Usefulness of the Urine Methylation Test (Bladder EpiCheck®) in Follow-Up Patients with Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer and Cytological Diagnosis of Atypical Urothelial Cells—An Institutional Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Cohort
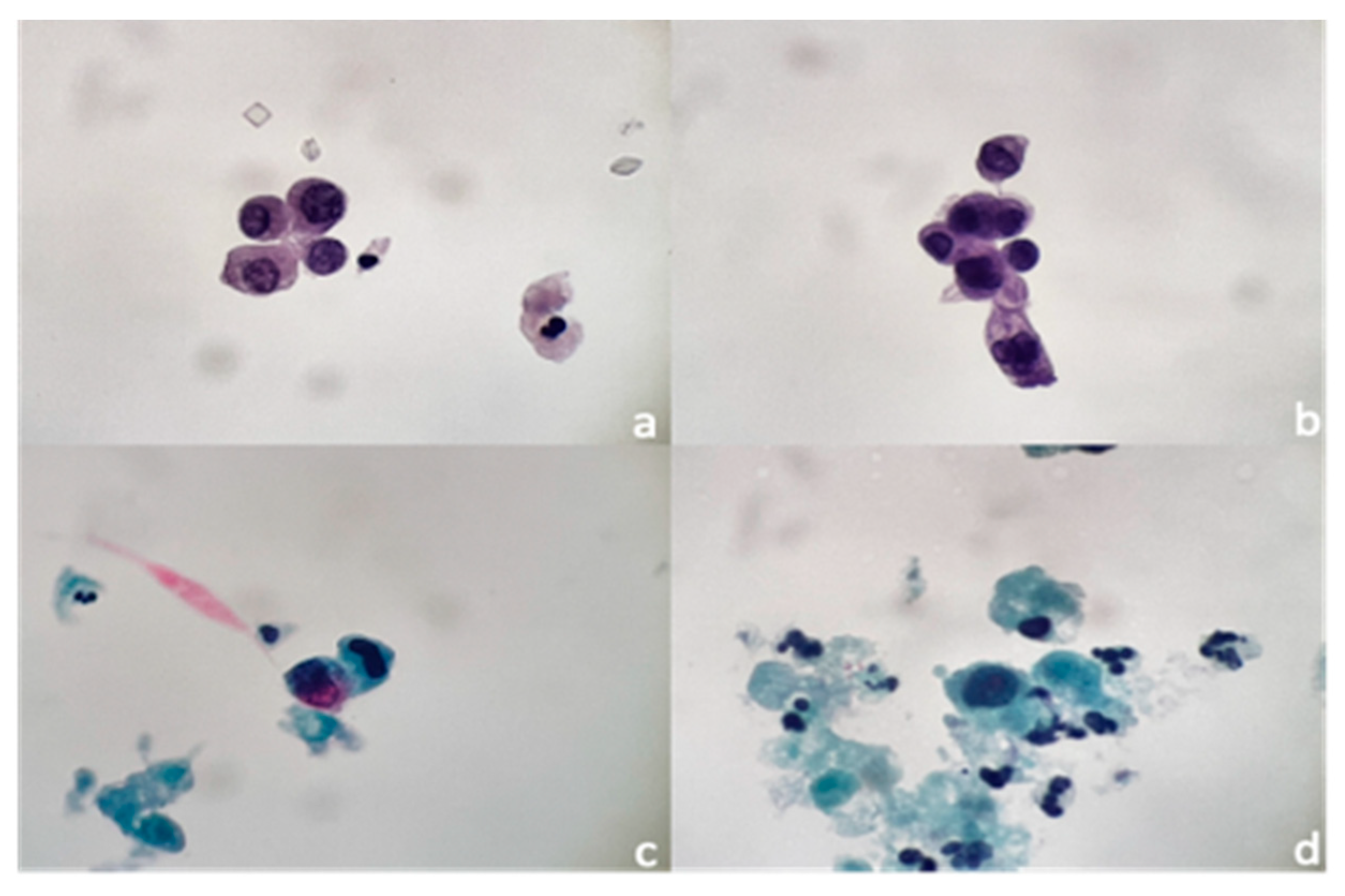
2.2. Urine Cytology Study
2.3. DNA Methylation Study (Bladder EpiCheck® Test)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Findings
3.2. Cytologic Findings
3.3. DNA Methylation Test (Bladder EpiCheck® Test) Findings
3.4. Relationship between Urinary Cytological Findings and the DNA Methylation Test (Bladder EpiCheck® Test)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richters, A.; Aben, K.K.H.; Kiemeney, L.A.L.M. The global burden of urinary bladder cancer: An update. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sievert, K.D.; Amend, B.; Nagele, U.; Schilling, D.; Bedke, J.; Horstmann, M.; Hennenlotter, J.; Kruck, S.; Stenzl, A. Economic aspects of bladder cancer: What are the benefits and costs? World J. Urol. 2009, 27, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sloan, F.A.; Yashkin, A.P.; Akushevich, I.; Inman, B.A. The Cost to Medicare of Bladder Cancer Care. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiener, H.G.; Mian, C.; Haitel, A.; Pycha, A.; Schatzl, G.; Marberger, M. Can urine bound diagnostic tests replace cystoscopy in the management of bladder cancer? J. Urol. 1998, 159, 1876–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyh, H.; Marberger, M.; Conort, P.; Sternberg, C.; Pansadoro, V.; Pagano, F.; Bassi, P.; Boccon-Gibod, L.; Ravery, V.; Treiber, U.; et al. Comparison of the BTA stat test with voided urine cytology and bladder wash cytology in the diagnosis and monitoring of bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 1999, 35, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rhijn, B.W.; van der Poel, H.G.; van der Kwast, T.H. Urine markers for bladder cancer surveillance: A systematic review. Eur. Urol. 2005, 47, 736–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, A.E.; van der Toom, E.E.; Vis, A.N.; Ket, J.C.F.; Bosschieter, J.; Heymans, M.W.; van Moorselaar, R.J.A.; Steenbergen, R.D.M.; Nieuwenhuijzen, J.A. A systematic review on mutation markers for bladder cancer diagnosis in urine. BJU Int. 2021, 127, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Paner, G.P.; Montironi, R.; Raspollini, M.R.; Cheng, L. Iatrogenic changes in the urinary tract. Histopathology 2017, 70, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Montironi, R.; Raspollini, M.R.; Cheng, L.; Netto, G.J. Iatrogenic pathology of the urinary bladder. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 35, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cakir, E.; Kucuk, U.; Pala, E.E.; Sezer, O.; Ekin, R.G.; Cakmak, O. Cytopathologic differential diagnosis of low-grade urothelial carcinoma and reactive urothelial proliferation in bladder washings: A logistic regression analysis. APMIS 2017, 125, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanfrancesco, J.; Jones, J.S.; Hansel, D.E. Diagnostically challenging cases: What are atypia and dysplasia? Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 40, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brimo, F.; Vollmer, R.T.; Case, B.; Aprikian, A.; Kassouf, W.; Auger, M. Accuracy of urine cytology and the significance of an atypical category. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 132, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bostwick, D.G.; Hossain, D. Does subdivision of the “atypical” urine cytology increase predictive accuracy for urothelial carcinoma? Diagn. Cytopathol. 2014, 42, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, K.; Rosen, L.; Coutsouvelis, C.; Fenelus, M.; Brenkert, R.; Klein, M.; Stone, G.; Raab, S.; Aziz, M.; Cocker, R. Accuracy and risk of malignancy for diagnostic categories in urine cytology at a large tertiary institution. Cancer Cytopathol. 2015, 123, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab, S.S.; Lenel, J.C.; Cohen, M.B. Low grade transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Cytologic diagnosis by key features as identified by logistic regression analysis. Cancer 1994, 74, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; Dey, P.; Kakkar, N.; Srinivasan, R.; Nijhawan, R. Malignant atypical cell in urine cytology: A diagnostic dilemma. Cytojournal 2006, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, G.A.; Al-Dousari, M.; Al-Ghamedi, D. Diagnostic significance of atypical category in the voided urine samples: A retrospective study in a tertiary care center. Urol. Ann. 2010, 2, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeb, R.; Messing, E.M. Gender, racial and age differences in bladder cancer incidence and mortality. Urol. Oncol. 2004, 22, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, F.A.; Yashkin, A.P.; Akushevich, I.; Inman, B.A. Longitudinal patterns of cost and utilization of medicare beneficiaries with bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 38, e11–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witjes, J.A. Follow-up in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: Facts and future. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 4047–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layfield, L.J.; Elsheikh, T.M.; Fili, A.; Nayar, R.; Shidham, V.; Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology. Review of the state of the art and recommendations of the Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology for urinary cytology procedures and reporting: The Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology Practice Guidelines Task Force. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2004, 30, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikou, P.; Lenos, M.; Papaioannou, D.; Vrettou, K.; Trigka, E.A.; Sousouris, S.; Constantinides, C. Evaluation of the Paris System in atypical urinary cytology. Cytopathology 2018, 29, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkan, G.; Elsheikh, T.; Kurtycz, D.; Minamiguchi, S.; Ohtani, H.; Piaton, E.; Savic, S.; Tabatabai, Z.; VandenBussche, C. Atypical Urothelial Cells (AUC). In The Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytology, 1st ed.; Dorothy, L., Rosenthal, A., Eva, M., Wojcik, B., Daniel, F.I., Kurtycz, C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Granados, R.; Duarte, J.A.; Corrales, T.; Camarmo, E.; Bajo, P. Applying the Paris System for Reporting Urine Cytology Increases the Rate of Atypical Urothelial Cells in Benign Cases: A Need for Patient Management Recommendations. Acta Cytol. 