DNase-1 Treatment Exerts Protective Effects in Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema via Regulating the Neutrophil Extracellular Traps after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Drug Administration
2.4. Mice SAH Model
2.5. Mortality and Neurological Deficits
2.6. The NPE Criteria
2.7. Lung Histopathology and Immunofluorescent Staining
2.8. qRT-PCR
2.9. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
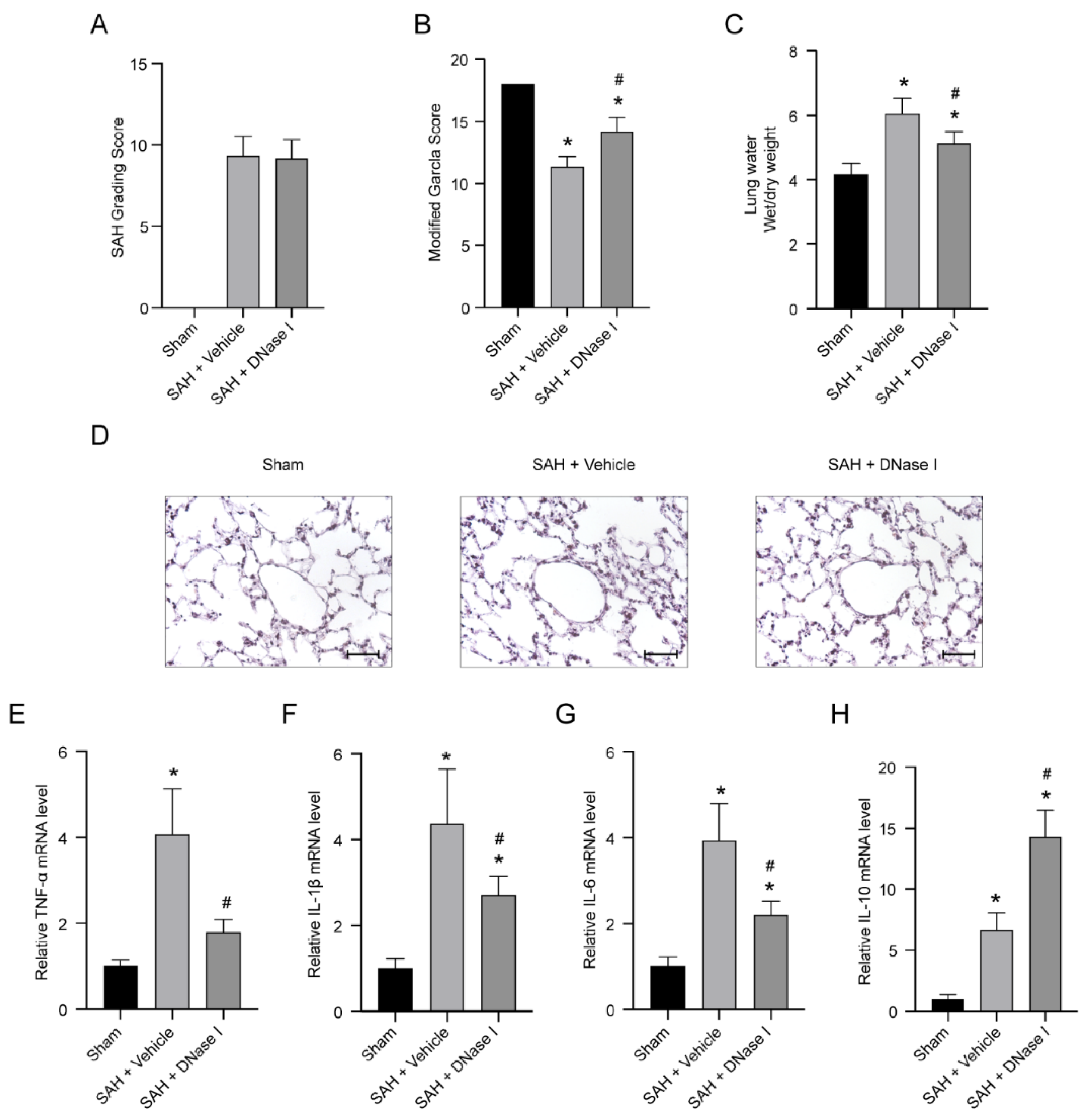
3.1. DNase-1 Treatment Relieves the Injury of NPE after SAH
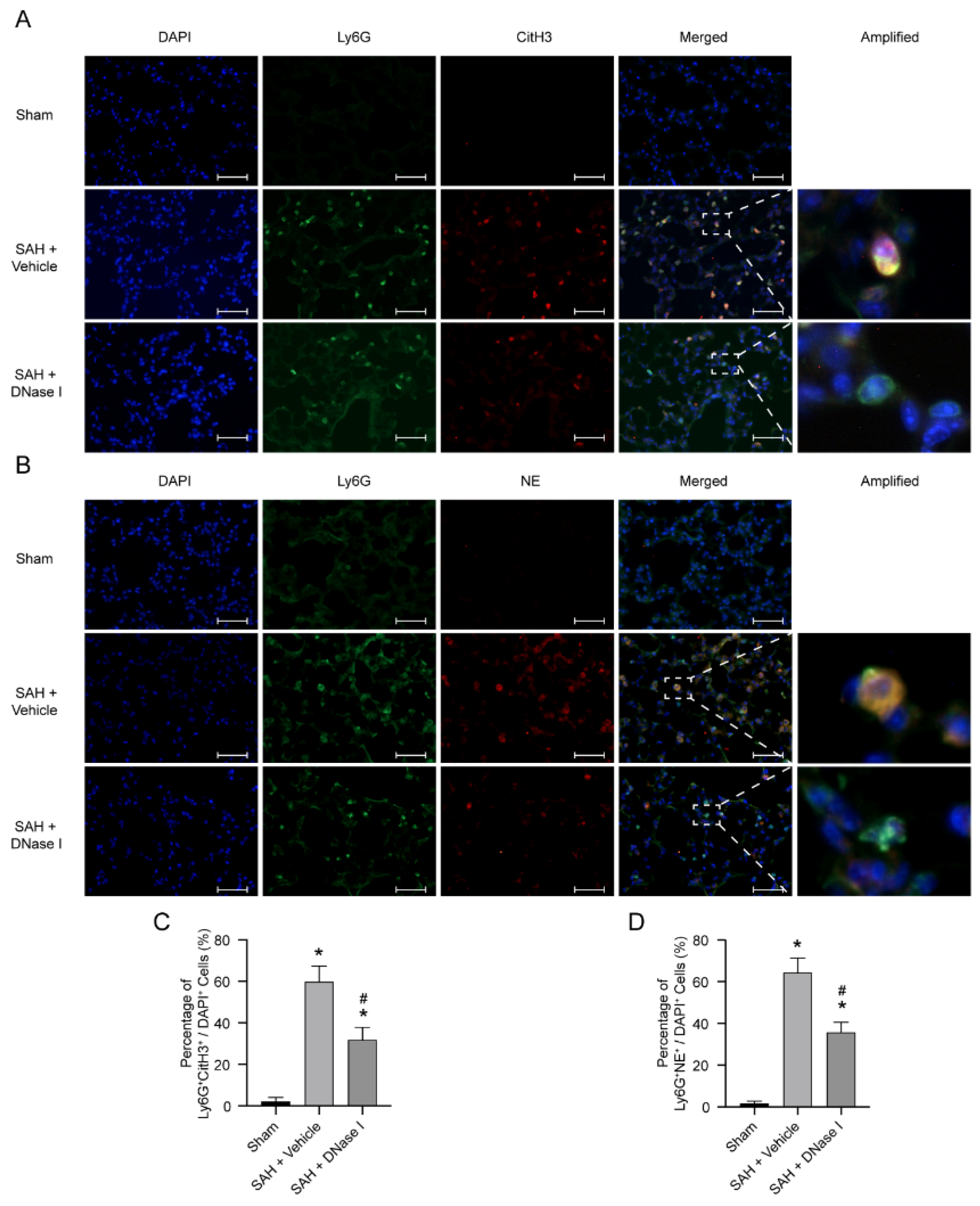
3.2. DNase-1 Treatment Inhibits NETs in NPE after SAH
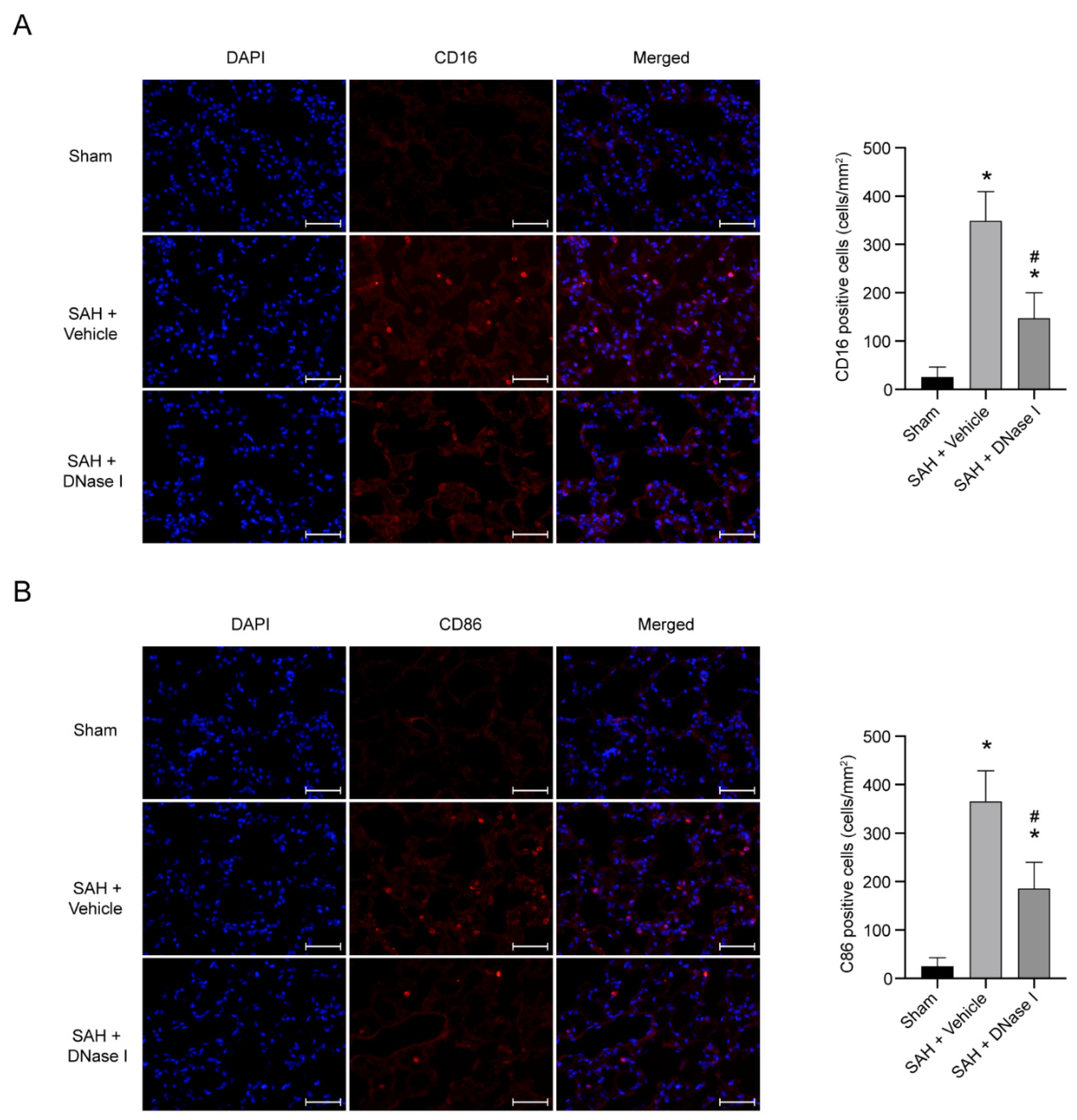
3.3. DNase-1 Treatment Reduces the Proinflammatory Subtype Transition of Macrophage in NPE after SAH
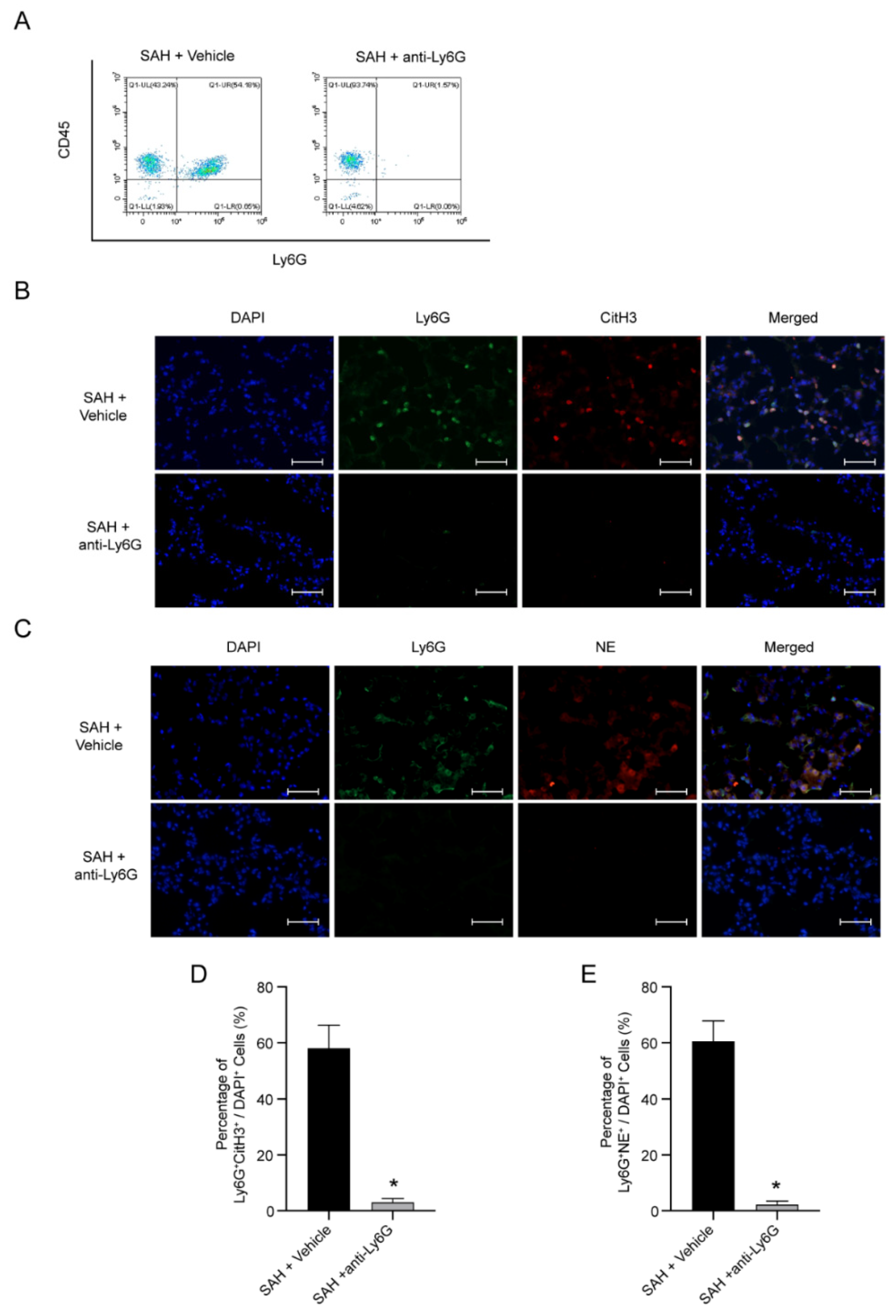
3.4. NETs Are Possible Pathogenic Mechanism of NPE after SAH
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Gijn, J.; Kerr, R.S.; Rinkel, G.J.E. Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet 2007, 369, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bederson, J.B.; Connolly, E.S.; Batjer, H.H.; Dacey, R.G.; Dion, J.E.; Diringer, M.; Duldner, J.E.; Harbaugh, R.; Patel, A.B.; Rosenwasser, R.H. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Stroke 2009, 40, 994–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garg, R.; Bar, B. Systemic Complications Following Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2017, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, A.; Audibert, G.; McDonnell, J.; Mertes, P.M. Neurogenic pulmonary edema. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2007, 51, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder, N.; The Participants in the International Multi-disciplinary Consensus Conference on the Critical Care Management of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage; Rabinstein, A. Cardiovascular