dioxide and helium pneumoperitoneum in pigs. Surg. Endosc. 1995, 9, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, E.M.; Monk, T.G.; Wolf, J.S.; Hicks, M.; Clayman, R.V.; Gardner, S.; Humphrey, P.A.; Sharp, T.; Martin, K. The effect of prolonged pneumoperitoneum on renal function in an animal model. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 1996, 182, 317–328. [Google Scholar]
- Gelman, S.; Mushlin, P.S. Catecholamine-induced Changes in the Splanchnic Circulation Affecting Systemic Hemodynamics. Anesthesiology 2004, 100, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddy, N.P.K.; Ravi, K.P.; Dhanalakshmi, P.; Annigeri, R.; Ramakrishnan, N.; Venkataraman, R. Epidemiology, outcomes and validation of RIFLE and AKIN criteria in acute kidney injury (AKI) in critically ill patients: Indian perspective. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navar, L.G. Physiology: Hemodynamics, endothelial function, renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system, sympathetic nervous system. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2014, 8, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winton, F.R. The influence of venous pressure on the isolated mammalian kidney. J. Physiol. 1931, 72, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, W.D.; Wégria, R.; Keating, R.P.; Ward, H.P. Effect of increased renal venous pressure on renal function. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1949, 157, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, B.E.; De Wardener, H.E. Intrarenal pressure. J. Physiol. 1954, 123, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semple, S.J.G.; DE Wardener, H.E. Effect of Increased Renal Venous Pressure on Circulatory “Autoregulation” of Isolated Dog Kidneys. Circ. Res. 1959, 7, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hinshaw, L.B.; Brake, C.M.; Iampietro, P.F.; Emerson, T.E. Effect of increased venous pressure on renal hemodynamics. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1963, 204, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopitkó, C.; Gondos, T.; Fülöp, T.; Medve, L. Reinterpreting Renal Hemodynamics: The Importance of Venous Congestion and Effective Organ Perfusion in Acute Kidney Injury. Am. J. Med Sci. 2020, 359, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, E.; Lockhart, J.C.; Larson, T.S. Relation between vasa recta blood flow and renal interstitial hydrostatic pressure during pressure natriuresis. Circ. Res. 1992, 71, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaffee, W.; Hodgins, S.; McGee, W.T. Tissue Edema, Fluid Balance, and Patient Outcomes in Severe Sepsis: An Organ Systems Review. J. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 33, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damman, K.; Navis, G.; Smilde, T.D.; Voors, A.A.; Van Der Bij, W.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Hillege, H.L. Decreased cardiac output, venous congestion and the association with renal impairment in patients with cardiac dysfunction. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2007, 9, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damman, K.; Van Deursen, V.M.; Navis, G.; Voors, A.A.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Hillege, H.L. Increased Central Venous Pressure Is Associated With Impaired Renal Function and Mortality in a Broad Spectrum of Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nohria, A.; Hasselblad, V.; Stebbins, A.; Pauly, D.F.; Fonarow, G.C.; Shah, M.; Yancy, C.W.; Califf, R.M.; Stevenson, L.W.; Hill, J.A. Cardiorenal Interactions: Insights From the ESCAPE Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirsch, A.J.; Hensle, T.W.; Chang, D.T.; Kayton, M.L.; Olsson, C.A.; Sawczuk, I.S. Renal effects of CO2 insufflation: Oliguria and acute renal dysfunction in a rat pneumoperitoneum model. Urology 1994, 43, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doty, J.M.; Saggi, B.H.; Sugerman, H.J.; Blocher, C.R.; Pin, R.; Fakhry, I.; Gehr, T.W.B.; Sica, D.A. Effect of Increased Renal Venous Pressure on Renal Function. J. Trauma Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 1999, 47, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, C.; Sade, M.; Kirkali, Z. Renal effects of carbon dioxide insufflation in rabbit pneumoretroperitoneum model. J. Endourol. 