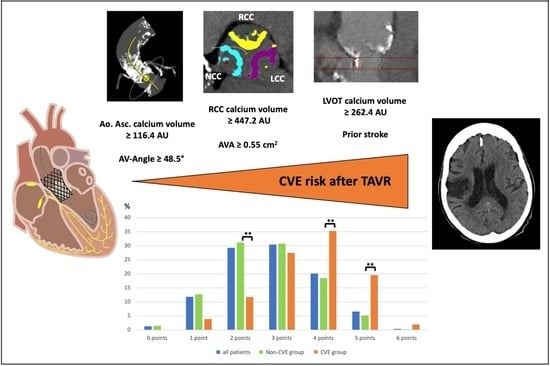
Cerebrovascular Events after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: The Difficulty in Predicting the Unpredictable
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Endpoints
2.3. Risk Score Assessment and Validation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Patient Characteristics
3.2. Study Endpoints
3.3. Model Development in the Derivation Cohort
3.4. Risk Model I for In-Hospital CVE with Pre-Procedural Assessment
3.5. Risk Model II for In-Hospital CVE with Post-Procedural Assessment
3.6. Comparison to Other Risk Scores for CVE Prediction
3.7. Validation of the New Risk Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of the Aortic Root’s Calcification Burden
4.2. Procedure-Related Factors
4.3. Patient-Related Factors
4.4. Antithrombotic and Anticoagulation Treatment after TAVR
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baumgartner, H.; Falk, V.; Bax, J.J.; De Bonis, M.; Hamm, C.; Holm, P.J.; Iung, B.; Lancellotti, P.; Lansac, E.; Rodriguez Muñoz, D.; et al. ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2739–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, S.A.; Nores, M.A.; James, T.M.; Rothenberg, M.; Kapila, A.; Cubeddu, R.J.; Stamou, S.C. Predictors and outcomes of stroke after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. J. Card. Surg. 2020, 35, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlastra, W.; Jimenez-Quevedo, P.; Tchétché, D.; Chandrasekhar, J.; de Brito, F.S., Jr.; Barbanti, M.; Kornowski, R.; Latib, A.; D’Onofrio, A.; Ribichini, F.; et al. Predictors, incidence, and outcomes of patients undergoing transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve implantation complicated by stroke from the center-collaboration. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 12, e007546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myat, A.; Buckner, L.; Mouy, F.; Cockburn, J.; Baumbach, A.; Banning, A.P.; Blackman, D.J.; Curzen, N.; MacCarthy, P.; Mullen, M.; et al. In-hospital stroke after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: A UK observational cohort analysis. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 97, E552–E559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auffret, V.; Regueiro, A.; Del Trigo, M.; Abdul-Jawad Altisent, O.; Campelo-Parada, F.; Chiche, O.; Puri, R.; Rodés-Cabau, J. Predictors of Early Cerebrovascular Events in Patients With Aortic Stenosis Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, S.; Agarwal, S.; Miller, D.C.; Webb, J.G.; Mack, M.; Ellis, S.; Herrmann, H.C.; Pichard, A.D.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Svensson, L.G.; et al. Insights into Timing, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in the PARTNER Trial (Placement of Aortic Transcatheter Valves). Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016, 9, e002981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Backer, O.; Butt, J.H.; Wong, Y.H.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Terkelsen, C.J.; Nissen, H.; Fosbøl, E.L.; Køber, L.; Søndergaard, L. Early and late risk of ischemic stroke after TAVR as compared to a nationwide background population. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 109, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nombela-Franco, L.; Webb, J.G.; De Jaegere, P.P.; Toggweiler, S.; Nuis, R.-J.; Dager, A.E.; Amat-Santos, I.J.; Cheung, A.; Ye, J.; Binder, R.K.; et al. Timing, predictive factors, and prognostic value of cerebrovascular events in a large cohort of patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Circulation 2012, 126, 3041–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orvin, K.; Levi, A.; Landes, U.; Bental, T.; Sagie, A.; Shapira, Y.; Vaknin-Assa, H.; Assali, A.; Kornowski, R. Usefulness of the CHA2DS2-VASc Score to Predict Outcome in Patients Who Underwent Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2018, 121, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, Y.; Yamawaki, M.; Araki, M.; Tada, N.; Naganuma, T.; Yamanaka, F.; Watanabe, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Shirai, S.; Hayashida, K.; et al. Impact of HAS-BLED score to predict trans femoral transcatheter aortic valve replacement outcomes. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 92, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, N.; Haga, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Enta, Y.; Miyasaka, M.; Inoue, H.; Taguri, M.; Ishii, K.; Hata, M.; Sakuma, M.; et al. Computed Tomography Score of Aortic Valve Tissue May Predict Cerebral Embolism During Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, 960–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, K.; Naganuma, T.; Tada, N.; Yamanaka, F.; Araki, M.; Shirai, S.; Higashimori, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayashida, K. The Predictors of Peri-Procedural and Sub-Acute Cerebrovascular Events Following TAVR from OCEAN-TAVI Registry. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 2020, 21, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veulemans, V.; Piayda, K.; Maier, O.; Bosbach, G.; Polzin, A.; Hellhammer, K.; Afzal, S.; Klein, K.; Dannenberg, L.; Zako, S.; et al. Aortic valve calcification is subject to aortic stenosis severity and the underlying flow pattern. Heart Vessel. 2020, 36, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, S.R.; Kodali, S.; Makkar, R.; Mehran, R.; Lazar, R.M.; Zivadinov, R.; Dwyer, M.G.; Jilaihawi, H.; Virmani, R.; Anwaruddin, S.; et al. Protection Against Cerebral Embolism During Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Mieghem, N.M.; Schipper, M.E.; Ladich, E.; Faqiri, E.; Van Der Boon, R.; Randjgari, A.; Schultz, C.; Moelker, A.; van Geuns, R.J.; Otsuka, F.; et al. Histopathology of embolic debris captured during transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Circulation 2013, 127, 2194–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlert, P.; Al-Rashid, F.; Döttger, P.; Mori, K.; Plicht, B.; Wendt, D.; Bergmann, L.; Kottenberg, E.; Schlamann, M.; Mummel, P.; et al. Cerebral embolization during transcatheter aortic valve implantation: A transcranial doppler study. Circulation 2012, 126, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, S.K.; Delahunty, N.; Menezes, L.J.; Perry, R.; Wong, B.; Reinthaler, M.; Ozkor, M.; Mullen, M.J. Patterns of solid particle embolization during transcatheter aortic valve implantation and correlation with aortic valve calcification. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2018, 31, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiman, N.S.; Maini, B.J.; Reardon, M.J.; Conte, J.; Katz, S.; Rajagopal, V.; Kauten, J.; Hartman, A.; McKay, R.; Hagberg, R.; et al. Neurological Events Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement and Their Predictors: A Report from the CoreValve Trials. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016, 9, e003551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roule, V.; Placente, A.; Sabatier, R.; Bignon, M.; Saplacan, V.; Ivascau, C.; Milliez, P.; Beygui, F. Angles between the aortic root and the left ventricle assessed by MDCT are associated with the risk of aortic regurgitation after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Heart Vessel. 2018, 33, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thourani, V.H.; O’Brien, S.M.; Kelly, J.J.; Cohen, D.J.; Peterson, E.D.; Mack, M.J.; Shahian, D.M.; Grover, F.L.; Carroll, J.D.; Brennan, J.M.; et al. Development and Application of a Risk Prediction Model for In-Hospital Stroke After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Report From The Society of Thoracic Surgeons/American College of Cardiology Transcatheter Valve Therapy Registry. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 107, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodés-Cabau, J.; Masson, J.B.; Welsh, R.C.; Garcia del Blanco, B.; Pelletier, M.; Webb, J.G.; Al-Qoofi, F.; Généreux, P.; Maluenda, G.; Thoenes, M.; et al. Aspirin Versus Aspirin Plus Clopidogrel as Antithrombotic Treatment Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement With a Balloon-Expandable Valve: The ARTE (Aspirin Versus Aspirin + Clopidogrel Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) Randomized Clinical Trial. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 10, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hioki, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Kozuma, K.; Nara, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Kataoka, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Takagi, K.; Araki, M.; Tada, N.; et al. Pre-procedural dual antiplatelet therapy in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation increases risk of bleeding. Heart 2017, 103, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangas, G.D.; Tijssen, J.G.; Wöhrle, J.; Søndergaard, L.; Gilard, M.; Möllmann, H.; Makkar, R.R.; Herrmann, H.C.; Giustino, G.; Baldus, S.; et al. A Controlled Trial of Rivaroxaban after Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Replacement. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.H.; Seo, W.K.; Park, M.S.; Kim, J.T.; Chung, J.W.; Bang, O.Y.; Kim, G.M.; Song, T.J.; Kim, B.J.; Heo, S.H.; et al. Effect of Statin Therapy on Outcomes of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke and Atrial Fibrillation. JAHA 2019, 8, e013941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wańkowicz, P.; Staszewski, J.; Dębiec, A.; Nowakowska-Kotas, M.; Szylińska, A.; Turoń-Skrzypińska, A.; Rotter, I. Pre-Stroke Statin Therapy Improves In-Hospital Prognosis Following Acute Ischemic Stroke Associated with Well-Controlled Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. JCM 2021, 10, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kassou, B.; Kandt, J.; Lohde, L.; Shamekhi, J.; Sedaghat, A.; Tabata, N.; Weber, M.; Sugiura, A.; Fimmers, R.; Werner, N.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Protamine Administration for Prevention of Bleeding Complications in Patients Undergoing TAVR. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 13, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Procedural | |||
| Atrial fibrillation | 0.99 | 0.55–1.77 | 0.965 |
| Porcelain aorta | 0.87 | 0.20–3.79 | 0.849 |
| Prior CVE | 2.30 | 1.09–4.86 | 0.029 * |
| Prior dialysis | 0.93 | 0.37–3.14 | 0.902 |
| AVA (cm2) | 0.94 | 0.44–1.98 | 0.866 |
| Cardiac index (l/min/m2) | 0.50 | 0.25–1.01 | 0.054 |
| IMT (mm) | 0.01 | 0.00–0.12 | <0.001 *** |
| Annulus ellipticity index | 0.93 | 0.85–1.01 | 0.088 |
| LVOT area (mm2) | 1.00 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.097 |
| Aortic angulation (°) | 1.03 | 1.00–1.06 | 0.072 |
| AV Agatston score (AU) | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.089 |
| RCC Agatston score (AU) | 1.68 | 0.94–3.02 | 0.082 |
| NCC Agatston score (AU) | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.048 * |
| LVOT Agatston score (AU) | 2.48 | 1.08–5.66 | 0.032 * |
| Ascending aorta Agatston score (AU) | 2.44 | 1.32–4.52 | 0.004 ** |
| Intra-Procedural | |||
| Prosthesis size (mm) | 0.90 | 0.80–1.00 | 0.055 |
| Self-expanding prosthesis | 0.85 | 0.48–1.51 | 0.578 |
| Procedure time (min) | 1.00 | 1.00–1.01 | 0.361 |
| Post-dilatation | 2.26 | 1.19–4.30 | 0.013 * |
| Use of protamine | 0.20 | 0.08–0.46 | <0.001 *** |
| Valve dislodgement | 1.10 | 0.38–3.23 | 0.860 |
| Snaring | 6.60 | 1.81–24.15 | 0.004 ** |
| Post-Procedural | |||
| Post-interventional AR ≥ II° | 3.29 | 1.29–8.35 | 0.012 * |
| Clopidogrel after TAVR | 0.50 | 0.27–0.91 | 0.023 * |
| (N)OAC after TAVR | 0.54 | 0.28–1.05 | 0.068 |
| Statin after TAVR | 0.61 | 0.35–1.08 | 0.089 |
| New pacemaker | 2.98 | 1.04–8.50 | 0.041 * |
| n = 577 patients | |||
| Parameter | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Procedural | |||
| Atrial fibrillation | 4.10 | 0.74–22.60 | 0.106 |
| Porcelain aorta | 5.62 | 0.40–78.83 | 0.200 |
| Prior CVE | 9.47 | 1.82–49.27 | 0.008 ** |
| Prior dialysis | 0.29 | 0.01–6.76 | 0.442 |
| AVA (cm2) | 1.03 | 0.82–1.30 | 0.783 |
| Cardiac index (l/min/m2) | 0.33 | 0.08–1.33 | 0.118 |
| IMT (mm) | <0.01 | <0.01–<0.01 | <0.001 *** |
| Annulus ellipticity index | 0.91 | 0.73–1.13 | 0.400 |
| LVOT area (mm2) | 0.99 | 0.98–1.00 | 0.004 ** |
| Aortic angulation (°) | 1.11 | 1.03–1.20 | 0.005 ** |
| AV Agatston score (AU) | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.447 |
| RCC Agatston score (AU) | 5.76 | 1.08–30.83 | 0.041 * |
| NCC Agatston score (AU) | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.591 |
| LVOT Agatston score (AU) | 3.58 | 0.91–13.98 | 0.067 |
| Central LVOT calcification | 0.63 | 0.16–2.48 | 0.510 |
| Ascending aorta Agatston score (AU) | 0.79 | 0.24–2.64 | 0.702 |
