Rapid Molecular Diagnosis of Genetically Inherited Neuromuscular Disorders Using Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
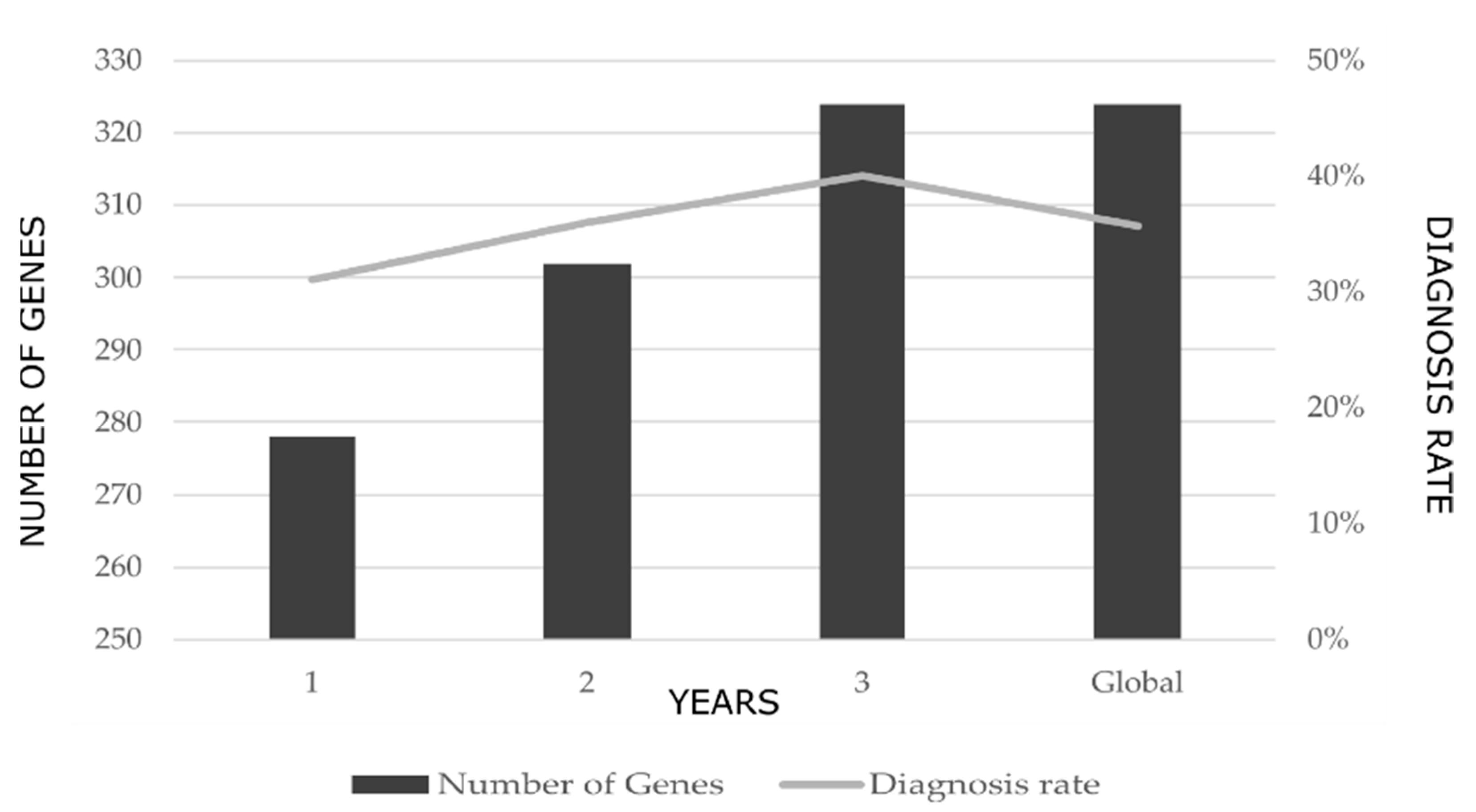
2.1. Diagnostic Rates
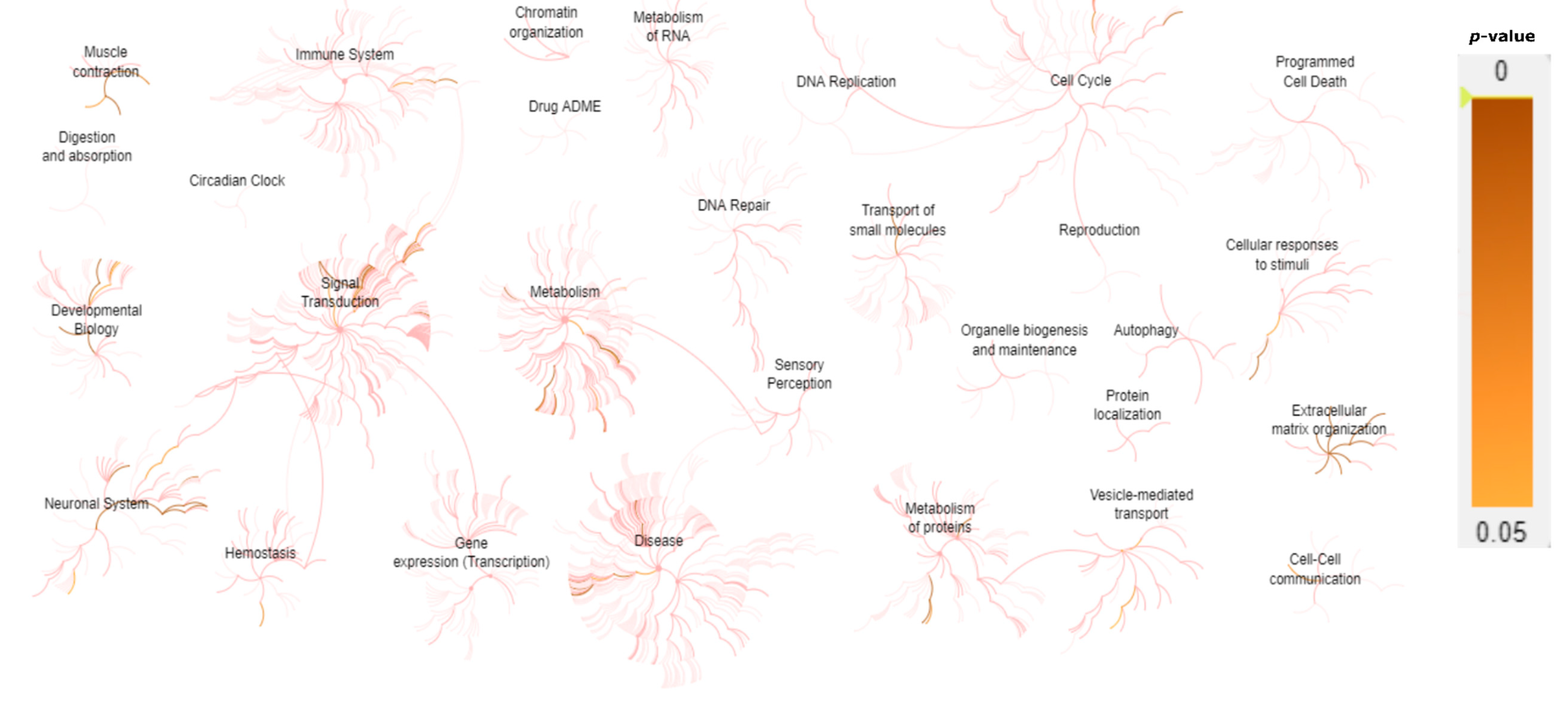
2.2. Genetic Findings
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Study Population
4.3. Gene Panel Design
4.4. Genetic Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Volk, A.E.; Kubisch, C. The Rapid Evolution of Molecular Genetic Diagnostics in Neuromuscular Diseases. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 30, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efthymiou, S.; Manole, A.; Houlden, H. Next-Generation Sequencing in Neuromuscular Diseases. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2016, 29, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolb, S.J.; Coffey, C.S.; Yankey, J.W.; Krosschell, K.; Arnold, W.D.; Rutkove, S.B.; Swoboda, K.J.; Reyna, S.P.; Sakonju, A.; Darras, B.T.; et al. Natural History of Infantile-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, N.G. Genetics of Neuromuscular Disorders. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2012, 49, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Zhong, X.; Liu, L.; Cui, S.; Yang, Y.; Kong, L. Genetic Analysis of 1051 Chinese Families with Duchenne/Becker Muscular Dystrophy. BMC Med. Genet. 2019, 20, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morena, J.; Gupta, A.; Hoyle, J.C. Charcot-Marie-Tooth: From Molecules to Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barp, A.; Ferrero, A.; Casagrande, S.; Morini, R.; Zuccarino, R. Circulating Biomarkers in Neuromuscular Disorders: What Is Known, What Is New. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argov, Z. Drug-Induced Neuromuscular Disorders; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-0-19-176777-7. [Google Scholar]
- Barrons, R.W. Drug-Induced Neuromuscular Blockade and Myasthenia Gravis. Pharmacotherapy 1997, 17, 1220–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Kazamel, M.; Warren, P.P. History of Electromyography and Nerve Conduction Studies: A Tribute to the Founding Fathers. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas. 2017, 43, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalco, R.S.; Snoeck, M.; Quinlivan, R.; Treves, S.; Laforét, P.; Jungbluth, H.; Voermans, N.C. Exertional Rhabdomyolysis: Physiological Response or Manifestation of an Underlying Myopathy? BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2016, 2, e000151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilhus, N.E.; Tzartos, S.; Evoli, A.; Palace, J.; Burns, T.M.; Verschuuren, J.J.G.M. Myasthenia Gravis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2019, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, B.; Antonellis, A.; Sumner, C.J.; Lieberman, A.P. Genetic Approaches to the Treatment of Inherited Neuromuscular Diseases. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, R55–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benarroch, L.; Bonne, G.; Rivier, F.; Hamroun, D. The 2021 Version of the Gene Table of Neuromuscular Disorders (Nuclear Genome). Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD 2020, 30, 1008–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evilä, A.; Arumilli, M.; Udd, B.; Hackman, P. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Assay for Detection of Mutations in Primary Myopathies. Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD 2016, 26, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, J.H.; Vasta, V.; Cho, A.; Lim, B.C.; Zhang, Q.; Eun, S.H.; Hahn, S.H. Utility of next Generation Sequencing in Genetic Diagnosis of Early Onset Neuromuscular Disorders. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 52, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, I.; Lopez, M.A.; Marafi, D.; Pehlivan, D.; Calame, D.G.; Abid, F.; Lotze, T.E. Clinical Exome Sequencing in the Diagnosis of Pediatric Neuromuscular Disease. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskell, G.T.; Adams, M.C.; Fan, Z.; Amin, K.; Guzman Badillo, R.J.; Zhou, L.; Bizon, C.; Chahin, N.; Greenwood, R.S.; Milko, L.V.; et al. Diagnostic Utility of Exome Sequencing in the Evaluation of Neuromuscular Disorders. Neurol. Genet. 2018, 4, e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waldrop, M.A.; Pastore, M.; Schrader, R.; Sites, E.; Bartholomew, D.; Tsao, C.-Y.; Flanigan, K.M. Diagnostic Utility of Whole Exome Sequencing in the Neuromuscular Clinic. Neuropediatrics 2019, 50, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yubero, D.; Natera-de Benito, D.; Pijuan, J.; Armstrong, J.; Martorell, L.; Fernàndez, G.; Maynou, J.; Jou, C.; Roldan, M.; Ortez, C.; et al. The Increasing Impact of Translational Research in the Molecular Diagnostics of Neuromuscular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, D.; O’Kelly, G.; Wu, G.; Haw, R.; Gillespie, M.; Matthews, L.; Caudy, M.; Garapati, P.; Gopinath, G.; Jassal, B.; et al. Reactome: A Database of Reactions, Pathways and Biological Processes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D691–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecroft, S.J.; Yau, K.S.; Allcock, R.J.N.; Mina, K.; Gooding, R.; Faiz, F.; Atkinson, V.J.; Wise, C.; Sivadorai, P.; Trajanoski, D.; et al. Targeted Gene Panel Use in 2249 Neuromuscular Patients: The Australasian Referral Center Experience. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Quereda, L.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Diaz-Manera, J.; Alonso-Perez, J.; Gallardo, E.; Nascimento, A.; Ortez, C.; Natera-de Benito, D.; Olive, M.; Gonzalez-Mera, L.; et al. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing in a Large Cohort of Genetically Undiagnosed Patients with Neuromuscular Disorders in Spain. Genes 2020, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Oh, H.M.; Park, H.J.; Cho, A.-R.; Lee, D.-W.; Jang, J.-H.; Jang, D.-H. Usefulness of Comprehensive Targeted Multigene Panel Sequencing for Neuromuscular Disorders in Korean Patients. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e00947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ankala, A.; da Silva, C.; Gualandi, F.; Ferlini, A.; Bean, L.J.H.; Collins, C.; Tanner, A.K.; Hegde, M.R. A Comprehensive Genomic Approach for Neuromuscular Diseases Gives a High Diagnostic Yield. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 77, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, D.; Schouten, M.I.; Stunnenberg, B.C.; Kusters, B.; Saris, C.G.J.; Erasmus, C.E.; van Engelen, B.G.; Bulk, S.; Verschuuren-Bemelmans, C.C.; Gerkes, E.H.; et al. Panel-Based Exome Sequencing for Neuromuscular Disorders as a Diagnostic Service. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2019, 6, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börklü-Yücel, E.; Demiriz, Ç.; Avcı, Ş.; Vanlı-Yavuz, E.N.; Eraslan, S.; Oflazer, P.; Kayserili, H. Clinical Exome Sequencing in Neuromuscular Diseases: An Experience from Turkey. Neurol. Sci. Off. J. Ital. Neurol. Soc. Ital. Soc. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 41, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winder, T.L.; Tan, C.A.; Klemm, S.; White, H.; Westbrook, J.M.; Wang, J.Z.; Entezam, A.; Truty, R.; Nussbaum, R.L.; McNally, E.M.; et al. Clinical Utility of Multigene Analysis in over 25,000 Patients with Neuromuscular Disorders. Neurol. Genet. 2020, 6, e412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savarese, M.; Di Fruscio, G.; Torella, A.; Fiorillo, C.; Magri, F.; Fanin, M.; Ruggiero, L.; Ricci, G.; Astrea, G.; Passamano, L.; et al. The Genetic Basis of Undiagnosed Muscular Dystrophies and Myopathies: Results from 504 Patients. Neurology 2016, 87, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, X.; Liang, W.-C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, V.W.; Chou, C.-H.; Huang, H.-D.; Lam, C.W.; Hsu, Y.-Y.; Lin, T.-S.; et al. Expanding Genotype/Phenotype of Neuromuscular Diseases by Comprehensive Target Capture/NGS. Neurol. Genet. 2015, 1, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reid, E.S.; Papandreou, A.; Drury, S.; Boustred, C.; Yue, W.W.; Wedatilake, Y.; Beesley, C.; Jacques, T.S.; Anderson, G.; Abulhoul, L.; et al. Advantages and Pitfalls of an Extended Gene Panel for Investigating Complex Neurometabolic Phenotypes. Brain J. Neurol. 2016, 139, 2844–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antoniadi, T.; Buxton, C.; Dennis, G.; Forrester, N.; Smith, D.; Lunt, P.; Burton-Jones, S. Application of Targeted Multi-Gene Panel Testing for the Diagnosis of Inherited Peripheral Neuropathy Provides a High Diagnostic Yield with Unexpected Phenotype-Genotype Variability. BMC Med. Genet. 2015, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saudi Mendeliome Group Comprehensive Gene Panels Provide Advantages over Clinical Exome Sequencing for Mendelian Diseases. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 134. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Itoh-Satoh, M.; Hayashi, T.; Nishi, H.; Koga, Y.; Arimura, T.; Koyanagi, T.; Takahashi, M.; Hohda, S.; Ueda, K.; Nouchi, T.; et al. Titin Mutations as the Molecular Basis for Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 291, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akinrinade, O.; Koskenvuo, J.W.; Alastalo, T.-P. Prevalence of Titin Truncating Variants in General Population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akinrinade, O.; Heliö, T.; Lekanne Deprez, R.H.; Jongbloed, J.D.H.; Boven, L.G.; van den Berg, M.P.; Pinto, Y.M.; Alastalo, T.