Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Vein and Venous Sinus Thrombosis—A Systematic Review
Abstract
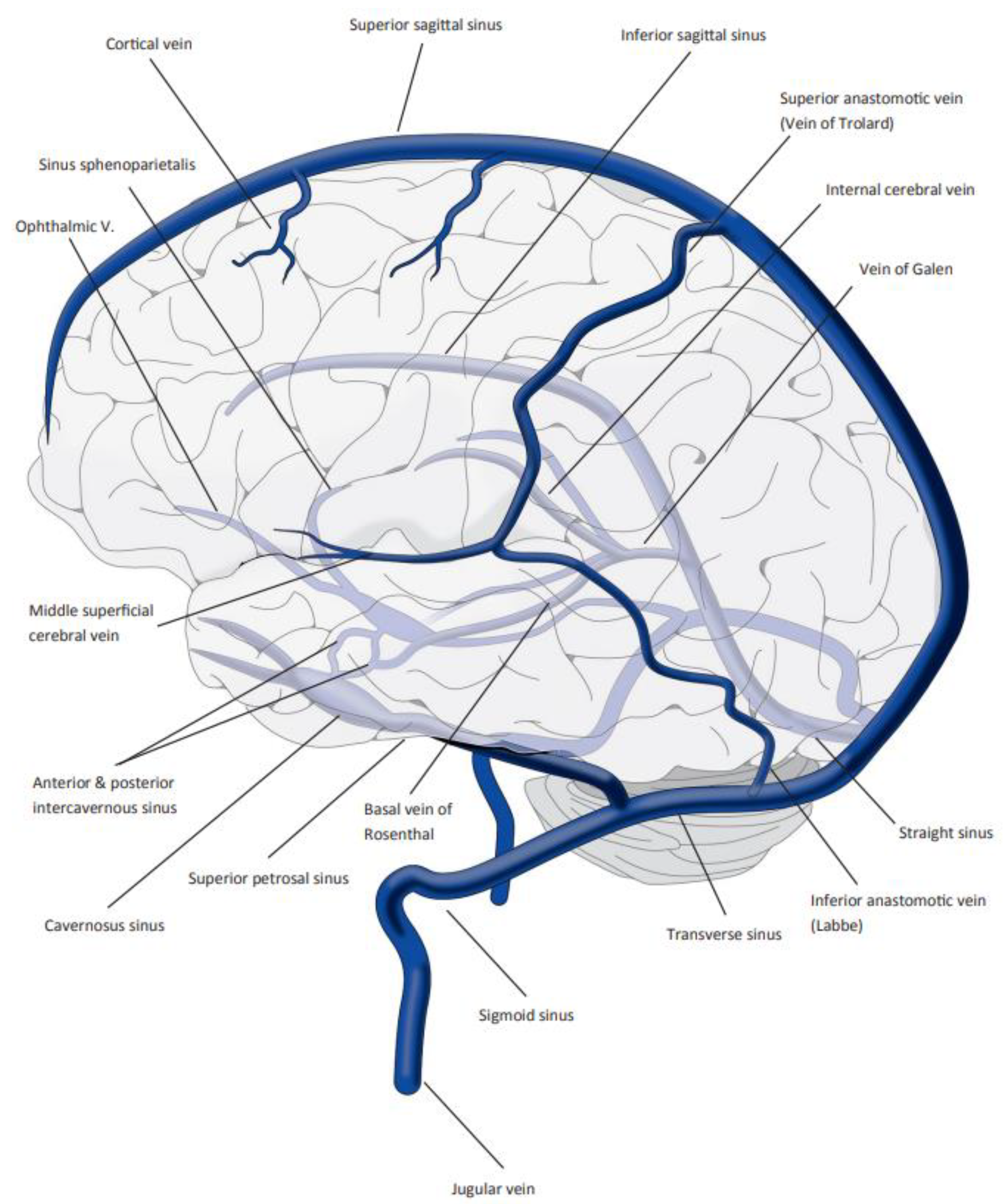
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hopper, A.H.; Klein, J.P. Cerebral Venous Thrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Bousser, M.; Ferro, J.M. Cerebral venous thrombosis: An update. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, J.M.; Zuurbier, S.M.; Aramideh, M.; Stam, J. The Incidence of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis a Cross-Sectional Study. Stroke 2012, 43, 3375–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stam, J. Thrombosis of the Cerebral Veins and Sinuses. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Mufti, F.; Amuluru, K.; Sahni, R.; Bekelis, K.; Karimi, R.; Ogulnick, J.; Cooper, J.; Overby, P.; Nuoman, R.; Tiwari, A.; et al. Cerebral Venous Thrombosis in COVID-19: A New York Metropolitan Cohort Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, V.; Nepal, G.; Dijamco, P.; Ishak, A.; Dagar, M.; Sarfraz, Z.; Shama, N.; Sarfraz, A.; Lnu, K.; Mitra, S.; et al. Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Following COVID-19 Vaccination: A Systematic Review. J. Prim. Care Community Health 2022, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Mattle, H.; Horvath, T.; Seiffge, D.; Heldner, M.; Meinel, T.; Bühlmann, M.; Prange, U.; Salmen, S.; Humm, A.; et al. Stroke Guidelines of the Bern Stroke Network. Available online: http://www.neurologie.insel.ch/fileadmin/Neurologie/Dokumente/Stroke_Center/Stroke_Guidelines_2021_English.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2022).
