Does Concurrent Distal Tibiofibular Joint Arthrodesis Affect the Nonunion and Complication Rates of Tibiotalar Arthrodesis?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Surgical Technique
2.3. Outcomes Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subjects
3.2. Postoperative Outcomes/Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barg, A.; Pagenstert, G.I.; Hugle, T.; Gloyer, M.; Wiewiorski, M.; Henninger, H.B.; Valderrabano, V. Ankle osteoarthritis: Etiology, diagnostics, and classification. Foot Ankle Clin. 2013, 18, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbachova, T.; Melenevsky, Y.V.; Latt, L.D.; Weaver, J.S.; Taljanovic, M.S. Imaging and Treatment of Posttraumatic Ankle and Hindfoot Osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Pérez, M.; González-Martín, D.; Vallejo-Márquez, M.; Godoy-Santos, A.L.; Valderrabano, V.; Tejero, S. Ankle Osteoarthritis Aetiology. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltzman, C.L.; Salamon, M.L.; Blanchard, G.M.; Huff, T.; Hayes, A.; Buckwalter, J.A.; Amendola, A. Epidemiology of ankle arthritis: Report of a consecutive series of 639 patients from a tertiary orthopaedic center. Iowa Orthop. J. 2005, 25, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tejero, S.; Prada-Chamorro, E.; González-Martín, D.; García-Guirao, A.; Galhoum, A.; Valderrabano, V.; Herrera-Pérez, M. Conservative Treatment of Ankle Osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrabano, V.; Horisberger, M.; Russell, I.; Dougall, H.; Hintermann, B. Etiology of ankle osteoarthritis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 1800–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Saltzman, C.L.; Chalayon, O.; Barg, A. Does the subtalar joint compensate for ankle malalignment in end-stage ankle arthritis? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alsayel, F.; Alttahir, M.; Mosca, M.; Barg, A.; Herrera-Pérez, M.; Valderrabano, V. Mobile Anatomical Total Ankle Arthroplasty-Improvement of Talus Recentralization. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barg, A.; Bettin, C.C.; Burstein, A.H.; Saltzman, C.L.; Gililland, J. Early Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Trabecular Metal Total Ankle Replacement Using a Transfibular Approach. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2018, 100, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvarda, P.; Peterhans, U.S.; Susdorf, R.; Barg, A.; Ruiz, R.; Hintermann, B. Long-Term Survival of HINTEGRA Total Ankle Replacement in 683 Patients: A Concise 20-Year Follow-Up of a Previous Report. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2022, 104, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, M.; Caravelli, S.; Vocale, E.; Massimi, S.; Censoni, D.; Di Ponte, M.; Fuiano, M.; Zaffagnini, S. Clinical Radiographical Outcomes and Complications after a Brand-New Total Ankle Replacement Design through an Anterior Approach: A Retrospective at a Short-Term Follow Up. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, C.; Stöbich, M.; Ruhs, B.; Kaufmann, C.; Pisecky, L.; Stevoska, S.; Gotterbarm, T.; Klotz, M.C. Intermediate to long-term clinical outcomes and survival analysis of the Salto Mobile Bearing total ankle prothesis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlin, C.; Khan, R.M.; Wilson, I.; Daniels, T.R.; Halai, M.; Pinsker, E.B. Living with Both a Total Ankle Replacement and an Ankle Fusion: A Qualitative Study from the Patients’ Perspective. Foot Ankle Int. 2021, 42, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerdekens, M.; Deschamps, K.; Wuite, S.; Matricali, G. The Biomechanical Behavior of Distal Foot Joints in Patients with Isolated, End-Stage Tibiotalar Osteoarthritis Is Not Altered Following Tibiotalar Fusion. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Klug, A.; Faul, P.; Hoffmann, R.; Manegold, S.; Gramlich, Y. Superiority of upper ankle arthrodesis over total ankle replacement in the treatment of end-stage posttraumatic ankle arthrosis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2021, 142, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.D.; Shofer, J.B.; Hansen, S.T., Jr.; Ledoux, W.R.; Sangeorzan, B.J. The Impact of Coronal Plane Deformity on Ankle Arthrodesis and Arthroplasty. Foot Ankle Int. 2021, 42, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Son, W.S.; Woo, I.H.; Park, C.H. Combined Transfibular and Anterior Approaches Increase Union Rate and Decrease Non-Weight-Bearing Periods in Ankle Arthrodesis: Combined Approaches in Ankle Arthrodesis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieder, S.; Nemecek, E.; Schuh, R.; Kolb, A.; Windhager, R.; Willegger, M. Radiographic Sagittal Tibio-Talar Offset in Ankle Arthrodesis-Accuracy and Reliability of Measurements. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terrell, R.D.; Montgomery, S.R.; Pannell, W.C.; Sandlin, M.I.; Inoue, H.; Wang, J.C.; SooHoo, N.F. Comparison of practice patterns in total ankle replacement and ankle fusion in the United States. Foot Ankle Int. 2013, 34, 1486–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Raikin, S.M. Ankle arthrodesis: The simple and the complex. Foot Ankle Clin. 2008, 13, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, N.A.; Gruen, G.S.; Conti, S.F. Ankle arthrodesis: Indications and techniques. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2000, 8, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalayon, O.; Wang, B.; Blankenhorn, B.; Jackson, J.B., 3rd; Beals, T.; Nickisch, F.; Saltzman, C.L. Factors affecting the outcomes of uncomplicated primary open ankle arthrodesis. Foot Ankle Int. 2015, 36, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, C.; Halikus, N.M.; Vu-Rose, T.; Ebramzadeh, E. A review of ankle arthrodesis: Predisposing factors to nonunion. Foot Ankle Int. 1994, 15, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Baker, L.; Perez, J.; Vulcano, E.; Kaplan, J.; Aiyer, A. Risk Factors for Nonunion Following Ankle Arthrodesis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Foot Ankle Spec. 2021, 1938640021998493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thordarson, D.B.; Kuehn, S. Use of demineralized bone matrix in ankle/hindfoot fusion. Foot Ankle Int. 2003, 24, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihal, A.; Gellman, R.E.; Embil, J.M.; Trepman, E. Ankle arthrodesis. Foot Ankle Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Foot Ankle Surg. 2008, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, Y.; Hannon, C.P.; Seow, D.; Kennedy, J.G. Ankle arthrodesis: A systematic approach and review of the literature. World J. Orthop. 2016, 7, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldthwait, J.E. An operation for the stiffening of the ankle-joint in infantile paralysis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 1908, S2–S5, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz, T. The use of the transfibular approach in arthrodesis of the ankle join. Am. J. Surg. 1942, 55, 550–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, A.B.; Pomeroy, G.C. Transfibular ankle arthrodesis with rigid internal fixation: An assessment of outcome. Foot Ankle Int. 2007, 28, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napiontek, M.; Jaszczak, T. Ankle arthrodesis from lateral transfibular approach: Analysis of treatment results of 23 feet treated by the modified Mann’s technique. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. Orthop. Traumatol. 2015, 25, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Min, W.K.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, S.D.; Kim, D.H. Transfibular ankle arthrodesis using burring, curettage, multiple drilling, and fixation with two retrograde screws through a single lateral incision. J. Orthop. Surg. 2016, 24, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paul, J.; Barg, A.; Horisberger, M.; Herrera, M.; Henninger, H.B.; Valderrabano, V. Ankle salvage surgery with autologous circular pillar fibula augmentation and intramedullary hindfoot nail. J. Foot Ankle Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Foot Ankle Surg. 2014, 53, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Barg, A.; Horisberger, M.; Herrera, M.; Henninger, H.B.; Valderrabano, V. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis with an intramedullary hindfoot nail and pillar fibula augmentation: Technical tip. Foot Ankle Int. 2015, 36, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flückiger, G.; Weber, M. The transfibular approach for ankle arthrodesis. Oper. Orthop. Traumatol. 2005, 17, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, B.J.; Gonzalez, T.; Smith, J.T.; Chiodo, C.P.; Bluman, E.M. Ankle arthritis: You can’t always replace it. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2016, 24, e29–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintermann, B.; Barg, A.; Knupp, M.; Valderrabano, V. Conversion of painful ankle arthrodesis to total ankle arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2009, 91, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuelli, F.G.; de Cesar Netto, C.; Maccario, C.; Paoli, T.; D’Ambrosi, R.; Indino, C. Reconstruction of a missing or insufficient distal fibula in the setting of a total ankle replacement: The Milanese technique. Foot Ankle Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Foot Ankle Surg. 2021, 28, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Kumai, T.; Tamai, S. Low tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the ankle. Results of a new operation in 18 patients. J. Bone Jt. Surg. British Vol. 1995, 77, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, T.M.; Beals, T.C.; Nickisch, F.; Saltzman, C.L.; Lyman, M.; Barg, A. Hindfoot arthrodesis with the blade plate: Increased risk of complications and nonunion in a complex patient population. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2016, 474, 2280–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera-Perez, M.; Andarcia-Banuelos, C.; Barg, A.; Wiewiorski, M.; Valderrabano, V.; Kapron, A.L.; De Bergua-Domingo, J.M.; Pais-Brito, J.L. Comparison of cannulated screws versus compression staples for subtalar arthrodesis fixation. Foot Ankle Int. 2015, 36, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boobbyer, G.N. The long-term results of ankle arthrodesis. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1981, 52, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, R.A.; Rongstad, K.M. Arthrodesis of the ankle: A critical analysis. Foot Ankle Int. 1998, 19, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, S.M.; Selvaraj, V.; Devadoss, S.; Devadoss, A. Transfibular ankle arthrodesis: A novel method for ankle fusion—A short term retrospective study. Indian J. Orthop. 