1998, 12, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopitkó, C.; Medve, L.; Gondos, T. Pathophysiology of renal blood supply. New Med. 2016, 20, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopitkó, C.; Medve, L.; Gondos, T. Renoprotective Postoperative Monitoring: What Is the Best Method for Computing Renal Perfusion Pressure? An Observational, Prospective, Multicentre Study. Nephron 2018, 139, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, J.; Raine, A.; Ledingham, J. Raised venous pressure: A direct cause of renal sodium retention in oedema? Lancet 1988, 331, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.H.; Fulenwider, J.T. Renal Decapsulation in the Prevention of Post-ischemic Oliguria. Ann. Surg. 1977, 186, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.; Wang, P.; Ding, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y. A Modified Model of the Abdominal Compartment Syndrome. J. Trauma Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 2011, 70, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, P.S.; Hong, J.; Windsor, J.A.; Itkin, M.; Phillips, A.R.J. Renal Lymphatics: Anatomy, Physiology, and Clinical Implications. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuttino, J.T.; Clark, R.L.; Jennette, J.C. Microradiographic demonstration of human intrarenal microlymphatic pathways. Urol. Radiol. 1989, 11, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, R.E.; Teague, R.A.; Gabel, J.C. Lymphatic drainage reduces intestinal edema and fluid loss. Lymphology 1998, 31, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ratnayake, B.; Escott, A.B.J.; Phillips, A.R.J.; Windsor, J.A. The anatomy and physiology of the terminal thoracic duct and ostial valve in health and disease: Potential implications for intervention. J. Anat. 2018, 233, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dumont, A.E.; Clauss, R.H.; Reed, G.E.; Tice, D.A. Lymph Drainage in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1963, 269, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosin, D.; Brasesco, O.; Varela, J.; Saber, A.A.; You, S.; Rosenthal, R.J.; Cohn, S.M. Low-Pressure Laparoscopy May Ameliorate Intracranial Hypertension and Renal Hypoperfusion. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. 2002, 12, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, S.E.; Bradley, G.P. The effect of increased intra-abdominal pressure on renal function in man 1. J. Clin. Investig. 1947, 26, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Seigneux, S.; Klopfenstein, C.-E.; Iselin, C.; Martin, P.-Y.; Meyrier, A. The risk of acute kidney injury following laparoscopic surgery in a chronic kidney disease patient. NDT Plus 2011, 4, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, G.H.; Morris, B. The lymphatics of the kidney and the formation of renal lymph. J. Physiol. 1971, 214, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rohn, D.A.; Stewart, R.H.; Elk, J.R.; Laine, G.A.; Drake, R.E. Renal lymphatic function following venous pressure elevation. Lymphology 1996, 29, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Földi, M. The volume of renal lymph-flow. Lancet 1963, 281, 831–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, A.J. Distribution of the lymphatics of the human kidney as shown in a case of carcinomatous permeation. Arch. Pathol. 1949, 47, 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Cockett, A.T. Lymphatic network of kidney I. anatomic and physiologic considerations. Urology 1977, 9, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuttino, J.T.; Jennette, J.C.; Clark, R.L.; Kwock, L. Renal medullary lymphatics: Microradiographic, light, and electron microscopic studies in pigs. Lymphology 1985, 18, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Rusznyak, I.; Foldi, M.; Szabo, G.; Pierre, R.L.S. Lymphatics and lymph circulation—Physiology and pathology. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1968, 255, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmali, R.J.; Suami, H.; Wood, C.G.; Karam, J.A. Lymphatic drainage in renal cell carcinoma: Back to the basics. Br. J. Urol. 2014, 114, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmes, M.J.; O’Morchoe, P.J.; O’Morchoe, C.C.C. Morphology of the intrarenal lymphatic system. Capsular and hilar communications. Am. J. Anat. 1977, 149, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranghino, A.; Segoloni, G.P.; Lasaponara, F.; Biancone, L. Lymphatic disorders after renal transplantation: New insights for an old complication. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keyl, M.J.; Scott, J.B.; Dabney, J.M.; Haddy, F.J.; Harvey, R.B.; Bell, R.D.; Ginn, H.E. Composition of canine renal hilar lymph. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1965, 209, 1031–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger, H.; Bonani, M.; Segerer, S. The role of lymphatics in renal inflammation. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2012, 27, 2634–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stuht, S.; Gwinner, W.; Franz, I.; Schwarz, A.; Jonigk, D.; Kreipe, H.; Kerjaschki, D.; Haller, H.; Mengel, M. Lymphatic Neoangiogenesis in Human Renal Allografts: Results from Sequential Protocol Biopsies. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdani, S.; Navis, G.; Hillebrands, J.-L.; Van Goor, H.; van den Born, J. Lymphangiogenesis in renal diseases: Passive bystander or active participant? Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2014, 16, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Akasaka, Y.; Kiguchi, H.; Akishima-Fukasawa, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Ito, K.; Kimura-Matsumoto, M.; Ishiguro, S.; Morita, H.; Sato, S.; et al. The human renal lymphatics under normal and pathological conditions. Histopathology 2006, 49, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cuttino, J.; Clark, R.; Fried, F.; Stevens, P. Microradiographic demonstration of pyelolymphatic backflow in the porcine kidney. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1978, 131, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bidgood, W.D.; Cuttino, J.T.; Clark, R.L.; Volberg, F.M. Pyelovenous and Pyelolymphatic Backflow During Retrograde Pyelography in Renal Vein Thrombosis. Investig. Radiol. 1981, 16, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobison, D.M. Routes of absorption in hydronephrosis; Experimentation with dyes in the totally obstructed ureter. Br. J. Urol. 1929, 1, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojo, A.; Kinugasa, S. Mechanisms of Glomerular Albumin Filtration and Tubular Reabsorption. Int. J. Nephrol. 2012, 2012, 481520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, R.; Smolders, I.; Dupont, A.G. Blood pressure and renal hemodynamic effects of angiotensin fragments. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seeliger, E.; Wronski, T.; Ladwig, M.; Dobrowolski, L.; Vogel, T.; Godes, M.; Persson, P.B.; Flemming, B. The renin-angiotensin system and the third mechanism of renal blood flow autoregulation. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 296, F1334–F1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiu, A.W.; Chang, L.S.; Birkett, D.H.; Babayan, R. Changes in urinary output and electrolytes during gaseous and gasless laparoscopy. Urol. Res. 1996, 24, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, S.; Nutting, A.; Feldman, L.S.; Vassiliou, M.C.; Andrew, C.G.; Demyttenaere, S.; Woo, D.; Carli, F.; Jutras, L.; Buthieu, J.; et al. Elucidating the relationship between cardiac preload and renal perfusion under pneumoperitoneum. Surg. Endosc. 2006, 20, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abassi, Z.; Bishara, B.; Karram, T.; Khatib, S.; Winaver, J.; Hoffman, A. Adverse effects of pneumoperitoneum on renal function: Involvement of the endothelin and nitric oxide systems. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R842–R850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimazutsu, K.; Uemura, K.; Auten, K.M.; Baldwin, M.F.; Belknap, S.W.; La Banca, F.; Jones, M.C.; McClaine, D.J.; McClaine, R.J.; Eubanks, W.S.; et al. Inclusion of a Nitric Oxide Congener in the Insufflation Gas Repletes S-Nitrosohemoglobin and Stabilizes Physiologic Status During Prolonged Carbon Dioxide Pneumoperitoneum. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2009, 2, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishara, B.; Ramadan, R.; Karram, T.; Awad, H.; Abu-Saleh, N.; Winaver, J.; Assadi, A.; Abassi, Z. Nitric oxide synthase inhibition aggravates the adverse renal effects of high but not low intraabdominal pressure. Surg. Endosc. 