Concordance between Different Criteria for Metabolic Syndrome in Peruvian Adults Undergoing Bariatric Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Criteria for Metabolic Syndrome
2.3. Other Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Metabolic Syndrome Diagnosis Criteria
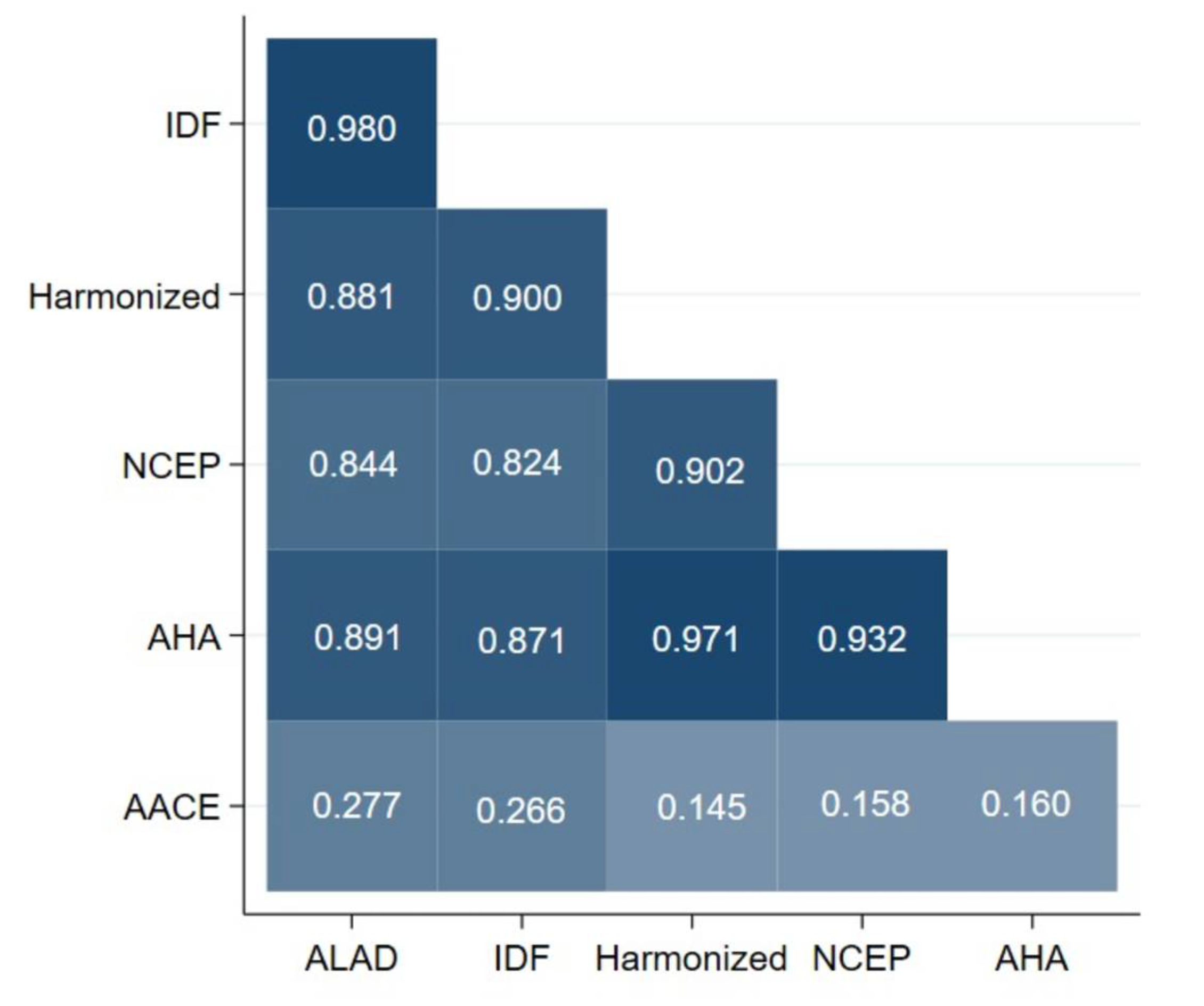
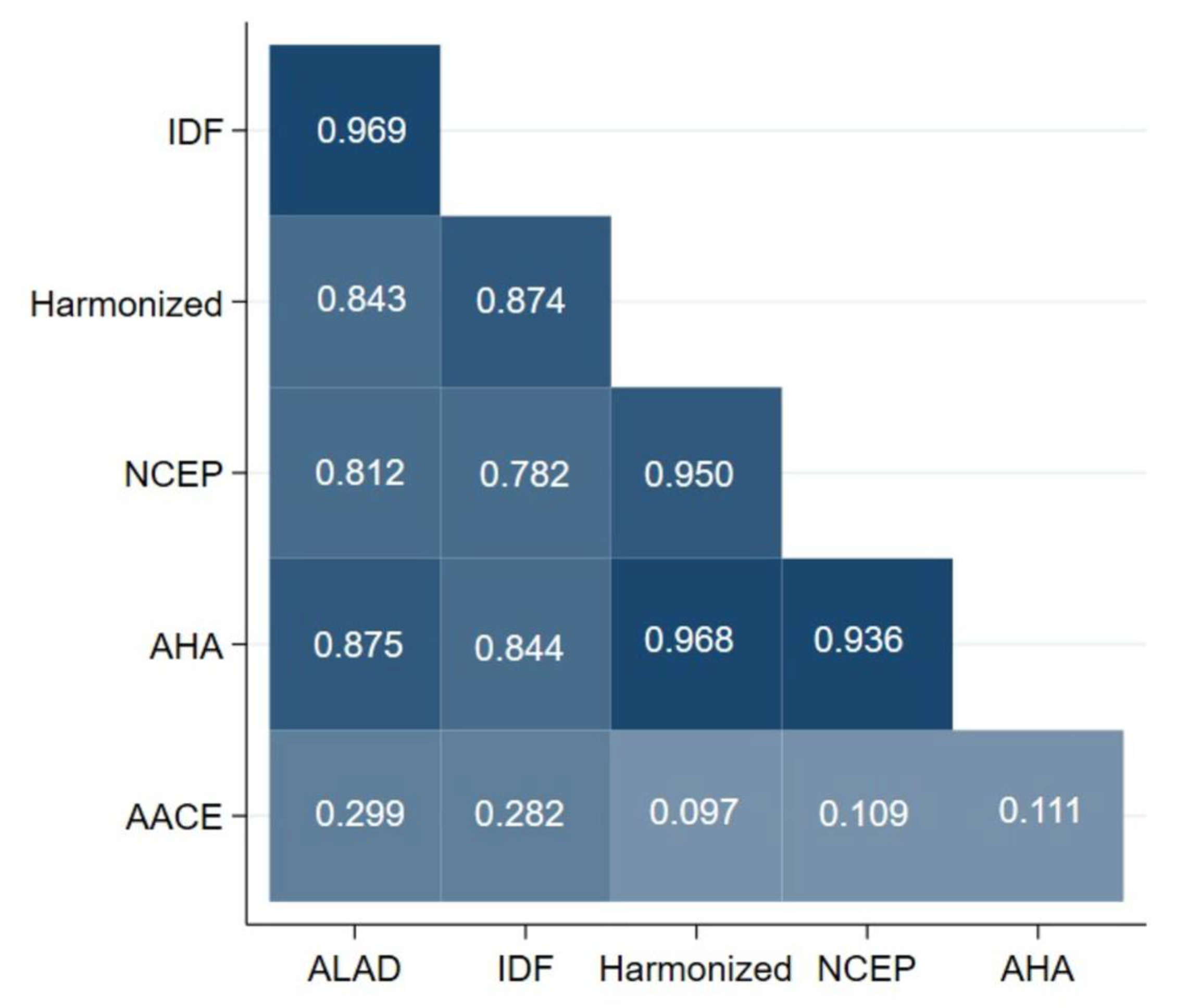
3.3. Concordance of Metabolic Syndrome Definitions
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Comparison with Other Studies
4.3. Results Interpretation
4.4. Relevance in Public Health and Clinical Practice
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rochlani, Y.; Pothineni, N.V.; Kovelamudi, S.; Mehta, J.L. Metabolic syndrome: Pathophysiology, management, and modulation by natural compounds. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 11, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleeman, J.I. Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III). J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2001, 285, 2486–2497. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C.M.; Landsman, P.B.; Teutsch, S.M.; Haffner, S.M. NCEP-defined metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and prevalence of coronary heart disease among NHANES III participants age 50 years and older. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grundy, S.M.; Brewer, H.B.; Cleeman, J.I.; Smith, S.C.; Lenfant, C. Definition of Metabolic Syndrome: Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association Conference on Scientific Issues Related to Definition. Circulation 2004, 109, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuzawa, Y.; Funahashi, T.; Nakamura, T. The concept of metabolic syndrome: Contribution of visceral fat accumulation and its molecular mechanism. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2011, 18, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shuai, X.; Tao, K.; Mori, M.; Kanda, T. Bariatric surgery for metabolic syndrome in obesity. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2015, 13, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Fu, X.H.; Peng, B.Q.; Luo, R.; Hu, J.K.; Cheng, Z. Resolution of metabolic syndrome and related metabolic disorders after bariatric surgery: Comparison of sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2018, 14, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bañares, S.J.; Real, L.R.; Segovia, J.C.; García-Almenta, M.M.; Egüez, K.L.; Carretero, J.I.B. Effects of gastric bypass on cardiovascular risk and resolution of comorbidities: Results at 5 years. Nutr. Hosp. 2020, 37, 750–756. