Changes in the Kinematics of Midfoot and Rearfoot Joints with the Use of Lateral Wedge Insoles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
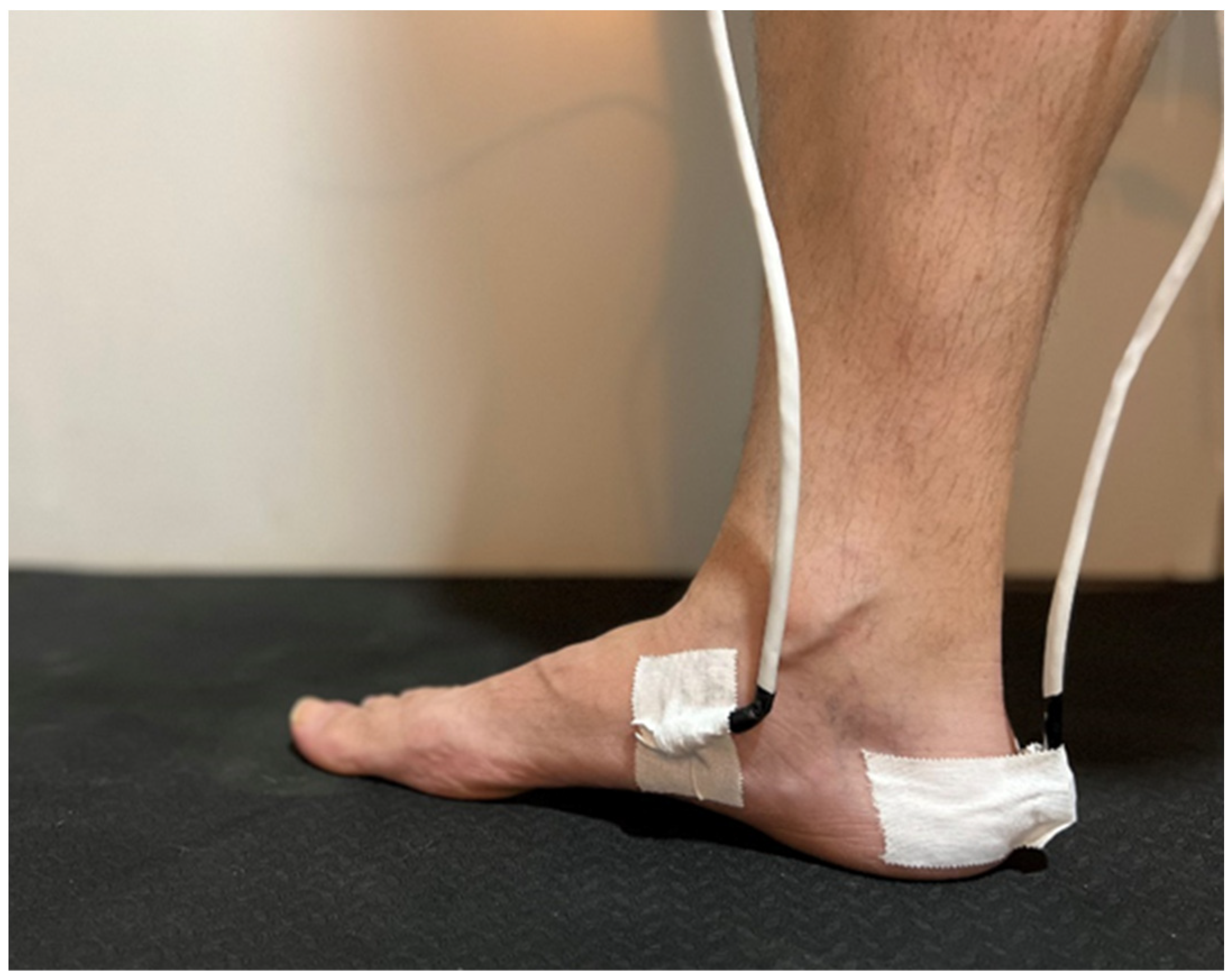
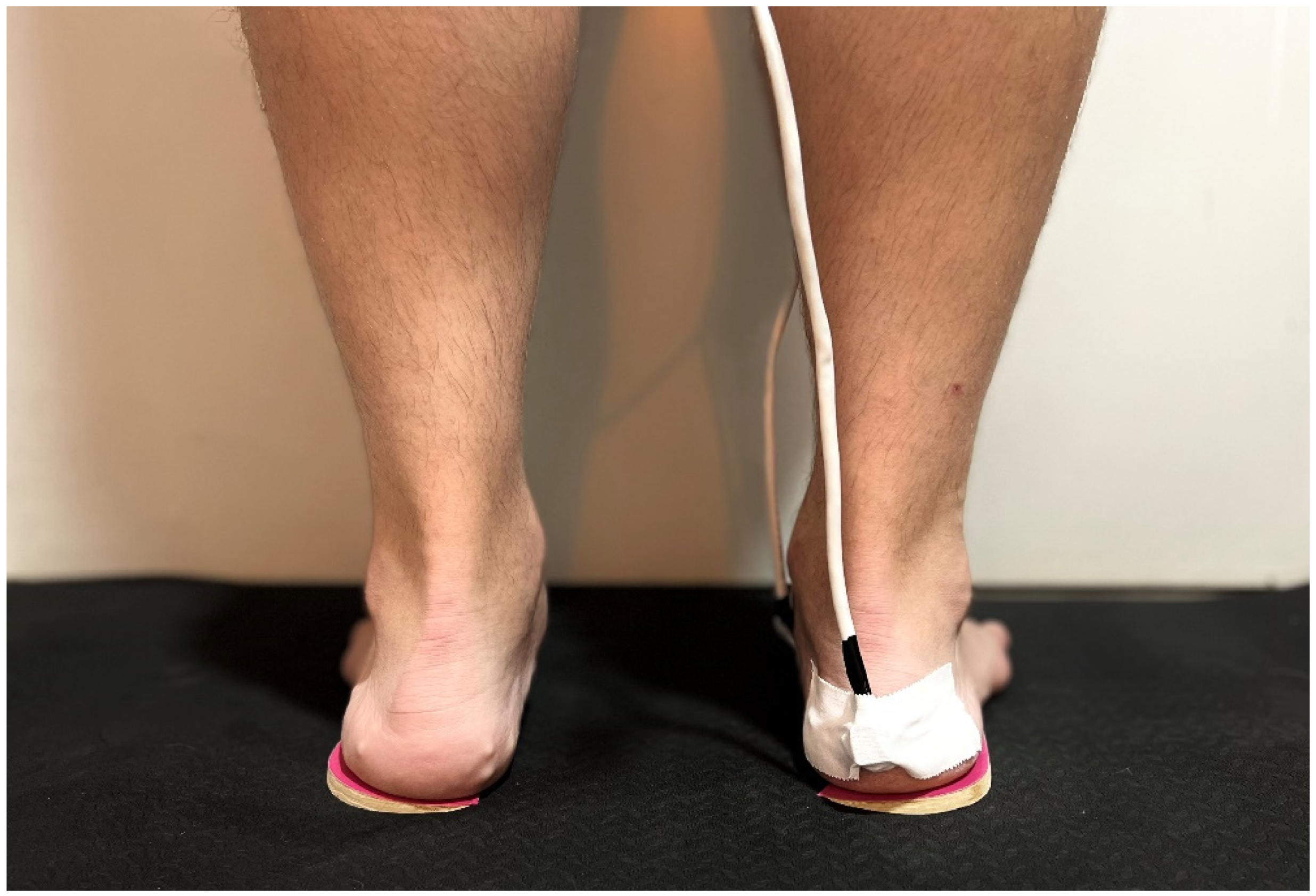
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Lateral Wedge Insoles
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baur, H.; Hirschmüller, A.; Müller, S.; Mayer, F. Neuromuscular activity of the peroneal muscle after foot orthoses therapy in runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-Z.; Lin, Y.-A.; Tai, W.-H.; Chen, C.-Y. Influence of Landing in Neuromuscular Control and Ground Reaction Force with Ankle Instability: A Narrative Review. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, K.G.; Kerr, Z.Y.; Mauntel, T.C.; Djoko, A.; Dompier, T.P.; Wikstrom, E. The Epidemiology of Lateral Ligament Complex Ankle Sprains in National Collegiate Athletic Association Sports. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheer, V.; Krabak, B.J. Musculoskeletal Injuries in Ultra-Endurance Running: A Scoping Review. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 664071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziai, P.; Benca, E.; von Skrbensky, G.; Graf, A.; Wenzel, F.; Basad, E.; Windhager, R.; Buchhorn, T. The role of the peroneal tendons in passive stabilisation of the ankle joint: An in vitro study. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2013, 21, 1404–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Palmieri-Smith, R.; Kipp, K. Muscle force contributions to ankle joint contact forces during an unanticipated cutting task in people with chronic ankle instability. J. Biomech. 2021, 124, 110566. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021929021003468 (accessed on 31 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Stotz, A.; John, C.; Gmachowski, J.; Rahlf, A.L.; Hamacher, D.; Hollander, K.; Zech, A. Effects of elastic ankle support on running ankle kinematics in individuals with chronic ankle instability and healthy controls. Gait Posture 2021, 87, 149–155. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0966636221001685 (accessed on 31 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Simpson, K.J. Chronic Ankle Instability Does Not Influence Tibiofemoral Contact Forces During Drop Landings Using a Musculoskeletal Model. J. Appl. Biomech. 2019, 35, 426–430. Available online: https://journals.humankinetics.com/view/journals/jab/35/6/article-p426.xml (accessed on 31 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Ridder, R.D.; Willems, T.; Vanrenterghem, J.; Robinson, M.A.; Palmans, T.; Roosen, P. Multi-segment foot landing kinematics in subjects with chronic ankle instability. Clin. Biomech. 