2009, 24, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishara, B.; Abu-Saleh, N.; Awad, H.; Goltsman, I.; Ramadan, R.; Khamaysi, I.; Abassi, Z. Pneumoperitoneum Aggravates Renal Function in Cases of Decompensated But Not Compensated Experimental Congestive Heart Failure: Role of Nitric Oxide. J. Urol. 2011, 186, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armaly, Z.; Abassi, Z. Deleterious Effects of Increased Intra-Abdominal Pressure on Kidney Function. Adv. Nephrol. 2014, 2014, 731657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naffaa, M.; Abu-Saleh, N.; Awad, H.; Khamaysi, I.; Karram, T.; Azzam, Z.S.; Abassi, Z.; Bishara, B. Acute obstructive jaundice and chronic cirrhosis protect against the adverse renal effects of pneumoperitoneum: Role of nitric oxide. Surg. Endosc. 2013, 27, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajuria, A.; Tay, C.; Shi, J.; Zhao, H.; Ma, D. Anesthetics attenuate ischemia–reperfusion induced renal injury: Effects and mechanisms. Acta Anaesthesiol. Taiwanica 2014, 52, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, M.; Bedja, D.; Thoburn, C.; Gabrielson, K.L.; Racusen, L.C.; Rabb, H. Acute renal venous obstruction is more detrimental to the kidney than arterial occlusion: Implication for murine models of acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2012, 302, F519–F525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.; Phillips, A.R.J.; Loveday, B.; Windsor, J.A. The Potential Role for Xanthine Oxidase Inhibition in Major Intra-abdominal Surgery. World J. Surg. 2007, 32, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, W.; Weinbroum, A.A. Oxidants as important determinants of renal apoptosis during pneumoperitoneum: A study in an isolated perfused rat kidney model. Surg. Endosc. 2011, 26, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, W.; Schreiber, L.; Szold, A.; Klausner, J.M.; Wienbroum, A.A. Renal oxidative stress following CO2 pneumoperitoneum-like conditions. Surg. Endosc. 2008, 23, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kers, J.; Leemans, J.C.; Linkermann, A. An Overview of Pathways of Regulated Necrosis in Acute Kidney Injury. Semin. Nephrol. 2016, 36, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouleti, C.; Mewton, N.; Germain, S. The no-reflow phenomenon: State of the art. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 108, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, C.; Rose, A.; Waite, T.D. Importance of Iron Complexation for Fenton-Mediated Hydroxyl Radical Production at Circumneutral pH. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrer, J.P. The Haber-Weiss reaction and mechanisms of toxicity. Toxicology 2000, 149, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Sawa, Y.; Nishimura, M.; Fukuyama, N.; Ichikawa, H.; Ohtake, S.; Nakazawa, H.; Matsuda, H. Peroxynitrite, a product between nitric oxide and superoxide anion, plays a cytotoxic role in the development of post-bypass systemic inflammatory response. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2004, 26, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sare, M.; Yilmaz, I.; Hamamci, D.; Birincioglu, M.; Özmen, M.; Yesilada, Ö. The effect of carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum on free radicals. Surg. Endosc. 2000, 14, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jávor, S.Z.; Shanava, K.; Hocsák, E.; Kürthy, M.; Lantos, J.; Borsiczky, B.; Takács, I.; Horváth, S.; Balatonyi, B.; Ferencz, S.; et al. Preconditioning is a method that may reduce the negative side-effect of pneumoperitoneum. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 2010, 2, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbuloglu, E.; Yildiz, H.; Senoglu, N.; Coskuner, I.; Yuzbasioglu, M.F.; Kilinc, M.; Dogan, Z.; Deniz, C.; Oksuz, H.; Kantarçeken, B.; et al. Protective Effects of Zinc, Pentoxifylline, and N-Acetylcysteine in an Animal Model of Laparoscopy-Induced Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury of the Small Intestine. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. 2011, 21, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanava, K.; Javor, S.; Kerkadze, V.; Abiatari, I. Protective effects of postconditioning in transvaginally created pneumoperitoneum. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 3861–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pallone, T.L.; Mattson, D.L. Role of nitric oxide in regulation of the renal medulla in normal and hypertensive kidneys. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2002, 11, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotou, A.; Trendelenburg, M.; Osthoff, M. The Lectin Pathway of Complement in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury—Review of Its Significance and the Potential Impact of Therapeutic Interference by C1 Esterase Inhibitor. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrar, C.A.; Easgari, E.; Schwaeble, W.J.; Sacks, S.H. Which pathways trigger the role of complement in ischaemia/reperfusion injury? Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorsuch, W.B.; Chrysanthou, E.; Schwaeble, W.; Stahl, G.L. The complement system in ischemia–reperfusion injuries. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kvarnström, A.; Sokolov, A.; Swartling, T.; Kurlberg, G.; Mollnes, T.E.; Bengtsson, A. Alternative Pathway Activation of Complement in Laparoscopic and Open Rectal Surgery. Scand. J. Immunol. 2012, 76, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, J.M. Triggers of inflammation after renal ischemia/reperfusion. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 123, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oksuz, H.; Bulbuloglu, E.; Senoglu, N.; Ciralik, H.; Yuzbasioglu, M.F.; Kilinc, M.; Dogan, Z.; Goksu, M.; Yildiz, H.; Ozkan, O.V.; et al. Re-Protective Effects of Pre- and Post-Laparoscopy Conditioning, Zinc, Pentoxifylline, and N-acetylcysteine in an Animal Model of Laparoscopy-Induced Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury of the Kidney. Ren. Fail. 2009, 31, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCudden, C.; Clark, E.G.; Akbari, A.; Kong, J.; Kanji, S.; Hiremath, S. N-Acetylcysteine Interference with Creatinine Measurement: An In Vitro Analysis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 1973–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodha, S.; Nazarian, S.; Adshead, J.M.; Vasdev, N.; Mohan, S.G. Effect of Pneumoperitoneum on Renal Function and Physiology in Patients Undergoing Robotic Renal Surgery. Curr. Urol. 2016, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seguro, A.C.; De Figueiredo, L.F.P.; Shimizu, M.H.M. N-acetylcysteine (NAC) Protects Against Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Following Prolonged Pneumoperitoneum in the Rat. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 175, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rifaioglu, M.M.; Davarci, M.; Nacar, A.; Alp, H.; Celik, M.; Sefil, N.K.; Inci, M. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) protects against acute urogenital injury following pneumoperitoneum in the rat. Ren. Fail. 2013, 36, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dogan, Z.; Yuzbasioglu, M.F.; Kurutas, E.B.; Yildiz, H.; Coskuner, I.; Senoglu, N.; Oksuz, H.; Bülbüloglu, E. Thiopental improves renal ischemia–reperfusion injury. Ren. Fail. 2010, 32, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Lei, C.-T.; Zhang, C. Interleukin-6 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Kidney Disease: An Update. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lingohr, P.; Dohmen, J.; Matthaei, H.; Konieczny, N.; Hoffmann, J.; Bölke, E.; Wehner, S.; Kalff, J.C. Cytokine expression in the visceral adipose tissue after laparoscopic and conventional surgery in a rodent model. Eur. J. Med Res. 2016, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozan, R.; Şare, M.; Yilmaz, T.U.; Yüksel, S.; Şeneş, M.; ÇAYCI, A.B.; Bozkurt, Ş. Effectiveness of new parameters in the evaluation of pneumoperitoneum-related acute kidney injury in rats. Turk. J. Med Sci. 2018, 48, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, L.A.; Hale, L.J. Insulin-like Growth Factors and Kidney Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhong, X.; Jin, J.; Li, J.; Meng, X.-M. Potential targeted therapy and diagnosis based on novel insight into growth factors, receptors, and downstream effectors in acute kidney injury and acute kidney injury-chronic kidney disease progression. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, S.; Hirschberg, R. Growth Hormone, the Insulin-Like Growth Factor System, and the Kidney. Endocr. Rev. 1996, 17, 423–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouvy, N.D.; Marquet, R.L.; Tseng, L.N.