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Zermeño, J.; Flores, R.O.; Del Río-Navarro, B.D.; Salgado-Arroyo, B.; Molina-Díaz, J.M. Efectos sobre el perfil metabólico, el índice de masa corporal, la composición corporal y la comorbilidad en adolescentes con obesidad mórbida, que han fallado al manejo conservador para bajar de peso, operados de manga gástrica laparoscópica. Reporte del primer grupo de cirugía bariátrica pediátrica en México. Gac. Med. Mex. 2018, 154 (Suppl. 2), 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, E.; Baena-Fustegueras, J.A.; de la Fuente, M.C.; Gutiérrez, L.; Bueno, M.; Ros, S.; Lecube, A. Advanced glycation end-products in morbid obesity and after bariatric surgery: When glycemic memory starts to fail. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2017, 64, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, V.; Neves, J.S.; Salazar, D.; Ferreira, M.J.; Oliveira, S.C.; Souteiro, P.; Pedro, J.; Magalhães, D.; Varela, A.; Belo, S.; et al. Long-Term Weight Loss and Metabolic Syndrome Remission after Bariatric Surgery: The Effect of Sex, Age, Metabolic Parameters and Surgical Technique—A 4-Year Follow-Up Study. Obes. Facts 2019, 12, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez- Álvarez, C.; Acosta-Torrecilla, A.O.; González- Dávila, E.; Arias, Á. Metabolic syndrome after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in patients with morbid obesity: Five years of follow-up, a before and after study. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 74, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lak, K.L.; Helm, M.C.; Kindel, T.L.; Gould, J.C. Metabolic Syndrome Is a Significant Predictor of Postoperative Morbidity and Mortality Following Bariatric Surgery. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2019, 23, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, C.; Bai, C.; Elariny, H.; Gopalakrishnan, P.; Quigley, C.; Garone, M.; Afendy, M.; Chan, O.; Wheeler, A.; Afendy, A.; et al. Metabolic Syndrome after Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2008, 18, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán, J.; González, A.; Aschner, P.; Bastarrachea, R. Consenso Latinoamericano de la Asociación Latinoamericana de Diabetes (ALAD). ALAD 2010, 18, 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Márquez-Sandoval, F.; MacEdo-Ojeda, G.; Viramontes-Hörner, D.; Fernández Ballart, J.D.; Salas Salvadó, J.; Vizmanos, B. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Latin America: A systematic review. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 1702–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruilope, L.M.; Nunes, A.C.; Nadruz, W.; Rodríguez, F.F.; Verdejo-Paris, J. Obesidad e hipertensión en Latinoamérica: Perspectivas actuales. Hipertens. Riesgo Vasc. 2018, 35, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, A.; Alvarez, V.; Carrasco, F. Epidemic of metabolic syndrome in Latin America. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2011, 18, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, H.; Sánchez, J.; Roldán, L.; Mendoza, F. Prevalencia del Sindrome Metabolico en personas a partir de 20 años de edad. Perú. 2005. Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 2009, 83, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, K.J.; Chirinos, J.L. Prevalence of risk factors for metabolic syndrome and its components in community kitchen users in a district in Lima, Peru. Rev. Peru Med. Exp. Salud. Publica 2018, 35, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kassi, E.; Pervanidou, P.; Kaltsas, G.; Chrousos, G. Metabolic syndrome: Definitions and controversies. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cabrera-Rode, E.; Stusser, B.; Cálix, W.; Orlandi, N.; Rodríguez, J.; Cubas-Dueñas, I.; Echevarría, R.; Álvarez, A. Diagnostic concordance between seven definitions of metabolic syndrome in overweight and obese adults. Rev. Peru Med. Exp. Salud. Publica 2017, 34, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.-C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention; National heart, lung, and blood institute; American heart association; World heart federation; International. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Ortiz, D.; Reyes-Pérez, A.; León, P.; Sánchez, H.; Mosti, M.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; Velázquez-Fernández, D.; Herrera, M.F. Assessment of two different diagnostic guidelines criteria (National Cholesterol Education Adult Treatment Panel III [ATP III] and International Diabetes Federation [IDF]) for the evaluation of metabolic syndrome remission in a longitudinal cohort of pati. Surgery 2016, 159, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomgarden, Z.T. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) consensus conference on the insulin resistance syndrome: 25–26 August 2002, Washington, DC. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vásquez, M.; Altamirano, C.; Álvarez, R.; Valdiviezo, A.; Cordero, G.; Añez, R.; Rojas, J.; Bermúdez, V. Prevalencia y nivel de concordancia entre tres definiciones de síndrome metabólico en la ciudad de cuenca-Ecuador. Avan Biomed. 2016, 5, 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Toro-Huamanchumo, C.J.; Pérez-Zavala, M.; Urrunaga-Pastor, D.; De La Fuente-Carmelino, L.; Benites-Zapata, V.A. Relationship between the short stature and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance markers in workers of a private educational institution in Peru. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo Hernández, J.L.; Cuevas González, M.J.; Galiana, M.A.; Romero Hernández, E.Y. Síndrome metabólico, un problema de salud pública con diferentes definiciones y criterios. Rev. Med. Univ. Veracruzana 2017, 7, 7–24. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, T.H.; Wang, B.; Natarajan, S. The Influence of Metabolic Syndrome in Predicting Mortality Risk Among US Adults: Importance of Metabolic Syndrome Even in Adults with Normal Weight. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2020, 17, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo, J.; Schargrodsky, H.; Champagne, B.; Silva, H.; Boissonnet, C.P.; Vinueza, R.; Torres, M.; Hernàndez, R.; Wilson, E. Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome in Latin America and its association with sub-clinical carotid atherosclerosis: The CARMELA cross sectional study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2009, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Measure | Metabolic Syndrome Criteria | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALAD | Harmonized | IDF | NCEP-ATP III | AHA/NHLBI | AACE | |
| Diagnosis criteria | Abdominal obesity plus 2 of this 4 | Any 3 of 5 | Increased WC plus any 2 of this 4 | Any 3 of this 5 | any 3 of 5 | IGT or IFG plus any of the following based on clinical judgment |
| Obesity | WC ≥ 94 cm (men) or ≥ 88 cm (women) | WC depends on the population/ country | WC with ethnicity specificity values | WC > 40 inches (men) and >35 inches (women) | WC > 40 inches (men) and >35 inches (women) | BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 |
| Dyslipidemia | TG > 150 mg/dL or Tx | TG ≥ 150 mg/dL or Tx | TG ≥ 150 mg/dL or Tx | TG ≥ 150 mg/dL or Tx | TG ≥ 150 mg/dL or T | TG ≥ 150 mg/dL and HDL-C < 40 mg/dL (men) and <50 mg/dL (women) |
| Dyslipidemia (second, separated criteria) | HDL-C < 40 mg/dL (men), <50 mg/dL (women) or Tx | HDL-C < 40 mg/dL (men) and <50 mg/dL (women) or Tx | HDL-C < 40 mg/dL (men) and <50 mg/dL (women) or Tx | HDL-C < 40 mg/dL (men) and <50 mg/dL (women) or Tx | HDL-C < 40 mg/dL (men) and <50 mg/dL (women) or Tx | |
| Blood pressure | SBP ≥ 130, DBP ≥ 85 mmHg, or Tx | SBP ≥ 130, DBP ≥ 85 mmHg, or Tx | SBP ≥ 130, DBP ≥ 85 mmHg, or Tx | SBP ≥ 130, DBP ≥ 85 mmHg, or Tx | SBP ≥ 130, DBP ≥ 85 mmHg, or Tx | SBP ≥ 130, DBP ≥ 85 mmHg or Tx |
| Glucose | IFG, IGT, or diabetes | Fasting glucose ≥ 100 mg/dL, or Tx | FPG ≥ 100 mg/dL or previously diagnosed T2DM | FPG ≥ 100 mg/dL or Tx | FPG ≥ 100 mg/dL or Tx | IGT or IFG (but not diabetes) |
| Other | - | - | - | - | - | other features of insulin resistance * |
| Variable | Total (n = 205) | Male (n = 78) | Female (n = 127) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) * | 36.7 ± 10.0 | 36.8 ± 9.9 | 36.7 ± 10.2 | 0.927 ** |
| Weight (kg) † | 100.2 (89.8–115.6) | 116.5 (104.0–131.3) | 93 (85.4–101.7) | <0.001 †† |
| Height (m) † | 1.63 (1.58–1.72) | 1.7 (1.7–1.8) | 1.6 (1.5–1.6) | <0.001 †† |
| BMI (kg/m2) † | 37.44 (33.93–40.77) | 39.4 (35.9–42.6) | 36.3 (33.3–39.5) | <0.001 †† |