2017, 61, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoni, G.; Morelli, M.B.; Amantini, C.; Battelli, N. Urinary Markers in Bladder Cancer: An Update. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maas, M.; Walz, S.; Stühler, V.; Aufderklamm, S.; Rausch, S.; Bedke, J.; Stenzl, A.; Todenhöfer, T. Molecular markers in disease detection and follow-up of patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 18, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porten, S.P. Epigenetic Alterations in Bladder Cancer. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2018, 19, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Duymich, C.E.; Weisenberger, D.J.; Liang, G. Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations in Bladder Cancer. Int. Neurourol. J. 2016, 20 (Suppl. S2), S84–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Andrea, D.; Soria, F.; Zehetmayer, S.; Gust, K.M.; Korn, S.; Witjes, J.A.; Shariat, S.F. Diagnostic accuracy, clinical utility and influence on decision-making of a methylation urine biomarker test in the surveillance of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2019, 123, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trenti, E.; D’Elia, C.; Mian, C.; Schwienbacher, C.; Hanspeter, E.; Pycha, A.; Kafka, M.; Degener, S.; Danuser, H.; Roth, S.; et al. Diagnostic predictive value of the Bladder EpiCheck test in the follow-up of patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Cytopathol. 2019, 127, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.M.; Li, H.X. Tumor heterogeneity and the potential role of liquid biopsy in bladder cancer. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocetto, F.; Barone, B.; Ferro, M.; Busetto, G.M.; La Civita, E.; Buonerba, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Terracciano, D.; Schalken, J.A. Liquid biopsy in bladder cancer: State of the art and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 170, 103577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierconti, F.; Martini, M.; Fiorentino, V.; Cenci, T.; Capodimonti, S.; Straccia, P.; Sacco, E.; Pugliese, D.; Cindolo, L.; Larocca, L.M.; et al. The combination cytology/epichek test in non muscle invasive bladder carcinoma follow-up: Effective tool or useless expence? Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, e17–e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochetti, G.; Rossi de Vermandois, J.A.; Maulà, V.; Cari, L.; Cagnani, R.; Suvieri, C.; Balducci, P.M.; Paladini, A.; Del Zingaro, M.; Nocentini, G.; et al. Diagnostic performance of the Bladder EpiCheck methylation test and photodynamic diagnosis-guided cystoscopy in the surveil-lance of high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: A single centre, prospective, blinded clinical trial. Urol. Oncol. 2022, 40, 105.e11–105.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Histopathological Diagnosis | LGUC | HGUC | CIS | No Cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (N) | 16 | 37 | 6 | 11 |
| Age (years) (minimum-maximum) | 58–82 | 50–91 | 53–65 | 49–76 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 15 | 31 | 6 | 6 |
