When Sugar Reaches the Liver: Phenotypes of Patients with Diabetes and NAFLD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Diabetes Clinical Phenotypes
3.1. Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity—The Metabolic Syndrome Paradigm
3.1.1. Epidemiology
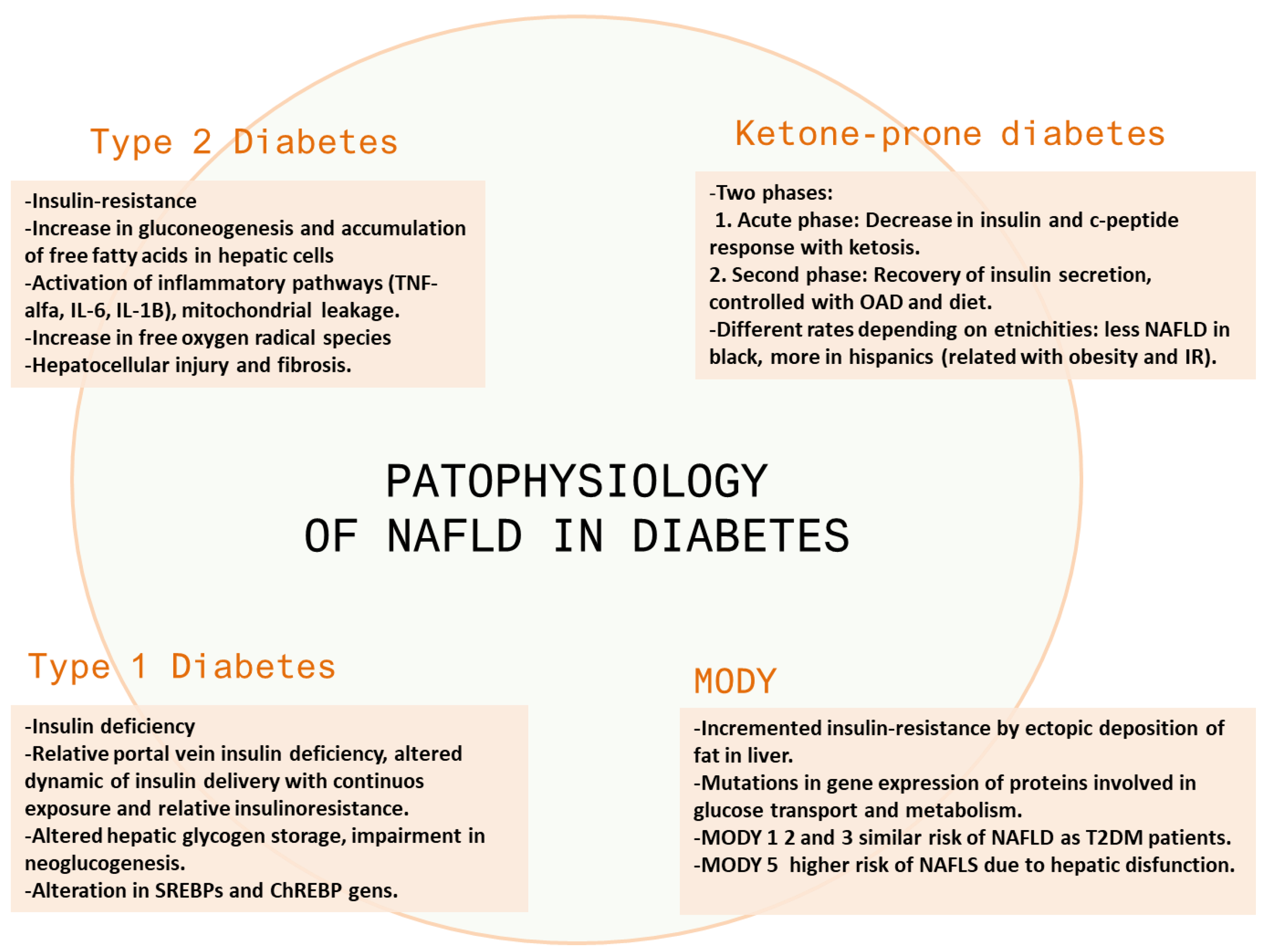
3.1.2. Pathophysiology
3.1.3. Clinical Manifestations
3.1.4. Management: Diagnosis and Interventions
- -
- Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) measures the average blood sugar levels over the prior 90 days. Hb1Ac 6.5% or higher is diagnostic of T2DM [67].
- -
- A fasting plasma glucose of more than 126 mg/dL is a very specific parameter, but its sensitivity has been reported to be unsatisfactory due to false negatives among individuals with impaired glucose tolerance [68].
- -
- The oral glucose tolerance test measures the blood sugar level before, and two hours after, 100 g glucose overload; the diagnosis is established when blood sugar is equal to or greater than 200 mg/dL [69].