2015, 30, 585–592. Available online: https://www.clinbiomech.com/article/S0268-003300106-0/fulltext (accessed on 31 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, B.; Garrett, M. Changes in ground reaction force during jump landing in subjects with functional instability of the ankle joint. Clin. Biomech. 2004, 19, 617–621. Available online: https://www.clinbiomech.com/article/S0268-0033(04)00050-6/fulltext (accessed on 31 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.S.; Davis, I.M.; Scholz, J.P.; Hamill, J.; Buchanan, T. High-arched runners exhibit increased leg stiffness compared to low-arched runners. Gait Posture 2004, 19, 263–269. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0966636203000870 (accessed on 31 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Sarrafian, S.K. Anatomy of the Foot and Ankle: Descriptive, Topographic, Functional, 3rd ed.; J.B. Lippincott Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, P.; Witchalls, J.; Waddington, G.; Adams, R. Risk factors associated with medial tibial stress syndrome in runners: A sysematic review and meta-analysis. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2013, 4, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boling, M.C.; Padua, D.A.; Marshall, S.W.; Guskiewicz, K.; Pyne, S.; Beutler, A. A prospective investigation of biomechanical risk factors for patellofemoral pain syndrome: The Joint Undertaking to Monitor and Prevent ACL Injury (JUMP-ACL) cohort. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 2108–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamiya, T.; Uchiyama, E.; Watanabe, K.; Suzuki, D.; Fujimiya, M.; Yamashita, T. Dynamic effect of the tibialis posterior muscle on the arch of the foot during cyclic axial loading. Clin. Biomech. 2012, 27, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, M.B.; Hamill, J.; Davis, I.S. Biomechanical and anatomic factors associated with a history of plantar fasciitis in female runners. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2009, 19, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saki, F.; Yalfani, A.; Fousekis, K.; Sodejani, S.H.; Ramezani, F. Anatomical risk factors of lateral ankle sprain in adolescent athletes: A prospective cohort study. Phys. Ther. Sport 2021, 48, 26–34. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1466853X20306040 (accessed on 4 April 2022). [CrossRef]
- Roster, B.; Michelier, P.; Giza, E. Peroneal Tendon Disorders. Clin. Sports Med. 2015, 34, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Gomez, R.; Gomez-Carrion, A.; Martinez-Sebastian, C.; Alou, L.; Sevillano, D.; Nuñez-Fernandez, A.; Sanz-Wozniak, P.; de la Cruz-Torres, B. Innovative Medial Cushioning Orthoses Affect Peroneus Longus Electromyographic Activity during Running. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakihana, W.; Torii, S.; Akai, M.; Nakazawa, K.; Fukano, M.; Naito, K. Effect of a lateral wedge on joint moments during gait in subjects with recurrent ankle sprain. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 84, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, M.; Babaee, T.; Daryabor, A.; Jalali, M. Effect of knee braces and insoles on clinical outcomes of individuals with medial knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Assist. Technol. 2021, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwood, C. The Midtarsal Joint Locking Mechanism. Foot Ankle Int. 2005, 26, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Gómez, R.; Becerro de Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E.; Calvo-Lobo, C.; Romero-Morales, C.; Martínez-Jiménez, E.M.; Palomo-López, P.; López-López, D. Heel Height as an Etiology of Hallux Abductus Valgus Development: An electromagnetic Static and Dynamic First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Study. Sensors 2019, 19, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corwall, M.W.; McPoil, T.G. Relative movement of the navicular bone during normal walking. Foot Ankle Int. 1999, 20, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez Carrión, Á.; de los Ángeles Atín Arratibel, M.; Morales Lozano, M.R.; Martínez Sebastián, C.; de la Cruz Torres, B.; Sánchez-Gómez, R. Kinematic Effect on the Navicular Bone with the Use of Rearfoot Varus Wedge. Sensors 2022, 22, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corwall, M.W.; McPoil, T.G. Motion of the Calcaneus, Navicular, and First Metatarsal During the Stance Phase of Walking. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2002, 92, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmond, A.C.; Crosbie, J.; Ouvrier, R.A. Development and validation of a novel rating system for scoring standing foot posture: The Foot Posture Index. Clin. Biomech. 2006, 21, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D.F.; Connolly, D.A.J.; Beynnon, B.D. Risk factors for lower extremity injury: A review of the literature. Br. J. Sports Med. 2003, 37, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corwall, M.W.; McPoil, T.G. Classification of Frontal Plane Rearfoot Motion Patterns During the Stance Phase of Walking. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2009, 99, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakihana, W.; Akai, M.; Yamasaki, N.; Takashima, T.; Nakazawa, K. Changes of joint moments in the gait of normal subjects wearing laterally wedged insoles. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 83, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uto, Y.; Maeda, T.; Kiyama, R.; Kawada, M.; Tokunaga, K.; Ohwatashi, A.; Fukudome, K.; Ohshige, T.; Yoshimoto, Y.; Yone, K. The Effects of a Lateral Wedge Insole on Knee and Ankle Joints During Slope Walking. J. Appl. Biomech. 