Platelet Count in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Prognostic Factor in COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
Statistical Analysis
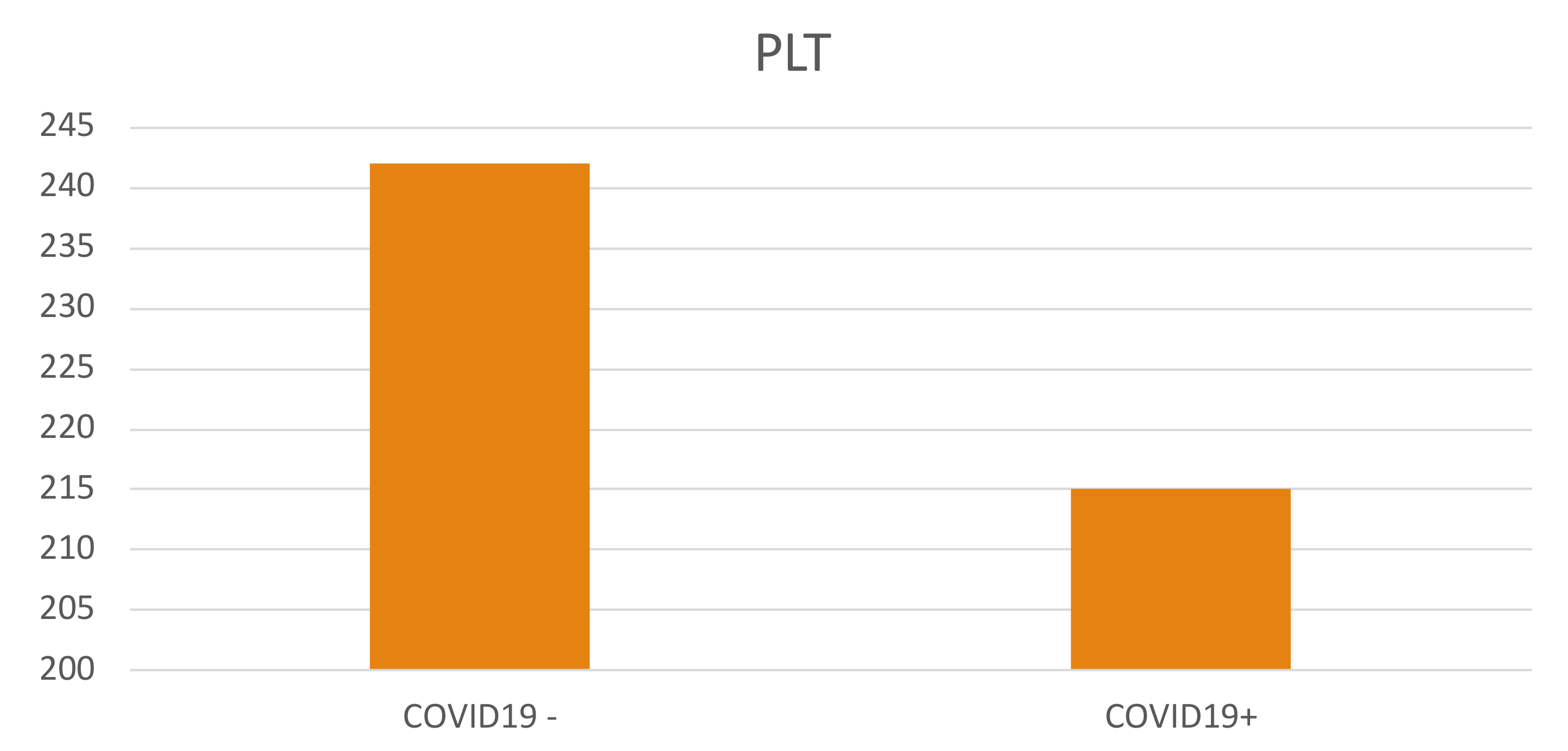
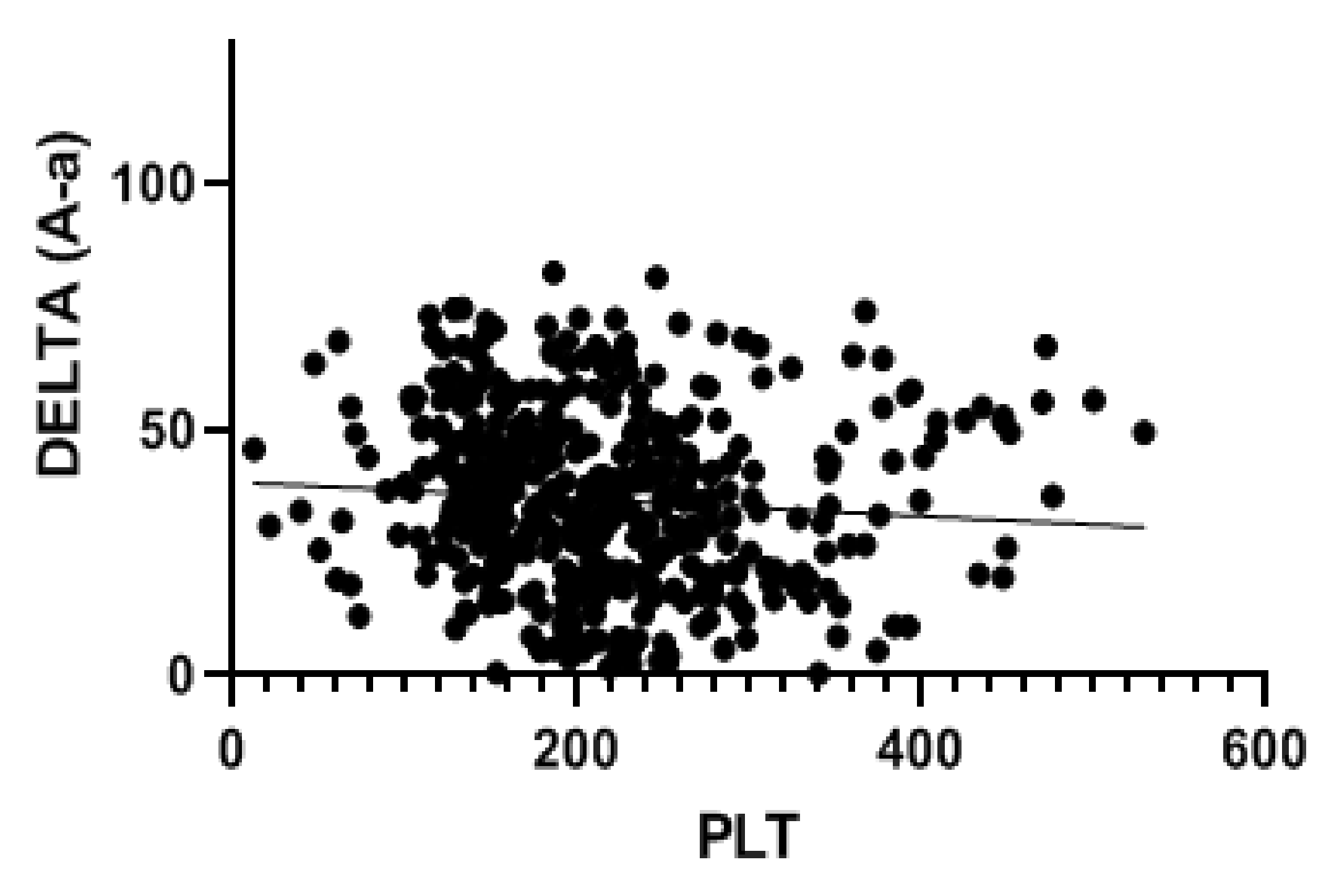
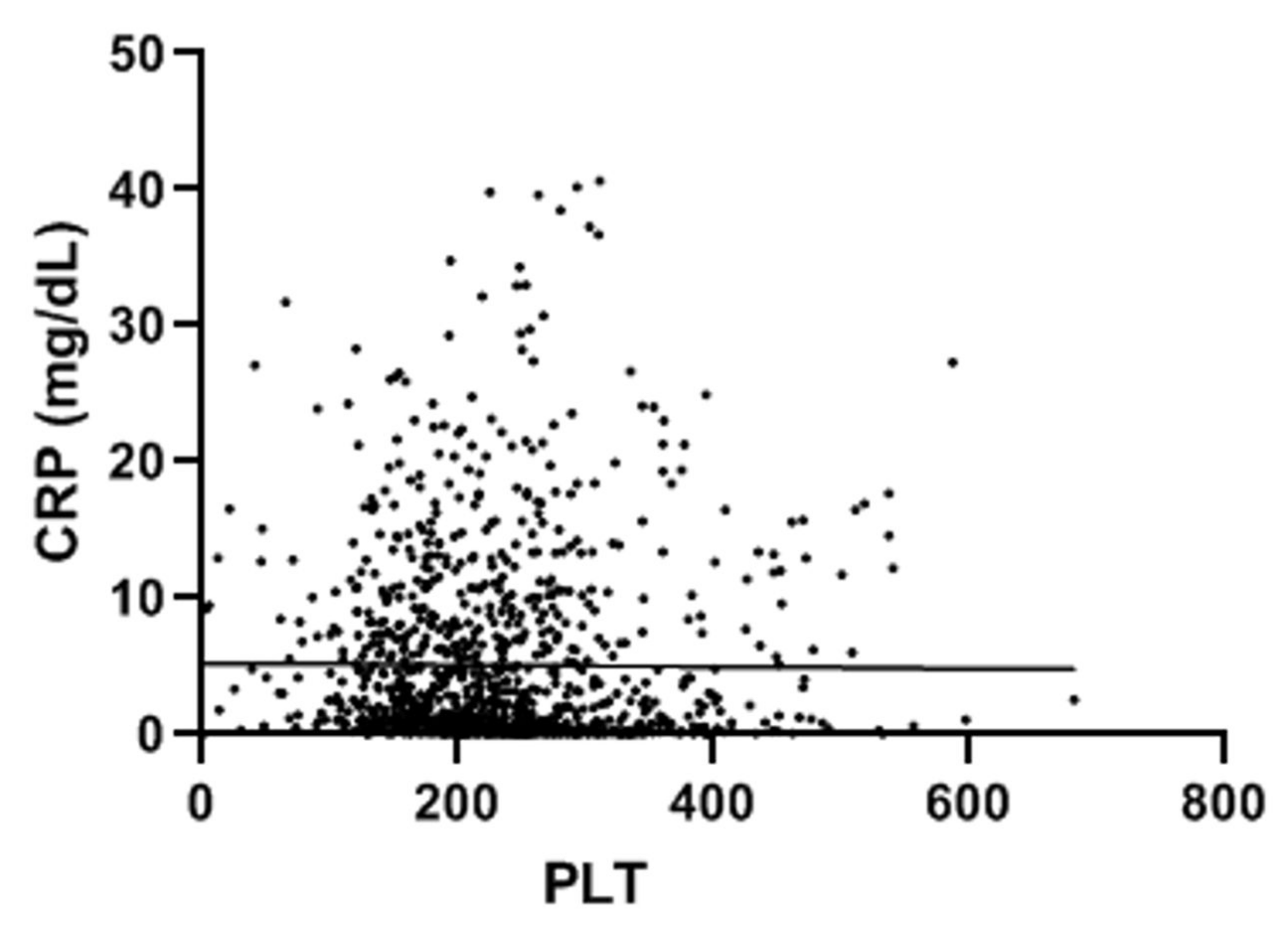
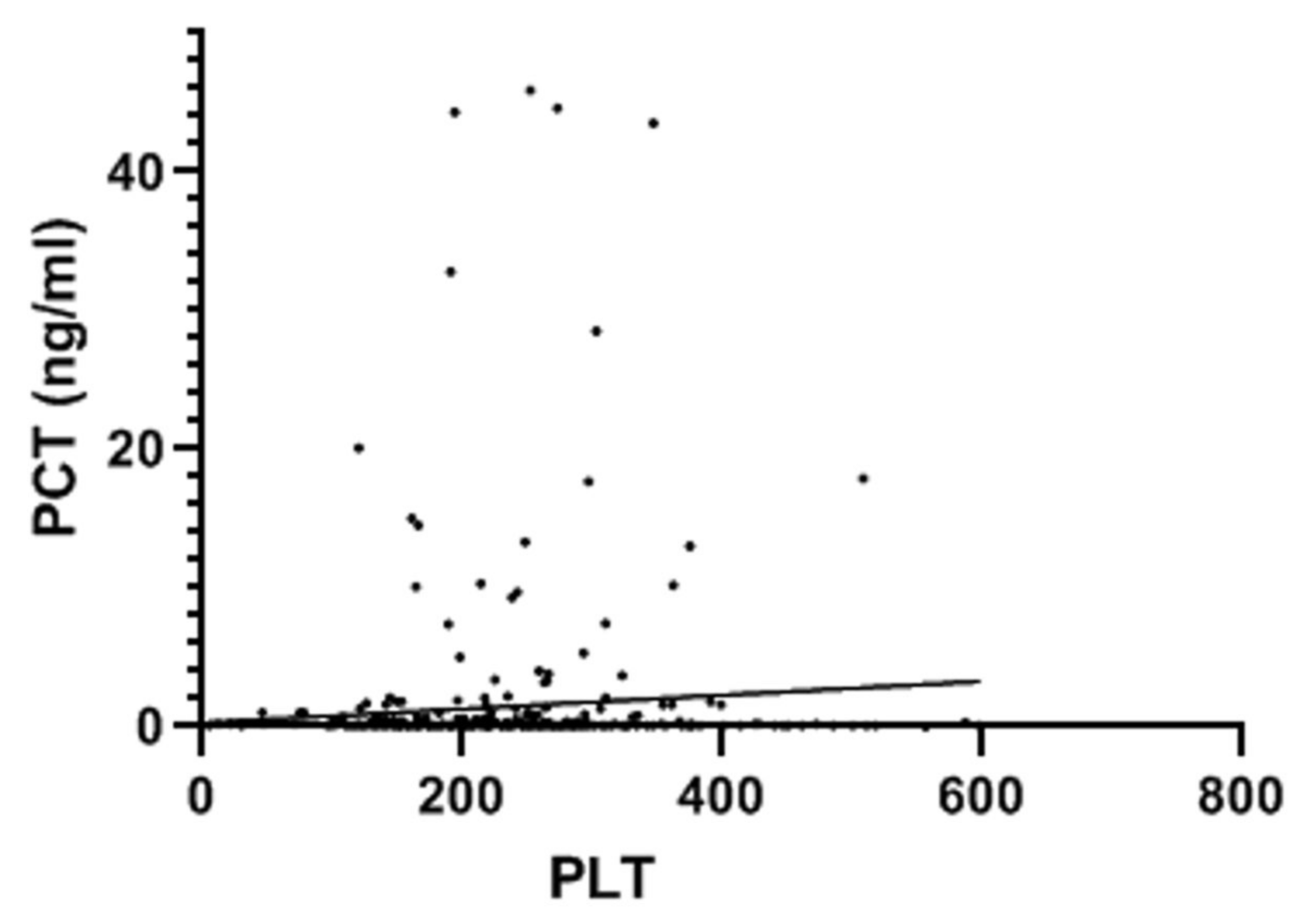
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simadibrata, D.M.; Pandhita, B.A.W.; Ananta, M.E.; Tango, T. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, a novel biomarker to predict the severity of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Intensive Care Soc. 2020, 23, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ardes, D.; Boccatonda, A.; Rossi, I.; Guagnano, M.T.; Santilli, F.; Cipollone, F.; Bucci, M. COVID-19 and RAS: Unravelling an Unclear Relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delshad, M.; Safaroghli-Azar, A.; Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, A.; Poopak, B.; Shokouhi, S.; Bashash, D. Platelets in the perspective of COVID-19; pathophysiology of thrombocytopenia and its implication as prognostic and therapeutic opportunity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 107995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccatonda, A.; Ianniello, E.; D’Ardes, D.; Cocco, G.; Giostra, F.; Borghi, C.; Schiavone, C. Can Lung Ultrasound be Used to Screen for Pulmonary Embolism in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia? Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2020, 7, 001748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, M.; Lili, L.; Hu, Y. Thrombocytopenia and thrombosis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 161. [Google Scholar]
- Amgalan, A.; Othman, M. Exploring possible mechanisms for COVID-19 induced thrombocytopenia: Unanswered questions. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1514–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, P.; Zhou, H. Delayed-phase thrombocytopenia in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M.; Thachil, J.; Iba, T.; Levy, J.H. Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e438–e440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.X.; Tyagi, T.; Jain, K.; Gu, V.W.; Lee, S.H.; Hwa, J.M.; Kwan, J.M.; Krause, D.S.; Lee, A.I.; Halene, S.; et al. Thrombocytopathy and endotheliopathy: Crucial contributors to COVID-19 thromboinflammation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 18, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Ortíz, J.; Deal, V.; Reyes, F.; Maldonado-Martínez, G.; Ledesma, N.; Staback, F.; Croft, C.; Pacheco, A.; Ortiz-Zuazaga, H.; Yost, C.C.; et al. Platelet-derived TLT-1 is a prognostic indicator in ALI/ARDS and prevents tissue damage in the lungs in a mouse model. Blood 2018, 132, 2495–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanderschueren, S.; De Weerdt, A.; Malbrain, M.; Vankersschaever, D.; Frans, E.; Wilmer, A.; Bobbaers, H. Thrombocytopenia and prognosis in intensive care. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 1871–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Duan, M.; Li, G.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Zhu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Christiani, D.C.; et al. Thrombocytopenia is associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome mortality: An international study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefrançais, E.; Ortiz-Muñoz, G.; Caudrillier, A.; Mallavia, B.; Liu, F.; Sayah, D.M.; Thornton, E.E.; Headley, M.; David, T.; Coughlin, T.D.S.R.; et al. The lung is a site of platelet biogenesis and a reservoir for haematopoietic progenitors. Nature 2017, 544, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manne, B.K.; Denorme, F.; Middleton, E.A.; Portier, I.; Rowley, J.W.; Stubben, C.; Petrey, A.C.; Tolley, N.D.; Guo, L.; Cody, M.; et al. Platelet gene expression and function in patients with COVID-19. Blood 2020, 136, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatim, N.; Boussier, J.; Chocron, R.; Hadjadj, J.; Philippe, A.; Gendron, N.; Barnabei, L.; Charbit, B.; Szwebel, T.-A.; Carlier, N.; et al. Platelet activation in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fard, M.B.; Fard, S.B.; Ramazi, S.; Atashi, A.; Eslamifar, Z. Thrombosis in COVID-19 infection: Role of platelet activation-mediated immunity. Thromb. J. 2021, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, C.; Miesbach, W.; Herrmann, E.; Sonntagbauer, M.; Raimann, F.J.; Zacharowski, K.; Weber, C.F.; Adam, E.H. Greater Fibrinolysis Resistance but No Greater Platelet Aggregation in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Anesthesiology 2021, 134, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, J.; Notz, Q.; Schlesinger, T.; Stumpner, J.; Kredel, M.; Sitter, M.; Schmid, B.; Kranke, P.; Schulze, H.; Meybohm, P.; et al. Point of care diagnostic of hypercoagulability and platelet function in COVID-19 induced acute respiratory distress syndrome: A retrospective observational study. Thromb. J. 2021, 19, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| All Patients (998) | COVID-19+ (489) | COVID-19− (509) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female sex | 957 (52.4%) | 301 (48.8%) | 453 (53.7%) | 0.089 |
| Hypertension | 561 (30.7%) | 238 (38.6) | 261 (31%) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 171 (9.4%) | 69 (11.2%) | 77 (9.1%) | 0.168 |
| COPD | 165 (9.0%) | 66 (10.7%) | 89 (10.5%) | <0.001 |
| Asthma | 70 (3.8%) | 18 (2.9%) | 42 (5%) | 0.200 |
| Other lung disease | 67 (3.7%) | 18 (2.9%) | 40 (4.7%) | 0.242 |
| Ischaemic cardiac disease | 148 (8.1%) | 49 (7.9%) | 85 (10.1%) | 0.002 |
| CKD | 122 (6.7%) | 48 (7.8%) | 62 (7.4%) | 0.068 |
| Stroke | 90 (4.9%) | 36 (5.8%) | 45 (5.3%) | 0.055 |