2017, 51, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripanich, Y.; Steadman, J.; Valderrabano, V.; Barg, A. Open ankle arthrodesis: Transfibular approach. Tech. Foot Ankle 2020, 19, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, H.; Fu, L.; Liang, H.; Wang, Z.; Men, J.; Feng, W. End-Stage Ankle Arthritis Treated by Ankle Arthrodesis with Screw Fixation through the Transfibular Approach: A Retrospective Analysis. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 12, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, R.A.; Aiyer, A.A.; Campbell, J.; Jeng, C.L.; Myerson, M.S. Reproducibility of computed tomography to evaluate ankle and hindfoot fusions. Foot Ankle Int. 2014, 35, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
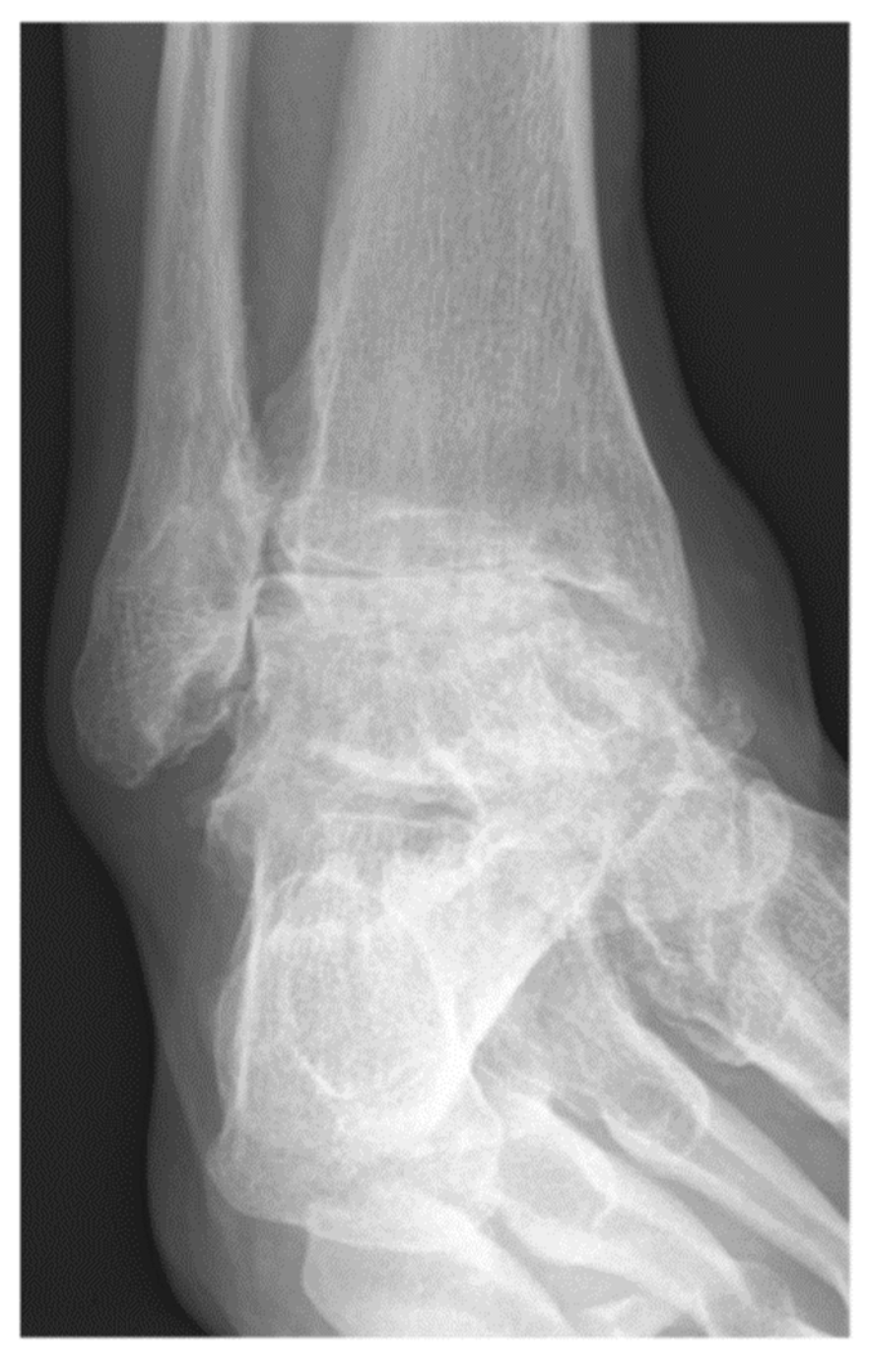

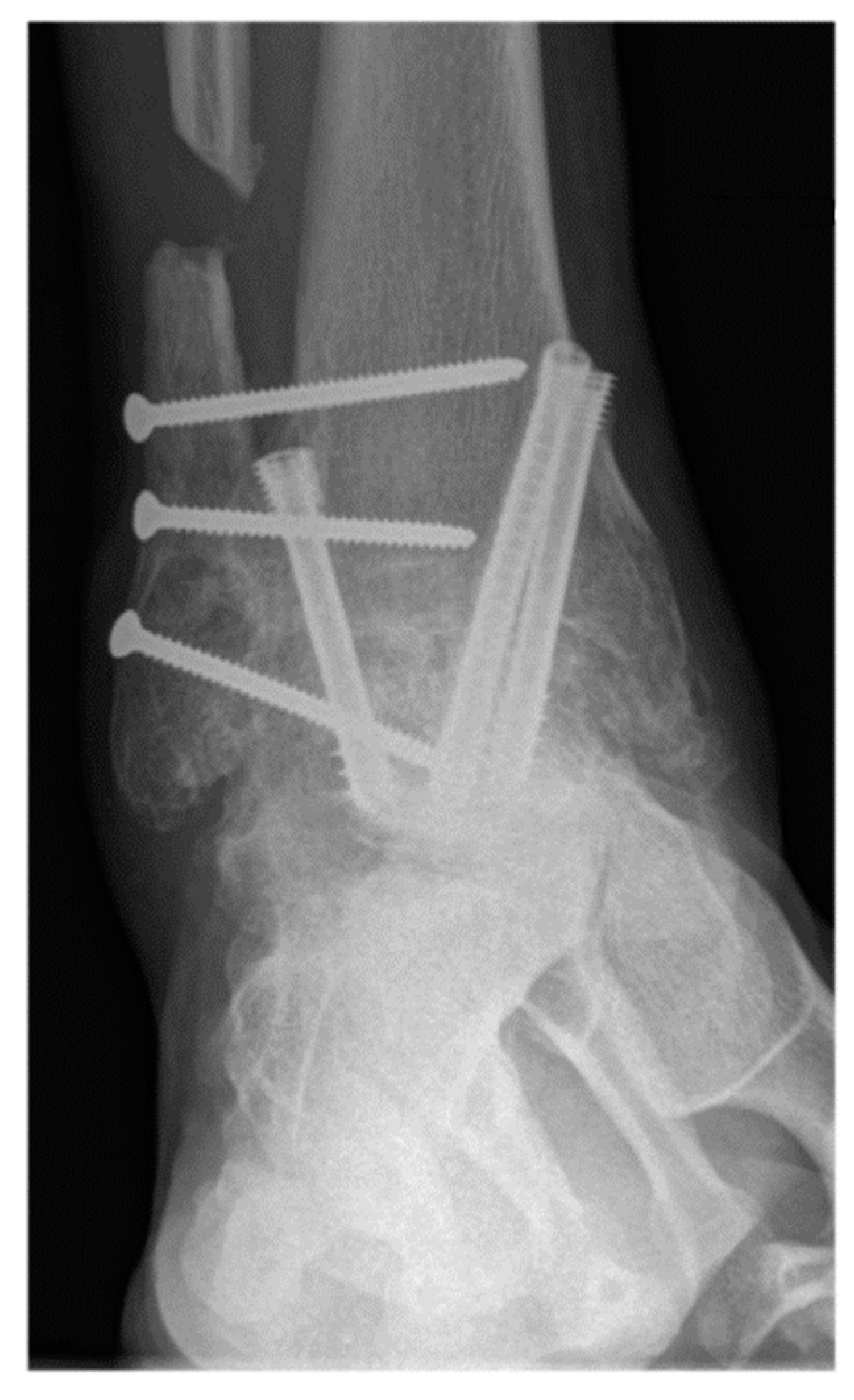
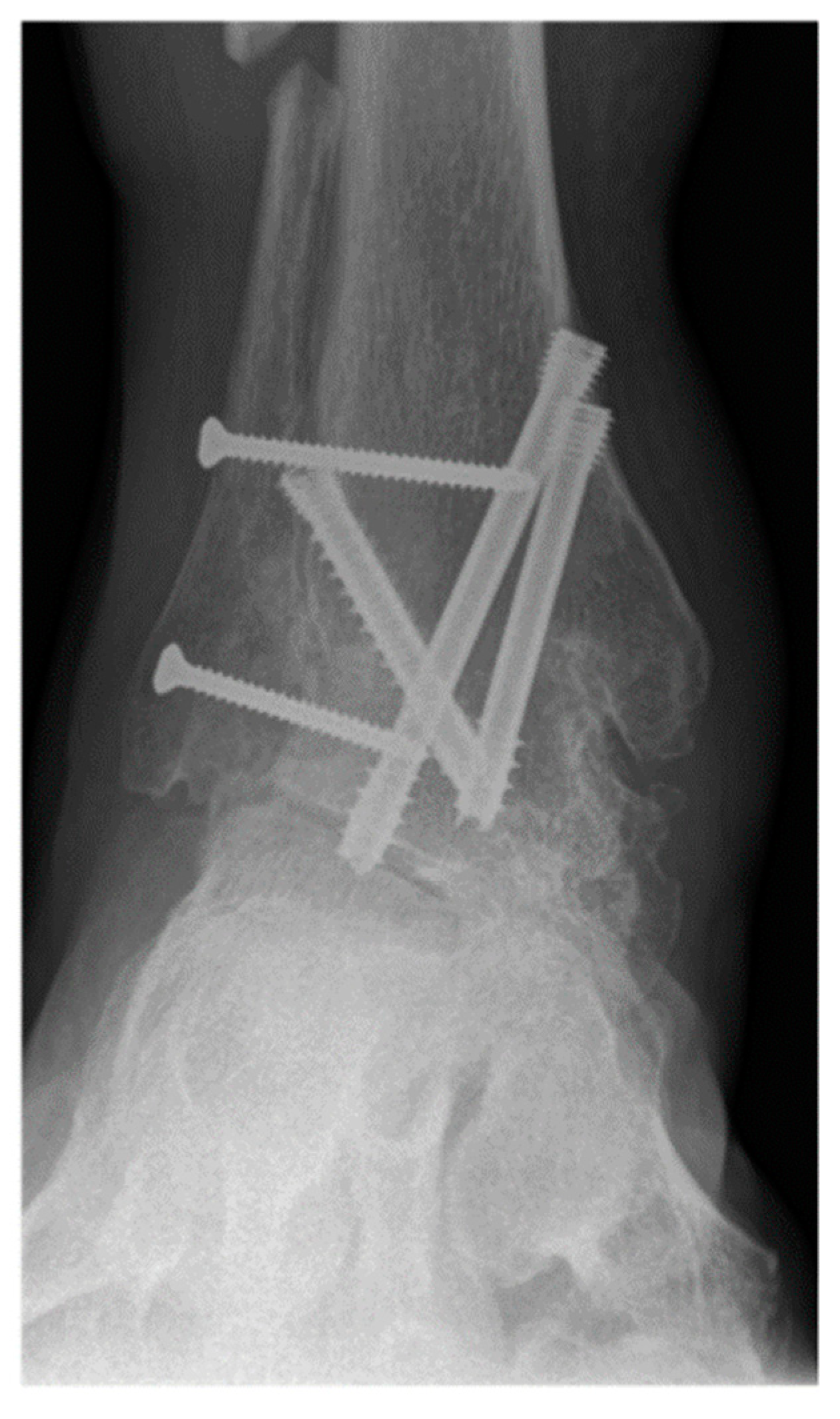
| Variable | With Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 227) | Without Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 92) | All Patients (n = 319) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years ± SD] | 58.8 ± 12.4 | 54.9 ± 15.7 | 57.7 ± 13.5 | 0.036 † |
| Gender (male) | 133 (58.6%) | 51 (55.4%) | 184 (57.7%) | 0.61 ‡ |
| BMI with range [kg/m2] | 29.2 (25.8–33.1) | 301 (26.4–34.2) | 29.4 (25.9–33.8) | 0.32 ˆ |
| Diabetes | 35 (15.4%) | 16 (17.4%) | 51 (16%) | 0.66 ‡ |
| Smokers | 34 (15%) | 13 (14.1%) | 47 (14.7%) | 0.85 ‡ |
| Right sided surgery | 117 (51.5%) | 51 (55.4%) | 168 (52.7%) | 0.53 ‡ |
| Pre-Operative Deformity | With Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 227) | Without Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 92) | All Patients (n = 319) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDTA with range [°] | 88° (86–91°) | 88° (85–90°) | 88° (85–91°) | 0.15 † |
| TTT with range [°] | 0° (−5–3°) | 0° (−2–3°) | 0° (−4–3°) | 0.21 † |
| CMA with range [°] | −5.1° (−19.3–12.9°) | −6.4° (−15.8–10.2°) | −5.8° (−17.5–11.9°) | 0.98 † |
| ADTA with range [°] | 82° (79–87°) | 82° (77–86°) | 82° (78–86.8°) | 0.18 † |
| Etiology | With Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 227) | Without Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 92) | All Patients (n = 319) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | 7 (3.1%) | 5 (5.4%) | 12 (3.8%) | |
| Secondary (including posttraumatic OA) | 220 (96.9%) | 87 (94.6%) | 307 (96.2%) | 0.34 † |
| Type of Fixation | With Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 227) | Without Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 92) | All Patients (n = 319) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blade plate | 5 (2.2%) | 11 (12.0%) | 16 (5.0%) | <0.001† |
| External fixation alone | 4 (1.8%) | 13 (14.1%) | 17 (5.3%) | |