and pulmonary complications of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2011, 15, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macmillan, C.S.; Grant, I.S.; Andrews, P.J. Pulmonary and cardiac sequelae of subarachnoid haemorrhage: Time for active management? Intensive Care Med. 2002, 28, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J. Neurological Perspectives of Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema. Eur. Neurol. 2019, 81, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šedý, J.; Kuneš, J.; Zicha, J. Pathogenetic Mechanisms of Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Sozen, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.H. Caspase-1 inhibitor prevents neurogenic pulmonary edema after subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice. Stroke 2009, 40, 3872–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorch, S.K.; Kubes, P. An emerging role for neutrophil extracellular traps in noninfectious disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, T.; Sun, S.; Wang, K.; Liu, B.; Wu, X.; Ding, W. DNase-1 Treatment Exerts Protective Effects in a Rat Model of Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saffarzadeh, M.; Juenemann, C.; Queisser, M.A.; Lochnit, G.; Barreto, G.; Galuska, S.P.; Lohmeyer, J.; Preissner, K.T. Neutrophil extracellular traps directly induce epithelial and endothelial cell death: A predominant role of histones. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortjens, B.; van Woensel, J.B.; Bem, R.A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Respiratory Disease: Guided anti-microbial traps or toxic webs? Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2017, 21, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrot, P.A.; Tellier, E.; Plantureux, L.; Crescence, L.; Robert, S.; Chareyre, C.; Daniel, L.; Secq, V.; Garcia, S.; Dignat-George, F.