| Symptoms | All Patients (998) | COVID-19+ (489) | COVID-19− (509) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fever | 1325 (72.6%) | 498 (80.7%) | 567 (67.3%) | <0.001 |
| Dyspnea | 641 (35.1%) | 243 (39.4%) | 283 (33.6%) | 0.305 |
| Cough | 803 (44.0%) | 305 (49.4%) | 324 (38.4%) | <0.001 |
| Conjunctivitis | 42 (2.3%) | 8 (1.3%) | 27 (3.2%) | 0.163 |
| Pharyngodynia | 203 (11.1%) | 38 (6.2%) | 107 (12.7%) | 0.000 |
| Headache | 225 (12.3%) | 55 (8.9%) | 99 (11.7%) | <0.001 |
| Asthenia | 317 (17.4%) | 112 (18.2%) | 141 (16.7%) | 0.477 |
| Myalgia/arthralgia | 219 (12.0%) | 76 (12.3%) | 98 (11.6%) | 0.900 |
| Diarrhea | 300 (16.4%) | 86 (13.9%) | 146 (17.3%) | 0.071 |
| Anosmia | 73 (4.0%) | 30 (4.9%) | 25 (3.0%) | 0.283 |
| Ageusia | 146 (8.0%) | 56 (9.1%) | 53 (6.3%) | 0.033 |
| Chest pain | 98 (5.4%) | 16 (2.6%) | 51 (6.0%) | 0.016 |
| All Patients (998) | COVID-19+ (489) | COVID-19− (509) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 57.0 ± 21.2 | 62.3 ± 19.3 | 57.3 ± 21.7 | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 128.3 ± 21.0 | 125.9 ± 20.2 | 129.4 ± 22.2 | 0.032 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 75.5 ± 12.8 | 74.6 ± 12.4 | 75.6 ± 13.4 | 0.159 |
| MAP (mmHg) | 68.4 ± 42.4 | 76.7 ± 36.1 | 68.8 ± 43.2 | 0.118 |
| HR (bpm) | 88.2 ± 16.9 | 88.9 ± 16.7 | 89.0 ± 17.1 | 0.95 |
| RR (a/min) | 18.8 ± 5.2 | 19.7 ± 5.5 | 18.7 ± 5.2 | <0.001 |
| Temperature (°C) | 36.9 ± 0.7 | 37.1 ± 0.8 | 36.9 ± 0.7 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boccatonda, A.; D’Ardes, D.; Rossi, I.; Grignaschi, A.; Lanotte, A.; Cipollone, F.; Guagnano, M.T.; Giostra, F. Platelet Count in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Prognostic Factor in COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4112. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144112
Boccatonda A, D’Ardes D, Rossi I, Grignaschi A, Lanotte A, Cipollone F, Guagnano MT, Giostra F. Platelet Count in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Prognostic Factor in COVID-19. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(14):4112. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144112
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoccatonda, Andrea, Damiano D’Ardes, Ilaria Rossi, Alice Grignaschi, Antonella Lanotte, Francesco Cipollone, Maria Teresa Guagnano, and Fabrizio Giostra. 2022. "Platelet Count in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Prognostic Factor in COVID-19" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 14: 4112. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144112
APA StyleBoccatonda, A., D’Ardes, D., Rossi, I., Grignaschi, A., Lanotte, A., Cipollone, F., Guagnano, M. T., & Giostra, F. (2022). Platelet Count in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Prognostic Factor in COVID-19. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(14), 4112. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144112