| External fixation + plate | 1 (0.4%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.3%) | |
| IM nail | 14 (6.2%) | 5 (5.4%) | 19 (6%) | |
| Plate | 11 (4.8%) | 47 (51.1%) | 58 (18.2%) | |
| Screws | 192 (84.6%) | 16 (17.4%) | 208 (65.2%) |
| Operative Approach | With Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 227) | Without Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 92) | All Patients (n = 319) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior | 8 (3.5%) | 47 (51.1%) | 55 (17.2%) | <0.001† |
| Lateral | 182 (80.2%) | 20 (21.7%) | 202 (63.3%) | |
| Medial | 0 (0%) | 3 (3.3%) | 3 (0.9%) | |
| Medial and anterior | 0 (0%) | 1 (1.1%) | 1 (0.3%) | |
| Medial and lateral | 31 (13.7%) | 10 (10.9%) | 41 (12.9%) | |
| Posterior | 6 (2.6%) | 11 (12%) | 17 (5.3%) |
| Autograft or Allograft | Type | With Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 227) | Without Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 92) | All Patients (n = 319) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autograft | Yes | 208 (91.6%) | 64 (69.6%) | 272 (85.3%) | <0.001† |
| Distal fibula ± distal tibia | 159 (70%) | 21 (22.8%) | 180 (56.4%) | ||
| Iliac crest | 5 (2.2%) | 7 (7.6%) | 12 (3.8%) | ||
| Proximal tibia | 44 (19.4%) | 35 (38%) | 79 (24.8%) | ||
| Unspecified | 0 (0%) | 1 (1.1%) | 1 (0.3%) | ||
| Allograft | Yes | 37 (16.3%) | 23 (25%) | 60 (18.8%) | 0.07 ‡ |
| Bone block | 6 (2.6%) | 7 (7.6%) | 13 (4.1%) | ||
| Cancellous chips | 25 (11%) | 11 (12%) | 36 (11.3%) | ||
| Cortical bone powder | 0 (0%) | 1 (1.1%) | 1 (0.3%) | ||
| DBM | 6 (2.6%) | 4 (4.3%) | 10 (3.1%) | 0.48 † | |
| BMP | 20 (8.8%) | 20 (21.7%) | 40 (12.5%) | 0.002‡ |
| Variable | With Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 227) | Without Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 92) | All Patients (n = 319) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonunion | 17 (7.5%) | 11 (12%) | 28 (8.8%) | 0.20 † |
| Months to union | 3.5 (1.4–18.2) | 4.1 (1.6–13.5) | 3.8 (2.9–6.2) | 0.72 ‡ |
Wound complications
| 59 (26%)
| 28 (30.4%)
| 87 (27.3%)
| 0.42 ‡ |
Thrombosis
| 11 (4.8%) 1 (0.4%) | 1 (1.1%) 1 (1.1%) | 12 (3.8%) 2 (0.6%) | 0.18 * |
| Rate of Return to OR | With Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 227) | Without Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 92) | All Patients (n = 319) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate (#/yr) | 55 (24.2%) 0.044/person year | 20 (21.7%) 0.056/ person year | 86 (27%) 0.053/person year | 0.89 † |
| Reason for Return to OR | With Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 227) | Without Tibiofibular Arthrodesis (n = 92) | All Patients (n = 319) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amputation | 4 (1.8%) | 4 (4.3%) | 8 (2.5%) | 0.12 † |
