The Supraclavicular Artery Island Flap for Pharynx Reconstruction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
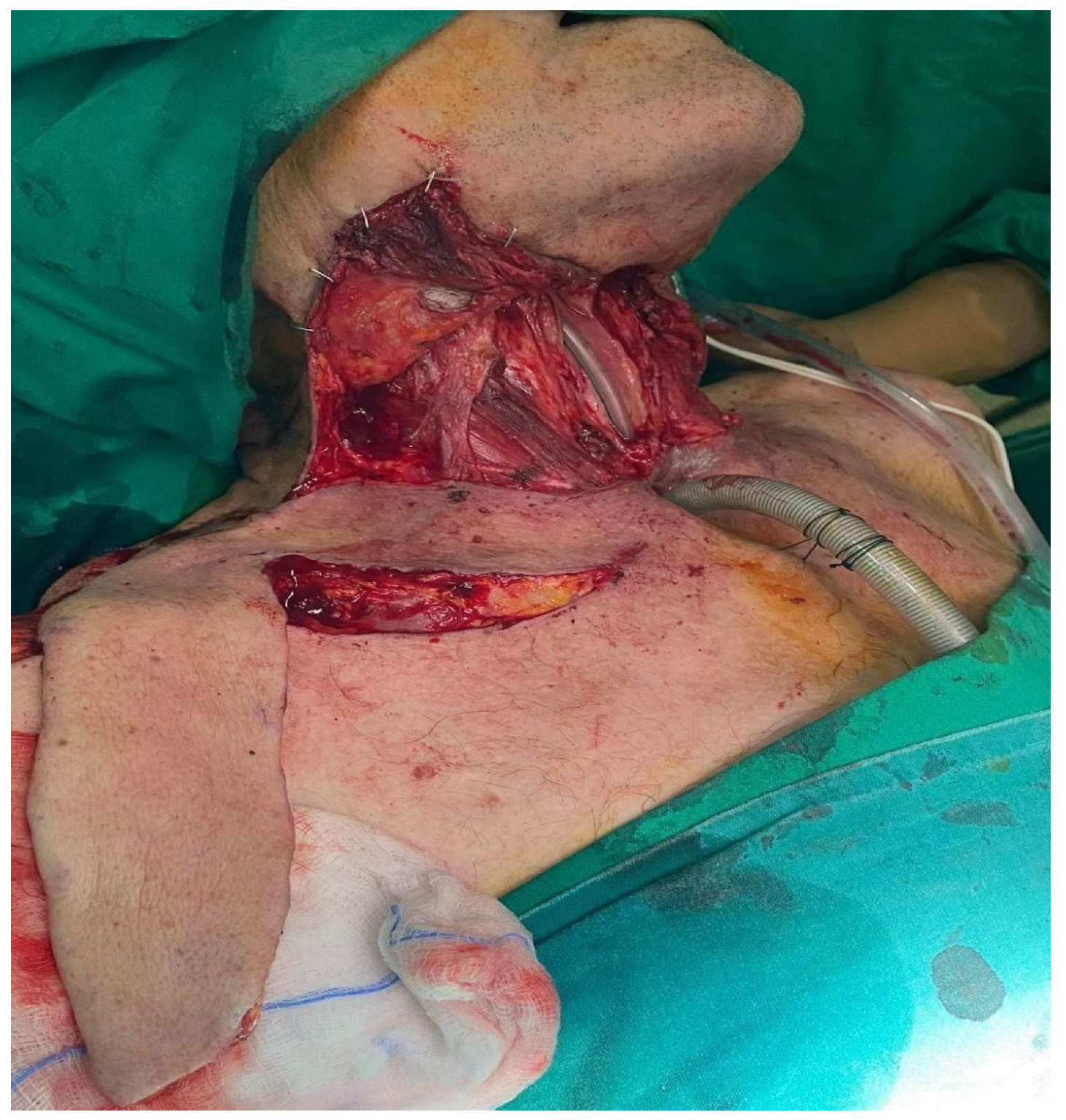
3.1. Case Reports
3.1.1. Case Report 1
3.1.2. Case Report 2
3.2. Review Results
3.2.1. Study Characteristics
3.2.2. Participant’s Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Surgical Technique
4.2. Complications
4.2.1. Pharyngocutaneous Fistulas
4.2.2. Flap Necrosis
4.2.3. Stenosis
4.2.4. Minor Complications
4.2.5. Donor Site
4.3. Contraindications
4.4. Reconstruction with RRF and ALT Free Flaps
4.5. COVID-19 Area and Use of SCAIF
4.6. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- BAHNO Statement on COVID-19 BAHNO—British Association of Head & NeckOncologists. Available online: https://www.bahno.org.uk/bahno_statement_on_covid-19.aspx (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Lamberty, B.G. The supra-clavicular axial patterned flap. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1979, 32, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallua, N.; Machens, H.G.; Rennekampff, O.; Becker, M.; Berger, A. The fasciocutaneous supraclavicular artery island flap for releasing postburn mentosternal contractures. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1997, 99, 1878–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.J.; Izzard, M.E.; Patel, R.S. Supraclavicular artery island flap for reconstructing defects in the head and neck region. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 19, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Murakami, G.; Abe, S.; Sakakura, I.; Yajima, I. Supraclavicular artery in Japanese: An anatomical basis for the flap using a pedicle containing a cervical, non-perforating cutaneous branch of the superficial cervical artery. Okajimas Polia Anat. Jpn. 2000, 77, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, A.S.; Wright, M.J.; Johnston, S.; Tandon, R.; Gupta, N.; Ward, K.; Hanemann, C.; Palacios, E.; Friedlander, P.L.; Chiu, E.S. The Use of Multislice CT Angiography Preoperative Study for Supraclavicular Artery Island Flap Harvesting. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2011, 69, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallua, N.; Demir, E. Postburn head and neck reconstruction in children with the fasciocutaneous supraclavicular artery island flap. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2008, 60, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennana, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (2018): CASP Systematic Review Checklist. Available online: https://casp-uk.bcdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/CASP-Systematic-ReviewChecklist_2018.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Bramer, W.M. Variation in number of hits for complex searches in Google Scholar. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2016, 104, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, E.S.; Liu, P.H.; Baratelli, R.; Lee, M.Y.; Chaffin, A.E.; Friedlander, P.L. Circumferential pharyngoesophageal reconstruction with a supraclavicular artery island flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 125, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.H.; Chiu, E.S. Supraclavicular artery flap: A new option for pharyngeal reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2009, 62, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerick, K.S.; Herr, M.A.; Deschler, D.G. Supraclavicular flap reconstruction following total laryngectomy. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucur, C.; Durmus, K.; Ozer, E. Supraclavicular artery island flap reconstruction of a contralateral partial laryngopharyngeal defect. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2015, 35, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, M.; Baumeister, P. Reconstruction of laryngopharyngectomy defects: Comparison between the supraclavicular artery island flap, the radial forearm flap, and the anterolateral thigh flap. Microsurgery 2019, 39, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnevale, C.; Tomás-Barberán, M.; Sarría-Echegaray, P.; Arancibia-Tagle, D.; García-Wagner, M.; Miralles-Cuadrado, J.; Til-Pérez, G. Partially tubulized U-shaped supraclavicular flap: An excellent option for reconstruction of circumferential pharyngeal defects. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2019, 72, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonnalagadda, S. Tubed supraclavicular flap reconstruction of total pharyngectomy defects for carcinoma hypopharynx. In Proceedings of the 4th European Otolaryngology-ENT Surgery Conference & 3rd International Conference on Craniofacial Surgery, Rome, Italy, 15–16 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Ding, Y.M.; Zhou, M.J.; Kuang, Y.X.; Ma, T.Y.; Chen, X.H. Application of bilateral supraclavicular artery island flaps in the repair of hypopharyngeal and cervical skin defects: A case report. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1380–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, D.; Vincent, A.G.; Wang, W.; Shokri, T.; Ducic, Y. Reconstructive Options during Nonfunctional Laryngectomy. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E1510–E1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Sanaei, A.; Jan, D.; Zolfaghary, M. Use of Supraclavicular Flap by End to Side Technique in Pharyngeal SCC: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Case Rep. Otolaryngol. 2021, 2021, 6619916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.W.; Ng, R.W.; Liu, L.; Chung, H.P.; Wei, W.I. Reconstruction of circumferential pharyngeal defects after tumour resection: Reference or preference. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2011, 64, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.F.; Chang, K.P.; Chen, C.H.; Shyu, V.B.; Kao, H.K. Outcomes of anterolateral thigh flap reconstruction for salvage laryngopharyngectomy for hypopharyngeal cancer after concurrent chemoradiotherapy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Hwang, K. Skin thickness of Korean adults. Surg. Radiol. Anat. J. 2002, 24, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Virtaniemi, J.A.; Kumpulainen, E.J.; Hirvikoski, P.P.; Johansson, R.T.; Kosma, V.M. The incidence and etiology of postlaryngectomy pharyngocutaneous fistulae. Head Neck 2001, 23, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokot, N.; Mazhar, K.; Reder, L.S.; Peng, G.L.; Sinha, U.K. The Supraclavicular Artery Island Flap in Head and Neck Reconstruction. JAMA Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 2003, 139, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Disa, J.J.; Pusic, A.L.; Hidalgo, D.A.; Cordeiro, P.G. Microvascular reconstruction of the hypopharynx: Defect classification, treatment algorithm, and functional outcome based on 165 consecutive cases. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2003, 111, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selber, J.C.; Xue, A.; Liu, J.; Hanasono, M.M.; Skoracki, R.J.; Chang, E.I.; Yu, P. Pharyngoesophageal reconstruction outcomes following 349 cases. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2014, 30, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsou, Y.A.; Hua, C.H.; Lin, M.H.; Tseng, H.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Shaha, A. Comparison of pharyngocutaneous fistula between patients followed by primary laryngopharyngectomy and salvage laryngopharyngectomy for advanced hypopharyngeal cancer. Head Neck 2010, 32, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razdan, S.N.; Albornoz, C.R.; Ro, T.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Disa, J.J.; McCarthy, C.M.; Stern, C.S.; Garfein, E.S.; Matros, E. Safety of the supraclavicular artery island flap in the setting of neck dissection and radiation therapy. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2015, 31, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sukato, D.C.; Timashpolsky, A.; Ferzli, G.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Gordin, E.A. Systematic review of supraclavicular artery island flap vs free flap in head and neck reconstruction. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 160, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granzow, J.W.; Suliman, A.; Roostaeian, J.; Perry, A.; Boyd, J.B. Supraclavicular artery island flap (SCAIF) vs. free fasciocutaneous flaps for head and neck reconstruction. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 148, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrysz-Forget, F.; Tabet, P.; Rahal, A.; Bissada, E.; Christopoulos, A.; Ayad, T. Free versus pedicled flaps for reconstruction of head and neck cancer defects: A systematic review. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 48, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Iwaki, S.; Higaki, E.; Abe, T.; Sawabe, M.; Beppu, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nishikawa, D.; Terada, H.; Hanai, N. Supraclavicular Artery Flap for Oral Reconstruction Prior to Esophagectomy during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Case Report. In Vivo 2021, 35, 3597–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, H.U.; Rashid, M.; Khan, N.; Ansari, S.S.; Bibi, N. Taking a step down on the reconstruction ladder for head and neck reconstruction during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Surg. 2021, 21, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.; Khan, Z.; Patterson, A.; Java, K.; Varley, I. Potential Benefits from the Use of the Supraclavicular Artery Island Flap for Immediate Soft-Tissue Reconstruction during the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2020, 19, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Electronic Databases | Search Strategy | Limits | Hits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pubmed | Pharynx reconstruction AND flap (MeSH Terms) | Publication date: 1 January 2000–31 December 2021 English language | 345 |
| ScienceDirect | Pharynx reconstruction AND flap (MeSH Terms) | Year 2000–2021 Limited to title, abstract, or author-specified keywords | 44 |
| Wiley Online Library | Pharynx reconstruction AND flap (MeSH Terms) | Year: January 2000–December 2021 Publication type Journals Limited to title, abstract, or keywords | 1 |
| Google Scholar | Pharynx reconstruction AND flap (MeSH Terms) | Publication date 2000–2021 Limit to title | 21 |
| Scopus | Pharynx reconstruction AND flap (MeSH Terms) | Publication date: 2000–2021 English language Limited to title, abstract, or keywords | 1 |
