Total Plasma Exchange in Neuromuscular Junction Disorders—A Single-Center, Retrospective Analysis of the Efficacy, Safety and Potential Diagnostic Properties in Doubtful Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study
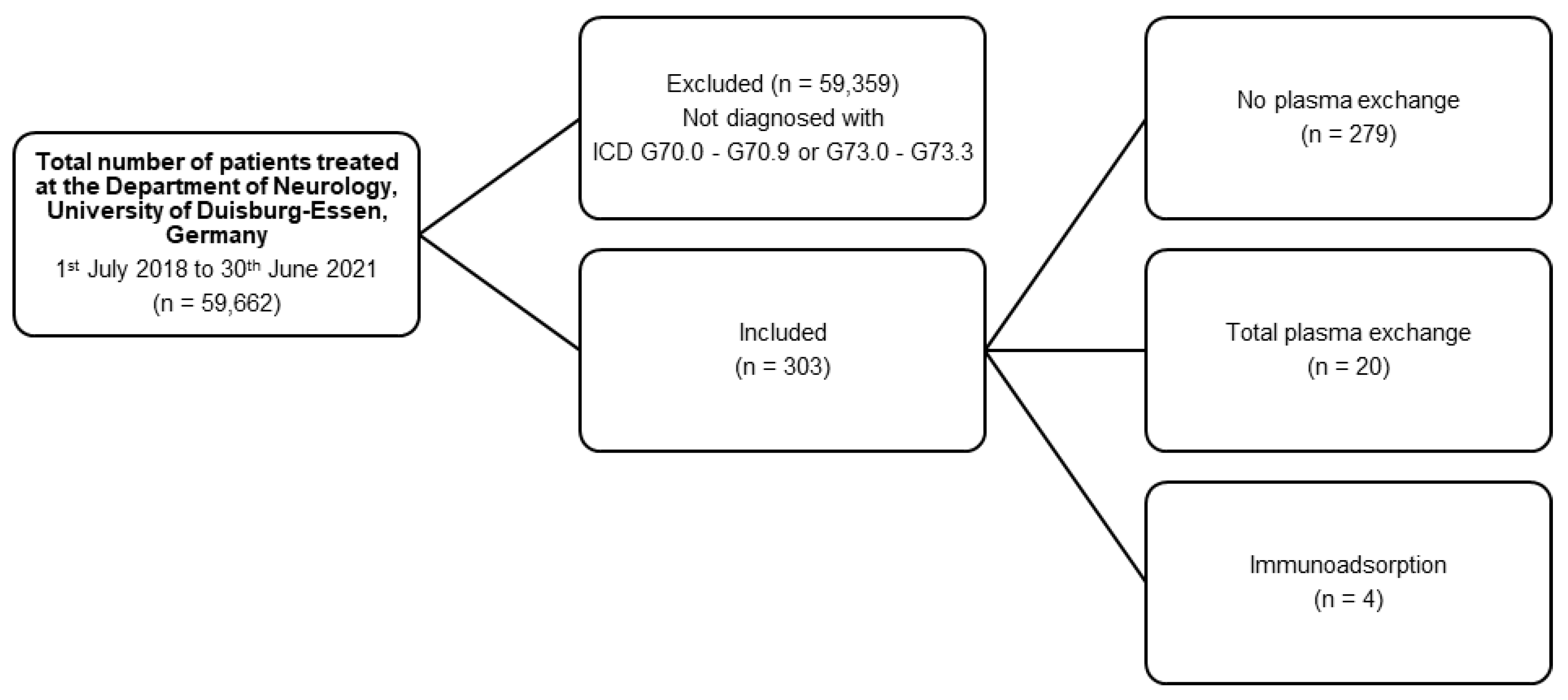
2.2. Patients
2.3. Plasma Exchange
2.4. Laboratory Analysis
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Diagnosis and Indication
3.2. Safety
4. Discussion
4.1. Patient Characteristics
4.2. Diagnostic Value of TPE
4.3. Safety of TPE
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melzer, N.; Ruck, T.; Fuhr, P.; Gold, R.; Hohlfeld, R.; Marx, A.; Melms, A.; Tackenberg, B.; Schalke, B.; Schneider-Gold, C.; et al. Clinical features, pathogenesis, and treatment of myasthenia gravis: A supplement to the Guidelines of the German Neurological Society. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 1473–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verschuuren, J.; Strijbos, E.; Vincent, A. Neuromuscular junction disorders. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 133, 447–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyka, K.V.; Brachman, D.B.; Pestronk, A.; Kao, I. Myasthenia gravis: Passive transfer from man to mouse. Science 1975, 190, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoch, W.; McConville, J.; Helms, S.; Newsom-Davis, J.; Melms, A.; Vincent, A. Auto-antibodies to the receptor tyrosine kinase MuSK in patients with myasthenia gravis without acetylcholine receptor antibodies. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, O.; Hamuro, J.; Motomura, M.; Yamanashi, Y. Autoantibodies to low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 in myasthenia gravis. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoser, B.; Eymard, B.; Datt, J.; Mantegazza, R. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS): A rare autoimmune presynaptic disorder often associated with cancer. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuuren, J.J.; Palace, J.; Murai, H.; Tannemaat, M.R.; Kaminski, H.J.; Bril, V. Advances and ongoing research in the treatment of autoimmune neuromuscular junction disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H. Assessment of Disease Activity, Structural Damage, and Function in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1868, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rider, L.G.; Werth, V.P.; Huber, A.M.; Alexanderson, H.; Rao, A.P.; Ruperto, N.; Herbelin, L.; Barohn, R.; Isenberg, D.; Miller, F.W. Measures of adult and juvenile dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and inclusion body myositis: Physician and Patient/Parent Global Activity, Manual Muscle Testing (MMT), Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ)/Childhood Health Assessment Questionnaire (C-HAQ), Childhood Myositis Assessment Scale (CMAS), Myositis Disease Activity Assessment Tool (MDAAT), Disease Activity Score (DAS), Short Form 36 (SF-36), Child Health Questionnaire (CHQ), physician global damage, Myositis Damage Index (MDI), Quantitative Muscle Testing (QMT), Myositis Functional Index-2 (FI-2), Myositis Activities Profile (MAP), Inclusion Body Myositis Functional Rating Scale (IBMFRS), Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI), Cutaneous Assessment Tool (CAT), Dermatomyositis Skin Severity Index (DSSI), Skindex, and Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, S118–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, D.; Nabavi Nouri, M.; Ng, E.; Nwe, P.; Bril, V. Comparison of IVIg and PLEX in patients with myasthenia gravis. Neurology 2011, 76, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Triantafyllou, N.I.; Grapsa, E.I.; Kararizou, E.; Psimenou, E.; Lagguranis, A.; Dimopoulos, A. Periodic therapeutic plasma exchange in patients with moderate to severe chronic myasthenia gravis non-responsive to immunosuppressive agents: An eight year follow-up. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2009, 13, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczeklik, W.; Wawrzycka, K.; Wludarczyk, A.; Sega, A.; Nowak, I.; Seczynska, B.; Fajfer, I.; Zajac, K.; Krolikowski, W.; Kozka, M. Complications in patients treated with plasmapheresis in the intensive care unit. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2013, 45, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergenthaler, P.; Stetefeld, H.R.; Dohmen, C.; Kohler, S.; Schonenberger, S.; Bosel, J.; Gerner, S.T.; Huttner, H.B.; Schneider, H.; Reichmann, H.; et al. Seronegative myasthenic crisis: A multicenter analysis. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 3904–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.J.; Morgan, M.B.; Lu, L.; Hatanaka, Y.; Hemmi, S.; Young, A.; Claussen, G.C. Different characteristic phenotypes according to antibody in myasthenia gravis. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2012, 14, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Utsugisawa, K.; Nagane, Y.; Satoh, T.; Terayama, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Kuwana, M. Classification of myasthenia gravis based on autoantibody status. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barohn, R.J.; McIntire, D.; Herbelin, L.; Wolfe, G.I.; Nations, S.; Bryan, W.W. Reliability testing of the quantitative myasthenia gravis score. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 841, 769–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.A. A simple and accurate method for prescribing plasma exchange. ASAIO Trans 1990, 36, M597–M599. [Google Scholar]
- Klingel, R.; Heibges, A.; Fassbender, C. Plasma exchange and immunoadsorption for autoimmune neurologic diseases—Current guidelines and future perspectives. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2009, 10, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipphardt, M.; Wallbach, M.; Koziolek, M.J. Plasma Exchange or Immunoadsorption in Demyelinating Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, A.; Connelly-Smith, L.; Aqui, N.; Balogun, R.A.; Klingel, R.; Meyer, E.; Pham, H.P.; Schneiderman, J.; Witt, V.; Wu, Y.; et al. Guidelines on the Use of Therapeutic Apheresis in Clinical Practice—Evidence-Based Approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: The Eighth Special Issue. J. Clin. Apher. 2019, 34, 171–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfes, L.; Pfeuffer, S.; Ruck, T.; Melzer, N.; Pawlitzki, M.; Heming, M.; Brand, M.; Wiendl, H.; Meuth, S.G. Therapeutic Apheresis in Acute Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis: Current Evidence and Unmet Needs-A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schimrigk, S.; Faiss, J.; Kohler, W.; Gunther, A.; Harms, L.; Kraft, A.; Ehrlich, S.; Eberl, A.; Fassbender, C.; Klingel, R.; et al. Escalation Therapy of Steroid Refractory Multiple Sclerosis Relapse with Tryptophan Immunoadsorption—Observational Multicenter Study with 147 Patients. Eur. Neurol. 2016, 75, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkubo, A.; Okado, T.; Sakurasawa, T.; Maeda, T.; Itagaki, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Miyamoto, S.; Seshima, H.; Kurashima, N.; Mori, T.; et al. Removal Characteristics of Immunoadsorption with the Tryptophan-Immobilized Column Using Conventional and Selective Plasma Separators in the Treatment of Myasthenia Gravis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2019, 23, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnerer, S.; Jacobi, J.; Schilling, R.; Grittner, U.; Marbin, D.; Gerischer, L.; Stascheit, F.; Krause, M.; Hoffmann, S.; Meisel, A. Burden of disease in myasthenia gravis: Taking the patient’s perspective. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 3050–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubuioc, A.M.; Kudebayeva, A.; Turuspekova, S.; Lisnic, V.; Leone, M.A. The epidemiology of myasthenia gravis. J. Med. Life 2021, 14, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinching, A.J.; Peters, D.K. Remission of myasthenia gravis following plasma-exchange. Lancet 1976, 2, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dau, P.C.; Lindstrom, J.M.; Cassel, C.K.; Denys, E.H.; Shev, E.E.; Spitler, L.E. Plasmapheresis and immunosuppressive drug therapy in myasthenia gravis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 297, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guptill, J.T.; Juel, V.C.; Massey, J.M.; Anderson, A.C.; Chopra, M.; Yi, J.S.; Esfandiari, E.; Buchanan, T.; Smith, B.; Atherfold, P.; et al. Effect of therapeutic plasma exchange on immunoglobulins in myasthenia gravis. Autoimmunity 2016, 49, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newsom-Davis, J.; Pinching, A.J.; Vincent, A.; Wilson, S.G. Function of circulating antibody to acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis: Investigation by plasma exchange. Neurology 1978, 28, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atan, R.; Crosbie, D.; Bellomo, R. Techniques of extracorporeal cytokine removal: A systematic review of the literature. Blood Purif. 2012, 33, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linker, C. Plasmapheresis in clinical medicine. West. J. Med. 1983, 138, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Pusey, C.D.; Levy, J.B. Plasmapheresis in immunologic renal disease. Blood Purif. 2012, 33, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdos, P.; Chevret, S.; Clair, B.; Tranchant, C.; Chastang, C. Clinical trial of plasma exchange and high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in myasthenia gravis. Myasthenia Gravis Clinical Study Group. Ann. Neurol. 1997, 41, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipe, T.S.; Davis, A.R.; Raval, J.S. Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in Myasthenia Gravis: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Evidence. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 662856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider-Gold, C.; Krenzer, M.; Klinker, E.; Mansouri-Thalegani, B.; Mullges, W.; Toyka, K.V.; Gold, R. Immunoadsorption versus plasma exchange versus combination for treatment of myasthenic deterioration. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2016, 9, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebadi, H.; Barth, D.; Bril, V. Safety of plasma exchange therapy in patients with myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve 2013, 47, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrom, J.M.; Seybold, M.E.; Lennon, V.A.; Whittingham, S.; Duane, D.D. Antibody to acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis. Prevalence, clinical correlates, and diagnostic value. Neurology 1976, 26, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ching, J.; Richards, D.; Lewis, R.A.; Li, Y. Myasthenia gravis exacerbation in association with antibody overshoot following plasmapheresis. Muscle Nerve 2021, 64, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldheim, J.; Deuschl, C.; Glas, M.