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps are associated with the pathogenesis of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in murine lupus. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 100, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, C.S.; Hahn, S.; Hasler, P.; Hoesli, I.; Lapaire, O.; Giaglis, S. Elevated Levels of Total Cell-Free DNA in Maternal Serum Samples Arise from the Generation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2016, 40, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.C.; Chuang, Y.H.; Tsai, Y.F.; Yu, H.P. Role of neutrophil extracellular traps following injury. Shock 2014, 41, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettcher, M.; Eschenburg, G.; Mietzsch, S.; Jiménez-Alcázar, M.; Klinke, M.; Vincent, D.; Tiemann, B.; Bergholz, R.; Reinshagen, K.; Fuchs, T.A. Therapeutic targeting of extracellular DNA improves the outcome of intestinal ischemic reperfusion injury in neonatal rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, H.; Fu, X.; Cai, J.; Sun, C.; Yu, M.; Peng, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Yu, Q.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps may be a Potential Target for Treating Early Brain Injury in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021, 13, 112–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Martínez, C.; Durán-Laforet, V.; García-Culebras, A.; Ostos, F.; Hernández-Jiménez, M.; Bravo-Ferrer, I.; Pérez-Ruiz, A.; Ballenilla, F.; Díaz-Guzmán, J.; Pradillo, J.M.; et al. Pharmacological Modulation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Reverses Thrombotic Stroke tPA (Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator) Resistance. Stroke 2019, 50, 3228–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, M.; Chen, X.; Lu, Z.; Bellanti, J.A.; Zheng, S.G. All trans-retinoic acid protects against acute ischemic stroke by modulating neutrophil functions through STAT1 signaling. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, H.H.; Shao, B.; Zhuang, J.F.; Peng, Y.C.; Chen, H.J.; Yu, Q.; Xu, C.R.; Fu, X.J.; Zhou, H.; Cao, Y.; et al. Naringenin reduces early brain injury in subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) mice: The role of the AMPK/SIRT3 signaling pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 72, 104043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Shrestha, S.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.; Yan, F.; Ying, G.; Gu, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, G. Melatonin-mediated mitophagy protects against early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Ying, G.; Zeng, H.; Zhou, H.; Cao, Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.; Fu, X.; Xu, H.; et al. Stimulator of IFN genes mediates neuroinflammatory injury by suppressing AMPK signal in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, Z.; Klebe, D.; Bian, H.; Krafft, P.R.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Role of P2X purinoceptor 7 in neurogenic pulmonary edema after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Qian, C.; Duan, H.; Cao, S.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Gu, C.; Yan, F.; Wang, L.; Chen, G. Melatonin attenuates neurogenic pulmonary edema via the regulation of inflammation and apoptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease, Nature reviews. Immunology 2018, 18, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehba, F.A. Rat endovascular perforation model. Transl. Stroke Res. 2014, 5, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Gijn, J.; Rinkel, G.J. Subarachnoid haemorrhage: Diagnosis, causes and management. Brain J. Neurol. 