2015, 31, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, K.; Nakai, Y.; Matsumoto, R.; Kiyama, R.; Kawada, M.; Ohwatashi, A.; Fukudome, K.; Ohshige, T.; Maeda, T. Effect of Foot Progression Angle and Lateral Wedge Insole on a Reduction in Knee Adduction Moment. J. Appl. Biomech. 2016, 32, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessery, Y.; Belzile, E.; Turmel, S.; Corbeil, P. Effects of foot orthoses with medial arch support and lateral wedge on knee adduction moment in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2017, 41, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duivenvoorden, T.; van Raaij, T.M.; Horemans, H.L.; Brouwer, R.W.; Bos, P.K.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.; Verhaar, J.A.; Reijman, M. Do Laterally Wedged Insoles or Valgus Braces Unload the Medial Compartment of the Knee in Patients with Osteoarthritis? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moyer, R.F.; Birmingham, T.B.; Dombroski, C.E.; Walsh, R.F.; Leitch, K.M.; Jenkyn, T.R.; Giffin, J.R. The lateral wedged insole with subtalar strapping significantly reduces dynamic knee load in the medial compartment: Gait analysis on patients with medial knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2007, 15, 932–936. [Google Scholar]
- Moyer, R.F.; Birmingham, T.B.; Dombroski, C.E.; Walsh, R.F.; Leitch, K.M.; Jenkyn, T.R.; Giffin, J.R. Combined Effects of a Valgus Knee Brace and Lateral Wedge Foot Orthotic on the External Knee Adduction Moment in Patients with Varus Gonarthrosis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Wada, M.; Uchida, K.; Sasaki, S.; Kawahara, H.; Yayama, T.; Kitade, I.; Kamei, K.; Kubota, M.; et al. Effects of Disease Severity on Response to Lateral Wedged Shoe Insole for Medial Compartment Knee Osteoarthritis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 1436–1441. Available online: https://www.archives-pmr.org/article/S0003-999300973-7/fulltext (accessed on 12 April 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Root, M.L.; Orien, W.P.; Weed, J.H. Normal and Abnormal Function of the Foot; Clinical Biomechanics Corp: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Felson, D.T.; Parkes, M.; Carter, S.; Liu, A.; Callaghan, M.J.; Hodgson, R.; Bowes, M.; Jones, R.K. The Efficacy of a Lateral Wedge Insole for Painful Medial Knee Osteoarthritis After Prescreening: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.A.; Takacs, J.; Krowchuk, N.M.; Hatfield, G.L.; Hinman, R.S.; Chang, R. Lateral wedges with and without custom arch support for people with medial knee osteoarthritis and pronated feet: An exploratory randomized crossover study. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2017, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hinman, R.S.; Bowles, K.A.; Metcalf, B.B.; Wrigley, T.V.; Bennell, K.L. Lateral wedge insoles for medial knee osteoarthritis: Effects on lower limb frontal plane biomechanics. Clin. Biomech. 2012, 27, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.J.; Marchesi, S.; Royer, T.; Davis, I.S. The effect of a subject-specific amount of lateral wedge on knee mechanics in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Res. 2007, 25, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, A.A.; Radwan, A.Y. Biomechanical changes accompanying unilateral and bilateral use of laterally wedged insoles with medial arch supports in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis. Clin. Biomech. 2011, 26, 783–789. Available online: https://www.clinbiomech.com/article/S0268-003300095-7/fulltext (accessed on 18 April 2022). [CrossRef]
- Chapman, G.J.; Parkes, M.J.; Forsythe, L.; Felson, D.T.; Jones, R.K. Ankle motion influences the external knee adduction moment and may predict who will respond to lateral wedge insoles?: An ancillary analysis from the SILK trial. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatfield, G.L.; Cochrane, C.K.; Takacs, J.; Krowchuk, N.M.; Chang, R.; Hinman, R.S.; Hunt, M.A. Knee and ankle biomechanics with lateral wedges with and without a custom arch support in those with medial knee osteoarthritis and flat feet. J. Orthop. Res. 2016, 34, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nester, C.J.; Hutchins, S.; Bowker, P. Effect of foot orthoses on rearfoot complex kinematics during walking gait. Foot Ankle Int. 2001, 22, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nester, C.; Van der Linden, M.; Bowker, P. Effect of Orthoses on the kinematics and kinetics of normal walking gait. Gait Posture 2003, 17, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.R.; Pinto, R.Z.; Trede, R.G.; Kirkwood, R.N.; Pertence, A.E.; Fonseca, S.T. Late rearfoot eversion and lower-limb internal rotation caused by changes in the interaction between forefoot and support surface. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2009, 99, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Liu, T.-H.; Shiang, T.-Y.; Hsu, W.-C. Modulations of Foot and Ankle Frontal Kinematics for Breaking and Propulsive Movement Characteristics during Side-Step Cutting with Varying Midsole Thicknesses. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2018, 2018, 9171502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Navicular | ||
| Axis (X): | NAVIC-DORFLEX | NAVIC-PLANFLEX |
| Axis (Y): | NAVIC-VAR | NAVIC-VAL |
| Axis (Z): | NAVIC-ADDUC | NAVIC-ABDUC |
| Calcaneus | ||
| Axis (X): | CALCA-DORFLEX | CALCA-PLANFLEX |
