Foundational Principles and Adaptation of the Healthy and Pathological Achilles Tendon in Response to Resistance Exercise: A Narrative Review and Clinical Implications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Anatomy Tailored for Function
2.1. Achilles Tendon Homeostasis and Structure
2.2. Force Transmission within the Achilles Tendon
2.3. Force Transmission within the Triceps Surae Muscle-Tendon Unit
3. Tendon Tissue Remodeling
3.1. Healthy Tissue Remodeling
3.2. Pathologic Tissue Remodeling
4. Biomechanical Considerations towards Optimal Exercise Prescription
4.1. Muscle Contraction Type
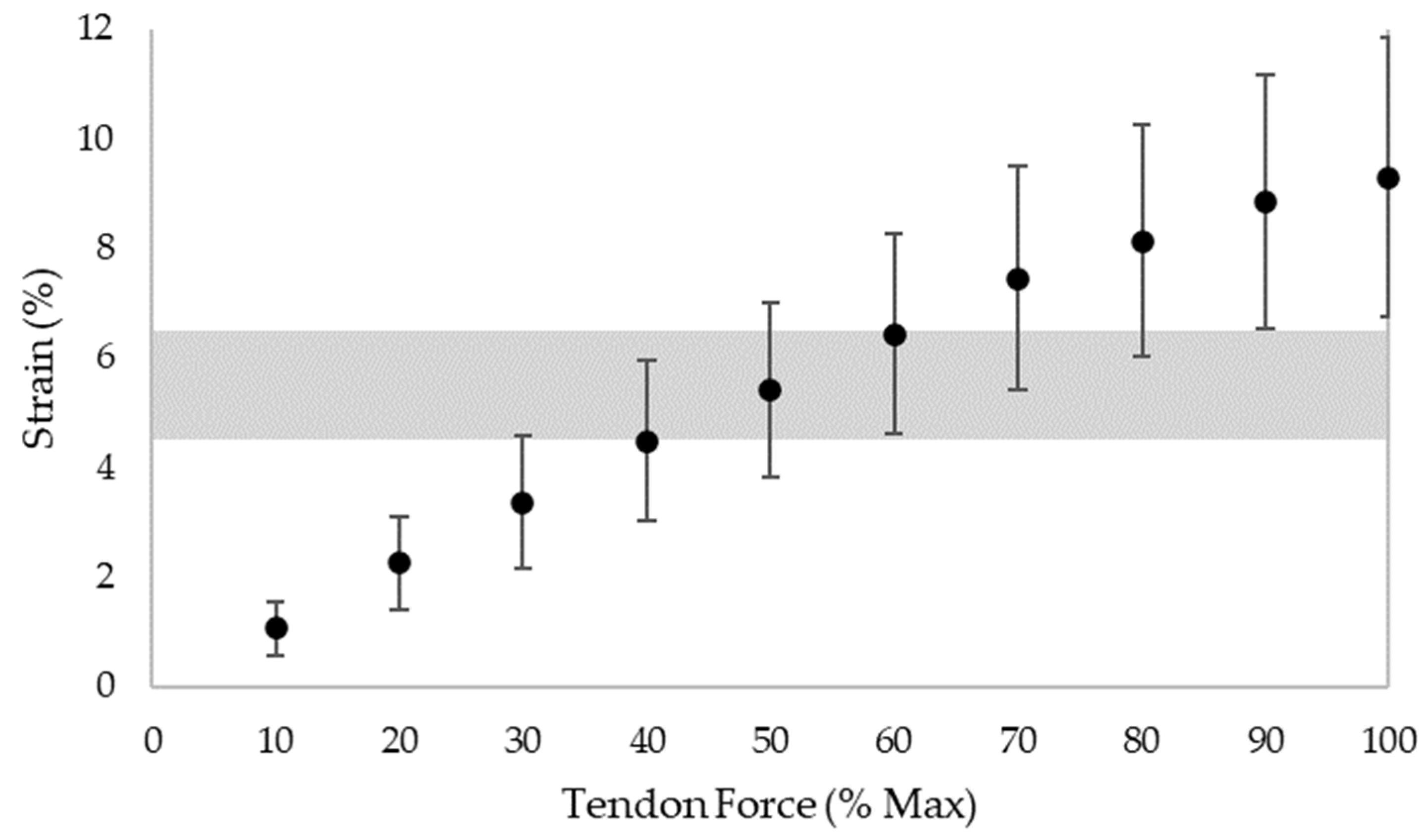
4.2. Load Intensity
4.3. Loading Frequency, Rate, and Duration
4.4. Exercise Positioning
4.5. Exercise Schedule
5. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Vos, R.-J.J.; van der Vlist, A.C.; Zwerver, J.; Meuffels, D.E.; Smithuis, F.; Van Ingen, R.; van der Giesen, F.; Visser, E.; Balemans, A.; Pols, M.; et al. Dutch multidisciplinary guideline on Achilles tendinopathy. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.L.; Chimenti, R.; Cuddeford, T.; Houck, J.; Matheson, J.W.; McDonough, C.M.; Paulseth, S.; Wukich, D.K.; Carcia, C.R. Achilles pain, stiffness, and muscle power deficits: Midportion achilles tendinopathy revision 2018. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2018, 48, A1–A38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, P.W.; Hart, D.A. Metabolic Influences on Risk for Tendon Disorders; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 9783319339436 3319339435. [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson, S.P.; Narici, M.V.; Maganaris, C.N.; Kjaer, M. Human tendon behaviour and adaptation, in vivo. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, R.M. Energy-saving mechanisms in walking and running. J. Exp. Biol. 1991, 160, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, T.; Kubo, K.; Kawakami, Y.; Fukashiro, S.; Kanehisa, H.; Maganaris, C.N. In vivo behaviour of human muscle tendon during walking. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 268, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, M.; Kaiser, E.; Milz, S. Structure-function relationships in tendons: A review. J. Anat. 2008, 212, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, A.S.; Duenwald-Kuehl, S.E.; Lakes, R.S.; Vanderby, R. Relationship between tendon stiffness and failure: A metaanalysis. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 115, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, G.M.; Hart, D.A. The interface of mechanical loading and biological variables as they pertain to the development of tendinosis. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2011, 11, 94–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.H.C. Mechanobiology of tendon. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 1563–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnicki, K.; Ochała-Kłos, A.; Rutowicz, B.; Pękala, P.A.; Tomaszewski, K.A. Functional anatomy, histology and biomechanics of the human Achilles tendon—A comprehensive review. Ann. Anat. 2020, 229, 151461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willy, R.W.; Halsey, L.; Hayek, A.; Johnson, H.; Willson, J.D. Patellofemoral joint and achilles tendon loads during overground and treadmill running. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2016, 46, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, J.; Richards, J.; Shore, H. Effects of minimalist and maximalist footwear on Achilles tendon load in recreational runners. Comp. Exerc. Physiol. 2015, 11, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almonroeder, T.; Willson, J.D.; Kernozek, T.W. The effect of foot strike pattern on achilles tendon load during running. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, J.R.; Corrigan, P.; Hullfish, T.J.; O’Rourke, P.; Silbernagel, K.G. Exercise Progression to Incrementally Load the Achilles Tendon. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffulli, N.; Sharma, P.; Luscombe, K.L. Achilles Tendinopathy: Aetiology and Management. J. R. Soc. Med. 2004, 97, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvanetti, A.; Cipolla, M.; Puddu, G. Overuse tendon injuries: Basic science and classification. Oper. Technol. Sport. Med. 1997, 5, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.; Squier, K.; Alfredson, H.; Bahr, R.; Cook, J.L.; Coombes, B.; De Vos, R.J.; Fu, S.N.; Grimaldi, A.; Lewis, J.S.; et al. ICON 2019: International Scientific Tendinopathy Symposium Consensus: Clinical Terminology. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jonge, S.; Van Den Berg, C.; De Vos, R.J.; Van Der Heide, H.J.L.; Weir, A.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; Tol, J.L. Incidence of midportion Achilles tendinopathy in the general population. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.D.; Hespanhol, L.C.; Yeung, S.S.; Costa, L.O.P. What are the Main Running-Related Musculoskeletal Injuries? Sports Med. 2012, 42, 891–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.O.; Rønnow, L.; Rasmussen, S.; Lind, M. A prospective study on time to recovery in 254 injured novice runners. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagas, I.F.; Fokkema, T.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; van Middelkoop, M.; de Vos, R.J. Incidence of Achilles tendinopathy and associated risk factors in recreational runners: A large prospective cohort study. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2020, 23, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujala, U.M.; Sarna, S.; Kaprio, J. Cumulative incidence of achilles tendon rupture and tendinopathy in male former elite athletes. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2005, 15, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvist, M. Achilles tendon injuries in athletes. Ann. Chir. Gynaecol. 1991, 80, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudell, G.M. Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2017, 34, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, N.H.; Fromme, P.; McCarthy, I.; Birch, H.L. Individual variation in achilles tendon morphology and geometry changes susceptibility to injury. Elife 2021, 10, e63204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obst, S.J.; Heales, L.J.; Schrader, B.L.; Davis, S.A.; Dodd, K.A.; Holzberger, C.J.; Beavis, L.B.; Barrett, R.S. Are the Mechanical or Material Properties of the Achilles and Patellar Tendons Altered in Tendinopathy? A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 2179–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, Y.; Tonogai, I.; Rosenbaum, A.J.; Shimozono, Y.; Kawano, H.; Kennedy, J.G. The Risk of Achilles Tendon Rupture in the Patients with Achilles Tendinopathy: Healthcare Database Analysis in the United States. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7021862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm, S.; Mersmann, F.; Arampatzis, A. Human tendon adaptation in response to mechanical loading: A systematic review and meta-analysis of exercise intervention studies on healthy adults. Sports Med. Open 2015, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, R.B.; Heinemeier, K.M.; Couppé, C.; Kjaer, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Effect of aging and exercise on the tendon. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 121, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrum, C.; Leow, P.; Epro, G.; König, M.; Meijer, K.; Karamanidis, K. Alterations in Leg Extensor Muscle-Tendon Unit Biomechanical Properties With Ageing and Mechanical Loading. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarczuk, S.L.; Maniar, N.; Opar, D.A.; Duhig, S.J.; Shield, A.; Barrett, R.S.; Bourne, M.N. Mechanical, Material and Morphological Adaptations of Healthy Lower Limb Tendons to Mechanical Loading: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sport. Med. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malliaras, P.; Barton, C.J.; Reeves, N.D.; Langberg, H. Achilles and patellar tendinopathy loading programmes: A systematic review comparing clinical outcomes and identifying potential mechanisms for effectiveness. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habets, B.; van Cingel, R.E.H.; Backx, F.J.G.; van Elten, H.J.; Zuithoff, P.; Huisstede, B.M.A. No Difference in Clinical Effects When Comparing Alfredson Eccentric and Silbernagel Combined Concentric-Eccentric Loading in Achilles Tendinopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2021, 9, 23259671211031254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, R.; Kongsgaard, M.; Hougs Kjær, B.; Øhlenschlæger, T.; Kjær, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Heavy slow resistance versus eccentric training as treatment for achilles tendinopathy: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, N.L.; Silbernagel, K.G.; Thorborg, K.; Kirwan, P.D.; Galatz, L.M.; Abrams, G.D.; Murrell, G.A.C.; McInnes, I.B.; Rodeo, S.A. Tendinopathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.; Watson, P.J.; Barry, S. Why are eccentric exercises effective for Achilles tendinopathy? Int. J. Sport. Phys. Ther. 2015, 10, 552–562. [Google Scholar]
- De Vos, R.J.; Heijboer, M.P.; Weinans, H.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; van Schie, H.T.M. Tendon structure’s lack of relation to clinical outcome after eccentric exercises in chronic midportion Achilles tendinopathy. J. Sport Rehabil. 2012, 21, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnussen, R.A.; Dunn, W.R.; Thomson, A.B. Nonoperative treatment of midportion achilles tendinopathy: A systematic review. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2009, 19, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, I.; McCormack, A. The implementation of resistance training principles in exercise interventions for lower limb tendinopathy: A systematic review. Phys. Ther. Sport 2021, 50, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbernagel, K.G.; Hanlon, S.; Sprague, A. Current clinical concepts: Conservative management of achilles tendinopathy. J. Athl. Train. 2020, 55, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arampatzis, A.; Peper, A.; Bierbaum, S.; Albracht, K. Plasticity of human Achilles tendon mechanical and morphological properties in response to cyclic strain. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 3073–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arampatzis, A.; Karamanidis, K.; Albracht, K. Adaptational responses of the human Achilles tendon by modulation of the applied cyclic strain magnitude. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 2743–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm, S.; Mersmann, F.; Tettke, M.; Kraft, M.; Arampatzis, A. Human Achilles tendon plasticity in response to cyclic strain: Effect of rate and duration. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 4010–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavizadeh, R.; Hojabrpour, P.; Eltit, F.; McDonald, P.C.; Dedhar, S.; McCormack, R.G.; Duronio, V.; Jafarnejad, S.M.; Scott, A. β1 integrin, ILK and mTOR regulate collagen synthesis in mechanically loaded tendon cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeilly, C.M.; Banes, A.J.; Benjamin, M.; Ralphs, J.R. Tendon cells in vivo form a three dimensional network of cell processes linked by gap junctions. J. Anat. 1996, 189, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, M.E.; Weinhold, P.S.; Siu, T.; Brown, T.D.; Banes, A.J. Comparison of cellular strain with applied substrate strain in vitro. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, E.; Ye, S.; Wang, W.; Bader, D.L.; Knight, M.M.; Lee, D.A. Gap junction permeability between tenocytes within tendon fascicles is suppressed by tensile loading. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2012, 11, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Screen, H.R.C. Hierarchical Approaches to Understanding Tendon Mechanics. J. Biomech. Sci. Eng. 2009, 4, 481–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Wu, J.P.; Allison, G.T.; Xu, J.; Rubenson, J.; Zheng, M.H.; Lloyd, D.G.; Gardiner, B.; Wang, A.; Kirk, T.B. Three dimensional microstructural network of elastin, collagen, and cells in Achilles tendons. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merza, E.; Pearson, S.; Lichtwark, G.; Ollason, M.; Malliaras, P. Immediate and long-term effects of mechanical loading on Achilles tendon volume: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Biomech. 2021, 118, 110289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komi, P.V. Relevance of in vivo force measurements to human biomechanics. J. Biomech. 1990, 23, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komi, P.V.; Fukashiro, S.; Jarvinen, M. Biomechanical loading of Achilles tendon during normal locomotion. Clin. Sports Med. 1992, 11, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtwark, G.A.; Wilson, A.M. Optimal muscle fascicle length and tendon stiffness for maximising gastrocnemius efficiency during human walking and running. J. Theor. Biol. 2008, 252, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.R.; MacIntosh, B.R. Achilles tendon strain energy in distance running: Consider the muscle energy cost. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 118, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szaro, P.; Witkowski, G.; Śmigielski, R.; Krajewski, P.; Ciszek, B. Fascicles of the adult human Achilles tendon—An anatomical study. Ann. Anat. 2009, 191, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handsfield, G.G.; Slane, L.C.; Screen, H.R.C. Nomenclature of the tendon hierarchy: An overview of inconsistent terminology and a proposed size-based naming scheme with terminology for multi-muscle tendons. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 3122–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, H.M.; Vázquez, O.T.; McGonagle, D.; Bydder, G.; Santer, R.M.; Benjamin, M. Development of the human Achilles tendon enthesis organ. J. Anat. 2008, 213, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, T.A.L.; Yerby, S.A.; Beaupré, G.S.; Carter, D.R. Mechanical properties of the human achilles tendon. Clin. Biomech. 2001, 16, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaerts, S.; Desmet, H.; Slagmolen, P.; Peers, K. Strain mapping in the Achilles tendon—A systematic review. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buehler, M.J. Atomistic and continuum modeling of mechanical properties of collagen: Elasticity, fracture, and self-assembly. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 1947–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosler, E.; Folkhard, W.; Knörzer, E.; Nemetschek-Gansler, H.; Nemetschek, T.; Koch, M.H.J. Stress-induced molecular rearrangement in tendon collagen. J. Mol. Biol. 1985, 182, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misof, K.; Rapp, G.; Fratzl, P. A new molecular model for collagen elasticity based on synchrotron x- ray scattering evidence. Biophys. J. 1997, 72, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.C. Collagen cross linking. Synthesis of collagen cross links in vitro with highly purified lysyl oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 251, 5786–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiser, K.; McCormick, R.J.; Rucker, R.B. Enzymatic and nonenzymatic cross-linking of collagen and elastin. FASEB J. 1992, 6, 2439–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.J.; Paul, R.G.; Knott, L. Mechanisms of maturation and ageing of collagen. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1998, 106, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.F.; Lu, Y.; Starborg, T.; Kadler, K.E. Collagen Fibril Assembly and Function. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 130, pp. 107–142. [Google Scholar]