| I&D (operative site) | 7 (3.1%) | 4 (4.3%) | 11 (3.4%) | |
| I&D (autograft site) | 1 (0.4%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.3%) | |
| I&D + ROH | 1 (0.4%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.3%) | |
| Osteotomy | 1 (0.4%) | 1 (1.1%) | 2 (0.6%) | |
| Relocation of peroneus brevis tendon | 1 (0.4%) | 1 (1.1%) | 2 (0.6%) | |
| Revision ankle arthrodesis | 14 (6.2%) | 3 (3.3%) | 17 (5.3%) | |
| ROH | 20 (8.8%) | 7 (7.6%) | 26 (8.2%) | |
| Soft tissue reconstruction | 2 (0.9%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (0.6%) | |
| Subtalar arthrodesis | 3 (1.3%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (0.9%) |
| Variables | Odds Ratio | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Inclusion of distal fibular strut autograft in tibiotalar fusion | 0.74 (0.29~2.08) | 0.55 |
| Year of surgery | 0.94 (0.84~1.05) | 0.27 |
| Age at time of surgery | 1.02 (0.99~1.06) | 0.29 |
| Male gender | 1.2 3(0.52~3.00) | 0.64 |
| Smoker | 0.90 (0.20~2.99) | 0.88 |
| +BMP | 0.60 (0.09~2.37) | 0.53 |
| Pre-operative MDTA | 1.03 (0.97~1.10) | 0.33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schlickewei, C.; Neumann, J.A.; Yarar-Schlickewei, S.; Riepenhof, H.; Valderrabano, V.; Frosch, K.-H.; Barg, A. Does Concurrent Distal Tibiofibular Joint Arthrodesis Affect the Nonunion and Complication Rates of Tibiotalar Arthrodesis? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123387
Schlickewei C, Neumann JA, Yarar-Schlickewei S, Riepenhof H, Valderrabano V, Frosch K-H, Barg A. Does Concurrent Distal Tibiofibular Joint Arthrodesis Affect the Nonunion and Complication Rates of Tibiotalar Arthrodesis? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(12):3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123387
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchlickewei, Carsten, Julie A. Neumann, Sinef Yarar-Schlickewei, Helge Riepenhof, Victor Valderrabano, Karl-Heinz Frosch, and Alexej Barg. 2022. "Does Concurrent Distal Tibiofibular Joint Arthrodesis Affect the Nonunion and Complication Rates of Tibiotalar Arthrodesis?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 12: 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123387
APA StyleSchlickewei, C., Neumann, J. A., Yarar-Schlickewei, S., Riepenhof, H., Valderrabano, V., Frosch, K.-H., & Barg, A. (2022). Does Concurrent Distal Tibiofibular Joint Arthrodesis Affect the Nonunion and Complication Rates of Tibiotalar Arthrodesis? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(12), 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123387