| Axis (Y): | CALCA-VAR | CALCA-VAL |
| Axis (Z): | CALCA-ADDUC | CALCA-ABDUC |
| Variable | n = 60 Mean ± SD (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 28.41 ± 8.89 (24.79–31.10) |
| FPI (scores) | 1.71 ± 1.47 (1.27–1.96) |
| Weight (kg) | 65.81 ± 12.68 (62.32–71.50) |
| Height (cm) | 166.74 ± 11.84 (163.56–171.09) |
| BARE | LWI4 | LWI7 | LWI10 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | SD | ICC | SEM | MDC | SD | ICC | SEM | MDC | SD | ICC | SEM | MDC | SD | ICC | SEM | MDC |
| (95%CI) | (95%CI) | (95%CI) | (95%CI) | |||||||||||||
| NAVIC-ADDUC | 0.779 | 0.831 | 0.32 | 0.887 | 2.174 | 0.981 | 0.303 | 0.841 | 2.485 | 0.993 | 0.197 | 0.546 | 2.272 | 0.992 | 0.208 | 0.577 |
| (0.740–0.894) | (0.970–0.988) | (0.990–0.996) | (0.987–0.995) | |||||||||||||
| NAVIC-ABDUC | 1.700 | 0.85 | 0.659 | 1.826 | 2.653 | 0.937 | 0.666 | 1.845 | 2.818 | 0.989 | 0.29 | 0.8045 | 2.957 | 0.984 | 0.378 | 1.050 |
| (0.770–0.905) | (0.903–0.960) | (0.984–0.993) | (0.975–0.990) | |||||||||||||
| NAVIC-PLANFLEX | 1.340 | 0.841 | 0.535 | 1.483 | 4.581 | 0.983 | 0.589 | 1.632 | 3.559 | 0.988 | 0.385 | 1.069 | 3.695 | 0.981 | 0.517 | 1.435 |
| (0.754–0.900) | (0.975–0.990) | (0.982–0.993) | (0.970–0.988) | |||||||||||||
| NAVIC-DORFLEX | 0.458 | 0.979 | 0.066 | 0.184 | 1.973 | 0.985 | 0.246 | 0.68 | 2.431 | 0.921 | 0.681 | 1.886 | 1.226 | 0.978 | 0.179 | 0.498 |
| (0.968–0.987) | (0.976–0.990) | (0.880–0.951) | (0.967–0.986) | |||||||||||||
| NAVIC-VAR | 0.947 | 0.985 | 0.115 | 0.32 | 2.082 | 0.995 | 0.152 | 0.421 | 1.590 | 0.986 | 0.186 | 1.887 | 1.417 | 0.994 | 0.112 | 0.311 |
| (0.977–0.991) | (0.992–0.997) | (0.979–0.991) | (0.990–0.996) | |||||||||||||
| NAVIC-VAL | 0.385 | 0.831 | 0.158 | 0.439 | 1.975 | 0.991 | 0.182 | 0.505 | 1.717 | 0.978 | 0.251 | 1.888 | 1.737 | 0.992 | 0.153 | 0.426 |
| (0.741–0.893) | (0.987–0.995) | (0.967–0.987) | (0.988–0.995) |
| BARE | LWI4 | LWI7 | LWI10 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | SD | ICC | SEM | MDC | SD | ICC | SEM | MDC | SD | ICC | SEM | MDC | SD | ICC | SEM | MDC |
| (95%CI) | (95%CI) | (95%CI) | (95%CI) | |||||||||||||
| CALCA-ADDUC | 0.307 | 0.967 | 0.056 | 0.155 | 2.662 | 0.995 | 0.179 | 0.497 | 2.422 | 0.997 | 0.131 | 0.365 | 2.814 | 0.995 | 0.195 | 0.541 |
| (0.948–0.979) | (0.993–0.997) | (0.995–0.998) | (0.993–0.997) | |||||||||||||
| CALCA-ABDUC | 1.062 | 0.862 | 0.394 | 1.093 | 2.793 | 0.955 | 0.593 | 1.644 | 2.275 | 0.987 | 0.259 | 0.721 | 3.012 | 0.997 | 0.159 | 0.442 |
| (0.788–0.913) | (0.931–0.972) | (0.980–0.992) | (0.996–0.998) | |||||||||||||
| CALCA-PLANFLEX | 0.900 | 0.883 | 0.307 | 0.852 | 4.315 | 0.998 | 0.189 | 0.524 | 4.068 | 0.996 | 0.231 | 0.639 | 3.558 | 0.998 | 0.146 | 0.405 |
| (0.821–0.926) | (0.997–0.999) | (0.995–0.998) | (0.997–0.999) | |||||||||||||