-P.; Myllykangas, S.; van Spaendonck-Zwarts, K.; et al. Relevance of Titin Missense and Non-Frameshifting Insertions/Deletions Variants in Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, D.S.; Lam, L.; Taylor, M.R.G.; Wang, L.; Teekakirikul, P.; Christodoulou, D.; Conner, L.; DePalma, S.R.; McDonough, B.; Sparks, E.; et al. Truncations of Titin Causing Dilated Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, A.M.; Ware, J.S.; Herman, D.S.; Schafer, S.; Baksi, J.; Bick, A.G.; Buchan, R.J.; Walsh, R.; John, S.; Wilkinson, S.; et al. Integrated Allelic, Transcriptional, and Phenomic Dissection of the Cardiac Effects of Titin Truncations in Health and Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 270ra6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roncarati, R.; Viviani Anselmi, C.; Krawitz, P.; Lattanzi, G.; von Kodolitsch, Y.; Perrot, A.; di Pasquale, E.; Papa, L.; Portararo, P.; Columbaro, M.; et al. Doubly Heterozygous LMNA and TTN Mutations Revealed by Exome Sequencing in a Severe Form of Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 21, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacKenzie, A.E.; Korneluk, R.G.; Zorzato, F.; Fujii, J.; Phillips, M.; Iles, D.; Wieringa, B.; Leblond, S.; Bailly, J.; Willard, H.F.; et al. The Human Ryanodine Receptor Gene: Its Mapping to 19q13.1, Placement in a Chromosome 19 Linkage Group, and Exclusion as the Gene Causing Myotonic Dystrophy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1990, 46, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, S.; van Ruitenbeek, E.; Fallon, P.; Johns, P.; Phadke, R.; Mein, R.; Mohammed, S.; Jungbluth, H. Parental Mosaicism in RYR1-Related Central Core Disease. Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD 2018, 28, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsutsumi, S.; Kamata, N.; Vokes, T.J.; Maruoka, Y.; Nakakuki, K.; Enomoto, S.; Omura, K.; Amagasa, T.; Nagayama, M.; Saito-Ohara, F.; et al. The Novel Gene Encoding a Putative Transmembrane Protein Is Mutated in Gnathodiaphyseal Dysplasia (GDD). Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 74, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Penttilä, S.; Palmio, J.; Suominen, T.; Raheem, O.; Evilä, A.; Muelas Gomez, N.; Tasca, G.; Waddell, L.B.; Clarke, N.F.; Barboi, A.; et al. Eight New Mutations and the Expanding Phenotype Variability in Muscular Dystrophy Caused by ANO5. Neurology 2012, 78, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, M.; Gelowani, V.; Xu, M.; Agrawal, S.A.; Li, Y.; Daiger, S.P.; Gibbs, R.; et al. SeqCNV: A Novel Method for Identification of Copy Number Variations in Targeted next-Generation Sequencing Data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagath, L.; Lehtokari, V.-L.; Välipakka, S.; Udd, B.; Wallgren-Pettersson, C.; Pelin, K.; Kiiski, K. An Extended Targeted Copy Number Variation Detection Array Including 187 Genes for the Diagnostics of Neuromuscular Disorders. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2018, 5, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nandhagopal, R.; Meftah, D.; Al-Kalbani, S.; Scott, P. Recessive Distal Motor Neuropathy with Pyramidal Signs in an Omani Kindred: Underlying Novel Mutation in the SIGMAR1 Gene. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishwarya, R.; Abdullah, C.S.; Morshed, M.; Remex, N.S.; Bhuiyan, S. Sigmar1’s Molecular, Cellular, and Biological Functions in Regulating Cellular Pathophysiology. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 705575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutary, S.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; Adams, D.; Loisel-Duwattez, J.; Schumacher, M.; Massaad, C.; Massaad-Massade, L. Treating PMP22 Gene Duplication-Related Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: The Past, the Present and the Future. Transl. Res. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2021, 227, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkozy, A.; Hicks, D.; Hudson, J.; Laval, S.H.; Barresi, R.; Hilton-Jones, D.; Deschauer, M.; Harris, E.; Rufibach, L.; Hwang, E.; et al. ANO5 Gene Analysis in a Large Cohort of Patients with Anoctaminopathy: Confirmation of Male Prevalence and High Occurrence of the Common Exon 5 Gene Mutation. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hicks, D.; Sarkozy, A.; Muelas, N.; Köehler, K.; Huebner, A.; Hudson, G.; Chinnery, P.F.; Barresi, R.; Eagle, M.; Polvikoski, T.; et al. A Founder Mutation in Anoctamin 5 Is a Major Cause of Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy. Brain J. Neurol. 2011, 134, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skott, H.; Muntean-Firanescu, C.; Samuelsson, K.; Verrecchia, L.; Svenningsson, P.; Malmgren, H.; Cananau, C.; Espay, A.J.; Press, R.; Solders, G.; et al. The Cerebellar Phenotype of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Neuropathy Type 4C. Cerebellum Ataxias 2019, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piscosquito, G.; Saveri, P.; Magri, S.; Ciano, C.; Gandioli, C.; Morbin, M.; Bella, D.D.; Moroni, I.; Taroni, F.; Pareyson, D. Screening for SH3TC2 Gene Mutations in a Series of Demyelinating Recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease (CMT4). J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. JPNS 2016, 21, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gosselin, I.; Thiffault, I.; Tétreault, M.; Chau, V.; Dicaire, M.-J.; Loisel, L.; Emond, M.; Senderek, J.; Mathieu, J.; Dupré, N.; et al. Founder SH3TC2 Mutations Are Responsible for a CMT4C French-Canadians Cluster. Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD 2008, 18, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaut, S.; Tranchant, C.; Drouot, N.; Rudolf, G.; Guissart, C.; Tarabeux, J.; Stemmelen, T.; Velt, A.; Fourrage, C.; Nitschké, P.; et al. Assessment of a Targeted Gene Panel for Identification of Genes Associated With Movement Disorders. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.M.; Biesecker, L.G.; Rehm, H.L. Overview of Specifications to the ACMG/AMP Variant Interpretation Guidelines. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2019, 103, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonorazky, H.D.; Naumenko, S.; Ramani, A.K.; Nelakuditi, V.; Mashouri, P.; Wang, P.; Kao, D.; Ohri, K.; Viththiyapaskaran, S.