3.2. Type 1 Diabetes (T1DM)
3.2.1. Epidemiology
3.2.2. Pathophysiology
3.2.3. Clinical Manifestations
3.2.4. Management: Diagnosis and Interventions
3.3. MODY Diabetes
3.3.1. Epidemiology
3.3.2. Pathophysiology
3.3.3. Clinical Manifestations
3.3.4. Management: Diagnosis and Interventions
3.4. Ketone-Prone Diabetes (KPD)
3.4.1. Epidemiology
3.4.2. Pathophysiology
3.4.3. Clinical Manifestations
3.4.4. Management: Diagnosis and Interventions
4. Algorithm of Diagnosis and Treatment
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Van Natta, M.L.; Clark, J.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Diehl, A.; Dasarathy, S.; Loomba, R.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.; Hameed, B.; et al. Prospective Study of Outcomes in Adults with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesini, G.; Brizi, M.; Morselli/labate, A.M.; Bianchi, G.; Bugianesi, E.; McCullough, A.J.; Forlani, G.; Melchionda, N. Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with insulin resistance. Am. J. Med. 1999, 107, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roden, M. Mechanisms of Disease: Hepatic steatosis in type 2 diabetes—pathogenesis and clinical relevance. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 2, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R.; Roden, M. NAFLD and diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.; Gaunt, P.; Aithal, G.; Barton, D.; Hull, D.; Parker, R.; Hazlehurst, J.M.; Guo, K.; Abouda, G.; A Aldersley, M.; et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet 2016, 387, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newsome, P.N.; Buchholtz, K.; Cusi, K.; Linder, M.; Okanoue, T.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sejling, A.-S.; Harrison, S.A. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Subcutaneous Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalek, M.F. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Another leap forward. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Tabas, I.; Pajvani, U.B. Mechanisms of Fibrosis Development in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitade, H.; Chen, G.; Ni, Y.; Ota, T. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance: New Insights and Potential New Treatments. Nutrients 2017, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report Website. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo-Martínez, G.; Valdés, S.; Soriguer, F.; Vendrell, J.; Urrutia, I.; Pérez, V.; Ortega, E.; Ocón, P.; Montanya, E.; Menéndez, E.; et al. Incidence of diabetes mellitus in Spain as results of the nation-wide cohort di@bet.es study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melmed, S.; Williams, R.H. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, 14th ed.; Elsevier/Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, B.; Gulanick, M.; Lamendola, C. Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2002, 16, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faselis, C.; Katsimardou, A.; Imprialos, K.; Deligkaris, P.; Kallistratos, M.S.; Dimitriadis, K. Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 18, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholongitas, E.; Pavlopoulou, I.; Papatheodoridi, M.; Markakis, G.E.; Bouras, E.; Haidich, A.; Papatheodoridis, G. Epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Europe: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2021, 34, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesini, G.; Brizi, M.; Bianchi, G.; Tomassetti, S.; Bugianesi, E.; Lenzi, M.; McCullough, A.J.; Natale, S.; Forlani, G.; Melchionda, N. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Feature of the Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wild, S.; Roglic, G.; Green, A.; Sicree, R.; King, H. Global Prevalence of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skinner, A.C.; Ravanbakht, S.N.; Skelton, J.A.; Perrin, E.M.; Armstrong, S.C. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity in US Children, 1999–2016. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20173459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sa, J.; Cho, B.-Y.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chung, J.; Choe, S.; Gazmararian, J.A.; Shin, J.C.; Lee, C.G.; Navarrette, G.; Han, T. Sex and racial/ethnic differences in the prevalence of overweight and obesity among U.S. college students, 2011–2015. J. Am. Coll. Health 2019, 69, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlsma-Rutte, A.; Rutters, F.; Elders, P.J.; Bot, S.D.; Nijpels, G. Socio-economic status and HbA1c in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 2018, 34, e3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canedo, J.R.; Miller, S.T.; Schlundt, D.; Fadden, M.K.; Sanderson, M. Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Diabetes Quality of Care: The Role of Healthcare Access and Socioeconomic Status. J. Racial Ethn. Health Disparities 2017, 5, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, M.; Rafiq, N.; Younossi, Z.M. Components of metabolic syndrome are independent predictors of mortality in patients with chronic liver disease: A population-based study. Gut 2010, 59, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.C.; Lad, A.; Breidenbach, J.D.; Blomquist, T.M.; Gunning, W.T.; Dube, P.; Kleinhenz, A.L.; Malhotra, D.; Haller, S.T.; Kennedy, D.J. Hyperglycemia induces key genetic and phenotypic changes in human liver epithelial HepG2 cells which parallel the Leprdb/J mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harada, S.; Miyagi, K.; Obata, T.; Morimoto, Y.; Nakamoto, K.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.R.; Tokuyama, S. Influence of hyperglycemia on liver inflammatory conditions in the early phase of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 69, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease as a Nexus of Metabolic and Hepatic Diseases. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Wahed, A.; Guilmeau, S.; Postic, C. Sweet Sixteenth for ChREBP: Established Roles and Future Goals. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 324–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labadzhyan, A.; Cui, J.; Péterfy, M.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.-D.I.; Hsueh, W.A.; Rotter, J.I.; Goodarzi, M.O. Insulin Clearance Is Associated with Hepatic Lipase Activity and Lipid and Adiposity Traits in Mexican Americans. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.S.B. Surrogate markers of insulin resistance: A review. World J. Diabetes 2010, 1, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krssak, M.; Brehm, A.; Bernroider, E.; Anderwald, C.; Nowotny, P.; Man, C.D.; Cobelli, C.; Cline, G.W.; Shulman, G.I.; Waldhaäusl, W.; et al. Alterations in Postprandial Hepatic Glycogen Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 3048–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tilg, H.; Diehl, A.M. Cytokines in Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschen, A.; Molnar, C.; Geiger, S.; Graziadei, I.; Ebenbichler, C.; Weiss, H.; Kaser, S.; Kaser, A.; Tilg, H. Anti-inflammatory effects of excessive weight loss: Potent suppression of adipose interleukin 6 and tumour necrosis factor expression. Gut 2010, 59, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Campbell–Sargent, C.; Mirshahi, F.; Rizzo, W.B.; Contos, M.J.; Sterling, R.K.; Luketic, V.A.; Shiffman, M.L.; Clore, J.N. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Association of insulin resistance and mitochondrial abnormalities. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.F.; Dufour, S.; Hariri, A.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Foo, J.N.; Zhang, X.-M.; Dziura, J.; Lifton, R.P.; Shulman, G.I. Apolipoprotein C3 Gene Variants in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carulli, L.; Canedi, I.; Rondinella, S.; Lombardini, S.; Ganazzi, D.; Fargion, S.; De Palma, M.; Lonardo, A.; Ricchi, M.; Bertolotti, M.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Interleukin-6−174G/C polymorphism is associated with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig. Liver Dis. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Gastroenterol. Ital. Assoc. Study Liver 2009, 41, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, K.; Yoneda, M.; Hyogo, H.; Ochi, H.; Mizusawa, S.; Ueno, T.; Chayama, K.; Nakajima, A.; Nakao, K.; Sekine, A. Association of the rs738409 polymorphism in PNPLA3 with liver damage and the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Med. Genet. 2010, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donnelly, K.L.; Smith, C.I.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Jessurun, J.; Boldt, M.D.; Parks, E.J. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, J.E.; Ramos-Roman, M.A.; Browning, J.D.; Parks, E.J. Increased De Novo Lipogenesis Is a Distinct Characteristic of Individuals with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeren, J.; Scheja, L. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and lipoprotein metabolism. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Dam-Larsen, S.; Adams, L.A.; Björnsson, E.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Mills, P.R.; Keach, J.C.; Lafferty, H.D.; Stahler, A.; et al. Liver Fibrosis, but No Other Histologic Features, Is Associated with Long-term Outcomes of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 389–397.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekstedt, M.; Hagström, H.; Nasr, P.; Fredrikson, M.; Stål, P.; Kechagias, S.; Hultcrantz, R. Fibrosis stage is the strongest predictor for disease-specific mortality in NAFLD after up to 33 years of follow-up. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hossain, N.; Afendy, A.; Stepanova, M.; Nader, F.; Srishord, M.; Rafiq, N.; Goodman, Z.; Younossi, Z. Independent Predictors of Fibrosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracanzani, A.L.; Valenti, L.; Bugianesi, E.; Andreoletti, M.; Colli, A.; Vanni, E.; Bertelli, C.; Fatta, E.; Bignamini, D.; Marchesini, G.; et al. Risk of severe liver disease in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with normal aminotransferase levels: A role for insulin resistance and diabetes. Hepatology 2008, 48, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atan, N.A.D.; Koushki, M.; Motedayen, M.; Dousti, M.; Sayehmiri, F.; Vafaee, R.; Norouzinia, M.; Gholami, R. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2017, 10 (Suppl. 1), S1–S7. [Google Scholar]
- Oberaigner, W.; Ebenbichler, C.; Oberaigner, K.; Juchum, M.; Schönherr, H.R.; Lechleitner, M. Increased cancer incidence risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Results from a cohort study in Tyrol/Austria. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marengo, A.; Rosso, C.; Bugianesi, E. Liver Cancer: Connections with Obesity, Fatty Liver, and Cirrhosis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armandi, A.; Bugianesi, E.; Valenti, L. Natural history of NASH. Liver Int. 2021, 41 (Suppl. 1), 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, R.M.; Price, J.F.; Glancy, S.; Perry, E.; Nee, L.D.; Hayes, P.C.; Frier, B.M.; Van Look, L.A.; Johnston, G.I.; Reynolds, R.M.; et al. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Hepatic Steatosis and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in People with Type 2 Diabetes: The Edinburgh Type 2 Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Targher, G.; Bertolini, L.; Padovani, R.; Rodella, S.; Tessari, R.; Zenari, L.; Day, C.; Arcaro, G. Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Its Association with Cardiovascular Disease among Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Targher, G.; Bertolini, L.; Padovani, R.; Rodella, S.; Zoppini, G.; Pichiri, I.; Sorgato, C.; Zenari, L.; Bonora, E. Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its association with cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteoni, C.A.; Younossi, Z.M.; Gramlich, T.; Boparai, N.; Liu∥, Y.C.; McCullough, A.J. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A spectrum of clinical and pathological severity. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, S.; Amato, M.C.; Di Marco, V.; Cammà, C.; Pizzolanti, G.; Barcellona, M.R.; Cabibi, D.; Galluzzo, A.; Sinagra, D.; Giordano, C.; et al. Visceral adiposity index is associated with significant fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 35, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, J.; Jaques, B.; Chattopadyhay, D.; Lochan, R.; Graham, J.; Das, D.; Aslam, T.; Patanwala, I.; Gaggar, S.; Cole, M.; et al. Hepatocellular cancer: The impact of obesity, type 2 diabetes and a multidisciplinary team. J. Hepatol. 2013, 60, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, K.; Hashimoto, E.; Komorizono, Y.; Koike, K.; Arii, S.; Imai, Y.; Shima, T.; Kanbara, Y.; Saibara, T.; Mori, T.; et al. Characteristics of Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Who Develop Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welzel, T.M.; Graubard, B.; Quraishi, S.; Zeuzem, S.; Davila, J.; El-Serag, H.B.; McGlynn, K. Population-Attributable Fractions of Risk Factors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the United States. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aleksandrova, K.; Boeing, H.; Nöthlings, U.; Jenab, M.; Fedirko, V.; Kaaks, R.; Lukanova, A.; Trichopoulou, A.; Trichopoulos, D.; Boffetta, P.; et al. Inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers and risk of liver and biliary tract cancer. Hepatology 2014, 60, 858–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, W.R.; Kim, H.J.; Therneau, T.M. Association between noninvasive fibrosis markers and mortality among adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States. Hepatology 2012, 57, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, L.A.; Harmsen, S.; Sauver, J.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Enders, F.; Therneau, T.; Angulo, P. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Increases Risk of Death among Patients with Diabetes: A Community-Based Cohort Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Targher, G.; Bertolini, L.; Rodella, S.; Zoppini, G.; Lippi, G.; Day, C.; Muggeo, M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is independently associated with an increased prevalence of chronic kidney disease and proliferative/laser-treated retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2007, 51, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adinolfi, L.E.; Petta, S.