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Lamberts, S.W.; Jeekel, H.; Bonjer, H.J. Laparoscopic vs conventional bowel resection in the rat. Earlier restoration of serum insulin-like growth factor 1 levels. Surg Endosc. 1998, 12, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, D.W.; Way, D.; Trigg, L.; Langton, D.; McGrath, B.P. Cardiovascular Effects of Volatile Anesthesia in Rabbits. Anesth. Analg. 1991, 73, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, N.D.; Leach, M.K.G.; Rosen, C.M. Effects of halothane, enflurane and isoflurane anaesthesia on renal plasma flow. Br. J. Anaesth. 1990, 65, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pac-Soo, C.K.; Wang, C.; Chakrabarti, M.K.; Whitwam, J.G. Comparison of the effects of inhalational anaesthetic agents on sympathetic activity in rabbits. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2000, 17, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Shibamoto, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Wang, H.-G.; Koyama, S. The Effects of Sevoflurane, Enflurane, and Isoflurane on Baroreceptor-Sympathetic Reflex in Rabbits. Anesth. Analg. 1996, 82, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seagard, J.L.; Hopp, F.A.; Bosnjak, Z.J.; Osborn, J.L.; Kampine, J.P. Sympathetic efferent nerve activity in conscious and isoflurane-anesthetized dogs. Anesthesiology 1984, 61, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, J.; Eriksson, S.; Rundgren, M. Losartan increases renal blood flow during isoflurane anesthesia in sheep. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2001, 45, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.T.; Ota-Setlik, A.; Fu, Y.; Nasr, S.H.; Emala, C.W. Differential Protective Effects of Volatile Anesthetics against Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury In Vivo. Anesthesiology 2004, 101, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemal Tolga, S.; Beliz, B.; Ayten, S. Volatile agents and renal transplantation. Glob. J. Anesthesiol. 2020, 7, 005–008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, H.; Sumita, S.; Wada, H.; Ura, T.; Ikemoto, T.; Nakai, T.; Kanno, M.; Satoh, T. Effects of Sevoflurane and Isoflurane on Renal Function and on Possible Markers of Nephrotoxicity. Anesthesiology 1998, 89, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazze, R.I. Fluorinated anaesthetic nephrotoxicity: An update. Can. Anaesth. Soc. J. 1984, 31 (Suppl. S3), S16–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukazawa, K.; Lee, H.T. Volatile anesthetics and AKI: Risks, mechanisms, and a potential therapeutic window. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.T.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.; Kim, N.; Iv, F.T.B.; D’Agati, V.D.; Emala, C.W., Sr. Isoflurane protects against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury and modulates leukocyte infiltration in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2007, 293, F713–F722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kopitkó, C.; Medve, L.; Gondos, T.; Soliman, K.M.M.; Fülöp, T. Mediators of Regional Kidney Perfusion during Surgical Pneumo-Peritoneum Creation and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury—A Review of Basic Physiology. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102728
Kopitkó C, Medve L, Gondos T, Soliman KMM, Fülöp T. Mediators of Regional Kidney Perfusion during Surgical Pneumo-Peritoneum Creation and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury—A Review of Basic Physiology. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(10):2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102728
Chicago/Turabian StyleKopitkó, Csaba, László Medve, Tibor Gondos, Karim Magdy Mohamed Soliman, and Tibor Fülöp. 2022. "Mediators of Regional Kidney Perfusion during Surgical Pneumo-Peritoneum Creation and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury—A Review of Basic Physiology" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 10: 2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102728
APA StyleKopitkó, C., Medve, L., Gondos, T., Soliman, K. M. M., & Fülöp, T. (2022). Mediators of Regional Kidney Perfusion during Surgical Pneumo-Peritoneum Creation and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury—A Review of Basic Physiology. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(10), 2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102728