- Buehler, M.J. Nanomechanics of collagen fibrils under varying cross-link densities: Atomistic and continuum studies. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 1, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herchenhan, A.; Kalson, N.S.; Holmes, D.F.; Hill, P.; Kadler, K.E.; Margetts, L. Tenocyte contraction induces crimp formation in tendon-like tissue. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2012, 11, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screen, H.R.C.; Lee, D.A.; Bader, D.L.; Shelton, J.C. An investigation into the effects of the hierarchical structure of tendon fascicles on micromechanical properties. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2004, 218, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraldsson, B.T.; Aagaard, P.; Qvortrup, K.; Bojsen-Moller, J.; Krogsgaard, M.; Koskinen, S.; Kjaer, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Lateral force transmission between human tendon fascicles. Matrix Biol. 2008, 27, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, V.B.; Handsfield, G.G.; Fernandez, J.W.; Lloyd, D.G.; Besier, T.F. Combining in silico and in vitro experiments to characterize the role of fascicle twist in the Achilles tendon. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landin, D.; Thompson, M.; Reid, M. Actions of Two Bi-Articular Muscles of the Lower Extremity: A Review Article. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2016, 8, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamner, S.R.; Delp, S.L. Muscle contributions to fore-aft and vertical body mass center accelerations over a range of running speeds. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm, S.; Mersmann, F.; Santuz, A.; Arampatzis, A. Enthalpy efficiency of the soleus muscle contributes to improvements in running economy. Proc. R. Soc. B 2021, 288, 20202784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alway, S.E.; MacDougall, J.D.; Sale, D.G.; Sutton, J.R.; McComas, A.J. Functional and structural adaptations in skeletal muscle of trained athletes. J. Appl. Physiol. 1988, 64, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friederich, J.A.; Brand, R.A. Muscle fiber architecture in the human lower limb. J. Biomech. 1990, 23, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, Y.; Ichinose, Y.; Fukunaga, T. Architectural and functional features of human triceps surae muscles during contraction. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albracht, K.; Arampatzis, A.; Baltzopoulos, V. Assessment of muscle volume and physiological cross-sectional area of the human triceps surae muscle in vivo. J. Biomech. 2008, 41, 2211–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, R.A.; Pedersen, D.R.; Friederich, J.A. The sensitivity of muscle force predictions to changes in physiologic cross-sectional area. J. Biomech. 1986, 19, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haxton, H.A. Absolute muscle force in the ankle flexors of man. J. Physiol. 1944, 103, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edama, M.; Kubo, M.; Onishi, H.; Takabayashi, T.; Inai, T.; Yokoyama, E.; Hiroshi, W.; Satoshi, N.; Kageyama, I. The twisted structure of the human Achilles tendon. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, e497–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gils, C.C.; Steed, R.H.; Page, J.C. Torsion of the human Achilles tendon. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 1996, 35, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugisaki, N.; Kawakami, Y.; Kanehisa, H.; Fukunaga, T. Effect of muscle contraction levels on the force-length relationship of the human Achilles tendon during lengthening of the triceps surae muscle-tendon unit. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 2168–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, W.H.; Franz, J.R. Do triceps surae muscle dynamics govern non-uniform Achilles tendon deformations? PeerJ 2018, 2018, 5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojsen-Møller, J.; Hansen, P.; Aagaard, P.; Svantesson, U.; Kjaer, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Differential displacement of the human soleus and medial gastrocnemius aponeuroses during isometric plantar flexor contractions in vivo. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.; Backman, L.J.; Speed, C. Tendinopathy: Update on pathophysiology. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 45, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, T.A.H.; Kannus, P.; Maffulli, N.; Khan, K.M. Achilles tendon disorders: Etiology and epidemiology. Foot Ankle Clin. 2005, 10, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.M.; Scott, A. Mechanotherapy: How physical therapists’ prescription of exercise promotes tissue repair. Br. J. Sports Med. 2009, 43, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, S.L.; Olmedo, M.L. Mechanotransduction: Relevance to physical therapist practice—Understanding our ability to affect genetic expression through mechanical forces. Phys. Ther. 2016, 96, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoczky, S.P.; Lavagnino, M.; Whallon, J.H.; Hoonjan, A. In situ cell nucleus deformation in tendons under tensile load; a morphological analysis using confocal laser microscopy. J. Orthop. Res. 2002, 20, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavagnino, M.; Arnoczky, S.P.; Tian, T.; Vaupel, Z. Effect of Amplitude and Frequency of Cyclic Tensile Strain on the Inhibition of MMP-1 mRNA Expression in Tendon Cells: An In Vitro Study. Connect. Tissue Res. 2003, 44, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skutek, M.; Van Griensven, M.; Zeichen, J.; Brauer, N.; Bosch, U. Cyclic mechanical stretching modulates secretion pattern of growth factors in human tendon fibroblasts. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 86, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.R.; Jones, G.C.; Legerlotz, K.; Riley, G.P. Cyclical strain modulates metalloprotease and matrix gene expression in human tenocytes via activation of TGFβ. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 2596–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, E.; Shelton, J.C.; Bader, D.L.; Lee, D.A. Differential regulation of gene expression in isolated tendon fascicles exposed to cyclic tensile strain in vitro. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arampatzis, A.; Mersmann, F.; Bohm, S. Individualized Muscle-Tendon Assessment and Training. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzolato, C.; Lloyd, D.G.; Zheng, M.H.; Besier, T.F.; Shim, V.B.; Obst, S.J.; Newsham-West, R.; Saxby, D.J.; Barrett, R.S. Finding the sweet spot via personalised Achilles tendon training: The future is within reach. Br. J. Sports Med. 2019, 53, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, S.P.; Hansen, P.; Aagaard, P.; Brønd, J.; Dyhre-Poulsen, P.; Bojsen-Moller, J.; Kjaer, M. Differential strain patterns of the human gastrocnemius aponeurosis and free tendon, in vivo. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2003, 177, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojsen-Møller, J.; Peter Magnusson, S. Mechanical properties, physiological behavior, and function of aponeurosis and tendon. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaer, M. Role of Extracellular Matrix in Adaptation of Tendon and Skeletal Muscle to Mechanical Loading. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 649–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, S.P.; Kjaer, M. The impact of loading, unloading, ageing and injury on the human tendon. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 1283–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesinger, H.P.; Kösters, A.; Müller, E.; Seynnes, O.R. Effects of Increased Loading on in Vivo Tendon Properties: A Systematic Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1885–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waugh, C.M.; Alktebi, T.; de Sa, A.; Scott, A. Impact of rest duration on Achilles tendon structure and function following isometric training. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouré, A.; Nordez, A.; Cornu, C. Effects of eccentric training on mechanical properties of the plantar flexor muscle-tendon complex. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 114, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obst, S.J.; Newsham-West, R.; Barrett, R.S. Changes in Achilles tendon mechanical properties following eccentric heel drop exercise are specific to the free tendon. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handsfield, G.G.; Greiner, J.; Madl, J.; Rog-Zielinska, E.A.; Hollville, E.; Vanwanseele, B.; Shim, V. Achilles Subtendon Structure and Behavior as Evidenced From Tendon Imaging and Computational Modeling. Front. Sports Act. Living 2020, 2, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbon, W.W.; Cooper, J.R.; Radcliffe, G.S. Distribution of sonographically detected tendon abnormalities in patients with a clinical diagnosis of chronic Achilles tendinosis. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2000, 28, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesinger, H.P.; Rieder, F.; Kösters, A.; Müller, E.; Seynnes, O.R. Are Sport-Specific Profiles of Tendon Stiffness and Cross-Sectional Area Determined by Structural or Functional Integrity? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesinger, H.P.; Rieder, F.; Kösters, A.; Müller, E.; Seynnes, O.R. Sport-specific capacity to use elastic energy in the patellar and Achilles tendons of elite athletes. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, K.; Morimoto, M.; Komuro, T.; Yata, H.; Tsunoda, N.; Kanehisa, H.; Fukunaga, T. Effects of plyometric and weight training on muscle-tendon complex and jump performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouré, A.; Nordez, A.; Cornu, C. Plyometric training effects on Achilles tendon stiffness and dissipative properties. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, K.E.; Connick, M.J.; Graham-Smith, P.; Pearson, S.J. Plyometric vs. Isometric Training Influences on Tendon Properties and Muscle Output. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 986–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.K.; Lien, Y.H.; Lin, K.H.; Shih, T.T.F.; Wang, T.G.; Wang, H.K. Relationships between three potentiation effects of plyometric training and performance. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, e80–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouré, A.; Nordez, A.; McNair, P.; Cornu, C. Effects of plyometric training on both active and passive parts of the plantarflexors series elastic component stiffness of muscle-tendon complex. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, L.A.; Dawson, B.T.; Rubenson, J. Effects of plyometric training on Achilles tendon properties and shuttle running during a simulated cricket batting innings. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, S.; Kulig, K. Tendinopathy alters mechanical and material properties of the Achilles tendon. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Child, S.; Bryant, A.L.; Clark, R.A.; Crossley, K.M. Mechanical properties of the achilles tendon aponeurosis are altered in athletes with achilles tendinopathy. Am. J. Sports Med. 2010, 38, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimenti, R.L.; Flemister, A.S.; Tome, J.; McMahon, J.M.; Flannery, M.A.; Xue, Y.; Houck, J.R. Altered tendon characteristics and mechanical properties associated with insertional achilles tendinopathy. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2014, 44, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulig, K.; Chang, Y.J.; Winiarski, S.; Bashford, G.R. Ultrasound-Based Tendon Micromorphology Predicts Mechanical Characteristics of Degenerated Tendons. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, N.L.; Wearing, S.C.; Smeathers, J.E. Achilles tendinopathy has an aberrant strain response to eccentric exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnamore, E.; Waugh, C.; Solomons, L.; Ryan, M.; West, C.; Scott, A. Transverse tendon stiffness is reduced in people with Achilles tendinopathy: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuliffe, S.; Tabuena, A.; McCreesh, K.; O’Keeffe, M.; Hurley, J.; Comyns, T.; Purtill, H.; O’Neill, S.; O’Sullivan, K. Altered strength profile in Achilles tendinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Athl. Train. 2019, 54, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, S.; Barry, S.; Watson, P. Plantarflexor strength and endurance deficits associated with mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy: The role of soleus. Phys. Ther. Sport 2019, 37, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasani, F.; Vallance, P.; Haines, T.; Munteanu, S.E.; Malliaras, P. Are Plantarflexor Muscle Impairments Present among Individuals with Achilles Tendinopathy and Do They Change with Exercise? A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Sports Med.-Open 2021, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öhberg, L.; Lorentzon, R.; Alfredson, H. Eccentric training in patients with chronic Achilles tendinosis: Normalised tendon structure and decreased thickness at follow up. Br. J. Sports Med. 2004, 38, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalabi, A.; Kristoffersen-Wilberg, M.; Svensson, L.; Aspelin, P.; Movin, T. Eccentric training of the gastrocnemius-soleus complex ion chronic achilles tendinopathy results in decreased tendon volume and intratendinous signal as evaluated by MRI. Am. J. Sports Med. 2004, 32, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhberg, L.; Alfredson, H. Effects on neovascularisation behind the good results with eccentric training in chronic mid-portion Achilles tendinosis? Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2004, 12, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, J.L.; Rio, E.; Purdam, C.R.; Docking, S.I. Revisiting the continuum model of tendon pathology: What is its merit in clinical practice and research? Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, B.T.; Smith, T.O.; Littlewood, C.; Sturrock, B. Do structural changes (eg, collagen/matrix) explain the response to therapeutic exercises in tendinopathy: A systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, M.; Bisset, L.; Newsham-West, R. Should we care about tendon structure? The disconnect between structure and symptoms in tendinopathy. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 45, 823–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.; Travers, M.; Gibson, W.; Chivers, P.; Debenham, J.; Docking, S.; Rio, E. Rate of Improvement of Pain and Function in Mid-Portion Achilles Tendinopathy with Loading Protocols: A Systematic Review and Longitudinal Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 1875–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, B.; Duarte, J.A. Physical therapy for tendinopathy: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Phys. Ther. Sport 2020, 46, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S.P.; Tarpenning, K.M.; Marino, F.E. Designing resistance training programmes to enhance muscular fitness: A review of the acute programme variables. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanish, W.D.; Rubinovich, R.T.; Curwin, S. Eccentric exercise in chronic tendinitis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1986, 208, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredson, H.; Pietilä, T.; Jonsson, P.; Lorentzon, R. Heavy-load eccentric calf muscle training for the treatment of chronic achilles tendinosis. Am. J. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silbernagel, K.G.; Thomeé, R.; Thomeé, P.; Karlsson, J. Eccentric overload training for patients with chronic Achilles tendon pain—A randomised controlled study with reliability testing of the evaluation methods. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2001, 11, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongsgaard, M.; Kovanen, V.; Aagaard, P.; Doessing, S.; Hansen, P.; Laursen, A.H.; Kaldau, N.C.; Kjaer, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Corticosteroid injections, eccentric decline squat training and heavy slow resistance training in patellar tendinopathy. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2009, 19, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, E.; Van Ark, M.; Docking, S.; Moseley, G.L.; Kidgell, D.; Gaida, J.E.; Van Den Akker-Scheek, I.; Zwerver, J.; Cook, J. Isometric contractions are more analgesic than isotonic contractions for patellar tendon pain: An in-season randomized clinical trial. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2017, 27, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatz, M.; Betsch, M.; Dirrichs, T.; Schrading, S.; Tingart, M.; Michalik, R.; Quack, V. Eccentric and Isometric Exercises in Achilles Tendinopathy Evaluated by the VISA-A Score and Shear Wave Elastography. Sports Health 2020, 12, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.; Radia, J.; Bird, K.; Rathleff, M.S.; Bandholm, T.; Jorgensen, M.; Thorborg, K. Acute sensory and motor response to 45-s heavy isometric holds for the plantar flexors in patients with Achilles tendinopathy. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019, 27, 2765–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, F.; Walshe, M.; O’Dwyer, T.; Bennett, K.; Mockler, D.; Bleakley, C. Exercise, orthoses and splinting for treating Achilles tendinopathy: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1564–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Head, J.; Mallows, A.; Debenham, J.; Travers, M.J.; Allen, L. The efficacy of loading programmes for improving patient-reported outcomes in chronic midportion Achilles tendinopathy: A systematic review. Musculoskelet. Care 2019, 17, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitkamp, H.S.J.; Kapitza, C. The Management of Mid-Portion Achilles Tendinopathy from a Physiotherapeutic Point of View: A Systematic Review. Sportverletz.-Sportschaden 2021, 35, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallows, A.; Head, J.; Goom, T.; Malliaras, P.; O’Neill, S.; Smith, B. Patient perspectives on participation in exercise-based rehabilitation for Achilles tendinopathy: A qualitative study. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2021, 56, 102450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.; Malliaras, P.; Goulis, J.; Auliffe, S.M. “it’s disappointing and it’s pretty frustrating, because it feels like it’s something that will never go away.” A qualitative study exploring individuals’ beliefs and experiences of Achilles tendinopathy. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Auliffe, S.; Synott, A.; Casey, H.; Mc Creesh, K.; Purtill, H.; O’Sullivan, K. Beyond the tendon: Experiences and perceptions of people with persistent Achilles tendinopathy. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2017, 29, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waugh, C.M.; Blazevich, A.J.; Fath, F.; Korff, T. Age-related changes in mechanical properties of the Achilles tendon. J. Anat. 2012, 220, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasani, F.; Haines, T.; Munteanu, S.E.; Schoch, P.; Vicenzino, B.; Malliaras, P. LOAD-intensity and time-under-tension of exercises for men who have Achilles tendinopathy (the LOADIT trial): A randomised feasibility trial. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escriche-Escuder, A.; Casanã, J.; Cuesta-Vargas, A.I. Load progression criteria in exercise programmes in lower limb tendinopathy: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e041433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kösters, A.; Wiesinger, H.P.; Bojsen-Møller, J.; Müller, E.; Seynnes, O.R. Influence of loading rate on patellar tendon mechanical properties in vivo. Clin. Biomech. 2014, 29, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, K.; Kanehisa, H.; Ito, M.; Fukunaga, T. Effects of isometric training on the elasticity of human tendon structures in vivo. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 91, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, K.; Kanehisa, H.; Fukunaga, T. Effects of different duration isometric contractions on tendon elasticity in human quadriceps muscles. J. Physiol. 2001, 536, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arampatzis, A.; Karamanidis, K.; Stafilidis, S.; Morey-Klapsing, G.; DeMonte, G.; Brüggemann, G.P. Effect of different ankle- and knee-joint positions on gastrocnemius medialis fascicle length and EMG activity during isometric plantar flexion. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 1891–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, D.; McNair, P.J.; Johnson, S.; Potts, G.; Witvrouw, E.; Mahieu, N. Electromyographic analysis of an eccentric calf muscle exercise in persons with and without Achilles tendinopathy. Phys. Ther. Sport 2012, 13, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakahara, T.; Kanehisa, H.; Kawakami, Y.; Fukunaga, T. Effects of knee joint angle on the fascicle behavior of the gastrocnemius muscle during eccentric plantar flexions. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2009, 19, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, R.D.; Clarke, J.; Kwah, L.K.; Diong, J.; Martin, J.; Clarke, E.C.; Bilston, L.E.; Gandevia, S.C. In vivo passive mechanical behaviour of muscle fascicles and tendons in human gastrocnemius muscle-tendon units. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 5257–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, B.; Lichtwark, G.A.; Cresswell, A.G. Reciprocal activation of gastrocnemius and soleus motor units is associated with fascicle length change during knee flexion. Physiol. Rep. 2014, 2, e12044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landin, D.; Thompson, M.; Reid, M. Knee and Ankle Joint Angles Influence the Plantarflexion Torque of the Gastrocnemius. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2015, 7, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orishimo, K.F.; Burstein, G.; Mullaney, M.J.; Kremenic, I.J.; Nesse, M.; McHugh, M.P.; Lee, S.J. Effect of Knee Flexion Angle on Achilles Tendon Force and Ankle Joint Plantarflexion Moment During Passive Dorsiflexion. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2008, 47, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, A.N.; Komi, P.V.; Brüggemann, G.P.; Lukkariniemi, J. Individual muscle contributions to the in vivo achilles tendon force. Clin. Biomech. 1998, 13, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.H.; Calder, J.D.; Antflick, J.; Bull, A.M.J.; Kedgley, A.E. Maximum dorsiflexion increases Achilles tendon force during exercise for midportion Achilles tendinopathy. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2021, 31, 1674–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slane, L.C.; Thelen, D.G. Non-uniform displacements within the Achilles tendon observed during passive and eccentric loading. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 2831–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, L.; Brito Carvalho, C.; Ampe, N.; Peers, K.; Bogaerts, S. An eccentric ankle heel drop into dorsiflexion as opposed to neutral causes more Achilles tendon tissue displacement, but not more non-uniformity. Transl. Sports Med. 2021, 4, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumbach, S.F.; Brumann, M.; Binder, J.; Mutschler, W.; Regauer, M.; Polzer, H. The influence of knee position on ankle dorsiflexion—A biometric study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.J.; Lacourpaille, L.; Freitas, S.R.; Mcnair, P.J.; Nordez, A. Effects of hip and head position on ankle range of motion, ankle passive torque, and passive gastrocnemius tension. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, B.; Bressel, E.; McNair, P.J.; Bressel, M.E. Effect of pelvic, hip, and knee position on ankle joint range of motion. Phys. Ther. Sport 2008, 9, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.J.; Freitas, S.R.; Hug, F.; Le Sant, G.; Lacourpaille, L.; Gross, R.; McNair, P.; Nordez, A. The potential role of sciatic nerve stiffness in the limitation of maximal ankle range of motion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, Y.; Kanehisa, H.; Fukunaga, T. The relationship between passive ankle plantar flexion joint torque and gastrocnemius muscle and achilles tendon stiffness: Implications for flexibility. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2008, 38, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaerts, S.; De Brito Carvalho, C.; Scheys, L.; Desloovere, K.; D’hooge, J.; Maes, F.; Suetens, P.; Peers, K. Evaluation of tissue displacement and regional strain in the Achilles tendon using quantitative high-frequency ultrasound. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, R.; Agergaard, A.-S.; Magnusson, S.P.; Svensson, R.B. Speckle tracking in healthy and surgically repaired human Achilles tendons at different knee angles-A validation using implanted tantalum beads. Transl. Sports Med. 2018, 1, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, N.L.; Clark, W.H.; Lewek, M.D.; Franz, J.R. The effects of triceps surae muscle stimulation on localized Achilles subtendon tissue displacements. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, 242135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenroth, L.; Thelen, D.; Franz, J. Biplanar ultrasound investigation of in vivo Achilles tendon displacement non-uniformity. Transl. Sports Med. 2019, 2, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.; Tan, C.W. Effectiveness of the alfredson protocol compared with a lower repetition-volume protocol for midportion achilles tendinopathy: A randomized controlled trial. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2014, 44, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handsfield, G.G.; Inouye, J.M.; Slane, L.C.; Thelen, D.G.; Miller, G.W.; Blemker, S.S. A 3D model of the Achilles tendon to determine the mechanisms underlying nonuniform tendon displacements. J. Biomech. 2017, 51, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Biomechanical Consideration | Section | Summary Points | Clinical Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle Contraction Type | Section 4.1 |
| |
| Load Intensity | Section 4.2 |
|
|
| Loading Frequency, Rate, and Duration | Section 4.3 |
|
|
| Exercise Positioning | Section 4.4 |
|
|
| Exercise Schedule | Section 4.5 |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merry, K.; Napier, C.; Waugh, C.M.; Scott, A. Foundational Principles and Adaptation of the Healthy and Pathological Achilles Tendon in Response to Resistance Exercise: A Narrative Review and Clinical Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164722
Merry K, Napier C, Waugh CM, Scott A. Foundational Principles and Adaptation of the Healthy and Pathological Achilles Tendon in Response to Resistance Exercise: A Narrative Review and Clinical Implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(16):4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164722
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerry, Kohle, Christopher Napier, Charlie M. Waugh, and Alex Scott. 2022. "Foundational Principles and Adaptation of the Healthy and Pathological Achilles Tendon in Response to Resistance Exercise: A Narrative Review and Clinical Implications" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 16: 4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164722
APA StyleMerry, K., Napier, C., Waugh, C. M., & Scott, A. (2022). Foundational Principles and Adaptation of the Healthy and Pathological Achilles Tendon in Response to Resistance Exercise: A Narrative Review and Clinical Implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(16), 4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164722