2001, 124 Pt 2, 249–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobelens, P.M.; Tiebosch, I.A.; Dijkhuizen, R.M.; van der Meide, P.H.; Zwartbol, R.; Heijnen, C.J.; Kesecioglu, J.; van den Bergh, W.M. Interferon-β attenuates lung inflammation following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.Y.; Sagher, O.; Keep, R.; Hua, Y.; Xi, G. Comparison of experimental rat models of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 2009, 65, 331–343, discussion 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busl, K.M.; Bleck, T.P. Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidyuk, G.; Soriano, S.G.; Goumnerova, L.; Mizrahi-Arnaud, A. Acute intraoperative neurogenic pulmonary edema during endoscopic ventriculoperitoneal shunt revision. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 110, 594–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, R.B.; Aguiar, P.H.; Zanetti, M.V.; Andrade, F.; Mandel, M.; Teixeira, M.J. Acute neurogenic pulmonary edema: Case reports and literature review. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2003, 15, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayah, D.M.; Mallavia, B.; Liu, F.; Ortiz-Muñoz, G.; Caudrillier, A.; DerHovanessian, A.; Ross, D.J.; Lynch, J.P., 3rd; Saggar, R.; Ardehali, A.; et al. Looney, Neutrophil extracellular traps are pathogenic in primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabbione, F.; Keitelman, I.A.; Iula, L.; Ferrero, M.; Giordano, M.N.; Baldi, P.; Rumbo, M.; Jancic, C.; Trevani, A.S. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Stimulate Proinflammatory Responses in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. J. Innate Immun. 2017, 9, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorvillo, N.; Cherpokova, D.; Martinod, K.; Wagner, D.D. Extracellular DNA NET-Works with Dire Consequences for Health. Circ. Res. 2019, 125, 