- Devianne, J.; Legris, N.; Crassard, I.; Bellesme, C.; Bejot, Y.; Guidoux, C.; Pico, F.; Germanaud, D.; Obadia, M.; Rodriguez, D.; et al. Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Outcome in a Cohort of Adolescents with Cerebral Venous Thrombosis. Neurology 2021, 97, e1920–e1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einhäupl, K.M.; Villringer, A.; Meister, W.; Mehraein, S.; Garner, C.; Pellkofer, M.; Haberl, R.L.; Pfister, H.W.; Schmiedek, P. Heparin treatment in sinus venous thrombosis. Lancet 1991, 338, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, S.F.T.M.; Stam, J.; for the Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Study Group. Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Anticoagulant Treatment with Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin for Cerebral Sinus Thrombosis. Stroke 1999, 30, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferro, J.M.; Canhão, P.; Stam, J.; Bousser, M.; Barinagarrementeria, F.; ISCVT Investigators. Prognosis of Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis Results of the International Study on Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis (ISCVT). Stroke 2004, 35, 664–670. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-K.; Mokin, M.; Hetts, S.W.; Fifi, J.F.; Bousser, M.; Fraser, J.F.; Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery. Current endovascular strategies for cerebral venous thrombosis: Report of the SNIS Standards and Guidelines Committee. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2018, 10, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, J.M.; Ferro, J.M.; Zuurbier, S.M.; Mink, M.S.; Canhão, P.; Crassard, I.; Majoie, J.B.; Reekers, J.A.; Houdart, E.; de Haan, R.J.; et al. Thrombolysis or anticoagulation for cerebral venous thrombosis: Rationale and design of the TO-ACT trial. Int. J. Stroke 2013, 8, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simaan, N.; Molad, J.; Peretz, S.; Filioglo, A.; Auriel, E.; Hallevi, H.; Seyman, E.; Barnea, R.; Cohen, J.E.; Leker, R.R.; et al. Characteristics of Cerebral Sinus Venous Thrombosis Patients Presenting with Intracerebral Hemorrhage. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Velat, G.J.; Hoh, B.L.; Mocco, J. Direct thrombolysis for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Neurosurg. Focus 2009, 27, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baker, M.D.; Opatowsky, M.J.; Wilson, J.A.; Glazier, S.S.; Morris, P.P. Rheolytic catheter and thrombolysis of dural venous sinus thrombosis: A case series. Neurosurgery 2001, 48, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canhao, P.; Falcao, F.; Ferro, J.M. Thrombolytics for cerebral sinus thrombosis: A systematic review. Cereb. Dis 2003, 15, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choulakian, A.; Alexander, M.J. Mechanical thrombectomy with the penumbra system for treatment of venous sinus thrombosis. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2010, 2, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowitz, B.T.; Bodily, L.M.; Jumaa, M.; Syed, Z.F.; Jovin, T.G. Manual aspiration thrombectomy for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2013, 5, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, J.; Rasmussen, P.A.; Masaryk, T.J.; Perl, J., II; Fiorella, D. Adjunctive rheolytic thrombectomy for central venous sinus thrombosis: Technical case report. Neurosurgery 2007, 60, E577–E578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Barge, D.V.; Bishop, F.S.; Stevens, E.A.; Eskandari, R.; Schmidt, R.H.; Skalabrin, E.J.; Ng, P.P. Intrasinus catheter-directed heparin infusion the treatment of dural venous sinus thrombosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, A.; Collinson, R.L.; Hurst, R.W.; Weigele, J.B. Rheolytic thrombectomy for cerebral sinus thrombosis. Neurocrit Care 2008, 9, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, Y.; Zhang, N.; He, L.; Shen, L.; Yan, K. Mechanical thrombectomy combined with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator thrombolysis in the venous sinus for the treatment of severe tcerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shui, S.F.; Li, T.F.; Han, X.W.; Ma, J.; Guo, D. Balloon dilatation and thrombus extraction for the treatment of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Neurol. India 2014, 62, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasay, M.; Bakshi, R.; Kojan, S.; Bobustuc, G.; Dubey, N.; Unwin, D.H. Nonrandomized comparison of local urokinase thrombolysis versus systemic heparin anticoagulation for superior sagittal sinus thrombosis. Stroke 2001, 32, 2310–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chow, K.Y.; Gobin, P.; Saver, J.; Kidwell, C.; Dong, P.; Viñuela, F. Endovascular Treatment of Dural Sinus Thrombosis with Rheolytic Thrombectomy and Intra-Arterial Thrombolysis. Stroke 2000, 31, 1420–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, A.A.; Rasheedi, J.K.; Kurdi, K.I.; Hasan, A.A.; Almekhlafi, M.A.; Baeesa, S.S. Endovascular suction thrombectomy for severe cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: A report of two cases. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2018, 13, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Ahmadpour, A.; Binyamin, T.; Dahlin, B.C.; Shahlaie, K.; Waldau, B. Management and outcome of spontaneous cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in a 5-year consecutive single-institution cohort. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2017, 9, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, H.; Mineharu, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Imamura, H.; Yamamato, S.; Todo, K.; Yamagami, H.; Sakai, N. Stenting for acute cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in the superior sagittal sinus. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2015, 21, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Liu, Y.; Gu, W.; Yang, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, F.; Zeng, F.; Wang, X. Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: Successful Treatment of Two Patients Using the Penumbra System and Review of Endovascular Approaches. Neuroradiol. J. 2015, 28, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Philips, M.F.; Bagley, L.J.; Sinson, G.P.; Raps, E.C.; Galetta, S.L.; Zager, E.L.; Hurst, R.W. Endovascular thrombolysis for symptomatic cerebral venous thrombosis. J. Neurosurg. 1999, 90, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandapat, S.; Samaniego, E.A.; Szeder, V.; Siddiqui, F.M.; Duckwiler, G.R.; Kiddy, U.; Guerrero, W.R.; Zheng, B.; Hasan, D.; Derdeyn, C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the use of large bore intermediate suction catheters alone or in combination for the treatment of acute cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: A multicenter experience. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2020, 26, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, F.; Weber, M.W.; Dandapat, S.; Scaife, S.; Buhnerkempe, M.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; Aksan, N.; Elias, A.; Coutinho, J.M. Endovascular Thrombolysis or Thrombectomy for Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: Study of Nationwide Inpatient Sample 2004–2014. J. Stroke Cereb. Dis. 2019, 6, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Shui, S.; Han, X.; Guo, D.; Li, T.; Yan, L. Mechanical thrombectomy with Solitaire AB stents for the treatment of intracranial venous sinus thrombosis. Acta Radiol. 2016, 57, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, D.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Endovascular treatment for hemorrhagic cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: Experience with 9 cases for 3 years. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C.; Liao, N.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Shen, C.; Yang, S.; Tsuei, Y. Endovascular Mechanical Thrombectomy and On-Site Chemical Thrombolysis for Severe Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Li, T.; Fan, Y. Efficacy of intravascular mechanical thrombectomy combined with thrombolysis and anticoagulant therapy in the treatment of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and its effect on neurological function and coagulation indices. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 6921–6928. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, J.M.; Zuurbier, S.M.; Bousser, M.; Ji, X.; Canhão, P.; Boos, Y.B.; Crassard, I.; Nunes, A.P.; Uyttenboogaart, M.; Chen, J.; et al. Effect of Endovascular Treatment with Medical Management vs Standard Care on Severe Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: The TO-ACT Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, E.M.; Case, D.; Nagae, L.M.; Honce, J.M.; Reyenga, W.; Seinfeld, J.; Poisson, S.; Leppert, M.H. The addition of endovascular intervention for dural venous sinus thrombosis: Single-center experience and review of literature. J. Stroke Cereb. Dis. 2017, 26, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, F.M.; Banerjee, C.; Zuurbier, S.M.; Hao, Q.; Ahn, C.; Pride, G.L.; Wasay, M.; Majoie, C.B.; Liebeskind, D.; Johnsin, M.; et al. Mechanical thrombectomy versus intrasinus thrombolysis for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: A non-randomized comparison. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2014, 20, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Liu, S.; Guan, S. The clinical analysis and treatment strategy of endovascular treatment for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis combined with intracerebral hemorrhage. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.H.; Hansen, K.; Truelsen, T.; Cronqvist, M.; Stavngaard, T.; Cortsen, M.E.; Holtmannspötter, M.; Højgaard, J.L.S.; Stensballe, J.; Welling, K.L.; et al. Endovascular treatment for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis—A single center study. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 35, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wu, F.; Liu, Y.; Duan, J.; Meng, R.; Chen, J.; Li, D.; Fan, Z.; Fisher, M.; Yang, Q.; et al. Predictors of successful endovascular treatment in severe cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Ann. Clin. Trans. Neur. 2019, 6, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Z. Balloon-Assisted Thrombectomy and Intrasinus Urokinase Thrombolysis for Severe Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 735540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, J.; Majoie, C.; Van Delden, O.M.; Van Lienden, K.P.; Reekers, J.A. Endovascular thrombectomy and thrombolysis for severe cerebral sinus thrombosis: A prospective study. Stroke 2008, 39, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, G.; Shin, J.H.; Song, Y.; Lee, D.H. Stenting of symptomatic lateral sinus thrombosis refractory to mechanical thrombectomy. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2019, 25, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Grigoryan, M.; Saleem, M.A.; Aytac, E.; Wallery, S.S.; Rodriguez, G.J.; Suri, M.F.K. Prolonged Microcatheter-Based Local Thrombolytic Infusion as a Salvage Treatment After Failed Endovascular Treatment for Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: A Multicenter Experience. Neurocrit Care 2018, 29, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styczen, H.; Tsogkas, I.; Liman, J.; Maus, V.; Psychogios, M.N. Endovascular Mechanical Thrombectomy for Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: A Single-Center Experience. World Neurosurg. 2019, 127, e1097–e1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokin, M.; Lopes, D.K.; Binning, M.J.; Veznedaroglu, E.; Liebman, K.M.; Arthur, A.S.; Doss, V.T.; Levy, E.I.; Siddiqui, A.H. Endovascular treatment of cerebral venous thrombosis: Contemporary multicenter experience. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2015, 21, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dashti, S.H.; Hu, V.C.; Fiorella, D.; Mitha, A.P.; Abuquerque, F.C.; McDougall, C.G. Mechanical thrombectomy as first-line treatment for venous sinus thrombosis: Technical considerations and preliminary results using the AngioJet device. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2011, 5, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J. Suction thrombectomy after balloon maceration for dural venous sinus thrombosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 365, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, F.R.; Høgedal, L.; Stilling, M.V.; Birkeland, P.F.; Schultz, M.K.; Rasmussen, J.N. Good clinical outcome after combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Dan. Med. J. 2013, 60, A4724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mammen, S.; Keshava, S.N.; Moses, V.; Aaron, S.; Ahmed, M.; Chiramel, G.K.; Mani, S.E.; Alexander, M. Role of penumbra mechanical thrombectomy device in acute dural sinus thrombosis. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2017, 27, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, T.; Dan, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Liu, J. Efficacy of Stent Thrombectomy Alone or Combined with Intermediate Catheter Aspiration for Severe Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: A Case-Series. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 783380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhi, G.; Parida, S.; Nicholson, P.; Senapati, S.B.; Padhy, B.P.; Medes Pareira, V. Mechanical Thrombectomy for Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Series. World Neurosurg. 2020, 140, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, A.C.O.; Hwang, A.C.; Chiu, R.H.Y.; Chan, D.Y.C.; Tsang, F.C.P.; Ho, W.S.; Lee, R.; Leung, G.K.K.; Lui, W.M. Combined aspiration thrombectomy and continuous intrasinus thrombolysis for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: Technical note and case series. Neuroradiology 2018, 60, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Xi, G.; Zhou, Z.H.; Xu, G.; Liu, X. Combined intraarterial and intravenous thrombolysis for severe cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2010, 29, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saposnik, G.; Barinagarrementeria, F.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Bushnell, C.D.; Cucchiara, B.; Cushman, M.; deVeber, G.; Ferro, J.M.; Tsai, F.Y. American Heart Association Stroke Council and the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Diagnosis and Management of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2011, 42, 1158–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferro, J.M.; Bousser, M.; Canhão, P.; Coutinho, J.M.; Crassard, I.; Dentali, F.; Di Minno, M.; Maino, A.; Martinelli, I.; Masuhr, F.; et al. European Stroke Organization guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of cerebral venous thrombosis—Endorsed by the European Academy of Neurology. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostovan, V.R.; Foroughi, R.; Rostami, M.; Almasi-Dooghaee, M.; Esmaili, M.; Akbar Bidaki, A.; Behzadi, Z.; Farzadfard, F.; Marbooti, H.; Rahimi-Jaberi, A.; et al. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis associated with COVID-19: A case series and literature review. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 3549–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, D.D.; Raz, E.; Shapiro, M.; Dehkharghani, S.; Yaghi, S.; Lillemoe, K.; Nossek, E.; Torres, J.; Jain, R.; Riina, H.A.; et al. Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Associated with COVID-19. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omari, A.; Kally, P.; Schimmel, O.; Kahana, A. Vision Loss Secondary to COVID-19 Associated Bilateral Cerebral Venous Sinus Thromboses. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 38, e65–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajjad, A.; Khan, A.F.; Jafri, L.; Kamal, A.K. Successful endovascular mechanical thrombectomy in anticoagulation-resistant COVID-19 associated cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e245405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, H.S.; Al-Ali, S.; Butler, B.; Rajapakse, D.; Nader, S.K.; Chavda, S.; Lamin, S. Mechanical Thrombectomy for Treatment of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis in Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2022, 43, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.E.; Luz, B.; Niehaus, L.; Bhogal, P.; Bäzner, H.; Henkes, H. Thrombocytopenia and Intracranial Venous Sinus Thrombosis after “COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca” Exposure. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleaver, J.; Ibitoye, R.; Morrison, H.; Flood, R.; Crewdson, K.; Marsh, A.; Abhinav, K.; Bosnell, R.; Crossley, R.; Mortimer, A. Endovascular treatment for vaccine-induced cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and thrombocytopenia following ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccination: A report of three cases. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurjar, H.; Dhallu, M.; Lvovsky, D.; Sadullah, S.; Chilimuri, S. A Rare Case of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccine-Associated Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Treated with Mechanical Thrombectomy. Am. J. Case Rep 2022, 23, e935355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirandola, L.; Arena, G.; Pagliaro, M.; Boghi, A.; Naldi, A.; Castellano, D.; Vaccarino, A.; Silengo, D.; Aprà, F.; Cavallo, R.; et al. Massive cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 serum: Case report of a successful multidisciplinary approach. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 1499–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.R.; Jin, J.Y.; Choi, S.W.; Kim, H.; Yoo, J.H.; Park, I.S.; Kim, S.R. Intracerebral Hemorrhage due to Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome after Vaccination against COVID-19: The First Fatal Case in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waraich, A.; Williams, G. Haematuria, a widespread petechial rash, and headaches following the Oxford AstraZeneca ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e245440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsy, M.; Harmer, J.R.; Guan, J.; Brock, A.A.; Ravindra, V.M.; Chung, L.S.; Tkach, A.; Majersik, J.J.; Park, M.S.; Schmidt, R.H. Outcomes in adults with cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: A retrospective cohort study. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 53, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, L.L.L.; Lye, P.P.S.; Yee, K.W.; Cunli, Y.; Ming, T.T.; Ho, A.F.; Sharma, V.K.; Chan, B.P.; Tan, B.Y.; Gopinathan, A. Deep Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Treatment Endovascular Case using Aspiration and Review of the Various Treatment Modalities. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2020, 30, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfefferkorn, T.; Crassard, I.; Linn, J.; Dichgans, M.; Boukobza, M.; Bousser, M. Clinical features, course and outcome in deep cerebral venous system thrombosis: An analysis of 32 cases. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 1839–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.B.; O’Duffy, A.E.; Kumar, A.B. Heparin Resistance and Anticoagulation Failure in a Challenging Case of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Neurohospitalist 2015, 6, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Feng, D.; Wang, T.; Xu, X.; Deng, R.; Zhou, X.; Chen, G. Endovascular Therapy Versus Anticoagulation for Treatment of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis A Meta-Analysis. Neurologist 2022, 27, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.; Saber, H.; Sadeghi, M.; Rajah, G.; Narayanan, S. Transvenous Endovascular Recanalization for Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019, 130, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, A.; Chen, C.H.