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Hagenacker, T. Simultaneous paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration, Lambert-Eaton syndrome and neuropathy associated with AGNA/anti-SOX1 and VGCC antibodies. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2021, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, H.C.; Hartung, H.P.; Hetzel, G.R.; Stuve, O.; Kieseier, B.C. Plasma exchange in neuroimmunological disorders: Part 2. Treatment of neuromuscular disorders. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaminski, H.J. Seronegative Myasthenia Gravis-A Vanishing Disorder? JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 1055–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrom, J. ‘Seronegative’ myasthenia gravis is no longer seronegative. Brain 2008, 131, 1684–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oosterhuis, H.; Bethlem, J. Neurogenic muscle involvement in myasthenia gravis. A clinical and histopathological study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1973, 36, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, D.S. Histological changes in the striped muscles in myasthenia gravis. J. Pathol. Bacteriol. 1953, 65, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Europa, T.A.; Nel, M.; Heckmann, J.M. A review of the histopathological findings in myasthenia gravis: Clues to the pathogenesis of treatment-resistance in extraocular muscles. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2019, 29, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautenbach, R.M.; Pillay, K.; Murray, A.D.N.; Heckmann, J.M. Extraocular Muscle Findings in Myasthenia Gravis Associated Treatment-Resistant Ophthalmoplegia. J. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2017, 37, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.F., Jr.; Utsugisawa, K.; Benatar, M.; Murai, H.; Barohn, R.J.; Illa, I.; Jacob, S.; Vissing, J.; Burns, T.M.; Kissel, J.T.; et al. Safety and efficacy of eculizumab in anti-acetylcholine receptor antibody-positive refractory generalised myasthenia gravis (REGAIN): A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre study. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, J.; van der Ven, W.H.; Schuurmans, J.; Roerhorst, S.; Cherpanath, T.G.V.; Lagrand, W.K.; Thoral, P.; Elbers, P.W.G.; Tuinman, P.R.; Scheeren, T.W.L.; et al. Definition and incidence of hypotension in intensive care unit patients, an international survey of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. J. Crit. Care 2021, 65, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, B.B.; Jaffrin, M.Y.; Ding, L.H.; Dohi, T. Membrane plasma separation through small-area, hollow-fiber filters. Artif. Organs 1986, 10, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siami, G.A.; Siami, F.S. Membrane plasmapheresis in the United States: A review over the last 20 years. Ther. Apher. 2001, 5, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totzeck, A.; Stettner, M.; Hagenacker, T. Early platelet and leukocyte decline in patients with neuroinflammatory disorders after intravenous immunoglobulins. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Demographics | |
|---|---|
| Mean age in years ± SEM, (range) | 53.2 ± 1.2 (14–91) |
| Male | 46,9% (n = 142) |
| Female | 53.1% (n = 161) |
| ICD [n] | |
| G70.0—Myasthenia gravis | 252 |
| G70.1—Toxic myoneural disorders | 3 |
| G70.2—Congenital and developmental myasthenia | 8 |
| G70.8—Other specified myoneural disorders | 10 |
| G70.9—Myoneural disorder, unspecified | 26 |
| G73.0—Myasthenic syndromes in endocrine diseases | 0 |
| G73.1—Lambert–Eaton syndrome in neoplastic disease | 2 |
| G73.2—Other myasthenic syndromes in neoplastic disease | 2 |
| G73.3—Myasthenic syndromes in other diseases classified elsewhere | 0 |