| SBP (mmHg) † | 120 (110.0–130.0) | 124.5 (120.0–130.0) | 117.0 (110.0–125.0) | <0.001 †† |
| DBP (mmHg) † | 80.0 (70–85) | 80.0 (75.0–86.0) | 75.0 (70.0–80.0) | <0.001 †† |
| Glucose (mg/dL) † | 92.0 (86.0–98.0) | 93.5 (86.0–101.0) | 92.0 (86.0–97.0) | 0.254 †† |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) † | 41.0 (36.0–49.0) | 37.5 (33.0–45.0) | 44.0 (37.0–52.0) | <0.001 †† |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) † | 154.0 (117.0–214.0) | 174.0 (127.0–235.0) | 143.0 (112.0–191.0) | 0.002 †† |
| Insulin (uU/mL) † | 23.2 (15.9–29.6) | 26.3 (19.4–37.9) | 20.5 (15.0–27.3) | <0.001 †† |
| HOMA-IR † | 5.3 (3.6–7.3) | 6.2 (4.5–9.1) | 4.8 (3.2–6.6) | <0.001 †† |
| WC (cm) † | 113.0 (104.0–124.0) | 123.0 (114.0–134.0) | 106.0 (100.0–117.0) | <0.001 †† |
| MetS Criteria | AACE n (%) | AHA/NHLBI n (%) | NCEP-ATP III n (%) | Harmonized n (%) | IDF n (%) | ALAD n (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | |
| Total | 47 (22.9) | 158 (77) | 111 (54.1) | 94 (45.9) | 104 (50.7) | 101 (49.3) | 114 (55.6) | 91 (44.4) | 122 (59.5) | 83 (40.5) | 120 (58.5) | 85 (41.5) |
| Male | 22 (28.2) | 56 (71.8) | 52 (66.7) | 26 (33.3) | 49 (62.8) | 29 (37.2) | 53 (68) | 25 (32.1) | 53 (68) | 25 (32.1) | 53 (68) | 25 (32.1) |
| Female | 25 (19.7) | 102 (80.3) | 59 (46.5) | 68 (53.5) | 55 (43.3) | 72 (56.7) | 61 (48.0) | 66 (52) | 69 (54.3) | 58 (45.7) | 67 (52.8) | 60 (47.2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Echevarria-Castro, N.; Silva-Parra, K.; Polar-Trinidad, M.; Sánchez-Vicente, J.C.; Salinas-Sedo, G.; Toro-Huamanchumo, C.J. Concordance between Different Criteria for Metabolic Syndrome in Peruvian Adults Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164692
Echevarria-Castro N, Silva-Parra K, Polar-Trinidad M, Sánchez-Vicente JC, Salinas-Sedo G, Toro-Huamanchumo CJ. Concordance between Different Criteria for Metabolic Syndrome in Peruvian Adults Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(16):4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164692
Chicago/Turabian StyleEchevarria-Castro, Nataly, Kevin Silva-Parra, Marcos Polar-Trinidad, Juan C. Sánchez-Vicente, Gustavo Salinas-Sedo, and Carlos J. Toro-Huamanchumo. 2022. "Concordance between Different Criteria for Metabolic Syndrome in Peruvian Adults Undergoing Bariatric Surgery" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 16: 4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164692
APA StyleEchevarria-Castro, N., Silva-Parra, K., Polar-Trinidad, M., Sánchez-Vicente, J. C., Salinas-Sedo, G., & Toro-Huamanchumo, C. J. (2022). Concordance between Different Criteria for Metabolic Syndrome in Peruvian Adults Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(16), 4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164692