-J.; Raper, D.M.; Ding, D.; Buell, T.; Mastorakos, P.; Liu, K.C. Endovascular mechanical thrombectomy for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: A systematic review. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2017, 9, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, K.; Joundi, R.A.; Aviv, R.I. An historical and contemporary review of endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Neurovasc Imaging. 2017, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjouei, S.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Farahmand, G.; Koza, E.; Mowla, A.; Sadr, A.V.; Kia, A.; Far, A.V.; Mondello, S.; Cernigliaro, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 and Stroke Characteristics A Report from the Multinational COVID-19 Stroke Study Group. Stroke 2021, 52, e117–e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowla, A.; Shakibajahromi, B.; Shahjouei, S.; Borhani-Haghighi, A.; Rahimian, N.; Baharvadhdat, H.; Naderi, S.; Khorvash, F.; Altafi, D.; Ebrahimzadeh, S.A.; et al. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis associated with SARS-CoV-2; a multinational case series. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 419, 117183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonagle, D.; De Marco, G.; Bridgewood, C. Mechanisms of Immunothrombosis in Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia (VITT) Compared to Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 121, 102662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, A.; Hirsch, J.A. Cerebral venous thrombosis after COVID-19 vaccination: The role for endovascular treatment. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2022, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Reference | Treatment | Outcome Assessment | Localization | Complications | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author (Year) | Study Type | Period | n (N) | Inclusion Criteria/Treatment Allocation | Pre-ICH | Endovascular Treatment | Control Group | FU (Month) | Outcome | Death | Recanal. | SSS | SS | Sig S | TS | DV | Catheter * | ICH ** | Other |
| Coutinho et al. (2020) [38] | RCT | 2011–2016 | 33 (67) | High probability of poor outcome, at least 1 of the following risk factors: mental status disorder, coma state (GCS <9), ICH, or thrombosis of the deep cerebral venous system (exclusion: duration from diagnosis of more than 10 days, pregnancy (women in the puerperium were eligible); thrombocytopenia (platelet count, <100 × 109/L), clinical and radiological signs of impending transtentorial herniation) | n = 22 | n = 33; LT (alteplase, urokinase; up to 72 h): n = 17 (52%); MT: n = 30 (91%) (AngioJet [n = 14], SR [n = 5], B [n = 3], aspiration (A) [n = 3; Penumbra], microcatheter [n = 3], other [n = 9]) | n = 34; standard care | 6, 12 | mRS 0–1 (12 months): n = 22 (67%) vs. n = 23 (68%); risk ratio 0.99 (95% CI 0.71–1.18) | 12 months; n = 4 (12%) [vs. n = 1 (3%)] | SSS (6–12 months): 79% vs. 52%, 1.52 (1.02–2.27); SS (6 months): 96% vs. 86%, 1.13 (0.95–1.33) | n = 23 (70%) | n = 17 (52%) | l: n = 12 r: n = 15 | l: n = 16 r: n = 22 | n = 14 (42%) | n = 3 (9%) | n = 6 (18%) (hem. compl.) | NA |
| Nyberg et al. (2017) [39] | retrosp | 2011–2015 | 29 (66) | SVT (anticoagulation), decision of treatment team | n = 17 (n = 10 in CC) | LT n = 29 (24–72 h); n = 21 additional MT (A, SR, B, AngioJet or combination; not specified) | n = 37; standard care | 3 | mRS 0–2: 22 vs. 30 (p = 1.0) | n = 6 (vs. n = 5) | n = 11; full (n = 8), partial (n = 3) | n = 25 | n = 0 | n = 21 | n = 25 | n = 7 | NN | n = 9 | NN |
| Siddiqui et al. (2014) [40] | retrosp | 1995–2012 | 63 (NN) | SVT (anticoagulation) and either coma (GCS < 9), ICH or deterioration | n = 29 | n = 63; n = 29 LT only, n = 34 MT (plus LT n = 27; AngioJet n = 28, A n = 3, SR n = 1. B n = 2) [LT bolus and continuously depending on recanalization] | NA | 3 | n = 53; mRS 0–1: n = 33 | n = 11 | full (n = 21), partial (n = 18) | NN | NN | NN | NN | NN | n = 5 | n = 3 | NN |
| Guo et al. (2020) [41] | retrosp | 2010–2019 | 56 (227 sc) | SVT under anticoagulation; ICH, lack of improvement or deterioration of symptoms | n = 56 | n = 56; LT only (n = 41; duration: 7 days); additional MT (n = 15) [SR n = 5, A n = 3, B n = 3, combined n = 4) | NA | 6 | n = 54; mRS 0–2: n = 49 | n = 3 | (full and partial); LT n = 39; MT n = 14 | NN | NN | NN | NN | NN | n = 0 | LT n = 7, MTn = 1 | NN |
| Andersen et al. (2020) [42] | retrosp | 2007–2018 | 28 (NN) | SVT under anticoagulation; clinical deterioration and/or impaired consciousness | n = 18 | n = 28; LT (n = 26; 12–72 h), A (n = 3), SR (n = 3), combined (more than 2 techniques; n = 4) incl. PTA and stenting (n = 2) | NA | 6 | mRS 0–2: n = 20 | n = 5 | full (n = 15), partial (n = 11), no (n = 2) | n = 16 | n = 15 | n = 15 | n = 16 | n = 7 | n = 1 (retrop. hem.) | n = 8 | NA |
| Yang et al. (2019) [43] | pros CS | 2014–2018 | 21 (27 sc) | SVT (anticoagulation) with: ICH, mental status impairment, coma (GCS < 9), DV thrombosis, cortical venous thrombosis, intracranial hypertension, or papilledema | NN | NN | NA | 12 | mRS 0–2: n = 21 | n = 0 | full (n = 5), partial (n = 9) | n = 16 | n = 0 | n = 17 | n = 19 | n = 14 | NN | NN | NN |