470–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudrillier, A.; Kessenbrock, K.; Gilliss, B.M.; Nguyen, J.X.; Marques, M.B.; Monestier, M.; Toy, P.; Werb, Z.; Looney, M.R. Platelets induce neutrophil extracellular traps in transfusion-related acute lung injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2661–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josefs, T.; Barrett, T.J.; Brown, E.J.; Quezada, A.; Wu, X.; Voisin, M.; Amengual, J.; Fisher, E.A. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote macrophage inflammation and impair atherosclerosis resolution in diabetic mice. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e134796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, H.; Chen, G. DNase-1 Treatment Exerts Protective Effects in Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema via Regulating the Neutrophil Extracellular Traps after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154349
Wu X, Guo Y, Zeng H, Chen G. DNase-1 Treatment Exerts Protective Effects in Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema via Regulating the Neutrophil Extracellular Traps after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(15):4349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154349
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xinyan, Yinghan Guo, Hanhai Zeng, and Gao Chen. 2022. "DNase-1 Treatment Exerts Protective Effects in Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema via Regulating the Neutrophil Extracellular Traps after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 15: 4349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154349
APA StyleWu, X., Guo, Y., Zeng, H., & Chen, G. (2022). DNase-1 Treatment Exerts Protective Effects in Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema via Regulating the Neutrophil Extracellular Traps after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(15), 4349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154349