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Nevola, R.; Coppola, C.; Narciso, V.; Rinaldi, L.; Calvaruso, V.; Pafundi, P.C.; Lombardi, R.; et al. Reduced incidence of type 2 diabetes in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection cleared by direct-acting antiviral therapy: A prospective study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 2408–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adinolfi, L.E.; Petta, S.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Coppola, C.; Narciso, V.; Nevola, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Calvaruso, V.; Staiano, L.; Di Marco, V.; et al. Impact of hepatitis C virus clearance by direct-acting antiviral treatment on the incidence of major cardiovascular events: A prospective multicentre study. Atherosclerosis 2020, 296, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sasso, F.C.; Pafundi, P.C.; Caturano, A.; Galiero, R.; Vetrano, E.; Nevola, R.; Petta, S.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Coppola, C.; Di Marco, V.; et al. Impact of direct acting antivirals (DAAs) on cardiovascular events in HCV cohort with pre-diabetes. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 2345–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emily, E.; Naik, R. Hemoglobin A1C; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549816/ (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Mannucci, E.; Ognibene, A.; Sposato, I.; Brogi, M.; Gallori, G.; Bardini, G.; Cremasco, F.; Messeri, G.; Rotella, C.M. Fasting plasma glucose and glycated haemoglobin in the screening of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Geol. Rundsch. 2003, 40, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, J.P. Oral Glucose Tolerance Testing. Aust. Fam. Physician 2012, 41, 391–393. [Google Scholar]
- Bazick, J.; Donithan, M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Kleiner, D.; Brunt, E.M.; Wilson, L.; Doo, E.; Lavine, J.; Tonascia, J.; Loomba, R. Clinical Model for NASH and Advanced Fibrosis in Adult Patients with Diabetes and NAFLD: Guidelines for Referral in NAFLD. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graupera, I.; Thiele, M.; Serra-Burriel, M.; Caballeria, L.; Roulot, D.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Fabrellas, N.; Guha, I.N.; Arslanow, A.; Expósito, C.; et al. Low Accuracy of FIB-4 and NAFLD Fibrosis Scores for Screening for Liver Fibrosis in the Population. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 21, S1542–S3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruvongvanich, V.; Wijarnpreecha, K.; Ungprasert, P. The utility of NAFLD fibrosis score for prediction of mortality among patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort study. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2017, 41, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Kumar, R.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, S. FIB-4 cut-off should be re-evaluated in patients with metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). J. Hepatol. 2020, 74, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Gailer, R.; Tanwar, S.; Trembling, P.; Parkes, J.; Rodger, A.; Suri, D.; Thorburn, D.; Sennett, K.; Morgan, S.; et al. Prospective evaluation of a primary care referral pathway for patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cusi, K. Time to Include Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in the Management of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hui, S.C.; So, H.-K.; Chan, D.F.; Wong, S.K.; Yeung, D.K.; Ng, E.K.; Chu, W.C. Validation of water-fat MRI and proton MRS in assessment of hepatic fat and the heterogeneous distribution of hepatic fat and iron in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 107, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernaez, R.; Lazo, M.; Bonekamp, S.; Kamel, I.; Brancati, F.L.; Guallar, E.; Clark, J.M. Diagnostic accuracy and reliability of ultrasonography for the detection of fatty liver: A meta-analysis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, R.S.; Taylor, R.J.; Bayliss, S.; Hagström, H.; Nasr, P.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Ishigami, M.; Toyoda, H.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Peleg, N.; et al. Association Between Fibrosis Stage and Outcomes of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1611–1625.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weng, G.; Dunn, W. Effect of alcohol consumption on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alukal, J.J.; Naqvi, H.A.; Thuluvath, P.J. Vaccination in Chronic Liver Disease: An Update. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatrath, H.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Chalasani, N. Dyslipidemia in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musso, G.; Cassader, M.; Rosina, F.; Gambino, R. Impact of current treatments on liver disease, glucose metabolism and cardiovascular risk in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 885–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Martinez-Perez, Y.; Calzadilla-Bertot, L.; Torres-Gonzalez, A.; Gra-Oramas, B.; Gonzalez-Fabian, L.; Friedman, S.L.; Diago, M.; Romero-Gomez, M. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 367–378.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.A.; Greenson, J.K.; Chao, C.; Anderson, L.; Peterman, D.; Jacobson, J.; Emick, D.; Lok, A.S.; Conjeevaram, H.S. One-Year Intense Nutritional Counseling Results in Histological Improvement in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Pilot Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.C.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Thodis, T.; Ward, G.; Trost, N.; Hofferberth, S.; O’Dea, K.; Desmond, P.V.; Johnson, N.; Wilson, A.M. The Mediterranean diet improves hepatic steatosis and insulin sensitivity in individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Murag, S.; Cholankeril, G.; Cheung, A.; Harrison, S.A.; Younossi, Z.M.; Ahmed, A. Physical Activity, Measured Objectively, Is Associated with Lower Mortality in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 1240–1247.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, P.; Paluszkiewicz, R.; Ziarkiewicz-Wróblewska, B.; Wróblewski, T.; Remiszewski, P.; Grodzicki, M.; Krawczyk, M. Liver Function in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Randomized to Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Versus Sleeve Gastrectomy. Ann. Surg. 2017, 266, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Barros, F.; Fonseca, A.B.M. Bariatric surgery during the evolution of fatty liver–A randomized clinical trial comparing gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy based on transient elastography. Clin. Obes. 2020, 10, e12393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez-Tapia, N.C.; I Tellez-Avila, F.; Barrientos-Gutierrez, T.; Mendez-Sanchez, N.; Lizardi-Cervera, J.; Uribe, M. Bariatric surgery for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in obese patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2010, CD007340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aithal, G.P.; Thomas, J.; Kaye, P.V.; Lawson, A.; Ryder, S.D.; Spendlove, I.; Austin, A.S.; Freeman, J.G.; Morgan, L.; Webber, J. Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Pioglitazone in Nondiabetic Subjects with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phielix, E.; Szendroedi, J.; Roden, M. The role of metformin and thiazolidinediones in the regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism and its clinical impact. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukeland, J.W.; Konopski, Z.; Eggesbø, H.B.; Von Volkmann, H.L.; Raschpichler, G.; Bjøro, K.; Haaland, T.; Løberg, E.M.; Birkeland, K. Metformin in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, controlled trial. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugianesi, E.; Gentilcore, E.; Manini, R.; Natale, S.; Vanni, E.; Villanova, N.; David, E.; Rizzetto, M.; Marchesini, G. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Metformin versus Vitamin E or Prescriptive Diet in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, W.W.; Thompson, K.; Grice, G.; Harrison, S.; Coyle, W. The effect of metformin and standard therapy versus standard therapy alone in nondiabetic patients with insulin resistance and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A pilot trial. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2009, 2, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuchay, M.S.; Krishan, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Farooqui, K.J.; Singh, M.K.; Wasir, J.S.; Bansal, B.; Kaur, P.; Jevalikar, G.; Gill, H.K.; et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Liver Fat in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial (E-LIFT Trial). Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaborit, B.; Ancel, P.; Abdullah, A.E.; Maurice, F.; Abdesselam, I.; Calen, A.; Soghomonian, A.; Houssays, M.; Varlet, I.; Eisinger, M.; et al. Effect of empagliflozin on ectopic fat stores and myocardial energetics in type 2 diabetes: The EMPACEF study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Harrison, S.A.; Francque, S.; Bedossa, P.; Lehert, P.; Serfaty, L.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Boursier, J.; Abdelmalek, M.; Caldwell, S.; et al. Elafibranor, an Agonist of the Peroxisome Proliferator−Activated Receptor−α and −δ, Induces Resolution of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis without Fibrosis Worsening. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1147–1159.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vries, M.; Westerink, J.; Kaasjager, K.H.A.H.; de Valk, H.W. Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 3842–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinhas-Hamiel, O.; Levek-Motola, N.; Kaidar, K.; Boyko, V.; Tisch, E.; Mazor-Aronovitch, K.; Graf-Barel, C.; Landau, Z.; Lerner-Geva, L.; Ben-David, R.F. Prevalence of overweight, obesity and metabolic syndrome components in children, adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 2014, 31, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewers, M.; Ludvigsson, J. Environmental risk factors for type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2016, 387, 2340–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Censin, J.C.; Nowak, C.; Cooper, N.; Bergsten, P.; Todd, J.A.; Fall, T. Childhood adiposity and risk of type 1 diabetes: A Mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, X.; Cai, X.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Y. Mechanisms of impaired pancreatic β-cell function in high-fat diet-induced obese mice: The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maahs, D.M.; West, N.A.; Lawrence, J.; Mayer-Davis, E.J. Epidemiology of Type 1 Diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 39, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Lawrence, J.; Dabelea, D.; Divers, J.; Isom, S.; Dolan, L.; Imperatore, G.; Linder, B.; Marcovina, S.; Pettitt, D.J.; et al. Incidence Trends of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes among Youths, 2002–2012. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chobot, A.; Polanska, J.; Brandt, A.; Deja, G.; Glowinska-Olszewska, B.; Pilecki, O.; Szadkowska, A.; Mysliwiec, M.; Jarosz-Chobot, P. Updated 24-year trend of Type 1 diabetes incidence in children in Poland reveals a sinusoidal pattern and sustained increase. Diabet. Med. 2017, 34, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrashova, A.; Reunanen, A.; Romanov, A.; Karvonen, A.; Viskari, H.; Vesikari, T.; Ilonen, J.; Knip, M.; Hyöty, H. A six-fold gradient in the incidence of type 1 diabetes at the eastern border of Finland. Ann. Med. 2005, 37, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, R.D.; Palmer, J.; Schloot, N.C.; Lernmark, A. Diabetes at the crossroads: Relevance of disease classification to pathophysiology and treatment. Diabetologia 2015, 59, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Guo, M.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X. Association between Pancreatic Atrophy and Loss of Insulin Secretory Capacity in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 6371231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regnell, S.E.; Lernmark, A. Hepatic Steatosis in Type 1 Diabetes. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2011, 8, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stadler, M.; Anderwald, C.; Pacini, G.; Zbýň, Š.; Promintzer-Schifferl, M.; Mandl, M.; Bischof, M.; Gruber, S.; Nowotny, P.; Luger, A.; et al. Chronic Peripheral Hyperinsulinemia in Type 1 Diabetic Patients After Successful Combined Pancreas-Kidney Transplantation Does Not Affect Ectopic Lipid Accumulation in Skeletal Muscle and Liver. Diabetes 2009, 59, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bumbu, A.; Moutairou, A.; Matar, O.; Fumeron, F.; Velho, G.; Riveline, J.; Gautier, J.; Marre, M.; Roussel, R.; Potier, L. Non-severe hypoglycaemia is associated with weight gain in patients with type 1 diabetes: Results from the Diabetes Control and Complication Trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 20, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.-S.; Kang, G.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, B.H.; Koo, S.-H. Regulation of glucose metabolism from a liver-centric perspective. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Chen, J.; Su, Z. Unraveling the Regulation of Hepatic Gluconeogenesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 9, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsten, P. Pathophysiology of Impaired Pulsatile Insulin Release. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2000, 16, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; George, J. Genetic contributions to NAFLD: Leveraging shared genetics to uncover systems biology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-M.; Yuan, R.-S.; Zhuang, W.-Y.; Sun, J.-H.; Wu, J.-Y.; Li, H.; Chen, J.-G. Schisandra polysaccharide inhibits hepatic lipid accumulation by downregulating expression of SREBPs in NAFLD mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iizuka, K.; Takao, K.; Yabe, D. ChREBP-Mediated Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: Involvement of the Gut Microbiota, Liver, and Adipose Tissue. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 587189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G.; Dauth, N.; Grimm, M.; Herrmann, E.; Bojunga, J.; Friedrich-Rust, M. Shear Wave Elastography Reveals a High Prevalence of NAFLD-related Fibrosis Even in Type 1 Diabetes. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, D.J.; Kaye, P.V.; Harris, R.; Suzuki, A.; Gazis, A.; Aithal, G.P. Prevalence and natural history of histologically proven chronic liver disease in a longitudinal cohort of patients with type 1 diabetes. Hepatology 2014, 60, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Bertolini, L.; Chonchol, M.; Rodella, S.; Zoppini, G.; Lippi, G.; Zenari, L.; Bonora, E. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is independently associated with an increased prevalence of chronic kidney disease and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasper, P.; Martin, A.; Lang, S.; Kütting, F.; Goeser, T.; Demir, M.; Steffen, H.-M. NAFLD and cardiovascular diseases: A clinical review. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 110, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.G.; Roelstraete, B.; Khalili, H.; Hagström, H.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Mortality in biopsy-confirmed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Results from a nationwide cohort. Gut 2020, 70, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dans, A.C.; Conde, J.B.; Arias, M.P. Incidencia y características clínicas al manifestarse la diabetes mellitus tipo 1 en niños de Galicia (España, 2001–2002). Ana. Pediatr. 2005, 62, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, A.; Willasch, A.; Ehehalt, S.; Hub, R.; Ranke, M.B. The DIARY group Baden- Wuerttemberg Ketoacidosis at onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children-frequency and clinical presentation. Pediatr. Diabetes 2003, 4, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, K.A.; Richardson, C.C.; Ravishankar, A.; Brigatti, C.; Liberati, D.; Lampasona, V.; Piemonti, L.; Morgan, D.; Feltbower, R.G.; Christie, M.R. Identification of Tetraspanin-7 as a Target of Autoantibodies in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.G.; Hattersley, A. The clinical utility of C-peptide measurement in the care of patients with diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2013, 30, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, A.; Ahmann, A.J.; Battelino, T.; Evert, A.; Hirsch, I.B.; Murad, M.H.; Winter, W.E.; Wolpert, H. Diabetes Technology—Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy and Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 3922–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.A.; Forlenza, G.P.; Bode, B.W.; Pinsker, J.E.; Levy, C.J.; Criego, A.B.; Hansen, D.W.; Hirsch, I.B.; Carlson, A.L.; Bergenstal, R.M.; et al. Multicenter Trial of a Tubeless, On-Body Automated Insulin Delivery System with Customizable Glycemic Targets in Pediatric and Adult Participants with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobry, E.C.; Hamburger, E.; Jaser, S.S. Impact of the Hybrid Closed-Loop System on Sleep and Quality of Life in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes and Their Parents. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2020, 22, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, A.L.; Sherr, J.L.; Shulman, D.I.; Garg, S.K.; Pop-Busui, R.; Bode, B.W.; Lilenquist, D.R.; Brazg, R.L.; Kaiserman, K.B.; Kipnes, M.S.; et al. Safety and Glycemic Outcomes During the MiniMed™ Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop System Pivotal Trial in Adolescents and Adults with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2022, 24, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 4. Comprehensive Medical Evaluation and Assessment of Comorbidities: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43 (Suppl. 1), S37–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kielgast, U.; Holst, J.J.; Madsbad, S. Antidiabetic Actions of Endogenous and Exogenous GLP-1 in Type 1 Diabetic Patients with and without Residual β-Cell Function. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zibar, K.; Ćuća, J.K.; Blaslov, K.; Bulum, T.; Duvnjak, L. Difference in glucagon-like peptide-1 concentrations between C-peptide negative type 1 diabetes mellitus patients and healthy controls. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thivolet, C.; Marchand, L.; Chikh, K. Inappropriate glucagon and GLP-1 secretion in individuals with long-standing type 1 diabetes: Effects of residual C-peptide. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dimitrios, P.; Michael, D.; Vasilios, K.; Konstantinos, S.; Konstantinos, I.; Ioanna, Z.; Konstantinos, P.; Spyridon, B.; Asterios, K.; Patoulias, D.; et al. Liraglutide as Adjunct to Insulin Treatment in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2020, 16, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Mingolla, L.; Rigolon, R.; Pichiri, I.; Cavalieri, V.; Zoppini, G.; Lippi, G.; Bonora, E.; Targher, G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is independently associated with an increased incidence of cardiovascular disease in adult patients with type 1 diabetes. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 225, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Zang, P.; Xu, S.; Song, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; Guo, Z.; Chen, J.; Lu, B.; Gu, P.; et al. Time in Range, as a Novel Metric of Glycemic Control, Is Reversely Associated with Presence of Diabetic Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Independent of HbA1c in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 5817074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, X.; Xiong, G.-H.; Yu, P.-F.; Liu, J.-P. The Correlation between Time in Range and Diabetic Microvascular Complications Utilizing Information Management Platform. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 8879085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, C.; Shen, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Cai, J.; Lu, W.; Zhu, W.; Hu, G.; Xia, T.; et al. Time in Range in Relation to All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 44, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajans, S.S.; Conn, J.W. Tolbutamide-induced Improvement in Carbohydrate Tolerance of Young People with Mild Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes 1960, 9, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajans, S.S.; Brown, M.B. Administration of Sulfonylureas Can Increase Glucose-Induced Insulin Secretion for Decades in Patients with Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young. Diabetes Care 1993, 16, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, B.; Hicks, S.; Shepherd, M.; Colclough, K.; Hattersley, A.T.; Ellard, S. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY): How many cases are we missing? Diabetologia 2010, 53, 2504–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estalella, I.; Rica, I.; de Nanclares, G.P.; Bilbao, J.R.; Vazquez, J.A.; Pedro, J.I.S.; Busturia, M.A.; Castaño, L. Spanish MODY Group Mutations in GCK and HNF-1? explain the majority of cases with clinical diagnosis of MODY in Spain. Clin. Endocrinol. 2007, 67, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Bescós, M.; Velho, G.; Chevre, J.; Vidal, J.; Sesmilo, G.; Bellanne-Chantelot, C.; Froguel, P.; Casamitjana, R.; Rivera-Fillat, F.; et al. Genetic and clinical characterisation of maturity-onset diabetes of the young in Spanish families. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2000, 142, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, M.; Shields, B.; Ellard, S.; Rubio-Cabezas, O.; Hattersley, A.T. A genetic diagnosis of HNF1A diabetes alters treatment and improves glycaemic control in the majority of insulin-treated patients. Diabet. Med. 2009, 26, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eide, S.; Ræder, H.; Johansson, S.; Midthjell, K.; Søvik, O.; Njølstad, P.R.; Molven, A. Prevalence ofHNF1A(MODY3) mutations in a Norwegian population (the HUNT2 Study). Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, M.A.; Garg, A. Monogenic Forms of Diabetes. In Diabetes in America, 3rd ed.; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (US); Cowie, C.C., Casagrande, S.S., Menke, A., Cissell, M.A., Eberhardt, M.S., Meigs, J.B., Gregg, E.W., Eds.; Bethesda: Rockville, MD, USA, 2018. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567994/ (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Garg, A. Lipodystrophies: Genetic and Acquired Body Fat Disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 3313–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Lipodystrophy: Time for a global registry and randomized clinical trials to assess efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness of established and novel medications. Metabolism 2017, 72, A4–A10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorenza, C.G.; Chou, S.H.; Mantzoros, C.S. Lipodystrophy: Pathophysiology and advances in treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 7, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.L.; Oral, E.A. Clinical Classification and Treatment of Congenital and Acquired Lipodystrophy. Endocr. Pract. 2010, 16, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, E.S.; Lungu, A.O.; Cochran, E.K.; Brown, R.; Ghany, M.G.; Heller, T.; Kleiner, D.; Gorden, P. The liver diseases of lipodystrophy: The long-term effect of leptin treatment. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araujo-Vilar, D.; Sánchez-Iglesias, S.; Guillín-Amarelle, C.; Castro, A.; Lage, M.; Pazos, M.; Rial, J.M.; Blasco, J.; Guillén-Navarro, E.; Domingo-Jiménez, R.; et al. Recombinant human leptin treatment in genetic lipodystrophic syndromes: The long-term Spanish experience. Endocrine 2014, 49, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, R.J.; Meehan, C.A.; Cochran, E.; Rother, K.I.; Kleiner, D.E.; Walter, M.; Gorden, P. Effects of Metreleptin in Pediatric Patients with Lipodystrophy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, R.J.; Araujo-Vilar, D.; Cheung, P.T.; Dunger, D.; Garg, A.; Jack, M.; Mungai, L.; Oral, E.A.; Patni, N.; Rother, K.I.; et al. The Diagnosis and Management of Lipodystrophy Syndromes: A Multi-Society Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 4500–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, T.; Onay, H.; Savage, D.B.; Temeloglu, E.; Uzum, A.K.; Kadioglu, P.; Altay, C.; Ozen, S.; Demir, L.; Cavdar, U.; et al. Familial partial lipodystrophy linked to a novel peroxisome proliferator activator receptor -γ (PPARG) mutation, H449L: A comparison of people with this mutation and those with classic codon 482 Lamin A/C (LMNA) mutations. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fajans, S.S. The definition of chemical diabetes. Metabolism 1973, 22, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tattersall, R.B.; Mansell, P.I. Maturity Onset-type Diabetes of the Young (MODY): One Condition or Many? Diabet. Med. 1991, 8, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, I.; Mir, A.; Saqib, M.A.N.; Naeem, M.; Marchand, L.; Polychronakos, C. Causal variants in Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)—A systematic review. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihoker, C.; Gilliam, L.K.; Ellard, S.; Dabelea, D.; Davis, C.; Dolan, L.M.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Imperatore, G.; Lawrence, J.M.; Marcovina, S.M.; et al. Prevalence, Characteristics and Clinical Diagnosis of Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young Due to Mutations in HNF1A, HNF4A, and Glucokinase: Results from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4055–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonald, T.; Ellard, S. Maturity onset diabetes of the young: Identification and diagnosis. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2013, 50, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broome, D.T.; Pantalone, K.M.; Kashyap, S.R.; Philipson, L.H. Approach to the Patient with MODY-Monogenic Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 106, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehlen, N.; Hilger, H.; Stock, F.; Gläser, B.; Guhl, J.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Seufert, J.; Laubner, K. 17q12 Deletion Syndrome as a Rare Cause for Diabetes Mellitus Type MODY5. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3601–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateus, J.C.; Rivera, C.; O’Meara, M.; Valenzuela, A.; Lizcano, F. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 5 a MULTISYSTEMIC disease: A CASE report of a novel mutation in the HNF1B gene and literature review. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clissold, R.L.; Hamilton, A.J.; Hattersley, A.T.; Ellard, S.; Bingham, C. HNF1B-associated renal and extra-renal disease—an expanding clinical spectrum. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 11, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajans, S.S.; Bell, G.I. MODY. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1878–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Besser, R.E.; Ludvigsson, J.; Jones, A.G.; McDonald, T.J.; Shields, B.M.; Knight, B.A.; Hattersley, A.T. Urine C-Peptide Creatinine Ratio Is a Noninvasive Alternative to the Mixed-Meal Tolerance Test in Children and Adults with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellard, S.; Bellanné-Chantelot, C.; Hattersley, A.T.; European Molecular Genetics Quality Network (EMQN) MODY Group. Best practice guidelines for the molecular genetic diagnosis of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bacon, S.; Kyithar, M.P.; Rizvi, S.R.; Donnelly, E.; McCarthy, A.; Burke, M.; Colclough, K.; Ellard, S.; Byrne, M.M. Successful maintenance on sulphonylurea therapy and low diabetes complication rates in a HNF1A-MODY cohort. Diabet. Med. 2015, 33, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anık, A.; Çatlı, G.; Abacı, A.; Böber, E. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY): An update. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 28, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, W.E.; MacLaren, N.K.; Riley, W.J.; Clarke, D.W.; Kappy, M.S.; Spillar, R.P. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of Youth in Black Americans. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 316, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpierrez, G.; Casals, M.M.C.; Gebhart, S.S.P.; Mixon, P.S.; Clark, W.S.; Phillips, L. Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Obese African-Americans. Diabetes 1995, 44, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpierrez, G.; Woo, W.; Hagopian, W.; Isaacs, S.D.; Palmer, J.P.; Gaur, L.K.; Nepom, G.T.; Clark, W.S.; Mixon, P.S.; Kitabchi, A. Immunogenetic analysis suggests different pathogenesis for obese and lean African-Americans with diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, S.I.; Chaiken, R.L.; Hirsch, S.; Harrington, P.; Lebovitz, H.E.; Banerji, M.A. Near-normoglycaemic remission in African-Americans with Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with recovery of beta cell function. Diabet. Med. 2001, 18, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobngwi, E.; Vexiau, P.; Lévy, V.; Lepage, V.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F.; Leblanc, H.; Mbanya, J.C.; Gautier, J.F. Metabolic and immunogenetic prediction of long-term insulin remission in African patients with atypical diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2002, 19, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.E. The Importance of β-Cell Failure in the Development and Progression of Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4047–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ladwa, M.; Bello, O.; Hakim, O.; Shojaee-Moradie, F.; Boselli, M.L.; Charles-Edwards, G.; Peacock, J.; Umpleby, A.M.; Amiel, S.A.; Bonadonna, R.C.; et al. Ethnic differences in beta cell function occur independently of insulin sensitivity and pancreatic fat in black and white men. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e002034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F.; Sobngwi, E.; Porcher, R.; Riveline, J.-P.; Kevorkian, J.-P.; Vaisse, C.; Charpentier, G.; Guillausseau, P.-J.; Vexiau, P.; Gautier, J.-F. Ketosis-Prone Type 2 Diabetes in Patients of Sub-Saharan African Origin: Clinical Pathophysiology and Natural History of Beta-Cell Dysfunction and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2004, 53, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerji, M.A.; Chaiken, R.L.; Huey, H.; Tuomi, T.; Norin, A.J.; Mackay, I.R.; Rowley, M.J.; Zimmet, P.Z.; E Lebovitz, H. GAD Antibody Negative NIDDM in Adult Black Subjects with Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Increased Frequency of Human Leukocyte Antigen DR3 and DR4: Flatbush Diabetes. Diabetes 1994, 43, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, M.A.; Lebovitz, H.E. Remission in Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus: Clinical Characteristics of Remission and Relapse in Black Patients. Medicine 1990, 69, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpierrez, G.E.; Kelly, J.P.; Navarrete, J.E.; Casals, M.M.; Kitabchi, A.E. Hyperglycemic Crises in Urban Blacks. Arch. Intern. Med. 1997, 157, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero-Piloña, A.; Raskin, P. Idiopathic Type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2001, 15, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, D.A.; Dodge, J.S.; Stewart, J. Geographic Patterns of Disease. N. Zealand Med. J. 1976, 83, 404–406. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, K.; Nonaka, K. Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Young Obese Japanese Men. Diabetes Care 1996, 19, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.C.; Mackay, I.R.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Hawkins, B.R.; Lam, K.S. Metabolic and immunologic features of Chinese patients with atypical diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, S.-H.; Sheu, W.H.-H.; Song, Y.-M.; Tseng, L.-N. The Occurrence of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Adults. Intern. Med. 2000, 39, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, E.H.; Guo, H.-R.; Wu, T.-J. Factors associated with discontinuing insulin therapy after diabetic ketoacidosis in adult diabetic patients. Diabet. Med. 2001, 18, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.R.; Troy, T.N.; Huo, D.; O’Brien, B.L.; Jensen, D.M.; Hart, J. Influence of ethnicity on histological differences in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bril, F.; Portillo-Sanchez, P.; Liu, I.-C.; Kalavalapalli, S.; Dayton, K.; Cusi, K. Clinical and Histologic Characterization of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in African American Patients. Diabetes Care 2017, 41, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lause, M.; Kamboj, A.; Faith, E.F. Dermatologic manifestations of endocrine disorders. Transl. Pediatr. 2017, 6, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Is universal screening appropriate? Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; LaVine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, K.E.; Klebanoff, M.J.; Tramontano, A.C.; Chung, R.T.; Hur, C. Screening for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 2016, 61, 2108–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGill, D.B.; Rakela, J.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Ott, B.J. A 21-year experience with major hemorrhage after percutaneous liver biopsy. Gastroenterology 1990, 99, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzigotti, A.; Tsochatzis, E.; Boursier, J.; Castera, L.; Cazzagon, N.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Petta, S.; Thiele, M. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis–2021 update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 659–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boursier, J.; Hagström, H.; Ekstedt, M.; Moreau, C.; Bonacci, M.; Cure, S.; Ampuero, J.; Nasr, P.; Tallab, L.; Canivet, C.M.; et al. Non-invasive tests accurately stratify patients with NAFLD based on their risk of liver-related events. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masarone, M.; Rosato, V.; Aglitti, A.; Bucci, T.; Caruso, R.; Salvatore, T.; Sasso, F.C.; Tripodi, M.F.; Persico, M. Liver biopsy in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Steatohepatitis represents the sole feature of liver damage. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rojano-Toimil, A.; Rivera-Esteban, J.; Manzano-Nuñez, R.; Bañares, J.; Martinez Selva, D.; Gabriel-Medina, P.; Ferrer, R.; Pericàs, J.M.; Ciudin, A. When Sugar Reaches the Liver: Phenotypes of Patients with Diabetes and NAFLD. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123286
Rojano-Toimil A, Rivera-Esteban J, Manzano-Nuñez R, Bañares J, Martinez Selva D, Gabriel-Medina P, Ferrer R, Pericàs JM, Ciudin A. When Sugar Reaches the Liver: Phenotypes of Patients with Diabetes and NAFLD. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(12):3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123286
Chicago/Turabian StyleRojano-Toimil, Alba, Jesús Rivera-Esteban, Ramiro Manzano-Nuñez, Juan Bañares, David Martinez Selva, Pablo Gabriel-Medina, Roser Ferrer, Juan M Pericàs, and Andreea Ciudin. 2022. "When Sugar Reaches the Liver: Phenotypes of Patients with Diabetes and NAFLD" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 12: 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123286
APA StyleRojano-Toimil, A., Rivera-Esteban, J., Manzano-Nuñez, R., Bañares, J., Martinez Selva, D., Gabriel-Medina, P., Ferrer, R., Pericàs, J. M., & Ciudin, A. (2022). When Sugar Reaches the Liver: Phenotypes of Patients with Diabetes and NAFLD. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(12), 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123286