| CALCA-DORFLEX | 0.796 | 0.891 | 0.263 | 0.729 | 2.772 | 0.996 | 0.176 | 0.488 | 2.337 | 0.993 | 0.186 | 0.517 | 2.603 | 0.996 | 0.164 | 0.455 |
| (0.833–0.931) | (0.994–0.997) | (0.990–0.996) | (0.994–0.997) | |||||||||||||
| CALCA-VAR | 0.484 | 0.896 | 0.156 | 0.433 | 1.689 | 0.989 | 0.181 | 0.499 | 1.458 | 0.979 | 0.209 | 0.581 | 1.686 | 0.995 | 0.124 | 0.344 |
| (0.840–0.934) | (0.983–0.993) | (0.968–0.987) | (0.992–0.997) | |||||||||||||
| CALCA-VAL | 0.900 | 0.978 | 0.135 | 0.374 | 2.017 | 0.998 | 0.086 | 0.239 | 2.618 | 0.997 | 0.127 | 0.354 | 2.493 | 0.991 | 0.232 | 0.644 |
| (0.965–0.986) | (0.997–0.999) | (0.996–0.998) | (0.987–0.995) |
| BARE | LWI 4 mm | LWI7 mm | LWI 10 mm | p-Value BARE | p-Value BARE | p-Value BARE | p-Value LWI 4 mm | p-Value LWI 4 mm | p-Value LWI 7 mm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Mean (degrees) | Mean (degrees) | Mean (degrees) | Mean (degrees) | vs. | vs. | vs. | vs. | vs. | vs. |
| ± SD (95% CI) | ± SD (95% CI) | ± SD (95% CI) | ± SD (95% CI) | LWI 4 mm | LWI 7 mm | LWI 10 mm | LWI 7 mm | LWI 10 mm | LWI 10 mm | |
| NAVIC-ADDUC | 0.51 ± 0.68 | 1.28 ± 2.18 | 1.50 ± 2.49 | 1.33 ± 2.27 | ||||||
| (0.33–0.68) | (0.73–1.82) | (0.84–2.11) | (0.74–1.91) | 0.2 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 0.3 | 0.76 | 2.67 | |
| NAVIC-ABDUC | 0.66 ± 1.7 | 1.58 ± 2.63 | 1.76 ± 2.81 | 2.01 ± 2.95 | ||||||
| (0.30–1.05) | (0.93–2.22) | (1.03–2.47) | (1.28–2.78) | 0.06 | 0.06 | <0.05 * | 1.33 | 0.051 | 1.2 | |
| NAVIC-PLANFLEX | 0.68 ± 1.34 | 3.02 ± 4.58 | 2.51 ± 3.55 | 2.48 ± 3.69 | ||||||
| (0.38–0.98) | (2.04–4.36) | (1.60–3.42) | (1.54–3.42) | <0.001 ** | <0.05 * | <0.001 ** | 2.4 | 1.26 | 2.7 | |
| NAVIC-DORFLEX | 0.31 ± 0.46 | 1.04 ± 1.97 | 1.36 ± 2.43 | 0.56 ± 1.22 | ||||||
| (0.19–0.42) | (0.53–1.53) | (0.78–1.94) | (0.26–0.88) | 0.11 | <0.05* | 2.661 | 0.72 | <0.05* | <0.05* | |
| NAVIC-VAR | 0.35 ± 0.95 | 1.23 ± 2.08 | 1.23 ± 1.60 | 0.98 ± 1.41 | ||||||
| (0.11–0.60) | (0.87–1.7) | (0.84–1.58) | (0.62–1.50) | <0.001 ** | <0.001 ** | <0.001 ** | 0.66 | 2.31 | 0.15 | |
| NAVIC-VAL | 0.27 ± 0.39 | 1.04 ± 1.98 | 0.96 ± 1.71 | 1.16 ± 1.73 | ||||||
| (0.18–0.35) | (0.53–1.54) | (0.53–1.40) | (0.71–1.60) | <0.05 * | <0.05 * | <0.001 ** | 2.13 | 0.35 | 0.06 |
| BARE | LWI 4 mm | LWI7 mm | LWI 10 mm | p-Value BARE | p-Value BARE | p-Value BARE | p-Value LWI 4 mm | p-Value LWI 4 mm | p-Value LWI 7 mm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Mean (degrees) | Mean (degrees) | Mean (degrees) | Mean (degrees) | vs. | vs. | vs. | vs. | vs. | vs. |
| ± SD (95% CI) | ± SD (95% CI) | ± SD (95% CI) | ± SD (95% CI) | LWI 4 mm | LWI 7 mm | LWI 10 mm | LWI 7 mm | LWI 10 mm | LWI 10 mm | |
| CALCA-ADDUC | 0.17 ± 0.68 | 1.76 ± 2.66 | 1.83 ± 2.42 | 1.91–2.81 | ||||||