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; et al. Expanding the Boundaries of RNA Sequencing as a Diagnostic Tool for Rare Mendelian Disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, 466–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köhler, S.; Carmody, L.; Vasilevsky, N.; Jacobsen, J.O.B.; Danis, D.; Gourdine, J.-P.; Gargano, M.; Harris, N.L.; Matentzoglu, N.; McMurry, J.A.; et al. Expansion of the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) Knowledge Base and Resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1018–D1027. Available online: https://hpo.jax.org/ (accessed on 28 February 2022). [CrossRef]
- The Phenomizer-Clinical Diagnostics with Similarity Searches in Ontologies. Available online: http://compbio.charite.de/phenomizer/ (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Agilent SureDesign. Available online: https://earray.chem.agilent.com/suredesign/index.htm?sessiontimeout=true (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Chen, K.; Wylie, T.; Larson, D.E.; McLellan, M.D.; Mardis, E.R.; Weinstock, G.M.; Wilson, R.K.; Ding, L. VarScan: Variant Detection in Massively Parallel Sequencing of Individual and Pooled Samples. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2283–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional Annotation of Genetic Variants from High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, I.; González-Castro, L.; Maynou, J.; Palacios, L.; Fernández, H.; Couce, M.L.; Fernández-Marmiesse, A. PattRec: An Easy-to-Use CNV Detection Tool Optimized for Targeted NGS Assays with Diagnostic Purposes. Genomics 2020, 112, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davydov, E.V.; Goode, D.L.; Sirota, M.; Cooper, G.M.; Sidow, A.; Batzoglou, S. Identifying a High Fraction of the Human Genome to Be under Selective Constraint Using GERP++. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1001025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollard, K.S.; Hubisz, M.J.; Rosenbloom, K.R.; Siepel, A. Detection of Nonneutral Substitution Rates on Mammalian Phylogenies. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siepel, A.; Bejerano, G.; Pedersen, J.S.; Hinrichs, A.S.; Hou, M.; Rosenbloom, K.; Clawson, H.; Spieth, J.; Hillier, L.W.; Richards, S.; et al. Evolutionarily Conserved Elements in Vertebrate, Insect, Worm, and Yeast Genomes. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1034–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2: Mutation Prediction for the Deep-Sequencing Age. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.F.; Shihab, H.A.; Mort, M.; Cooper, D.N.; Gaunt, T.R.; Campbell, C. FATHMM-XF: Accurate Prediction of Pathogenic Point Mutations via Extended Features. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quang, D.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X. DANN: A Deep Learning Approach for Annotating the Pathogenicity of Genetic Variants. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The Mutational Constraint Spectrum Quantified from Variation in 141,456 Humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Jegga, A.; Zhang, K.; White, P.S.; Zhang, G. Novel Phenotype–Disease Matching Tool for Rare Genetic Diseases. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Biological System | Associated Genes |