| Patient [no.] | Gender | Age [y] | Decrement | MGFA | QMG | Steroids | CH-I | 3,4-DAP | AZA | MMF | IVIg | RITUX | ECU | ACh-R | MuSK | LRP4 | P/Q type | N type | Titin | Thymoma | Improvement | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | f | 74 | - | n/a | n/a | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | COPD/Frailty |
| 2 | f | 63 | + | I | 3 | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Blepharospasm |
| 3 | f | 78 | - | I | 22 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | MG |
| 4 | m | 41 | - | I | 3 | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | MG |
| 5 | f | 75 | - | IIIA | 13 | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | MG |
| 6 | m | 58 | - | IIB | 12 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | MG |
| 7 | m | 81 | - | V | 17 | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | MG |
| 8 | f | 24 | + | IVB | 11 | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | MG |
| 9 | f | 78 | - | V | 22 | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | (+) | MG |
| 10 | m | 84 | + | V | 17 | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | MG |
| 11 | m | 81 | + | IVB | 23 | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | MG |
| 12 | m | 76 | - | IIIB | 7 | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | MG |
| 13 | f | 87 | + | IVB | 23 | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | MG |
| 14 | m | 64 | - | IVB | 10 | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | + | MG |
| 15 | m | 38 | + | IVB | 9 | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | MG |
| 16 | f | 41 | + | IVB | 24 | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | MG |
| 17 | f | 77 | + | IVB | 14 | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | MG |
| 18 | m | 59 | + | V | 28 | + | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | MG |
| 19 | m | 77 | - | n/a | n/a | + | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | LEMS |
| 20 | m | 54 | - | n/a | 6 | + | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | LEMS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Totzeck, A.; Jahn, M.; Stolte, B.; Thimm, A.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Hagenacker, T. Total Plasma Exchange in Neuromuscular Junction Disorders—A Single-Center, Retrospective Analysis of the Efficacy, Safety and Potential Diagnostic Properties in Doubtful Diagnosis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154383
Totzeck A, Jahn M, Stolte B, Thimm A, Kleinschnitz C, Hagenacker T. Total Plasma Exchange in Neuromuscular Junction Disorders—A Single-Center, Retrospective Analysis of the Efficacy, Safety and Potential Diagnostic Properties in Doubtful Diagnosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(15):4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154383
Chicago/Turabian StyleTotzeck, Andreas, Michael Jahn, Benjamin Stolte, Andreas Thimm, Christoph Kleinschnitz, and Tim Hagenacker. 2022. "Total Plasma Exchange in Neuromuscular Junction Disorders—A Single-Center, Retrospective Analysis of the Efficacy, Safety and Potential Diagnostic Properties in Doubtful Diagnosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 15: 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154383
APA StyleTotzeck, A., Jahn, M., Stolte, B., Thimm, A., Kleinschnitz, C., & Hagenacker, T. (2022). Total Plasma Exchange in Neuromuscular Junction Disorders—A Single-Center, Retrospective Analysis of the Efficacy, Safety and Potential Diagnostic Properties in Doubtful Diagnosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(15), 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154383