| Yang et al. (2021) [44] | retrosp | 2017–2019 | 23 (NN) | SVT (anticoagulation) with: deterioration after the initiation of anticoagulation, lethargy or coma, venous infarction with hemorrhagic transformation or ICH | n = 8 | n = 23; MT (B) plus LT (urokinase) | NA | 6 | n = 21; mRS 0–1: n = 21 | n = 0 | full (n = 9), partial (n = 13) | n = 20 | n = 11 | n = 21 | n = 21 | NN | n = 2 (failure) | n = 1 | NN |
| Stam et al. (2008) [45] | pros CS | NN | 20 (NN) | SVT (heparin) with assumed poor prognosis: altered mental status, coma, extensive edema, ICH, infarction | n = 14 | n = 20, LT only (n = 15 additional MT [rheolytic catheter]) | NA | 3 (−6) | mRS 0–2: n = 12 | n = 6 | NN | NN | NN | NN | NN | n = 20 | NN | n = 1 (ICH progress) | NN |
| Lu et al. (2019) [46] | retrosp | 2015–2018 | 14 (NN) | SVT (best medical treatment); decision of treatment team | n = 1 | n = 14; MT (SR or A, combination), additional stenting in n = 5 (in case of failure of SR or A; re- occlusion) | NA | 2 (−16) | n = 5 (stenting); mRS 0–1: n = 4 | n = 0 | NN | n = 0 | n = 0 | n = 0 | n = 5 | NA | NN | n = 2 (increase) | NN |
| Qureshi et al. (2018) [47] | retrosp | 2006–2011/2016/2017 | 14 (NN) | SVT (anticoagulation), deterioration | n = 7 | n = 13 LT, MT: AngioJet n = 9, B n = 2, SR n = 2 (combined) [LT bolus, up to 22 h after MT in case of incomplete recanalization] | NA | 1 (−3) | mRS 0–2: n = 10 | n = 1 | full (n = 3), partial (n = 4) | n = 10 | n = 1 | n = 10 | n = 13 | n = 0 | NN | NN | NN |
| Styczen et al. (2019) [48] | retrosp | 2011–2018 | 13 (NN) | SVT (heparin) with assumed poor prognosis: altered mental status or coma, involvement of DV, ICH | n = 7 | n = 13; MT (A n = 4, A plus SR n = 9) | NA | 3 (median) | mRS 0–2: n = 12 | n = 1 | full (n = 4), partial (n = 7) | n = 9 | n = 5 | n = 7 | n = 10 | NN | n = 1 (perf) | n = 3 | NN |
| Mokin et al. (2015) [49] | retrosp | 2010–2013 | 13 (NN) | SVT (plus/minus anticoagulation), decision of treatment team | NN | n = 13 (LT n = 2 [sinus or ia]; A n = 2; LT plus A n = 3; A plus SR n = 2; AngioJet n = 2, combined n = 3) | NA | 3 | n = 11; mRS 0–2: n = 5 | n = 1 | full (n = 5), partial (n = 8) | n = 10 | n = 7 | n = 0 | n = 11 | n = 0 | NN | NN | NN |
| Dashti et al. (2011) [50] | retrosp | 2009/2010 | 13 (NN) | NA; decision of treatment team | NN | n = 13; AngioJet | NA | NN | n = 9; mRS 0–1: n = 7 | n = 2 | full (n = 6), partial (n = 7) | n = 9 | NN | NN | NN | NN | NN | NN | n = 1 (re- occl) |
| Lee et al. (2016) [51] | retrosp | 2008–2015 | 10 (NN) | SVT under anticoagulation; MT in case of ICH, deep venous thrombosis, deterioration | n = 9 | n = 10; MT (B plus A [combination]) plus LT (n = 3; before 2013; bolus) | NA | 3 | mRS 0–1: n = 8 | n = 1 | NN | n = 6 | n = 3 | n = 5 | n = 9 | NA | n = 0 | n = 1 | NN |
| Poulsen et al. (2013) [52] | retrosp | 2007–2011 | 9 (NN) | SVT (anticoagulation), deterioration | n = 4 | n = 6 MT (n = 5 prior LT [24–72 h]; not specified); n = 5 LT only | NA | 6 | mRS 0–2: n = 8 | n = 1 | full (n = 2), partial (n = 4) | n = 5 | n = 4 | n = 0 | n = 9 | n = 0 | n = 0 | n = 1 (SAH) | n = 3 (hem. [eVD]) |
| Mammen et al. (2017) [53] | retrosp | (4 years) | 8 (243 sc) | SVT (anticoagulation), no response or deterioration | n = 1 | n = 8 (MT, A [Penumbra] plus additional B (n = 7) and LT (n = 3; bolus) | NA | 6 | mRS 0–2: n = 5 | n = 1 | full (n = 3), partial (n = 4) | n = 5 | n = 5 | n = 2 | n = 6 | n = 3 | n = 0 | n = 0 | n = 0 |
| Peng et al. (2021) [54] | retrosp | 2017–2020 | 7 (NN) | SVT (anticoagulation); one risk factor (poor outcome): coma (GCS < 9), ICH, DV thrombosis | n = 4 | n = 7 MT (SR; plus A n = 4; plus B n = 4; plus heparin n = 4, plus LT n = 1 [bolus]) | NA | 3 | mRS 0–2: n = 6 | n = 0 | full (n = 4), partial (n = 3) | n = 7 | n = 0 | n = 4 | n = 5 | n = 0 | n = 0 | n = 0 | n = 0 |
| Mehdi et al. (2020) [55] | retrosp | 2018/2019 | 7 (NN) | SVT (anticoagulation), clinical and imaging deterioration (no signs of herniation) | n = 3 | n = 7 (MT; A) plus LT (n = 4; bolus 20 min) | NA | 1 (3, 6) | mRS 0–1: n = 5 | n = 0 | partial (n = 7) | n = 6 | n = 4 | n = 0 | n = 3 | n = 0 | n = 0 | n = 0 | n = 0 |
| Tsang et al. (2018) [56] | CS | 2014–2018 | 6 (NN) | SVT (anticoagulation) with deterioration or ICH | NN | n = 6; MT (A [Penumbra]) plus LT (urokinase) | NA | 3 | mRS 0–1: n = 5 | n = 1 | NN | n = 5 | n = 2 | n = 3 | n = 4 | NN | n = 0 | n = 0 | n = 0 |
| Jankowitz et al. (2013) [19] | retrosp | 2009–2011 | 6 (27 sc) | SVT (best medical treatment); clinical (progressive deficits, coma) or radiological (hem., edema) deterioration | n = 4 | n = 6; MT (A) (n = 6), additional LT n = 4 (bolus) | NA | 6 | mRS 0–2: n = 4 | n = 1 | n = 6 | n = 3 | n = 2 | n = 1 | n = 3 | NA | n = 0 | NN | n = 0 |