| Intra-Procedural | |||
| Prosthesis size (mm) | 1.32 | 0.90–1.93 | 0.158 |
| Self-expanding prosthesis | 0.15 | 0.02–0.91 | 0.039 * |
| Procedure time (min) | 0.99 | 0.97–1.01 | 0.308 |
| Post-dilatation | 0.33 | 0.01–11.22 | 0.541 |
| Use of protamine | 0.03 | 0.00–0.24 | 0.001 ** |
| Valve dislodgement | <0.01 | <0.01–<0.01 | 0.996 |
| Post-interventional AR ≥ II° | 25.73 | 0.92–718.63 | 0.056 |
| Snaring | 105 × 109 | 0.00–>105 × 109 | 0.997 |
| Post-Procedural | |||
| Clopidogrel after TAVR | 0.36 | 0.06–2.20 | 0.266 |
| (N)OAC after TAVR | 16.08 | 2.65–97.69 | 0.003 ** |
| Statin after TAVR | 5.32 | 1.18–23.99 | 0.030 * |
| New pacemaker | 8.17 | 0.36–183.79 | 0.186 |
| n = 345 patients, Nagelkerke R2 = 0.57, p < 0.001 *** | |||
| Parameter | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prior CVE | 1.94 | 0.85–4.43 | 0.114 |
| AVA (≥0.55 cm2) | 3.11 | 1.16–8.34 | 0.024 * |
| Aortic angulation (≥48.5°) | 2.32 | 1.20–4.49 | 0.013 * |
| RCC Agatston score (≥447.2 AU) | 1.80 | 0.94–3.44 | 0.077 |
| LVOT Agatston score (≥262.4 AU) | 2.01 | 1.08–3.75 | 0.028 * |
| Ascending aorta Agatston score (≥116.4 AU) | 2.21 | 1.17–4.17 | 0.015 * |
| n = 532 patients, Nagelkerke R2 = 0.12, p < 0.001 *** | |||
| Parameter | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prior CVE | 1.86 | 0.75–4.66 | 0.183 |
| AVA (≥0.55 cm2) | 3.18 | 1.11–9.13 | 0.031 * |
| Aortic angulation (≥48.5°) | 2.49 | 1.24–5.01 | 0.010 * |
| RCC Agatston score (≥447.2 AU) | 1.98 | 0.98–4.02 | 0.057 |
| LVOT Agatston score (≥262.4 AU) | 2.46 | 1.27–4.78 | 0.008 ** |
| Ascending aorta Agatston score (≥116.4 AU) | 2.28 | 1.15–4.49 | 0.018 * |
| Non-use of protamine | 5.12 | 1.76–14.83 | 0.003 ** |
| AR ≥ II° | 2.77 | 0.91–8.42 | 0.072 |
| Snaring | 5.30 | 0.98–28.65 | 0.053 |
| No clopidogrel after TAVR | 2.64 | 1.22–5.72 | 0.013 * |
| No (N)OAC after TAVR | 2.49 | 1.23–5.03 | 0.011 * |
| n = 532 patients, Nagelkerke R2 = 0.23, p = 0.006 ** | |||
| Parameter | AUC | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modell I | 0.73 | 0.66–0.80 | <0.001 *** |
| Modell II | 0.79 | 0.73–0.86 | <0.001 *** |
| EuroSCORE II | 0.50 | 0.43–0.58 | 0.950 |
| STS score | 0.57 | 0.49–0.65 | 0.120 |
| HAS-BLED | 0.59 | 0.51–0.69 | 0.027 * |
| CHA2DS2-VASc | 0.62 | 0.55–0.70 | 0.004 ** |
| Parameter | AUC | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modell I | 0.35 | 0.18–0.52 | 0.092 |
| Modell II | 0.42 | 0.24–0.60 | 0.359 |
| EuroSCORE II | 0.60 | 0.44–0.76 | 0.251 |
| STS score | 0.47 | 0.29–0.65 | 0.716 |
| HAS-BLED | 0.44 | 0.28–0.61 | 0.514 |
| CHA2DS2-VASc | 0.39 | 0.24–0.54 | 0.204 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maier, O.; Bosbach, G.; Piayda, K.; Afzal, S.; Polzin, A.; Westenfeld, R.; Jung, C.; Kelm, M.; Zeus, T.; Veulemans, V. Cerebrovascular Events after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: The Difficulty in Predicting the Unpredictable. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3902. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133902
Maier O, Bosbach G, Piayda K, Afzal S, Polzin A, Westenfeld R, Jung C, Kelm M, Zeus T, Veulemans V. Cerebrovascular Events after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: The Difficulty in Predicting the Unpredictable. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(13):3902. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133902
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaier, Oliver, Georg Bosbach, Kerstin Piayda, Shazia Afzal, Amin Polzin, Ralf Westenfeld, Christian Jung, Malte Kelm, Tobias Zeus, and Verena Veulemans. 2022. "Cerebrovascular Events after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: The Difficulty in Predicting the Unpredictable" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 13: 3902. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133902
APA StyleMaier, O., Bosbach, G., Piayda, K., Afzal, S., Polzin, A., Westenfeld, R., Jung, C., Kelm, M., Zeus, T., & Veulemans, V. (2022). Cerebrovascular Events after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: The Difficulty in Predicting the Unpredictable. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(13), 3902. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133902