| Cochrane Library | Pharynx reconstruction AND flap (MeSH Terms) | Publication date: 2000–2021 | 0 |
| 412 Total hits |
| Article | Study Type, Setting | N | Defect | Type of SCAIF | Radio/Chemotherapy Prior Surgery (n/N) | Flap Size (cm) | Complications (n) | Revision Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chiu et al. (2008) [11] | Retrospective, New Orleans, LA | 20 | Partial or total laryngopharyngectomy | Circumferential pedicled flap | 18/20 | 7 × 19.5 | Leak—Pharyngocutaneous fistula (6) Sensation to the shoulder when swallowing (4) Strictures—stenosis (2) | - |
| Liu and Chiu (2009) [12] | Case series, New Orleans, LA | 6 | Partial pharyngectomy | Pedicled | 6/6 | 6.5 × 20 | Small leak—Pharyngocutaneous fistula (2) | - |
| Emerick et al. (2014) [13] | Retrospective, Boston, USA | 15 | Total laryngectomy | Pedicled | 12/15 | 5.8 × 8.3 | Pharyngocutaneous fistula (3, Radiation +) Near-complete flap loss (1, Radiation +) Incision dehiscence (1, Radiation −) | 1 |
| Kucur et al. (2015) [14] | Retrospective | 1 | Partial laryngopharyngectomy | Pedicled contralateral | 1/1 | Pharyngocutaneous fistula (1, Radiation +) | - | |
| Reiter et al. (2018) [15] | Retrospective, Germany | 18 | Partial or total laryngopharyngectomy | 7/18 | Partial flap loss (1, Radiation +) Pharyngocutaneous fistula (2, 1 Radiation +) Stenosis (2, Radiation +) Gastric tube dependency (5, 2 Radiation +) | 1 | ||
| Carnevale et al. (2019) [16] | Retrospective, Spain | 5 | Total laryngectomy | U-shaped | 3/5 | 7.5 × 20 | Pharyngocutaneous fistula (1) Seroma (1) | - |
| Jonnalagadda (2019) [17] | Retrospective, India | 7 | Total laryngectomy | Circumferential | 5/7 | 5.5 × 9 | Pharyngocutaneous fistula (4) | 1 |
| Zhou et al. (2020) [18] | Retrospective, China | 1 | Partial laryngopharyngectomy | Bilateral | 1/1 | 7 × 4 and 10 × 7 | - | |
| Escalante et al. (2021) [19] | Retrospective, USA | 18 | Total laryngectomy | 18/18 | Pharyngocutaneous fistula (7) | 3 | ||
| Ahmadi et al. (2021) [20] | Case report, Iran | 1 | Partial laryngopharyngectomy | Tubed, end-to-side technique | 0/1 | - | ||
| Total | 10 articles | 92 | 71/92 | Pharyngocutaneous fistula (26) Flap loss (2) Stenosis (4) | 6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolaidou, E.; Pantazi, G.; Sovatzidis, A.; Vakouli, S.; Vardaxi, C.; Evangelopoulos, I.; Gougousis, S. The Supraclavicular Artery Island Flap for Pharynx Reconstruction. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113126
Nikolaidou E, Pantazi G, Sovatzidis A, Vakouli S, Vardaxi C, Evangelopoulos I, Gougousis S. The Supraclavicular Artery Island Flap for Pharynx Reconstruction. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(11):3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113126
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolaidou, Eirini, Glykeria Pantazi, Apostolos Sovatzidis, Stella Vakouli, Chrysoula Vardaxi, Iraklis Evangelopoulos, and Spyridon Gougousis. 2022. "The Supraclavicular Artery Island Flap for Pharynx Reconstruction" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 11: 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113126
APA StyleNikolaidou, E., Pantazi, G., Sovatzidis, A., Vakouli, S., Vardaxi, C., Evangelopoulos, I., & Gougousis, S. (2022). The Supraclavicular Artery Island Flap for Pharynx Reconstruction. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(11), 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113126