| Yue et al. (2010) [57] | retrosp | 2005–2008 | 6 (28 sc) | SVT (anticoagulation) with deterioration or assumed poor prognosis: coma, altered mental state, seizure, space-occupying lesions (edema or [hemorrhagic] infarct) | n = 2 | n = 6; MT (B) plus ia T (urokinase) | NA | 3 (−6) | mRS 0: n = 5 | n = 1 | full (n = 5) | n = 6 | n = 4 | n = 6 | n = 6 | n = 20 | n = 0 | n = 0 | n = 0 |
| Reference | Etiology | Laboratory Findings | Treatment | Outcome | Location | Complications | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author (Year) | Study Type | n | COVID-19 (C-19), VITT | d (After Index) | Treatment Allocation | Endovascular Treatment | mRS | Recanalization | |||
| Ostovan et al. (2021) [62] | case series | 1 (of 9) | C-19 | 5 (?) | TP (140 T/uL), elevated D-dimer levels (>10.000 ng/mL) | ICH | LT plus MT (A) | 6 | full | SSS, TS | NN |
| Cavalcanti et al. (2020) [63] | case series | 1 (of 3) | C-19 | 10 | TP (141 T/uL), elevated D-dimer levels (>55.000 ng/mL) | edema, rapid deterioration | MT (A) plus LT (micro-catheter, cont.) | 6 | partial | SSS, TS, SS, DV | NN |
| Omari et al. (2022) [64] | case report | 1 | C-19 | 30 | NN | visual deterioration, intracranial hypertension | NN | NN | NN | TS, S Sig | blindness |
| Sajjad et al. (2021) [65] | case report | 1 | C-19 | 20 | TP (NN), PF4 antibodies (NN), elevated D-dimer levels (6.3 mg/L) | ICH plus edema, coma, deterioration | Fogarty catheter | 2 | full | SSS | NN |
| Chew et al. (2021) [66] | case series | 6 | VITT (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) * | 10 (−14) | TP (11 T-91 T/uL), PF4 antibodies and D-dimer levels NN | ICH (n = 5), progressive thrombus material, deterioration (coma) | Aspiration (Penumbra) | 0–1: n = 3; 6: n = 2 | satisf. (n = 5) | NN | n = 1 (ICH-progression) |
| Wolf et al. (2021) [67] | case series | 3 | VITT (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) | 4 (−17) | TP (60 T–92 T/uL), PF4 antibodies (positive), elevated D-dimer levels (2120–22,800 ng/mL) | SAH (1); ICH (2); coma due to bilateral thalamic edema (3) | MT (A [1, 3] plus B [2]) | 0 (1, 3); 1 (2) | full | SSS, TS (1), SSS, TS, S Sig (2) | 2 MT sessions needed (2) |
| Cleaver at al. (2021) [68] | case series | 3 | VITT (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) | 8 (−27) | TP (85 T/uL [1], 23 T/uL [2], 35 T/uL [3]); PF4-antibodies positive (all), elevated D-dimer levels (15.83–30.34 μg/mL) | progr. ICH/SAH, edema and deterioration (1); progr. ICH and thrombus material (2); new ICH, status epilepticus, intubation (3) | MT (A [1], A plus SR [2]) | 2 (all) | full (2), partial (1, 3) | SSS (1), SS, S Sig, TS (2), SSS, S Sig, TS (3) | NN |
| Gurjar et al. (2022) [69] | case report | 1 | VITT (mRNA-1273 vaccine) ** | 3 months | TP (139 T/uL), PF4 antibodies (negative), elevated D-dimer levels (16.666 ng/mL) | coma, progressive symptoms | MT (not specified) | 3 | full | SSS, TS, S Sig | NN |
| Mirandola et al. (2022) [70] | case report | 1 | VITT (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) | 15 | TP (40 T/uL), PF4 antibodies (positive), elevated D-dimer levels (18 mcg/mL) | progressive thrombus material, edema, coma and seizure requiring intubation | MT (A plus SR) | 0 | partial (SS), full (rest) | SSS, SS, TS, S Sig | NN |
| Choi et al. (2021) [71] | case report | 1 | VITT (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) | 12 | TP (14 T/uL), PF4 antibodies (positive), elevated D-dimer levels (>32.5 mg/L [reference: < 0.5]) | progressive coma | MT (not specified) | 6 | full | S Sig | NN |
| Waraich et al. (2021) [72] | case report | 1 | VITT (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) | 13 | TP (14 T/uL), PF4 antibodies NN, elevated D-dimer levels (62.342 ng/mL) | deterioration, SAH, seizures requiring CPR | NN | NN (2 ***) | full | SSS, TS, S Sig | NN |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bücke, P.; Hellstern, V.; Cimpoca, A.; Cohen, J.E.; Horvath, T.; Ganslandt, O.; Bäzner, H.; Henkes, H. Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Vein and Venous Sinus Thrombosis—A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144215
Bücke P, Hellstern V, Cimpoca A, Cohen JE, Horvath T, Ganslandt O, Bäzner H, Henkes H. Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Vein and Venous Sinus Thrombosis—A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(14):4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144215
Chicago/Turabian StyleBücke, Philipp, Victoria Hellstern, Alexandru Cimpoca, José E. Cohen, Thomas Horvath, Oliver Ganslandt, Hansjörg Bäzner, and Hans Henkes. 2022. "Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Vein and Venous Sinus Thrombosis—A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 14: 4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144215
APA StyleBücke, P., Hellstern, V., Cimpoca, A., Cohen, J. E., Horvath, T., Ganslandt, O., Bäzner, H., & Henkes, H. (2022). Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Vein and Venous Sinus Thrombosis—A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(14), 4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144215