|---|---|
| Muscle contraction | ACTA1, ATP2A1, CASQ1, CAV3, DES, DMD, DYSF, KCNJ12, MYBPC1, MYH3, MYH8, NEB, ORAI1, RYR1, SCN4A, SCN10A, STIM1, TAZ, TCAP, TDP1, TNNT1, TNNT3, TNNI2, TPM2, TPM3, TTN |
| Glycogen metabolism | AGL, GAA, GBE1, GYG1, GYS1, PYGM, PHKB, PHKA1 |
| Extracellular matrix organization/ degradation | AGRN, CAPN3, COL1A2, COL6A1, COL6A2, COL6A3, COL6A6, COL12A1, COL13A1, DAG1, DMD, DST, FBN2, FBLN5, ITGA7, LAMA2, LAMB2, LRP4, MME, MUSK, PLEC, TNXB, TTR |
| O-linked glycosylation | B3GNT2, B3GALNT2, DAG1, LARGE, POMK, POMGNT1, POMGNT2, POMT1, POMT2 |
| NCAM signaling for neurite out-growth/ interactions | AGRN, HRAS, CACNA1S, COL6A1, COL6A2, COL6A3, COL6A6, SPTBN4 |
| EGR2 and SOX10-mediated initiation of Schwann cell myelination | ADGRG6, DAG1, DRP2, EGR2, GJB1, PRX, LAMA2, LAMB2, MPZ, PMP22, TAZ |
| tRNA Aminoacylation | AARS, DARS2, GARS, HARS, KARS, MARS, WARS, YARS, YARS2 |
| Nervous system development | ADGRG6, AGRN, CACNA1S, CNTN1, CNTNAP1, COL6A1, COL6A2, COL6A3, COL6A6, DAG1, DNM2, DRP2, EGR2, GJB1, HRAS, LAMA2, LAMB2, MPZ, MYH14, PIP5K1C, PMP22, PRX, SCN4A, SCN10A, SPTBN4, TAZ |
| Presynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors | CHRNA1, CHRND, CHRNE, CHRNG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbosa-Gouveia, S.; Vázquez-Mosquera, M.E.; González-Vioque, E.; Hermida-Ameijeiras, Á.; Sánchez-Pintos, P.; de Castro, M.J.; León, S.R.; Gil-Fournier, B.; Domínguez-González, C.; Camacho Salas, A.; et al. Rapid Molecular Diagnosis of Genetically Inherited Neuromuscular Disorders Using Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102750
Barbosa-Gouveia S, Vázquez-Mosquera ME, González-Vioque E, Hermida-Ameijeiras Á, Sánchez-Pintos P, de Castro MJ, León SR, Gil-Fournier B, Domínguez-González C, Camacho Salas A, et al. Rapid Molecular Diagnosis of Genetically Inherited Neuromuscular Disorders Using Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(10):2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102750
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbosa-Gouveia, Sofia, Maria Eugenia Vázquez-Mosquera, Emiliano González-Vioque, Álvaro Hermida-Ameijeiras, Paula Sánchez-Pintos, Maria José de Castro, Soraya Ramiro León, Belén Gil-Fournier, Cristina Domínguez-González, Ana Camacho Salas, and et al. 2022. "Rapid Molecular Diagnosis of Genetically Inherited Neuromuscular Disorders Using Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 10: 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102750
APA StyleBarbosa-Gouveia, S., Vázquez-Mosquera, M. E., González-Vioque, E., Hermida-Ameijeiras, Á., Sánchez-Pintos, P., de Castro, M. J., León, S. R., Gil-Fournier, B., Domínguez-González, C., Camacho Salas, A., Negrão, L., Fineza, I., Laranjeira, F., & Couce, M. L. (2022). Rapid Molecular Diagnosis of Genetically Inherited Neuromuscular Disorders Using Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(10), 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102750