| Female | 1 | 6 | 0 | 5 |
| Cytological diagnosis (PSC) | ||||
| I | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| II | 5 | 11 | 1 | 1 |
| III | 3 | 14 | 4 | 8 |
| IV | 3 | 10 | 1 | 2 |
| V | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| DNA methylation test | ||||
| Positive | 3 | 12 | 2 | 0 |
| Negative | 12 | 24 | 4 | 11 |
| Invalid | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Primary tumor (Bladder) | ||||
| Yes | 16 | 34 | 6 | 0 |
| No | 0 | 3 | 0 | 11 |
| Cystoscopy | ||||
| Positive | 3 | 11 | 2 | 0 |
| Negative | 11 | 22 | 2 | 5 |
| Unrealized | 2 | 4 | 2 | 6 |
| Follow-up time (years) | ||||
| <1 | 1 | 9 | 4 | 10 |
| 2–5 | 10 | 15 | 1 | 1 |
| 6–10 | 4 | 9 | 1 | 0 |
| >10 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Recurrence | ||||
| Yes | 11 | 16 | 2 | 11 |
| No | 5 | 21 | 4 | 0 |
| Treatment | ||||
| BCG | 4 | 28 | 6 | 0 |
| Mitomycin | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Chemotherapy | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Surgery | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| No | 10 | 3 | 0 | 11 |
| Non-Muscle Invasive Carcinoma | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bladder EpiCheck® | Cytology | |
| Sensitivity | 91.67% | 90% |
| Specificity | 91.89% | 88.89% |
| PPV | 78.57% | 81.82% |
| NPV | 97.14% | 94.12% |
| Non-Muscle Invasive Carcinoma | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bladder EpiCheck® | Cytology | |
| Sensitivity | 85.71% | 90.91% |
| Specificity | 92.31% | 83.33% |
| PPV | 70.59% | 62.50% |
| NPV | 96.77% | 96.77% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peña, K.B.; Riu, F.; Hernandez, A.; Guilarte, C.; Badia, J.; Parada, D. Usefulness of the Urine Methylation Test (Bladder EpiCheck®) in Follow-Up Patients with Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer and Cytological Diagnosis of Atypical Urothelial Cells—An Institutional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133855
Peña KB, Riu F, Hernandez A, Guilarte C, Badia J, Parada D. Usefulness of the Urine Methylation Test (Bladder EpiCheck®) in Follow-Up Patients with Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer and Cytological Diagnosis of Atypical Urothelial Cells—An Institutional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(13):3855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133855
Chicago/Turabian StylePeña, Karla B., Francesc Riu, Anna Hernandez, Carmen Guilarte, Joan Badia, and David Parada. 2022. "Usefulness of the Urine Methylation Test (Bladder EpiCheck®) in Follow-Up Patients with Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer and Cytological Diagnosis of Atypical Urothelial Cells—An Institutional Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 13: 3855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133855
APA StylePeña, K. B., Riu, F., Hernandez, A., Guilarte, C., Badia, J., & Parada, D. (2022). Usefulness of the Urine Methylation Test (Bladder EpiCheck®) in Follow-Up Patients with Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer and Cytological Diagnosis of Atypical Urothelial Cells—An Institutional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(13), 3855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133855