| (0.10–0.24) | (1.08–2.44) | (1.21–2.46) | (1.19–2.63) | <0.001 ** | <0.001 ** | <0.001 ** | 1.73 | 1.19 | 2.05 | |
| CALCA-ABDUC | 0.55 ± 1.06 | 1.67 ± 2.79 | 1.60 ± 2.27 | 1.84 ± 3.00 | ||||||
| (0.30–0.79) | (0.98–2.36) | (1.02–2.18) | (1.07–2.62) | <0.05 * | <0.05 * | <0.05 * | 2.31 | 1.67 | 1.01 | |
| CALCA-PLANFLEX | 0.35 ± 0.90 | 2.88 ± 4.31 | 3.07 ± 4.07 | 2.61 ± 3.56 | ||||||
| (0.15–0.57) | (1.76–3.98) | (2.01–4.11) | (1.70–3.53) | <0.001 ** | <0.001 ** | <0.001 ** | 0.54 | 0.99 | 2.88 | |
| CALCA-DORFLEX | 0.37 ± 0.79 | 1.60 ± 2.77 | 1.42 ± 2.34 | 1.36 ± 2.60 | ||||||
| (0.18–0.56) | (0.89–2.31) | (0.81–2.02) | (0.69–2.02) | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.38 | 2.41 | 1.38 | 1.65 | |
| CALCA-VAR | 0.20 ± 0.49 | 1.30 ± 1.70 | 1.21 ± 1.45 | 1.06 ± 1.69 | ||||||
| (0.09–0.31) | (0.86–1.73) | (0.54–1.57) | (0.62–1.49) | <0.001 ** | <0.001 ** | <0.001 ** | 2.74 | 0.23 | 0.22 | |
| CALCA-VAL | 0.40 ± 0.90 | 1.08 ± 2.01 | 1.74 ± 2.61 | 1.47 ± 2.50 | ||||||
| (0.17–0.63) | (0.56–1.60) | (1.06–2.41) | (0.83–2.11) | 0.19 | <0.001 ** | <0.001 ** | <0.05 * | <0.05 * | 2.55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez Carrión, Á.; Atín Arratibe, M.d.l.Á.; Morales Lozano, M.R.; Martínez Rincón, C.; Martínez Sebastián, C.; Saura Sempere, Á.; Nuñez-Fernandez, A.; Sánchez-Gómez, R. Changes in the Kinematics of Midfoot and Rearfoot Joints with the Use of Lateral Wedge Insoles. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4536. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154536
Gómez Carrión Á, Atín Arratibe MdlÁ, Morales Lozano MR, Martínez Rincón C, Martínez Sebastián C, Saura Sempere Á, Nuñez-Fernandez A, Sánchez-Gómez R. Changes in the Kinematics of Midfoot and Rearfoot Joints with the Use of Lateral Wedge Insoles. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(15):4536. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154536
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez Carrión, Álvaro, Maria de los Ángeles Atín Arratibe, Maria Rosario Morales Lozano, Carmen Martínez Rincón, Carlos Martínez Sebastián, Álvaro Saura Sempere, Almudena Nuñez-Fernandez, and Rubén Sánchez-Gómez. 2022. "Changes in the Kinematics of Midfoot and Rearfoot Joints with the Use of Lateral Wedge Insoles" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 15: 4536. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154536
APA StyleGómez Carrión, Á., Atín Arratibe, M. d. l. Á., Morales Lozano, M. R., Martínez Rincón, C., Martínez Sebastián, C., Saura Sempere, Á., Nuñez-Fernandez, A., & Sánchez-Gómez, R. (2022). Changes in the Kinematics of Midfoot and Rearfoot Joints with the Use of Lateral Wedge Insoles. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(15), 4536. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154536







